- 1深入浅出RabbitMQ:顺序消费、死信队列和延时队列_rabbitmq消费顺序性
- 2以太坊搭建联盟链_76a.one
- 3单相全桥逆变原理及仿真实验
- 4Android Studio Gradle
- 5微软发布新的Copilot+ PCs 是微软推出的一系列高性能、智能化的 Windows 个人电脑。
- 6leetcode 27. 移除元素_nums.erase
- 7华为OD机试Java - 螺旋数字矩阵
- 8西门子SICAR汽车行业标准程序及图纸详解,源码提供,适用于博途编写,含安全程序与安装要求
- 9Web系统常见安全漏洞介绍及解决方案-CSRF攻击_csrf通常和什么联合使用
- 10区块链入门教程(1)--概述_区块链开发入门
mysql 四种分区方式_mysql分割
赞
踩
1、什么是表分区?
mysql数据库中的数据是以文件的形势存在磁盘上的,默认放在/mysql/data下面(可以通过my.cnf中的datadir来查看),一张表主要对应着三个文件,一个是frm存放表结构的,一个是myd存放表数据的,一个是myi存表索引的。如果一张表的数据量太大的话,那么myd,myi就会变的很大,查找数据就会变的很慢,这个时候我们可以利用mysql的分区功能,在物理上将这一张表对应的三个文件,分割成许多个小块,这样呢,我们查找一条数据时,就不用全部查找了,只要知道这条数据在哪一块,然后在那一块找就行了。如果表的数据太大,可能一个磁盘放不下,这个时候,我们可以把数据分配到不同的磁盘里面去。
表分区,是指根据一定规则,将数据库中的一张表分解成多个更小的,容易管理的部分。从逻辑上看,只有一张表,但是底层却是由多个物理分区组成。
2、表分区与分表的区别
分表:指的是通过一定规则,将一张表分解成多张不同的表。比如将用户订单记录根据时间成多个表。 分表与分区的区别在于:分区从逻辑上来讲只有一张表,而分表则是将一张表分解成多张表。
3、表分区有什么好处?
(1)与单个磁盘或文件系统分区相比,可以存储更多的数据。
(2)对于那些已经失去保存意义的数据,通常可以通过删除与那些数据有关的分区,很容易地删除那些数据。相反地,在某些情况下,添加新数据的过程又可以通过为那些新数据专门增加一个新的分区,来很方便地实现。
(3)一些查询可以得到极大的优化,这主要是借助于满足一个给定WHERE语句的数据可以只保存在一个或多个分区内,这样在查找时就不用查找其他剩余的分区。因为分区可以在创建了分区表后进行修改,所以在第一次配置分区方案时还不曾这么做时,可以重新组织数据,来提高那些常用查询的效率。
(4)涉及到例如SUM()和COUNT()这样聚合函数的查询,可以很容易地进行并行处理。这种查询的一个简单例子如 “SELECT salesperson_id, COUNT (orders) as order_total FROM sales GROUP BY salesperson_id;”。通过“并行”,这意味着该查询可以在每个分区上同时进行,最终结果只需通过总计所有分区得到的结果。
5)通过跨多个磁盘来分散数据查询,来获得更大的查询吞吐量。
4、分区表的限制因素
(1)一个表最多只能有1024个分区。
(2)MySQL5.1中,分区表达式必须是整数,或者返回整数的表达式。在MySQL5.5中提供了非整数表达式分区的支持。
(3)如果分区字段中有主键或者唯一索引的列,那么多有主键列和唯一索引列都必须包含进来。即:分区字段要么不包含主键或者索引列,要么包含全部主键和索引列。
(4)分区表中无法使用外键约束。
(5)MySQL的分区适用于一个表的所有数据和索引,不能只对表数据分区而不对索引分区,也不能只对索引分区而不对表分区,也不能只对表的一部分数据分区。
5、如何判断当前MySQL是否支持分区?
- mysql> show variables like '%partition%';
- +-------------------+-------+
- | Variable_name | Value |
- +-------------------+-------+
- | have_partitioning | YES |
- +-------------------+-------+
- 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
have_partintioning 的值为YES,表示支持分区。
6、MySQL支持的分区类型有哪些?
(1)RANGE分区:基于属于一个给定连续区间的列值,把多行分配给分区。
(2)LIST分区:类似于按RANGE分区,区别在于LIST分区是基于列值匹配一个离散值集合中的某个值来进行选择。
(3)HASH分区:基于用户定义的表达式的返回值来进行选择的分区,该表达式使用将要插入到表中的这些行的列值进行计算。这个函数可以包含MySQL 中有效的、产生非负整数值的任何表达式。
(4)KEY分区:类似于按HASH分区,区别在于KEY分区只支持计算一列或多列,且MySQL服务器提供其自身的哈希函数。必须有一列或多列包含整数值。
说明:在MySQL5.1版本中,RANGE,LIST,HASH分区要求分区键必须是INT类型,或者通过表达式返回INT类型。但KEY分区的时候,可以使用其他类型的列(BLOB,TEXT类型除外)作为分区键。
6.1、RANGE分区
根据范围分区,范围应该连续但是不重叠,使用PARTITION BY RANGE, VALUES LESS THAN关键字。不使用COLUMNS关键字时RANGE括号内必须为整数字段名或返回确定整数的函数。
6.1.1、根据数值范围
- drop table if exists employees;
- create table employees(
- id int not null,
- fname varchar(30),
- lname varchar(30),
- hired date not null default '1970-01-01',
- separated date not null default '9999-12-31',
- job_code int not null default 0,
- store_id int not null default 0
- )engine=myisam default charset=utf8
- partition by range(store_id)(
- partition p0 values less than (6),
- partition p1 values less than (11),
- partition p2 values less than (16),
- partition p3 values less than (21)
- );
-
-
- insert into employees (id,fname,lname,hired,store_id) values(1,'张三','张','2015-05-04',1);
- insert into employees (id,fname,lname,hired,store_id) values(2,'李四','李','2016-10-01',5);
- insert into employees (id,fname,lname,hired,store_id) values(3,'王五','王','2016-11-14',10);
- insert into employees (id,fname,lname,hired,store_id) values(4,'赵六','赵','2017-08-24',15);
- insert into employees (id,fname,lname,hired,store_id) values(5,'田七','田','2018-05-20',20);

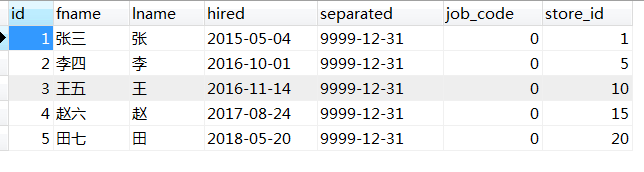

按照这种分区方案,在商店1到5工作的雇员相对应的所有行被保存在分区P0中,商店6到10的雇员保存在P1中,依次类推。注意,每个分区都是按顺序进行定义,从最低到最高。这是PARTITION BY RANGE 语法的要求。
对于包含数据(6,'亢八','亢','2018-06-24',13)的一个新行,可以很容易地确定它将插入到p2分区中。
insert into employees (id,fname,lname,hired,store_id) values(6,'亢八','亢','2018-06-24',13);
但是如果增加了一个编号为第21的商店(7,'周九','周','2018-07-24',21),将会发生什么呢?在这种方案下,由于没有规则把store_id大于20的商店包含在内,服务器将不知道把该行保存在何处,将会导致错误。
- insert into employees (id,fname,lname,hired,store_id) values(7,'周九','周','2018-07-24',21);
- ERROR 1526 (HY000): Table has no partition for value 21
要避免这种错误,可以通过在CREATE TABLE语句中使用一个“catchall” VALUES LESS THAN子句,该子句提供给所有大于明确指定的最高值的值:
- create table employees(
- id int not null,
- fname varchar(30),
- lname varchar(30),
- hired date not null default '1970-01-01',
- separated date not null default '9999-12-31',
- job_code int not null default 0,
- store_id int not null default 0
- )engine=myisam default charset=utf8
- partition by range(store_id)(
- partition p0 values less than (6),
- partition p1 values less than (11),
- partition p2 values less than (16),
- partition p3 values less than (21),
- partition p4 values less than MAXVALUE
- );

