声明
- 其实很好奇Android系统中的一些关键守护进程服务的作用;
- 暂且大概分析下它们的作用,这样有助于理解整个系统的工作过程;
- ADB本身也是个复杂的系统,最近在处理ADB相关的修改工作,后续相关adbd的会再添加进来;
0 写在前面的
- 只要是操作系统,不用说的就是其中肯定会运行着一些很多守护进程(daemon)来完成很多杂乱的工作。通过系统中的init.rc文件也可以看出来,其中每个service中就包含着系统后台服务进程。
- 而这些服务被分为:core类服务(adbd/servicemanager/healthd/lmkd/logd/vold)和main类服务;
- main类服务又分为:网络类服务(netd/mdnsd/mtpd/rild)、图形及媒体类服务(surfaceflinger/bootanimation/mediaserver/dnnserver)、其他类服务(installd/keystore/debuggerd/sdcard/Zygote)
1 adbd的作用

adbd是Android系统特有的ADB功能中运行在手机/平板端的守护进程,其在/init.usb.rc中的启动配置为:
- # adbd is controlled via property triggers in init.<platform>.usb.rc
- service adbd /sbin/adbd --root_seclabel=u:r:su:s0
- class core
- socket adbd stream 660 system system
- disabled
- seclabel u:r:adbd:s0
调试者可以直接在PC上使用adb命令对设备进行调试,也可以通过ddms命令间接调试。在调试之前,要在系统开发者模式中打开“USB调试”的开关,其在底层其实是通过修改系统属性sys.usb.config的值为adb时打开的。
在默认情况下,adbd是以uid root的权限启动的。不过它确实还会通过函数drop_privileges()主动把自己降到uid shell : shell,和几个GID权限,所在源码目录为:~/LineageOS/system/core/adb/daemon/main.cpp
- static void drop_privileges(int server_port) {
- std::unique_ptr<minijail, void (*)(minijail*)> jail(minijail_new(),
- &minijail_destroy);
-
- // Add extra groups:
- // AID_ADB to access the USB driver
- // AID_LOG to read system logs (adb logcat)
- // AID_INPUT to diagnose input issues (getevent)
- // AID_INET to diagnose network issues (ping)
- // AID_NET_BT and AID_NET_BT_ADMIN to diagnose bluetooth (hcidump)
- // AID_SDCARD_R to allow reading from the SD card
- // AID_SDCARD_RW to allow writing to the SD card
- // AID_NET_BW_STATS to read out qtaguid statistics
- // AID_READPROC for reading /proc entries across UID boundaries
- gid_t groups[] = {AID_ADB, AID_LOG, AID_INPUT,
- AID_INET, AID_NET_BT, AID_NET_BT_ADMIN,
- AID_SDCARD_R, AID_SDCARD_RW, AID_NET_BW_STATS,
- AID_READPROC};
- minijail_set_supplementary_gids(jail.get(),
- sizeof(groups) / sizeof(groups[0]),
- groups);
-
- // Don't listen on a port (default 5037) if running in secure mode.
- // Don't run as root if running in secure mode.
- if (should_drop_privileges()) {
- drop_capabilities_bounding_set_if_needed();
-
- minijail_change_gid(jail.get(), AID_SHELL);
- minijail_change_uid(jail.get(), AID_SHELL);
- // minijail_enter() will abort if any priv-dropping step fails.
- minijail_enter(jail.get());
-
- D("Local port disabled");
- } else {
- // minijail_enter() will abort if any priv-dropping step fails.
