- 1NB-IoT物联网开发技巧和应用:专栏总述_nb-iot开发实战
- 2C++与Rust操作裸指针的比较
- 3探索未来:ElectronBot——你的桌面级小机器人伙伴
- 4【报错记录】Python文件读取时报错FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: ‘xxx‘_python filenotfounderror: [errno 2] no such file o
- 52024年最受欢迎的AI工具大汇总(建议收藏)_最好的ai软件2024
- 6大数据带你挖掘打车的秘籍(2)
- 7logback配置错误记录_logback appender filter
- 8爆火的AI直播换脸应用Deep-Live-Cam整合包来了!6G显存可跑!
- 9electron打包vue项目到debian操作系统踩坑_an unhandled rejection has occurred inside forge:
- 10中国数据库前世今生:90年代的群雄争霸与技术革新
【Spring Boot】手撕搜索引擎项目,深度复盘在开发中的重难点和总结(长达两万6千字的干货,系好安全带,要发车了......)_spring boot 搜索引擎
赞
踩
搜索引擎
简单点来说就是模拟实现一个属于自己的小百度,通过这前端网页输入关键字,后端返回响应的结果,由于百度的搜索极其复杂,我们在模拟时只用实现返回文章的标题,链接以及部分包含关键字内容的正文即可。
如下图中:搜索ArrayList关键字,点击搜索一下,就会出现如下的页面。
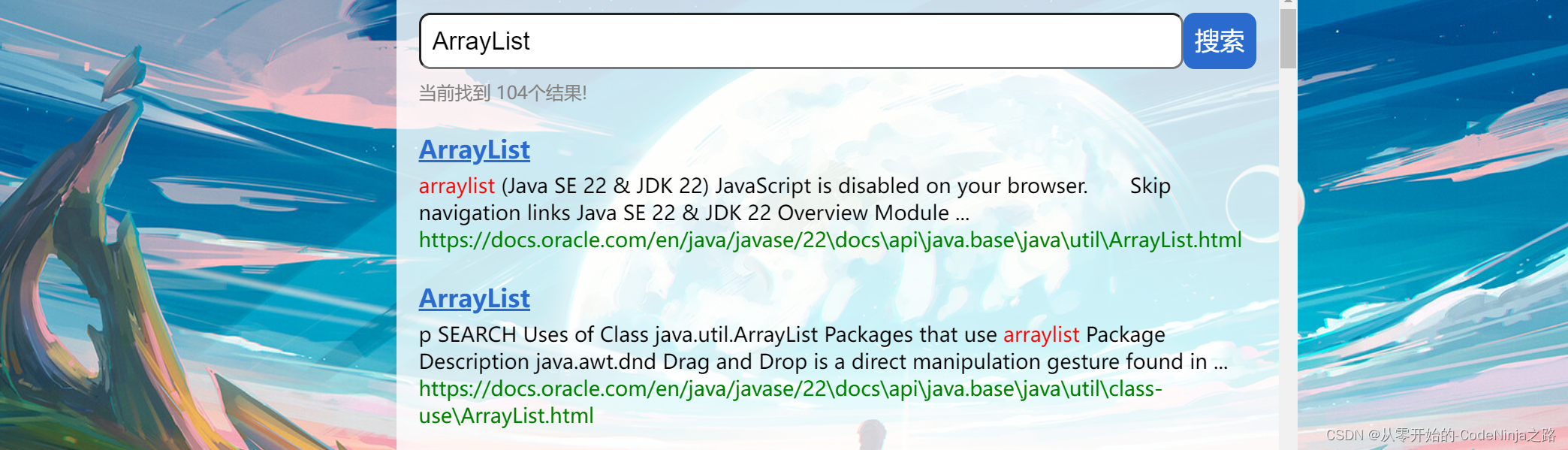
搜索引擎的本质就是输入一个查询词,得到若干个搜索结果,其中包含了标题,展示url、点击url以及部分正文内容。
搜索引擎的核心思路
因为百度是包含了很多很多信息,我们无法取到(说实话,哪怕取到了自己的电脑也会跑宕机,
),所以我们来实现范围搜索,就是在所给的固定的范围内进行搜索,这里我采用的是JDK21的辅助文档,
前提是必须把这个压缩包给下载下来哈,不下载可没法操作嘞,这里我就把关于22版本的链接放在这了,直接下载解压就好,链接:https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/javase-jdk22-doc-downloads.html,当然了使用其他的版本也都一样的。
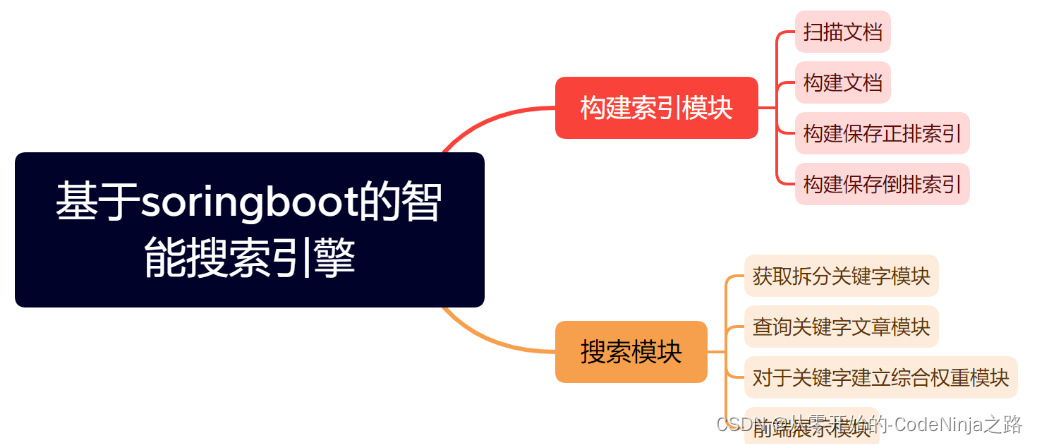
首先我将项目分为了四大模块哈:
- 解析模块
- 排序模块
- 搜索模块
其中两大最重要的模块的总体实现思路如下图:
一、解析模块
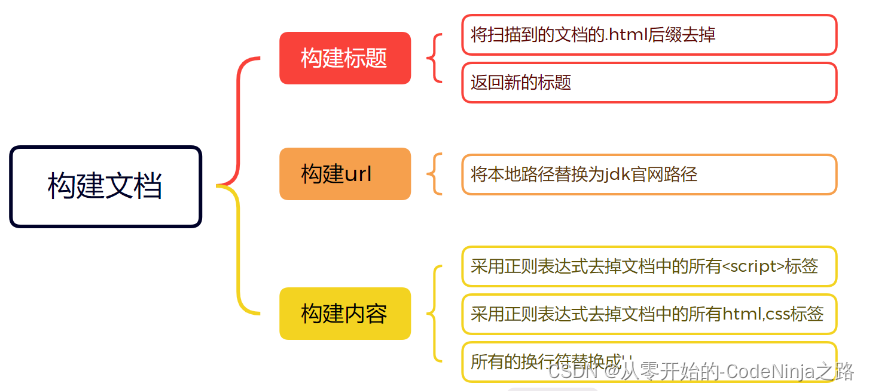
在本篇文章中,解析文件模块所要创建的类名为----Parser,整体的思路是先创建一个文件集合(List)用来保存从引入压缩包解析后的所有以.html结尾的文件,在遍历每一个文件进行解析他们的标题,URL以及响应正文,并且将每个文件解析好的结果传给创建排序模块进行排序(只是后话了,为了节省时间进行的 ,就是每解析一个以.html结尾的文件,就将其进行排序)。
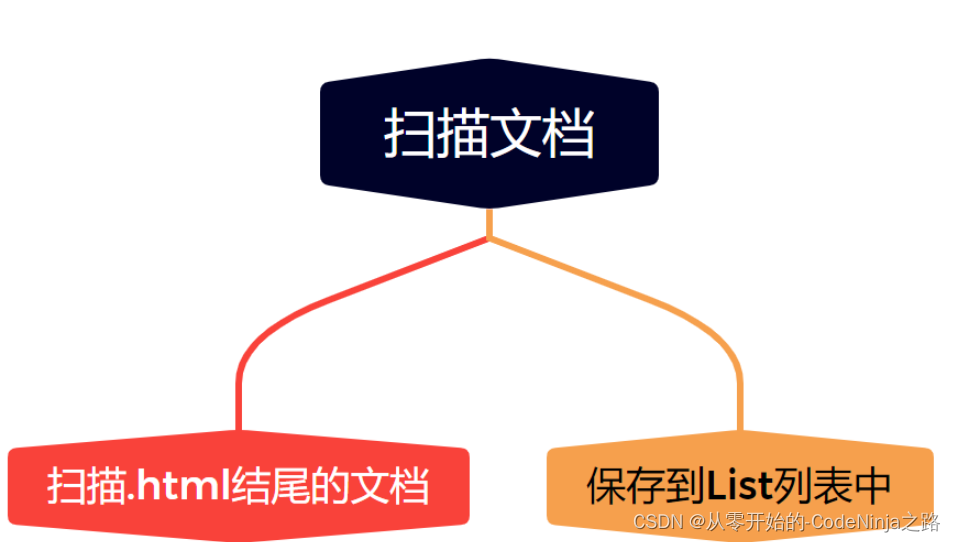
1.1 枚举所有文件
首先将下载好的压缩包解压过后,将文件的路径以字符串的形式写入IDEA,创建方法名为enumFile的方法来解析文件,应为一个文件下有许多文件夹,我们要将他们全部遍历进行存储,这里我采用的是递归的方法来读取该路径下的所有文件,创建数组来保存该一级目录下的文件,其中肯定也包含文件夹,在遍历该数组,如果该文件的文件是以.html结尾的,那么直接保存到集合中即可,如果是文件夹那么通过递归进行再次遍历,直到将引入的压缩包下的所有以.html结尾的文件全部保存到集合中,然后返回集合,实现的代码如下。
private void enumFile(String inputFile, List<File> fileList) {
File file=new File(inputFile);
File[]files=file.listFiles();
for(File file1:files){
if(file1.isFile()){
if(file1.getAbsolutePath().endsWith(".html")){
fileList.add(file1);
