热门标签
热门文章
- 1深度学习自学2.0_深度学习麋了鹿 unet
- 2阿里云ubuntu部署mqtt,设备终端以及web端引入mqtt进行数据交互_ubuntu20.04 mosquitto配置mqtt mosquitto.conf
- 32023年全国职业技能大赛软件测试环境搭建及系统部署答案_2023全国职业院校技能大赛环境安装答案
- 4MacOS 签名+公证 APP (codesign macos公证)_mac安装包公证
- 5机器翻译:引入注意力机制的Encoder-Decoder深度神经网络训练实战中英文互译(完结篇)_encoder-decoder 机器翻译
- 6Qt中实用功能小合集_qt功能
- 7elasticsearch+canal增量、全量同步_es增量同步
- 8职业发展规划指南:如何成为成功的产品经理
- 9R语言入门——笔记(二)--包(package)的使用及RStudio的使用,加载包和数据集_rstudio中数据集kegg如何加载
- 10Prometheus运维十 监控MySQL_prometheus mysql questions
当前位置: article > 正文
leetcode 797. 所有可能的路径(C++、java)_有向无环图 leetcode
作者:盐析白兔 | 2024-05-12 06:41:47
赞
踩
有向无环图 leetcode
给你一个有 n 个节点的 有向无环图(DAG),请你找出所有从节点 0 到节点 n-1 的路径并输出(不要求按特定顺序)
二维数组的第 i 个数组中的单元都表示有向图中 i 号节点所能到达的下一些节点,空就是没有下一个结点了。
译者注:有向图是有方向的,即规定了 a→b 你就不能从 b→a 。
示例 1:

输入:graph = [[1,2],[3],[3],[]] 输出:[[0,1,3],[0,2,3]] 解释:有两条路径 0 -> 1 -> 3 和 0 -> 2 -> 3
示例 2:
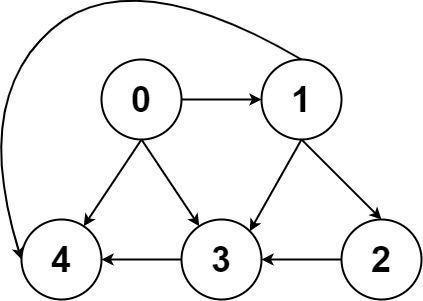
输入:graph = [[4,3,1],[3,2,4],[3],[4],[]] 输出:[[0,4],[0,3,4],[0,1,3,4],[0,1,2,3,4],[0,1,4]]
示例 3:
输入:graph = [[1],[]] 输出:[[0,1]]
示例 4:
输入:graph = [[1,2,3],[2],[3],[]] 输出:[[0,1,2,3],[0,2,3],[0,3]]
示例 5:
输入:graph = [[1,3],[2],[3],[]] 输出:[[0,1,2,3],[0,3]]
提示:
n == graph.length2 <= n <= 150 <= graph[i][j] < ngraph[i][j] != i(即,不存在自环)graph[i]中的所有元素 互不相同- 保证输入为 有向无环图(DAG)
C++
- class Solution {
- public:
- void dfs(vector <vector<int>> &res, vector<int> &tmp, int k) {
- if (k == graph.size() - 1) {
- res.push_back(tmp);
- return;
- }
- vector<int> vec = graph[k];
- for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++) {
- tmp.push_back(vec[i]);
- dfs(res, tmp, vec[i]);
- tmp.pop_back();
- }
- }
-
- vector <vector<int>> allPathsSourceTarget(vector <vector<int>> &graph) {
- this->graph = graph;
- vector <vector<int>> res;
- vector<int> tmp;
- tmp.push_back(0);
- dfs(res, tmp, 0);
- return res;
- }
-
- private:
- vector <vector<int>> graph;
- };

java
- class Solution {
- List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
- int[][] g;
- int n;
- List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
-
- public void dfs(int k) {
- if (k == n - 1) {
- res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
- return;
- }
- int[] vec = g[k];
- for (int i = 0; i < vec.length; i++) {
- tmp.add(vec[i]);
- dfs(vec[i]);
- tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);
- }
- }
-
- public List<List<Integer>> allPathsSourceTarget(int[][] graph) {
- g = graph;
- n = graph.length;
- tmp.add(0);
- dfs(0);
- return res;
- }
- }

声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/盐析白兔/article/detail/558000
推荐阅读
相关标签