- minijail_enter(jail.get());
-
- if (root_seclabel != nullptr) {
- if (selinux_android_setcon(root_seclabel) < 0) {
- LOG(FATAL) << "Could not set SELinux context";
- }
- }
- std::string error;
- std::string local_name =
- android::base::StringPrintf("tcp:%d", server_port);
- if (install_listener(local_name, "*smartsocket*", nullptr, 0,
- &error)) {
- LOG(FATAL) << "Could not install *smartsocket* listener: "
- << error;
- }
- }
- }
在user-debug版本的系统中(系统属性为ro.debuggable=0),还可以通过adb root命令让adbd恢复root权限(通过修改系统属性service.adb.root=1)。adb作用不用多说,查看他的help即可:
- C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\platform-tools>adb.exe --help
- Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.40
- Version 4986621
- Installed as C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\platform-tools\adb.exe
-
- global options:
- -a listen on all network interfaces, not just localhost
- -d use USB device (error if multiple devices connected)
- -e use TCP/IP device (error if multiple TCP/IP devices available)
- -s SERIAL use device with given serial (overrides $ANDROID_SERIAL)
- -t ID use device with given transport id
- -H name of adb server host [default=localhost]
- -P port of adb server [default=5037]
- -L SOCKET listen on given socket for adb server [default=tcp:localhost:5037]
-
- general commands:
- devices [-l] list connected devices (-l for long output)
- help show this help message
- version show version num
-
- networking:
- connect HOST[:PORT] connect to a device via TCP/IP [default port=5555]
- disconnect [HOST[:PORT]]
- disconnect from given TCP/IP device [default port=5555], or all
- forward --list list all forward socket connections
- forward [--no-rebind] LOCAL REMOTE
- forward socket connection using:
- tcp:<port> (<local> may be "tcp:0" to pick any open port)
- localabstract:<unix domain socket name>
- localreserved:<unix domain socket name>
- localfilesystem:<unix domain socket name>
- dev:<character device name>
- jdwp:<process pid> (remote only)
- forward --remove LOCAL remove specific forward socket connection
- forward --remove-all remove all forward socket connections
- ppp TTY [PARAMETER...] run PPP over USB
- reverse --list list all reverse socket connections from device
- reverse [--no-rebind] REMOTE LOCAL
- reverse socket connection using:
- tcp:<port> (<remote> may be "tcp:0" to pick any open port)
- localabstract:<unix domain socket name>
- localreserved:<unix domain socket name>
- localfilesystem:<unix domain socket name>
- reverse --remove REMOTE remove specific reverse socket connection
- reverse --remove-all remove all reverse socket connections from device
-
- file transfer:
- push [--sync] LOCAL... REMOTE
- copy local files/directories to device
- --sync: only push files that are newer on the host than the device
- pull [-a] REMOTE... LOCAL
- copy files/dirs from device
- -a: preserve file timestamp and mode
- sync [all|data|odm|oem|product|system|vendor]
- sync a local build from $ANDROID_PRODUCT_OUT to the device (default all)
- -l: list but don't copy
- shell:
- shell [-e ESCAPE] [-n] [-Tt] [-x] [COMMAND...]
- run remote shell command (interactive shell if no command given)
- -e: choose escape character, or "none"; default '~'
- -n: don't read from stdin
- -T: disable PTY allocation
- -t: force PTY allocation
- -x: disable remote exit codes and stdout/stderr separation
- emu COMMAND run emulator console command
-
- app installation:
- install [-lrtsdg] [--instant] PACKAGE
- install-multiple [-lrtsdpg] [--instant] PACKAGE...
- push package(s) to the device and install them
- -l: forward lock application
- -r: replace existing application
- -t: allow test packages
- -s: install application on sdcard
- -d: allow version code downgrade (debuggable packages only)
- -p: partial application install (install-multiple only)
- -g: grant all runtime permissions
- --instant: cause the app to be installed as an ephemeral install app
- uninstall [-k] PACKAGE
- remove this app package from the device
- '-k': keep the data and cache directories
-
- backup/restore:
- to show usage run "adb shell bu help"
-
- debugging:
- bugreport [PATH]
- write bugreport to given PATH [default=bugreport.zip];
- if PATH is a directory, the bug report is saved in that directory.
- devices that don't support zipped bug reports output to stdout.