}
}else{
enumFile(file1.getAbsolutePath(),fileList);
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
代码实现的结果如下:
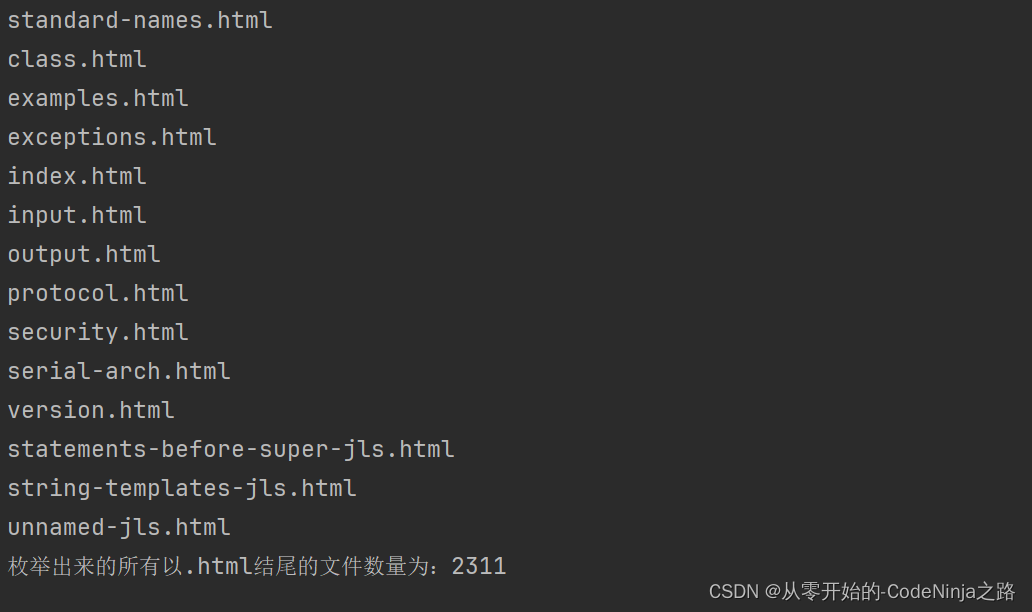
从这里可以看出,该压缩包中的所有以.html的文件已经全部被我们枚举出来了,其全部数量为2311
1.2 解析每个文件的标题,URL以及正文
这里我们创建一个方法名为parseHtml,该方法内包含三个分别用来解析标题,URL以及正文的方法
该方法为:
private void parseHtml(File file) { //解析html的标题 String title=parseHtmlTitle(file); //解析html的url String url= parseHtmlUrl(file); //解析html的正文 //String content= parseHtmlContent(file); //解析html的正文通过正则表达式 String content=parseHtmlContentByRegex(file); //每解析一个文件就创造一个正排索引和倒排索引 index.createIndex(title,url,content); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
其中title字符串用来接收parseHtmlTitle方法解析回来的文件标题
其中url字符串用来接收parseHtmlUrl方法解析回来的文件标题
其中content字符串用来接收parseHtmlContentByRegex方法解析回来的文件标题
(这里的解析文件正文是最难的一部分,其它两个极其简单)
然后将解析的三部分传入index类用来创建索引(这个我们接下来说)
1.2.1 解析标题
解析文件标题很简单,因为前面读取文件时,每个文件不是以.html结尾的吗,那我们直接选取该文件名再去掉它的后缀,例如文件名:arraylist.html,我们直接去掉.html只要前面的arraylist即可
代码如下:
private String parseHtmlTitle(File file) {
return file.getName().replaceAll(".html","");
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
我就说 很简单吧,我直接把字符串中的.html用空串替代就完了
1.2.2 解析URL
其实解析URL也是极其简单的,就是要考验眼力,别给看错了就行,就是把官网上的该页面的链接截取前半段,
在把你下载解析好的该文件的路径的后半段截下来,两端一填充就完美了,不够在拼接好以后要自己先试试看能否访问哈,访问不了就不怪我辽
…
代码如下:
private String parseHtmlUrl(File file) {
//C:\Users\xia\IdeaProjects\SearchProject \docs\api\java.base\java\\util
//file:///C:/Users/xia/IdeaProjects/SearchProject/docs/api/java.base/java/util/ArrayList.html
//https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/22/docs/api/java.base/java/util/ArrayList.html
String s=file.getAbsolutePath().substring("C:\\Users\\xia\\IdeaProjects\\SearchProject".length());
return "https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/22"+s;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
1.2.3 解析正文
首先老样子我们还是先介绍一下关于解析正文的思路哈,读取一个文件的内容是不是首先要运用到学过的读取数据流里的FileReader(这个是读取字节流),回顾一下还有一个是读取字符流的为OutPut…啥的,跑题了哈,然后将读取的数据存在一个字符串中,在遇到换行以及大空格后将其替换成空字符串。