6.1.2、根据TIMESTAMP范围
- drop table if exists quarterly_report_status;
- create table quarterly_report_status(
- report_id int not null,
- report_status varchar(20) not null,
- report_updated timestamp not null default current_timestamp on update current_timestamp
- )
- partition by range(unix_timestamp(report_updated))(
- partition p0 values less than (unix_timestamp('2008-01-01 00:00:00')),
- partition p1 values less than (unix_timestamp('2008-04-01 00:00:00')),
- partition p2 values less than (unix_timestamp('2008-07-01 00:00:00')),
- partition p3 values less than (unix_timestamp('2008-10-01 00:00:00')),
- partition p4 values less than (unix_timestamp('2009-01-01 00:00:00')),
- partition p5 values less than (unix_timestamp('2009-04-01 00:00:00')),
- partition p6 values less than (unix_timestamp('2009-07-01 00:00:00')),
- partition p7 values less than (unix_timestamp('2009-10-01 00:00:00')),
- partition p8 values less than (unix_timestamp('2010-01-01 00:00:00')),
- partition p9 values less than maxvalue
- );

6.1.3、根据DATE、DATETIME范围
添加COLUMNS关键字可定义非integer范围及多列范围,不过需要注意COLUMNS括号内只能是列名,不支持函数;多列范围时,多列范围必须呈递增趋势:
- drop table if exists member;
- create table member(
- firstname varchar(25) not null,
- lastname varchar(25) not null,
- username varchar(16) not null,
- email varchar(35),
- joined date not null
- )
- partition by range columns(joined)(
- partition p0 values less than ('1960-01-01'),
- partition p1 values less than ('1970-01-01'),
- partition p2 values less than ('1980-01-01'),
- partition p3 values less than ('1990-01-01'),
- partition p4 values less than maxvalue
- )
6.1.4、根据多列范围
- drop table if exists rc3;
- create table rc3(
- a int,
- b int
- )
- partition by range columns(a,b)(
- partition p0 values less than (0,10),
- partition p1 values less than (10,20),
- partition p2 values less than (20,30),
- partition p3 values less than (30,40),
- partition p4 values less than (40,50),
- partition p5 values less than (maxvalue,maxvalue)
- )
6.1.5、RANGE分区在如下场合特别有用
- drop table if exists staff;
- create table staff(
- id int not null,
- fname varchar(30),
- lname varchar(30),
- hired date not null default '1970-01-01',
- separated date not null default '9999-12-31',
- job_code int not null default 0,
- store_id int not null default 0
- )engine=myisam default charset=utf8
- partition by range(year(separated))(
- partition p0 values less than (1991),
- partition p1 values less than (1996),
- partition p2 values less than (2001),
- partition p4 values less than MAXVALUE
- );

(1)当需要删除一个分区上的“旧的”数据时,只删除分区即可。如果你使用上面最近的那个例子给出的分区方案,你只需简单地使用”alter table staff drop partition p0;”来删除所有在1991年前就已经停止工作的雇员相对应的所有行。对于有大量行的表,这比运行一个如”delete from staff WHERE year(separated) <= 1990;”这样的一个DELETE查询要有效得多。
(2)想要使用一个包含有日期或时间值,或包含有从一些其他级数开始增长的值的列。
(3)经常运行直接依赖于用于分割表的列的查询。例如,当执行一个如”select count(*) from staff where year(separated) = 200 group by store_id;”这样的查询时,MySQL可以很迅速地确定只有分区p2需要扫描,这是因为余下的分区不可能包含有符合该WHERE子句的任何记录。
6.2、LIST分区
根据具体数值分区,每个分区数值不重叠,使用PARTITION BY LIST、VALUES IN关键字。跟Range分区类似,不使用COLUMNS关键字时List括号内必须为整数字段名或返回确定整数的函数。
类似于按RANGE分区,区别在于LIST分区是基于列值匹配一个离散值集合中的某个值来进行选择。
LIST分区通过使用“PARTITION BY LIST(expr)”来实现,其中“expr”是某列值或一个基于某个列值、并返回一个整数值的表达式,然后通过“VALUES IN (value_list)”的方式来定义每个分区,其中“value_list”是一个通过逗号分隔的整数列表。
假定有20个音像店,分布在4个有经销权的地区,如下表所示:
====================
地区 商店ID 号
北区 3, 5, 6, 9, 17
东区 1, 2, 10, 11, 19, 20
西区 4, 12, 13, 14, 18
中心区 7, 8, 15, 16
- drop table if exists staff;
- create table staff(
- id int not null,
- fname varchar(30),
- lname varchar(30),
- hired date not null default '1970-01-01',
- separated date not null default '9999-12-31',
- job_code int not null default 0,
- store_id int not null default 0
- )
- partition by list(store_id)(
- partition pNorth values in (3,5,6,9,17),
- partition pEast values in (1,2,10,11,19,20),
- partition pWest values in (4,12,13,14,18),
- partition pCentral values in (7,8,15,16)
- );

这使得在表中增加或删除指定地区的雇员记录变得容易起来。例如,假定西区的所有音像店都卖给了其他公司。那么与在西区音像店工作雇员相关的所有记录(行)可以使用查询“ALTER TABLE staff DROP PARTITION pWest;”来进行删除,它与具有同样作用的DELETE(删除)“DELETE FROM staff WHERE store_id IN (4,12,13,14,18);”比起来,要有效得多。
如果试图插入列值(或分区表达式的返回值)不在分区值列表中的一行时,那么“INSERT”查询将失败并报错。
当插入多条数据出错时,如果表的引擎支持事务(Innodb),则不会插入任何数据;如果不支持事务,则出错前的数据会插入,后面的不会执行。
与Range分区相同,添加COLUMNS关键字可支持非整数和多列。
6.3、HASH分区
Hash分区主要用来确保数据在预先确定数目的分区中平均分布,Hash括号内只能是整数列或返回确定整数的函数,实际上就是使用返回的整数对分区数取模。
要使用HASH分区来分割一个表,要在CREATE TABLE 语句上添加一个“PARTITION BY HASH (expr)”子句,其中“expr”是一个返回一个整数的表达式。它可以仅仅是字段类型为MySQL整型的一列的名字。此外,你很可能需要在后面再添加一个“PARTITIONS num”子句,其中num是一个非负的整数,它表示表将要被分割成分区的数量。
如果没有包括一个PARTITIONS子句,那么分区的数量将默认为1
- drop table if exists staff;
- create table staff(
- id int not null,
- fname varchar(30),
- lname varchar(30),
- hired date not null default '1970-01-01',
- separated date not null default '9999-12-31',
- job_code int not null default 0,
- store_id int not null default 0
- )
- partition by hash(store_id)
- partitions 4;
-
-
- drop table if exists staff;
- create table staff(
- id int not null,
- fname varchar(30),
- lname varchar(30),
- hired date not null default '1970-01-01',
- separated date not null default '9999-12-31',
- job_code int not null default 0,
- store_id int not null default 0
- )
- partition by hash(year(hired))
- partitions 4;

Hash分区也存在与传统Hash分表一样的问题,可扩展性差。MySQL也提供了一个类似于一致Hash的分区方法-线性Hash分区,只需要在定义分区时添加LINEAR关键字。
- drop table if exists staff;
- create table staff(
- id int not null,
- fname varchar(30),
- lname varchar(30),
- hired date not null default '1970-01-01',
- separated date not null default '9999-12-31',
- job_code int not null default 0,
- store_id int not null default 0
- )
- partition by hash(store_id)
- partitions 4;
-
-
- drop table if exists staff;
- create table staff(
- id int not null,
- fname varchar(30),
- lname varchar(30),
- hired date not null default '1970-01-01',
- separated date not null default '9999-12-31',
- job_code int not null default 0,
- store_id int not null default 0
- )
- partition by hash(year(hired))
- partitions 4;

线性哈希功能,它与常规哈希的区别在于,线性哈希功能使用的一个线性的2的幂(powers-of-two)运算法则,而常规哈希使用的是求哈希函数值的模数。
6.4、KEY分区
Key分区与Hash分区很相似,只是Hash函数不同,定义时把Hash关键字替换成Key即可,同样Key分区也有对应与线性Hash的线性Key分区方法。
- drop table if exists staff;
- create table staff(
- id int not null,
- fname varchar(30),
- lname varchar(30),
- hired date not null default '1970-01-01',
- separated date not null default '9999-12-31',
- job_code int not null default 0,
- store_id int not null default 0
- )
- partition by key(store_id)
- partitions 4;
在KEY分区中使用关键字LINEAR和在HASH分区中使用具有同样的作用,分区的编号是通过2的幂(powers-of-two)算法得到,而不是通过模数算法。
另外,当表存在主键或唯一索引时可省略Key括号内的列名,Mysql将按照主键-唯一索引的顺序选择,当找不到唯一索引时报错。