- jdwp list pids of processes hosting a JDWP transport
- logcat show device log (logcat --help for more)
- security:
- disable-verity disable dm-verity checking on userdebug builds
- enable-verity re-enable dm-verity checking on userdebug builds
- keygen FILE
- generate adb public/private key; private key stored in FILE,
- public key stored in FILE.pub (existing files overwritten)
- scripting:
- wait-for[-TRANSPORT]-STATE
- wait for device to be in the given state
- State: device, recovery, sideload, or bootloader
- Transport: usb, local, or any [default=any]
- get-state print offline | bootloader | device
- get-serialno print <serial-number>
- get-devpath print <device-path>
- remount remount partitions read-write
- reboot [bootloader|recovery|sideload|sideload-auto-reboot]
- reboot the device; defaults to booting system image but
- supports bootloader and recovery too. sideload reboots
- into recovery and automatically starts sideload mode,
- sideload-auto-reboot is the same but reboots after sideloading.
- sideload OTAPACKAGE sideload the given full OTA package
- root restart adbd with root permissions
- unroot restart adbd without root permissions
- usb restart adb server listening on USB
- tcpip PORT restart adb server listening on TCP on PORT
- internal debugging:
- start-server ensure that there is a server running
- kill-server kill the server if it is running
- reconnect kick connection from host side to force reconnect
- reconnect device kick connection from device side to force reconnect
- reconnect offline reset offline/unauthorized devices to force reconnect
- environment variables:
- $ADB_TRACE
- comma-separated list of debug info to log:
- all,adb,sockets,packets,rwx,usb,sync,sysdeps,transport,jdwp
- $ADB_VENDOR_KEYS colon-separated list of keys (files or directories)
- $ANDROID_SERIAL serial number to connect to (see -s)
