- 1android 圆形相机预览拍照_Flutter自定义相机,Flutter相册选择照片
- 2字典树 - 核心思想及其代码实现_字典树如何构建
- 3Stable Diffusion干货教程:3种用AI高清放大图片方法_stable diffusion后期处理
- 4递归算法简单实现_请用递归编程实现。
- 5LLM——大语言模型完整微调策略指南_大语言模型微调
- 6vue3 组合式 API:setup()_setup组合式的order-in-components如何配置
- 7根号10在Java中写成_开根号_乐鑫科技笔试题_牛客网
- 8前端环境搭建:node.js、npm的下载和安装
- 9论文阅读-Transformer Layers as Painters
- 10【2024软件测试面试必会技能】Selenium(5):元素定位的介绍及使用_最新f12selenium元素定位
2024年建议收藏!献给Python初学者的22个入门小项目,练手必备!_python项目
赞
踩
print(“You win!”, player, “covers”, computer)
player_score+=1
elif player == “Scissors”:
if computer == “Rock”:
print(“You lose…”, computer, “smashes”, player)
cpu_score+=1
else:
print(“You win!”, player, “cut”, computer)
player_score+=1
elif player==‘E’:
print(“Final Scores:”)
print(f"CPU:{cpu_score}")
print(f"Plaer:{player_score}")
break
else:
print(“That’s not a valid play. Check your spelling!”)
computer = random.choice(choices)
8、维基百科文章摘要
使用一种简单的方法从用户提供的文章链接中生成摘要。
你可以使用爬虫获取文章数据,通过提取生成摘要。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import re
import requests
import heapq
from nltk.tokenize import sent_tokenize,word_tokenize
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
url = str(input(“Paste the url”\n"))num = int(input(“Enter the Number of Sentence you want in the summary”))
num = int(num)
headers = {‘User-Agent’: ‘Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/58.0.3029.110 Safari/537.3’}#url = str(input(“Paste the url…”))
res = requests.get(url,headers=headers)summary = “”
soup = BeautifulSoup(res.text,‘html.parser’) content = soup.findAll(“p”)
for text in content:
summary +=text.text
def clean(text): text = re.sub(r"[[0-9]*]“,” ",text)
text = text.lower() text = re.sub(r’\s+'," “,text) text = re.sub(r”,“,” ",text)
return text
summary = clean(summary)
print(“Getting the data…\n”)
##Tokenixing
sent_tokens = sent_tokenize(summary)
summary = re.sub(r"[^a-zA-z]“,” ",summary)
word_tokens = word_tokenize(summary)
Removing Stop words
word_frequency = {}stopwords = set(stopwords.words(“english”))
for word in word_tokens:
if word not in stopwords:
if word not in word_frequency.keys():
word_frequency[word]=1
else:
word_frequency[word] +=1
maximum_frequency = max(word_frequency.values())
print(maximum_frequency)
for word in word_frequency.keys():
word_frequency[word] = (word_frequency[word]/maximum_frequency)
print(word_frequency)
sentences_score = {}
for sentence in sent_tokens:
for word in word_tokenize(sentence):
if word in word_frequency.keys(): if (len(sentence.split(" "))) <30:
if sentence not in sentences_score.keys():
sentences_score[sentence] = word_frequency[word]
else:
sentences_score[sentence] += word_frequency[word]
print(max(sentences_score.values()))
def get_key(val):
for key, value in sentences_score.items():
if val == value:
return key
key = get_key(max(sentences_score.values()))print(key+“\n”)
print(sentences_score)
summary = heapq.nlargest(num,sentences_score,key=sentences_score.get)print(" ".join(summary))summary = " ".join(summary)
9、随机密码生成器
创建一个程序,可指定密码长度,生成一串随机密码。
创建一个数字+大写字母+小写字母+特殊字符的字符串。根据设定的密码长度随机生成一串密码。
import random
passlen = int(input(“enter the length of password”))
s="abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz01234567890ABCDEFGHIJKLNNOPQRSTUVWXYz!简#$x^6a()?p=.join(random.sample(s.passlen )
print§
enter the length of password6
za1gBe
10、闹钟
编写一个创建闹钟的Python脚本。
你可以使用date-time模块创建闹钟,以及playsound库播放声音。
from datetime import datetime
from playsound import playsound
alarm_time = input(“Enter the time of alarm to be set:HH:MM:SS\n”)
alarm_hour=alarm_time[0:2]
alarm_minute=alarm_time[3:5]
alarm_seconds=alarm_time[6:8]
alarm_period = alarm_time[9:11].upper()
print(“Setting up alarm…”)
while True:
now = datetime.now()
current_hour = now.strftime(“%I”)
current_minute = now.strftime(“%M”)
current_seconds = now.strftime(“%S”)
current_period = now.strftime(“%p”)
if(alarm_period==current_period):
if(alarm_hour==current_hour):
if(alarm_minute==current_minute):
if(alarm_seconds==current_seconds):
print(“Wake Up!”)
playsound(‘audio.mp3’) ## download the alarm sound from link
break
11、文字冒险游戏
编写一个有趣的Python脚本,通过为路径选择不同的选项让用户进行有趣的冒险。
name = str( input(“Enter Your Mame\n”))
print(f"{name} you are stuck in a forest.Your task is to get out from the forest withoutdieing")
print(“You are walking threw forest and suddenly a wolf comes in your way.Now Youoptions.”)
print("1.Run 2. climb The Nearest Tree ")
user = int(input(“choose one option 1 or 2”))
if user = 1:
print(“You Died!!”)
elif user = 2:
print(“You Survived!!”)
else:
print(“Incorrect Input”)
Add a loop and increase the story as much as you can
12、有声读物
编写一个Python脚本,用于将Pdf文件转换为有声读物。
借助pyttsx3库将文本转换为语音。
要安装的模块:
pyttsx3
PyPDF2
import pyttsx3,PyPDF2
DdfReader = pyPDF2.PdfFileReader(open( "file.pdf’,"rb’))
speaker = pyttsx3.init()
for page_num in range(pdfReader.numPages):
text =pdfReader.getPage(page_num).extractText()
speaker.say(text)
speaker.runAndwait()
speaker.stopo()
13、货币换算器
编写一个Python脚本,可以将一种货币转换为其他用户选择的货币。
使用Python中的API,或者通过forex-python模块来获取实时的货币汇率。
安装:forex-python
from forex _python.converter import CurrencyRatesc = CurrencyRates()
amount = int(input(“Enter The Amount You Want To Convert\n”))
from_currency = input( “From\n” )-upper()
to_currency = input( “To\n”).upper()
print(from_currency,“To”,to_currency , amount)
result = c.convert(from_currency, to_currency, amount)
print(result)
14、天气应用
编写一个Python脚本,接收城市名称并使用爬虫获取该城市的天气信息。
你可以使用Beautifulsoup和requests库直接从谷歌主页爬取数据。
安装:
requests
BeautifulSoup
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
headers = {‘User-Agent’: ‘Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/58.0.3029.110 Safari/537.3’}
def weather(city):
city=city.replace(" “,”+")
res = requests.get(f’https://www.google.com/search?q={city}&oq={city}&aqs=chrome.0.35i39l2j0l4j46j69i60.6128j1j7&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8’,headers=headers)
print(“Searching in google…\n”)
soup = BeautifulSoup(res.text,‘html.parser’)
location = soup.select(‘#wob_loc’)[0].getText().strip()
time = soup.select(‘#wob_dts’)[0].getText().strip()
info = soup.select(‘#wob_dc’)[0].getText().strip()
weather = soup.select(‘#wob_tm’)[0].getText().strip()
print(location)
print(time)
print(info)
print(weather+“°C”)
print(“enter the city name”)
city=input()
city=city+" weather"
weather(city)
15、人脸检测
编写一个Python脚本,可以检测图像中的人脸,并将所有的人脸保存在一个文件夹中。
可以使用haar级联分类器对人脸进行检测。它返回的人脸坐标信息,可以保存在一个文件中。
安装:
OpenCV
下载:haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml
import cv2
Load the cascade
face_cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier(‘haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml’)
Read the input image
img = cv2.imread(‘images/img0.jpg’)
Convert into grayscale
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
Detect faces
faces = face_cascade.detectMultiScale(gray, 1.3, 4)
Draw rectangle around the faces
for (x, y, w, h) in faces:
cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), (255, 0, 0), 2)
crop_face = img[y:y + h, x:x + w]
cv2.imwrite(str(w) + str(h) + ‘_faces.jpg’, crop_face)
Display the output
cv2.imshow(‘img’, img)
cv2.imshow(“imgcropped”,crop_face)
cv2.waitKey()
16、提醒应用
创建一个提醒应用程序,在特定的时间提醒你做一些事情(桌面通知)。
Time模块可以用来跟踪提醒时间,toastnotifier库可以用来显示桌面通知。
安装:win10toast
from win10toast import ToastNotifier
import time
toaster = ToastNotifier()
try:
print(“Title of reminder”)
header = input()
print(“Message of reminder”)
text = input()
print(“In how many minutes?”)
time_min = input()
time_min=float(time_min)
except:
header = input(“Title of reminder\n”)
text = input(“Message of remindar\n”)
time_min=float(input(“In how many minutes?\n”))
time_min = time_min * 60
print(“Setting up reminder…”)
time.sleep(2)
print(“all set!”)
time.sleep(time_min)
toaster.show_toast(f"{header}",
f"{text}",
duration=10,
threaded=True)
while toaster.notification_active(): time.sleep(0.005)
17、Hangman
创建一个简单的命令行hangman游戏。
创建一个密码词的列表并随机选择一个单词。现在将每个单词用下划线“”表示,给用户提供猜单词的机会,如果用户猜对了单词,则将“”用单词替换。
import time
import random
name = input("What is your name? ")
print ("Hello, " + name, “Time to play hangman!”)
time.sleep(1)
print (“Start guessing…\n”)
time.sleep(0.5)
A List Of Secret Words
words = [‘python’,‘programming’,‘treasure’,‘creative’,‘medium’,‘horror’]
word = random.choice(words)
guesses = ‘’
turns = 5
while turns > 0:
failed = 0
for char in word:
if char in guesses:
print (char,end=“”)
else:
print (“_”,end=“”),
failed += 1
if failed == 0:
print (“\nYou won”)
break
guess = input(“\nguess a character:”)
guesses += guess
if guess not in word:
turns -= 1
print(“\nWrong”)
print(“\nYou have”, + turns, ‘more guesses’)
if turns == 0:
print (“\nYou Lose”)
18、文章朗读器
编写一个Python脚本,自动从提供的链接读取文章。
import pyttsx3
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
url = str(input(“Paste article url\n”))
def content(url):
res = requests.get(url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(res.text,‘html.parser’)
articles = []
for i in range(len(soup.select(‘.p’))):
article = soup.select(‘.p’)[i].getText().strip()
articles.append(article)
contents = " ".join(articles)
return contents
engine = pyttsx3.init(‘sapi5’)
voices = engine.getProperty(‘voices’)
engine.setProperty(‘voice’, voices[0].id)
def speak(audio):
engine.say(audio)
engine.runAndWait()
contents = content(url)
print(contents) ## In case you want to see the content
#engine.save_to_file
#engine.runAndWait() ## In case if you want to save the article as a audio file
19、获取谷歌搜索结果
创建一个脚本,可以根据查询条件从谷歌搜索获取数据。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
headers = {‘User-Agent’: ‘Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/58.0.3029.110 Safari/537.3’}
def google(query):
query = query.replace(" “,”+")
try:
url = f’https://www.google.com/search?q={query}&oq={query}&aqs=chrome…69i57j46j69i59j35i39j0j46j0l2.4948j0j7&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8’
res = requests.get(url,headers=headers)
soup = BeautifulSoup(res.text,‘html.parser’)
except:
print(“Make sure you have a internet connection”)
try:
try:
ans = soup.select(‘.RqBzHd’)[0].getText().strip()
except:
try:
title=soup.select(‘.AZCkJd’)[0].getText().strip()
try:
ans=soup.select(‘.e24Kjd’)[0].getText().strip()
except:
如果你也是看准了Python,想自学Python,在这里为大家准备了丰厚的免费学习大礼包,带大家一起学习,给大家剖析Python兼职、就业行情前景的这些事儿。
一、Python所有方向的学习路线
Python所有方向路线就是把Python常用的技术点做整理,形成各个领域的知识点汇总,它的用处就在于,你可以按照上面的知识点去找对应的学习资源,保证自己学得较为全面。
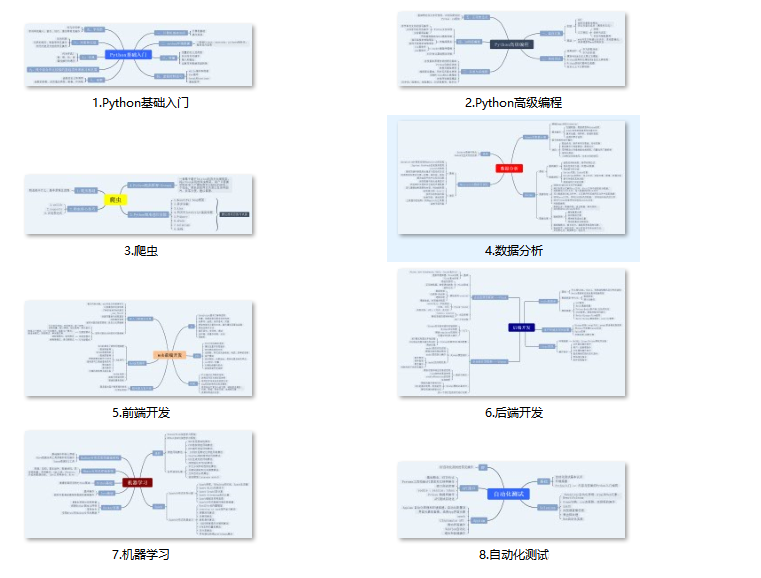
二、学习软件
工欲善其必先利其器。学习Python常用的开发软件都在这里了,给大家节省了很多时间。
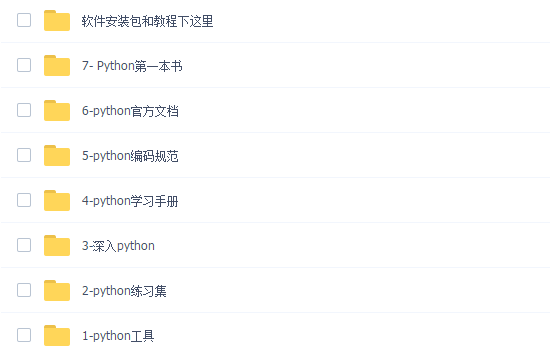
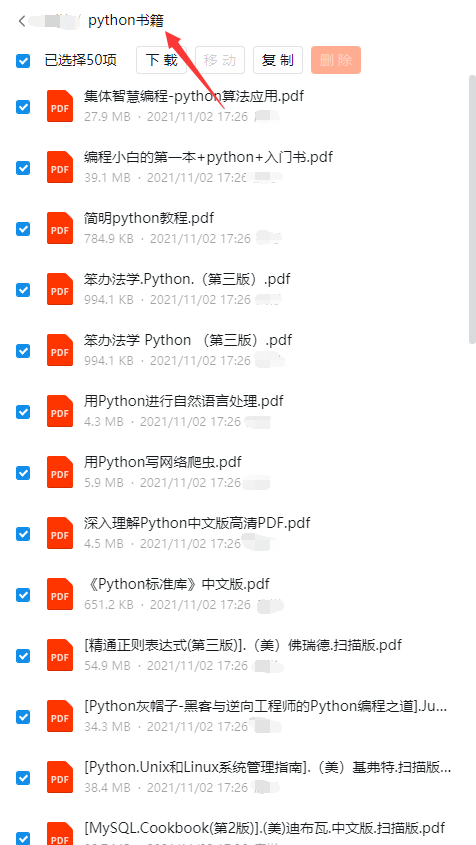
三、全套PDF电子书
书籍的好处就在于权威和体系健全,刚开始学习的时候你可以只看视频或者听某个人讲课,但等你学完之后,你觉得你掌握了,这时候建议还是得去看一下书籍,看权威技术书籍也是每个程序员必经之路。
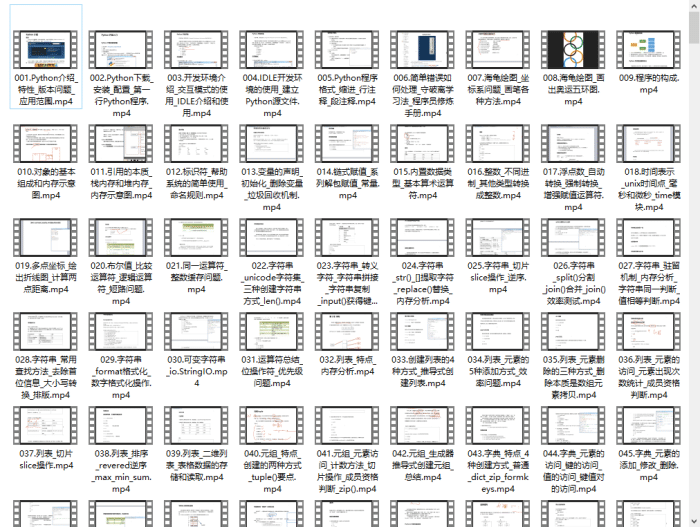
四、入门学习视频
我们在看视频学习的时候,不能光动眼动脑不动手,比较科学的学习方法是在理解之后运用它们,这时候练手项目就很适合了。
四、实战案例
光学理论是没用的,要学会跟着一起敲,要动手实操,才能将自己的所学运用到实际当中去,这时候可以搞点实战案例来学习。
五、面试资料
我们学习Python必然是为了找到高薪的工作,下面这些面试题是来自阿里、腾讯、字节等一线互联网大厂最新的面试资料,并且有阿里大佬给出了权威的解答,刷完这一套面试资料相信大家都能找到满意的工作。
成为一个Python程序员专家或许需要花费数年时间,但是打下坚实的基础只要几周就可以,如果你按照我提供的学习路线以及资料有意识地去实践,你就有很大可能成功!
最后祝你好运!!!
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!



