- 1PostgreSQL可拔插存储引擎表定义机制
- 2springboot 将@Service映射成为Restful服务_spring 如何将另外一个服务的端口映射成接口
- 3如何使用Github Action优雅的同步国外镜像到DockerHub或私有仓库_github actions登录dockerhub
- 4blender2.8 视频编辑:影片的伸缩与剪切_blender 剪辑缩放动画
- 5牛客网常见算法思路 (二)排序_牛客项目经历怎么排序
- 6几大空三软件的图像坐标系的原点
- 7Ubuntu 20.04使用Livox Mid-360_livox mid360 ubuntu20
- 8macOS Sonoma 14.4 (23E214) 正式版发布,ISO、IPSW、PKG 下载_macos sonoma pkg
- 95款好用且免费项目管理工具_csdn 免费项目管理工具
- 10【SmartApi】接口测试工具本地化Mock数据服务方案
【C++】string 之 assign、at、append函数的学习_string assign
赞
踩
前言
在学习string类的过程中,我发现了assign这个函数,感觉很有用,就来记录一下
assign函数原型:
void assign(size_type n, const T& x = T());
void assign(const_iterator first, const_iterator last);
- 1
- 2
- 3
assign函数有两种使用方式:
第一种:容器名.assign (a, b);
容器名.assign (a, b);
- 1
将vector中的内容清空,并给予a个b元素
下面给出一个例子:
#include<iostream> #include<vector> using namespace std; int main() { vector<int>v1{ 1,2,3 }; //创建一个容器v1 元素类型是int 有三个元素 v1.assign(2, 5); for (int val : v1) { cout << val << endl; } cout << "--------------------" << endl; v1.assign(4, 5); for (int val : v1) { cout << val << endl; } cout << "--------------------" << endl; int a = 2; int b = 3; int n = a * b; int x; v1.assign(n, x); for (int val : v1) { cout << val << endl; } cout << "--------------------" << endl; return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
通过上面这个例子,我们可以发现,首先,在传入新的元素之前,assign函数会先清空vector中的内容,之后,再传入新的数据,并且,无论是传入一个变量,还是传入未初始化的变量,都可以实现assign的功能
注意:第一个元素,即要传入的元素个数不能是未初始化的变量,不然程序会报错
第二种:容器名2.assign(容器名1.begin(),容器名1.end());
容器名2.assign(容器名1.begin(),容器名1.end());
- 1
提示:
这种使用方法的含义就是:
将容器1中的begin()和end()之间的元素放到容器2中,包含起始位置和终止位置。同样的,也是先清空容器2中的内容
下面给出一个例子:
#include<iostream> #include<vector> using namespace std; int main() { vector<int>v1{ 1,2,3 }; vector<int>v2{ 1,2 }; v2.assign(v1.begin(), v1.end()); for (int val : v2) { cout << val << endl; } cout << "--------------" << endl; v2.assign(v1.begin() + 1, v1.end() - 1); for (int val : v2) { cout << val << endl; } cout << "--------------" << endl; return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
通过上面这些例子,相信我们就可以基本明白assign是如何使用的了
at函数
函数源码
vector<_Tp, _Allocator>::at(size_type __n)
{
if (__n >= size())
this->__throw_out_of_range();
return this->__begin_[__n];
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
了解即可,不用深究
at函数的使用
arr[3]与arr.at(3)的效果是一样的,只是使用at函数,不会发生越界访问的情况,更加安全
举个例子:
#include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; int main() { vector<int>arr{ 1,2,3,4,5 }; for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) { cout << arr.at(i) << endl; } //cout << arr.at(5) << endl; return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
运行结果:
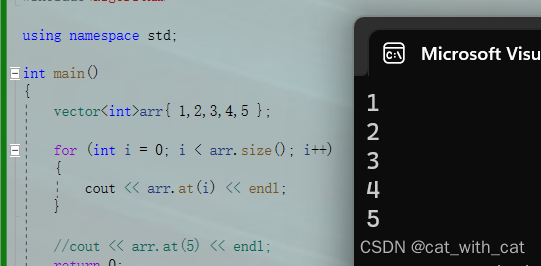
相信通过上面的学习,我们已经明白了如何使用at函数
append函数
接下来,我们来学习append函数
用法1:完全复制
格式:
append函数的使用格式:
字符串1.append(字符串2);
- 1
例子:
下面,举一个例子,方便大家理解:
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { string a = "qaz"; string b = "wsx"; string c = "edc"; cout << a << endl; a.append(b); cout << a << endl; a.append(b + c); cout << a; return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
运行结果:
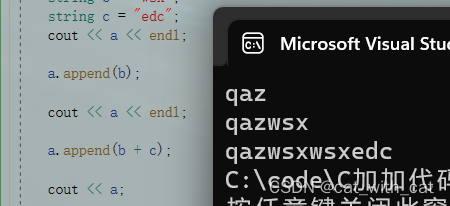
通过上面这个例子,我们可以知道虽然append函数一次只能复制一个字符串,但这个字符串是可以先运算的,比如:b+c
用法2:部分复制(后面的字符)
append除了复制全部内容以外,还可以选取部分进行复制
格式:
使用格式:
字符串1.append(字符串2,起始位置index,复制元素个数n);
- 1
作用:
将字符串2中第index个位置开始(包含起始位置的元素),共n个元素,拷贝到字符串1的末尾
例子:
下面给出一段代码,方便大家理解:
#include<iostream> using std::string; using std::cout; using std::endl; int main() { string a = "hello"; string b = "world"; cout << a << endl; a.append(b, 2, 3); cout << a << endl; return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
运行结果:
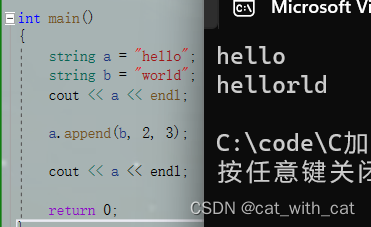
特别的:
当只传入起始位置index,而不传入复制元素个数n的时候,编译器默认拷贝到字符串末尾
用法3:部分复制(前面的字符)
格式:
字符串1.append(C语言风格的字符串2,复制元素的个数n);
- 1
将字符串2中从开始位置算起,共复制n个元素放到字符串1的末尾
例子:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string a = "hello";
const char* b = "world";
a.append(b, 3);
cout << a << endl;
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
运行结果:
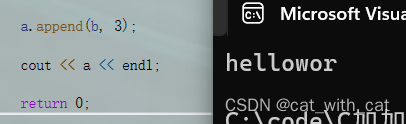
注意:
当直接传入字符串的时候,编译器默认它是C语言风格的字符串
例子如下:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string a = "hello";
a.append("world", 5);
cout << a << endl;
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
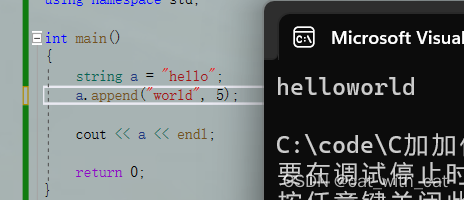
用法4:复制相同字符
格式:
字符串1.append(复制字符的个数n,复制的字符ch);
- 1
作用:
将n个ch复制到字符串1的后面
例子:
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { string a = "hello"; char c = '!'; a.append(3, c); cout << a << endl; int n = 4; a.append(n, 'h'); cout << a << endl; return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
运行结果:
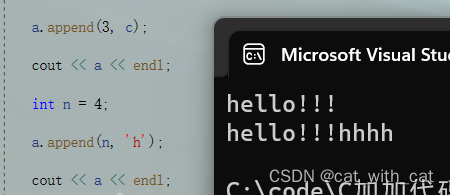
结语
对于assign、at和append函数的学习和介绍到这里就结束了,希望这篇文章对你有帮助,我们下次见~