- $ANDROID_LOG_TAGS tags to be used by logcat (see logcat --help)
2 ADB的安全认证
由于ADB这个接口具有功能非常强大的调试和跟踪功能,尽管它是以shell这个uid的身份运行,但由于shell这个uid是好几个组(log、graphic等)的成员,这也使得它具有很强的能力。使用ADB可以访问到用户的个人数据,也能把任意APP、Native层可执行文件上传到设备中。因此,在Android 4.3 以后的Android系统中引入了公钥认证机制(前提是ro.adb.secure=1时),把ADB的安全性进一步提升。
AUTH消息将作为对OPEN消息的响应,发送到电脑端,要求在其执行任何命令之前,先完成认证。AUTH消息的参数总是一个TOKEN,它是由移动设备中的随机数发生器(/dev/urandom)生成的一个大小为20个字节的随机数数组。移动设备端将等待电脑端用自己的私钥(该私钥应该己经生成,并存放在$HOME/.android/adbkey这个文件中)对这个TOKEN 进行签名,然后回复一个AUTH SIGNATURE消息,把用私钥签名过的随机数数组放在这个消息里返回给移动设备端。如果移动设备知道相应的公钥,那么验证就能继续,而且如过验证通过了,该会话就会切换到online状态上去。
因为所有这一切都依赖于公钥,这就产生了一个先有鸡还是先有蛋的问题:怎么让移动端事先就知道这个公钥,并将其用于验证呢?解决方案是允许电脑端响应一个AUTHRSAPUBLICKEY消息。因为此时这个公钥是不可信的,ADB将把这个公钥通过/dev/socket/adbd这个UDS传递给system_server(特别是由com.android.server.usb.UsbDeviceManager启动的UsbDebuggingManager ),然后,system_server将会弹出一个对话框(com.android.server.usb.UsbDebuggingActivity),要求用户确认该公钥的指纹(MD5 Hash)。如果用户选择信任该公钥,这个公钥就会被添加到adb的key store(位于/data/misc/adb/adb_key)中去。作为厂商的话可以重新编译adbd,删掉这一功能(相关代码位于adb_auth_client.c中的adb_auth_confirm_key()函数中),所在源码目录:~/LineageOS/system/core/adb/adb_auth_client.cpp
- void adb_auth_confirm_key(unsigned char *key, size_t len, atransport *t)
- {
- char msg[MAX_PAYLOAD_V1];
- int ret;
-
- if (!usb_transport) {
- usb_transport = t;
- t->AddDisconnect(&usb_disconnect);
- }
-
- if (framework_fd < 0) {
- D("Client not connected");
- needs_retry = true;
- return;
- }
-
- if (key[len - 1] != '\0') {
- D("Key must be a null-terminated string");
- return;
- }
-
- ret = snprintf(msg, sizeof(msg), "PK%s", key);
- if (ret >= (signed)sizeof(msg)) {
- D("Key too long. ret=%d", ret);
- return;
- }
- D("Sending '%s'", msg);
-
- ret = unix_write(framework_fd, msg, ret);
- if (ret < 0) {
- D("Failed to write PK, errno=%d", errno);
- return;
- }
- }
-
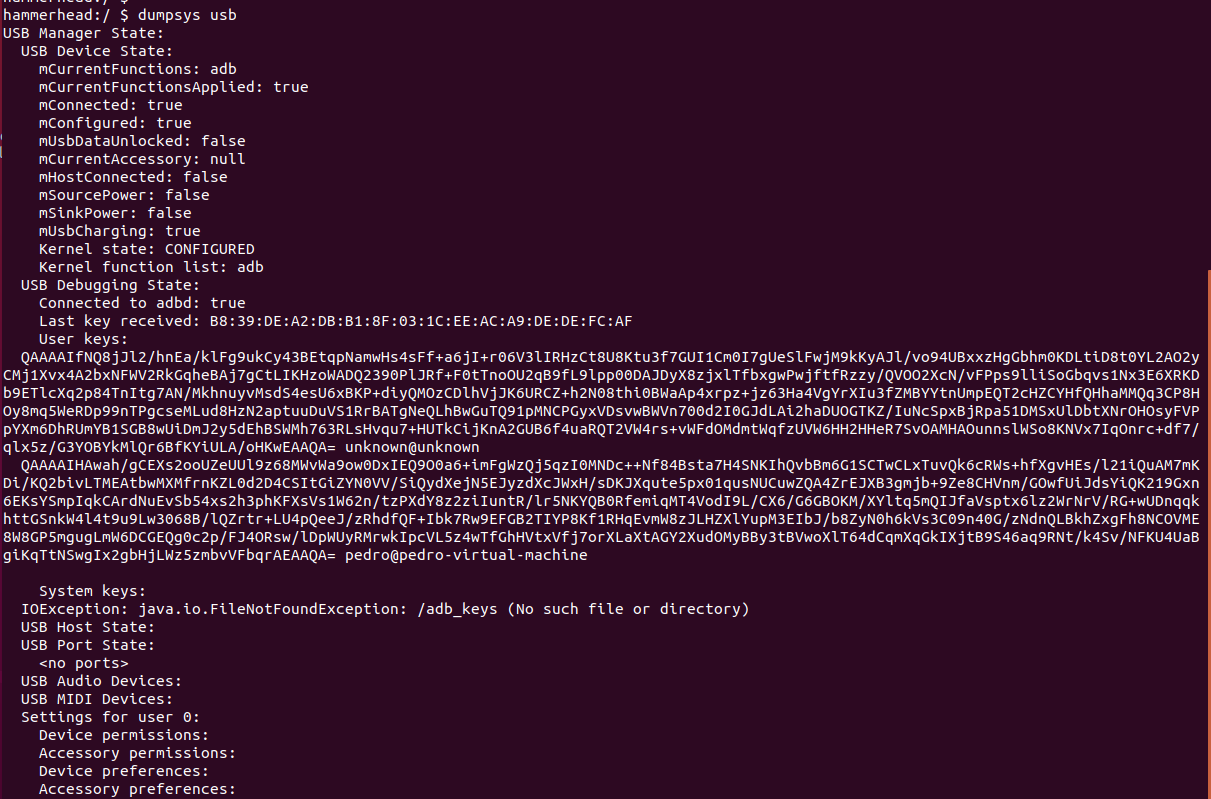
输入dumpsys usb命令,你就能看到当前的USB调试状态以及当前使用的adb_keys,如下图所示: