- 1android_brightness_resolving_android brightnesssliderview
- 2计算机鹅点云,CVPR 2020 | 用于点云中3D对象检测的图神经网络
- 3基于Springboot的疫情物资管理系统(有报告)。Javaee项目,springboot项目。
- 4华为鸿蒙学习笔记_华为 鸿蒙 如何学习
- 5解决wget无法下载GLDAS数据的问题_wget username/password authentication failed.
- 6【后台部署】Windows服务器部署RuoYi-Vue前后端分离项目_win本地怎么运行若依项目
- 7机器学习导论:概念、分类与应用场景
- 8常见异常
- 9鸿蒙开发实例 | ArkUI JS飞机大战游戏开发_鸿蒙版飞机大战
- 10【鸿蒙 HarmonyOS 4.0】开发工具安装_鸿蒙ide工具
transformer位置编码以及代码解释_transformer位置编码代码
赞
踩
Transformer 是combination-invariant的。也就是说,混洗输入嵌入不会改变transformer的输出。然而,嵌入的位置也包含重要信息。为了使各自的模型意识到这一点,提出了许多不同的嵌入位置表示(Vaswani 等人,2017)。
Absolute Position Embedding
ViT
位置嵌入被加入到补丁嵌入中以保留位置信息。使用标准的可学习 1D 位置嵌入,因为没有观察到使用更先进的 2D 感知位置嵌入带来的显着性能提升。生成的嵌入向量序列用作编码器的输入。
- self.cls_token = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, 1, embed_dim))
- self.pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, num_patches + self.num_tokens, embed_dim))
- self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_ratio)
- …
- nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.cls_token, std=0.02)
- nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.pos_embed, std=0.02)
- …
- x = self.patch_embed(x) # [B, 196, 768]
- cls_token = self.cls_token.expand(x.shape[0], -1, -1) #[B, 1, 768]
- x = torch.cat((cls_token, x), dim=1) # [B, 197, 768]
- x = self.pos_drop(x + self.pos_embed)
代码知识:
# 创建两个tensor a = torch.randn(2, 2, 1) b = torch.randn(1, 2, 1) # 直接相加不会会报错 c = a + b
PVT
vit是柱状结构,但是PVT不是柱状,所以在每一个stage均进行了重新编码。
- for i in range(num_stages):
- pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, num_patches, embed_dims[i]))
- pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_rate)
-
-
- setattr(self, f"pos_embed{i + 1}", pos_embed)
-
初始化:
- for i in range(num_stages):
- pos_embed = getattr(self, f"pos_embed{i + 1}")
- trunc_normal_(pos_embed, std=.02)
重采样:
- def _get_pos_embed(self, pos_embed, patch_embed, H, W):
- if H * W == self.patch_embed.num_patches:
- return pos_embed
- else:
- return F.interpolate(
- pos_embed.reshape(1, patch_embed.H, patch_embed.W, -1).permute(0, 3, 1, 2),
- size=(H, W), mode="bilinear").reshape(1, -1, H * W).permute(0, 2, 1)
前馈:
- for i in range(self.num_stages):
- patch_embed = getattr(self, f"patch_embed{i + 1}")
- pos_embed = getattr(self, f"pos_embed{i + 1}")
- pos_drop = getattr(self, f"pos_drop{i + 1}")
- block = getattr(self, f"block{i + 1}")
- x, (H, W) = patch_embed(x)
-
- if i == self.num_stages - 1:
- cls_tokens = self.cls_token.expand(B, -1, -1)
- x = torch.cat((cls_tokens, x), dim=1)
- pos_embed_ = self._get_pos_embed(pos_embed[:, 1:], patch_embed, H, W)
- pos_embed = torch.cat((pos_embed[:, 0:1], pos_embed_), dim=1)
- else:
- pos_embed = self._get_pos_embed(pos_embed, patch_embed, H, W)
-
- x = pos_drop(x + pos_embed)
- ...

Relative position bias
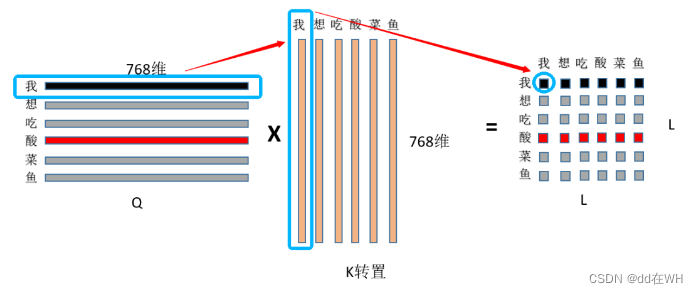
绝对位置编码是在计算注意力之前,直接将位置嵌入加到patch嵌入中。相对位置编码指的是在计算自注意力时,将相对位置偏差 B添加到嵌入的权重矩阵中。最近的许多工作(Liu 等人,2021b;Chen 等人,2021b)表明 RPB 的表现优于其他位置表示。

嵌入的长度为L(下图中L=6),则权重矩阵表示每个嵌入互相之间的关系,所以大小为(L,L),因此B的大小也是(L,L),表示的是每个嵌入之间的相对距离。
Swin Transformer
例如:每个窗口包含M*M个patch,M=3,也就是嵌入长度为9,B的大小为(9,9)。对于M*M个patch,沿着行方向和列方向的相对位置取值在【-2,2】之间,因此先初始化一个(2M-1,2M-1)大小的偏置矩阵。 偏置矩阵B的值则从
中获取。
初始化
- window_size = [3, 3]
-
- relative_position_bias_table = nn.Parameter(
- torch.zeros((2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1)))
- trunc_normal_(relative_position_bias_table, std=.02)
- print(relative_position_bias_table)
[ 0.0170, -0.0079, -0.0149, -0.0078, -0.0052, -0.0192, 0.0162, -0.0523, 0.0186, -0.0113, -0.0179, -0.0243, -0.0049, -0.0174, -0.0311, 0.0066, 0.0098, -0.0068, -0.0029, -0.0073, -0.0181, -0.0250, 0.0035, 0.0284, -0.0055] 【注】以上只是其中一次初始化
接下来做的是从中取值得到B,
中一共25个值,只要得到大小为(9,9)的下标矩阵,就可以从中取值,得到(9,9)的B。所以需要创建相对位置下标矩阵:
首先得到原始的相对位置关系:
- coords_h = torch.arange(window_size[0])
- coords_w = torch.arange(window_size[1])
- coords = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([coords_h, coords_w])) # 2, Wh, Ww
- coords_flatten = torch.flatten(coords, 1) # 2, Wh*Ww
- relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None, :] # 2, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
- relative_coords = relative_coords.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww, 2
- print(relative_coords.shape, relative_coords)
torch.Size([9, 9, 2]) 2个维度,分别表示行方向和列方向,比如第一行表示第一个patch嵌入与其他patch嵌入的相对位置关系
[ 0, 0],[ 0, -1], [ 0, -2], [-1, 0], [-1, -1], [-1, -2], [-2, 0], [-2, -1], [-2, -2] #第一行数据
去除负数,每个数值均加2。
- relative_coords[:, :, 0] += window_size[0] - 1 # shift to start from 0
- relative_coords[:, :, 1] += window_size[1] - 1
- print(relative_coords)
[2, 2], [2, 1], [2, 0], [1, 2],[1, 1], [1, 0], [0, 2],[0, 1],[0, 0] #第一行数据
二维相对位置改为一维相对位置:(如同读取二进制数据那样,计算出(i,j)在二进制数据的哪个位置)
- relative_coords[:, :, 0] *= 2 * window_size[1] - 1
- print(relative_coords.shape, relative_coords)
[10, 2], [10, 1],[10, 0], [ 5, 2],[ 5, 1], [ 5, 0], [ 0, 2],[ 0, 1],[ 0, 0]], #第一行数据
- relative_position_index = relative_coords.sum(-1) # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
- print(relative_position_index.shape, relative_position_index)
[12, 11, 10, 7, 6, 5, 2, 1, 0] #第一行数据
整个相对位置下标矩阵为:
[12, 11, 10, 7, 6, 5, 2, 1, 0],
[13, 12, 11, 8, 7, 6, 3, 2, 1],
[14, 13, 12, 9, 8, 7, 4, 3, 2],
[17, 16, 15, 12, 11, 10, 7, 6, 5],
[18, 17, 16, 13, 12, 11, 8, 7, 6],
[19, 18, 17, 14, 13, 12, 9, 8, 7],
[22, 21, 20, 17, 16, 15, 12, 11, 10],
[23, 22, 21, 18, 17, 16, 13, 12, 11],
[24, 23, 22, 19, 18, 17, 14, 13, 12]
B的值则是根据以上下标矩阵在中取值。
- relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias_table[relative_position_index.view(-1)].view(
- window_size[0] * window_size[1], window_size[0] * window_size[1], -1)
- relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous()
- print(relative_position_bias)
[[[-0.0049, -0.0243, -0.0179, -0.0523, 0.0162, -0.0192, -0.0149, -0.0079, 0.0170],
[-0.0174, -0.0049, -0.0243, 0.0186, -0.0523, 0.0162, -0.0078, -0.0149, -0.0079],
[-0.0311, -0.0174, -0.0049, -0.0113, 0.0186, -0.0523, -0.0052, -0.0078, -0.0149],
[-0.0068, 0.0098, 0.0066, -0.0049, -0.0243, -0.0179, -0.0523, 0.0162, -0.0192],
[-0.0029, -0.0068, 0.0098, -0.0174, -0.0049, -0.0243, 0.0186, -0.0523, 0.0162],
[-0.0073, -0.0029, -0.0068, -0.0311, -0.0174, -0.0049, -0.0113, 0.0186, -0.0523],
[ 0.0035, -0.0250, -0.0181, -0.0068, 0.0098, 0.0066, -0.0049, -0.0243, -0.0179],
[ 0.0284, 0.0035, -0.0250, -0.0029, -0.0068, 0.0098, -0.0174, -0.0049, -0.0243],
[-0.0055, 0.0284, 0.0035, -0.0073, -0.0029, -0.0068, -0.0311,-0.0174, -0.0049]]]
如公式那样,将B加到QK得到的关系矩阵中。
attn = attn + relative_position_bias.unsqueeze(0)Crossformer-Dynamic Position Bias
DPB也是相对位置编码的一种。但是其并不是从中获取B的值,而是直接对相对位置进行编码。对于一个group_size=3的窗口,同样的,相对位置关系一共有25种,用代码表示为:
- group_size = [3, 3]
- position_bias_h = torch.arange(1 - group_size[0], group_size[0])
- position_bias_w = torch.arange(1 - group_size[1], group_size[1])
- biases = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([position_bias_h, position_bias_w])) # 2, 2Wh-1, 2W2-1
- biases = biases.flatten(1).transpose(0, 1).float()
- print(biases.shape)
- print(biases)
torch.Size([25, 2])
[-2., -2.],[-2., -1.],[-2., 0.],[-2., 1.],[-2., 2.],
[-1., -2.],[-1., -1.],[-1., 0.],[-1., 1.],[-1., 2.],
[ 0., -2.],[ 0., -1.],[ 0., 0.],[ 0., 1.],[ 0., 2.],
[ 1., -2.],[ 1., -1.],[ 1., 0.],[ 1., 1.],[ 1., 2.],
[ 2., -2.],[ 2., -1.],[ 2., 0.],[ 2., 1.],[ 2., 2.]
对以上相对位置通过一个可训练模块进行重新编码:
DPB 的结构如下图 所示。其非线性变换由三个全连接层组成,具有层归一化和 ReLU。 DPB的输入维度为2,即(Δxij,Δyij),中间层的维度设置为D/4,其中D是嵌入的维度。输出 Bij 是一个标量,对第 i 个和第 j 个嵌入之间的相对位置特征进行编码。
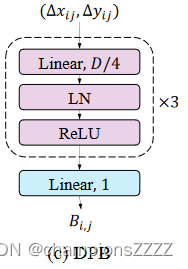
- class DynamicPosBias(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, dim, num_heads, residual):
- super().__init__()
- self.residual = residual
- self.num_heads = num_heads
- self.pos_dim = dim // 4
- self.pos_proj = nn.Linear(2, self.pos_dim)
- self.pos1 = nn.Sequential(
- nn.LayerNorm(self.pos_dim),
- nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
- nn.Linear(self.pos_dim, self.pos_dim),
- )
- self.pos2 = nn.Sequential(
- nn.LayerNorm(self.pos_dim),
- nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
- nn.Linear(self.pos_dim, self.pos_dim)
- )
- self.pos3 = nn.Sequential(
- nn.LayerNorm(self.pos_dim),
- nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
- nn.Linear(self.pos_dim, self.num_heads)
- )
- def forward(self, biases):
- if self.residual:
- pos = self.pos_proj(biases) # 2Wh-1 * 2Ww-1, heads
- pos = pos + self.pos1(pos)
- pos = pos + self.pos2(pos)
- pos = self.pos3(pos)
- else:
- pos = self.pos3(self.pos2(self.pos1(self.pos_proj(biases))))
- return pos

将相对位置关系输入到该模块中,得到了类似于的偏置矩阵。随后处理与SwinTSF相同。