代码如下
private String readFile(File file) { StringBuilder stringBuilder=new StringBuilder(); try(BufferedReader bufferedReader=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file),1024*1024)){ while(true){ int c=bufferedReader.read(); if(c==-1){ break; } char ch=(char)c; if(ch=='\n'||ch=='\t'){ ch=' '; } stringBuilder.append(ch); } }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } return stringBuilder.toString(); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
这里解释一下为什么不直接用FileReader而是将其嵌套在StringBuilde中,因为直接使用FileReader表示每次是从硬板中读取数据,这样以来读取速度就会非常之慢,而采用StringBUilder则是在内存中开辟一块空间,这里我们开辟空间用来保存从硬盘中读来的数据,在接下来的使用中直接从内存中读取就会比从硬盘中读取快10倍不止
private String parseHtmlContentByRegex(File file ){
String content=readFile(file);
//通过正则表达式去掉正文中的<script>标签
content=content.replaceAll("<script.*?>(.*?)</script>"," ");
//通过正则表达式去掉正文中的其它标签
content=content.replaceAll("<.*?>"," ");
通过正则表达式合并多个空格
content = content.replaceAll("\\s+", " ");
return content;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
然后通过正则表达式将该字符串中所有的以
1.3 线程池优化代码
因为之前的代码都是有一个线程来进行解析,会很慢,这里我们采用多线程来解决,首先就是创建一个拥有10个线程的池子,以方便后面在用的时候直接从池子里拿就行,然后创建一个计数器用来判断是否全部执行完(每解析一个文件,计数器就会+1),在计数器等于我们解析我文件数量后就停止线程,销毁线程池,然后调用index类中将结果进行字符化保存在本地文件中
代码如下;
public void runByThread() throws InterruptedException { List<File> fileList=new ArrayList<>(); //枚举所有以.html结尾的文件 enumFile(INPUT_FILE,fileList); long start=System.currentTimeMillis(); //创建一个包含10个线程的线程池 ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10); //创建一个计数器来表示文件的数量 CountDownLatch countDownLatch=new CountDownLatch(fileList.size()); for(File file:fileList){ executorService.submit(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { parseHtml(file); log.info("文件名:"+file.getName()+"文件路径:"+file.getAbsolutePath()); countDownLatch.countDown(); } }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); index.save(); long end=System.currentTimeMillis(); log.info("多线程所消耗的时间:"+(end-start)+"ms"); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
整体的Parser的代码放在在文章最后了~
二 、创建排序模块
总体的思路为:
- 构建正排索引、
- 倒排索引、
- 序列化,
- 反序列
四大方法
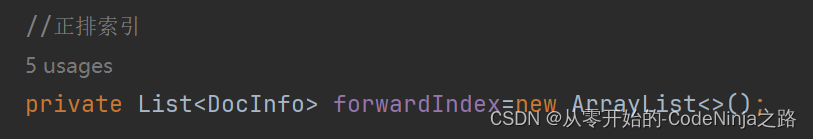
其中构建
正排索引:就是根据每篇文章的id来搜索该文章,并将该文件章的所有信息查找出来,正排索引就是使用一个集合来保存所有文章的id,这里我命名为forwordIndex
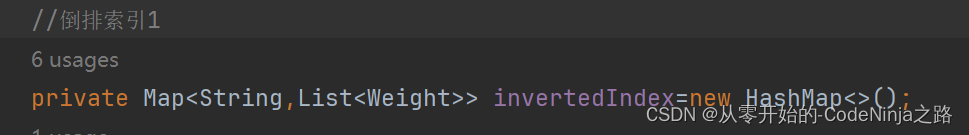
倒排索引:通过输入的关键词搜索到与其全部有关的文章,这里使用Map来实现,通过一个词来获取一个与其相关的集合,这个集合内包含的是每篇与这个关键词有联系的文章id
2.1 构建正排索引
构建正排很简单,直接把从parse传过来的标题、URl以及正文进行封装成一个类放在存储的集合中就行
代码如下:
private DocInfo CreateForwardIndex(String title, String url, String content) {
DocInfo docInfo=new DocInfo();
docInfo.setTitle(title);
docInfo.setUrl(url);
docInfo.setContent(content);
synchronized (lock1){
docInfo.setId(forwardIndex.size());
forwardIndex.add(docInfo);
}
return docInfo;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
2.2 构建倒排索引
构建倒排索引的总体思路是:首先将传进来的文章的标题以及正文进行分词,就是根据我们大众认识的分成多个组合在一块的词组,然后将每篇文章的分词结果进行权重比较(权重:该文章出现的次数越多,权重越大),权重最大的放在该词集合的最前面,方便用户直接看到。
引入Ansj分词库
我们在将单词存入倒排索引表中的时候,其实是将正排索引表中存储的标题还有内容进行分词,统计权重后才存入表中的,而分词的操作中,我们需要引入分词库ansj
<!-- Java 版本的一个分词库,本身是支持中文分词的,只是咱的文档中没有中文。但英文分词它也支持 -->
<!-- https://github.com/NLPchina/ansj_seg -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.ansj</groupId>
<artifactId>ansj_seg</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6</version>
</dependency>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
代码如下:
private void createInvertedIndex(DocInfo docInfo) { class WordCount{ public int titleCount; public int contentCount; public WordCount(){}; } Map<String,WordCount> wordCountMap=new HashMap<>(); //先对标题进行分词 List<Term>terms=ToAnalysis.parse( docInfo.getTitle()).getTerms(); for(Term term:terms){ String temp=term.getName(); WordCount wordCount=wordCountMap.get(temp); if(wordCount==null){ WordCount newWordCount=new WordCount(); newWordCount.titleCount=10; newWordCount.contentCount=0; wordCountMap.put(temp,newWordCount); }else { wordCount.titleCount+=10; } } //对正文进行分词 List<Term>terms1=ToAnalysis.parse( docInfo.getContent()).getTerms(); for(Term term:terms1){ String temp=term.getName(); WordCount wordCount=wordCountMap.get(temp); if(wordCount==null){ WordCount newWordCount=new WordCount(); newWordCount.titleCount=0; newWordCount.contentCount=1; wordCountMap.put(temp,newWordCount); }else { wordCount.contentCount+=1; } } //统计完成,开始合并 Set<Map.Entry<String, WordCount>>entrySet= wordCountMap.entrySet(); for(Map.Entry<String, WordCount> entry:entrySet){ synchronized (lock2){ String s=entry.getKey(); Integer sum=entry.getValue().contentCount+entry.getValue().titleCount; Weight weight=new Weight(sum,docInfo.getId()); List<Weight>weightList=invertedIndex.get(s); if(weightList==null){ List<Weight>newList=new ArrayList<>(); newList.add(weight); invertedIndex.put(s,newList); }else { invertedIndex.get(s).add(weight); } } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
2.3 序列化
序列化简单来说就是游戏里的存档,这里我们是先创建两个文件用来保存正排索引和倒排索引的结果,然后使用内置的函数将我们的数据转为字符串,然后存储在提前创建好的文档中、
内置函数如下:
private ObjectMapper objectMapper=new ObjectMapper();
- 1
代码如下:
/** * 加载到文件 */ public void save(){ long start=System.currentTimeMillis(); File indexPathFile=new File(SAVE_LOAD_FILE); if(!indexPathFile.exists()){ indexPathFile.mkdirs(); } File forwordFile=new File(SAVE_LOAD_FILE+"forword.txt"); File invertedFile=new File(SAVE_LOAD_FILE+"inverted.txt"); try{ objectMapper.writeValue(forwordFile,forwardIndex); objectMapper.writeValue(invertedFile,invertedIndex); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } long end=System.currentTimeMillis(); log.info("保存文件成功,消耗时间:"+(end-start)+"ms"); };
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
2.4 反序列化
序列化是将内容转字符串写入文件中,那么反序列化就是将该文件中存储的数据以一定的格式再次读取到原来的形式中。
代码如下:
public void load(){ long start=System.currentTimeMillis(); try { File forwordFile = new File(SAVE_LOAD_FILE + "forword.txt"); File invertedFile = new File(SAVE_LOAD_FILE + "inverted.txt"); forwardIndex= objectMapper.readValue(forwordFile, new TypeReference<List<DocInfo>>() { }); invertedIndex = objectMapper.readValue(invertedFile, new TypeReference<Map<String, List<Weight>>>() { }); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } long end=System.currentTimeMillis(); log.info("加载文件成功,消耗时间:"+(end-start)+"ms"); };
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
三、搜索模块
其实搜索模块主要分为两大部分:
- 引入停用词,将正文中无关紧要的数据给屏蔽掉
- 优化正文内容,由于正文过长,我们定位其中的关键字进行部分输出
- 权重合并,将不同权重的文章进行排序
我们在前端输入一个词,然后根据词去倒排+正排索引中去搜索,然后就可以获得文档列表
3.1 引入停用词
首先停用词是一个文档,我们将该文档读取后保存在一个Map中,在后面的正文筛选中如果包含该词则直接忽略掉即可.
代码如下:
private void loadStopWords(String stopWordPath) {
try {
BufferedReader bufferedReader=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(stopWordPath));
while (true){
String line=bufferedReader.readLine();
if(line==null){
break;
}
stopWords.add(line);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
3.2 优化正文内容
因为一篇文章的正文内容非常多,在搜索中也不是全部输出,而是输出其中一部分包含标题的部分正文,这里我们定位输入的关键词在正文中查找下标,然后以查找到的下标为中心进行左右范围截取进行输出,这里我采取的是下标中心词的前后个80个词作为正文输出.
代码如下:
private String updateContent(String content, List<Term> termList) { int index=-1; for(Term term:termList){ String word=term.getName(); index=content.toLowerCase().indexOf(" "+word+" "); if(index>=0){ break; } } if(index==-1){ if(content.length()<160){ return content; } return content.substring(0,160)+"..."; } int start=index<60?0:index-60; String desc=""; if(start+160>content.length()){ desc=content.substring(start); }else{ desc=content.substring(start,start+160)+"..."; } for(Term term:termList){ String word=term.getName(); //(?i)表示不区分大小写进行替换 desc=desc.replaceAll("(?i) "+word+" ","<i> "+word+" </i>"); //自己加的 desc=desc.replaceAll("\\s"," "); } return desc; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
3.3 权重合并
通过对于不同的权重进行排序,将权重比较大的文章id放在搜索的前面,方便用户在搜索显示时的页面上最先出现的就是关键字最多的一篇文章

实现代码如下:
public List<Result> search(String query){ List<Term> oldTerm=ToAnalysis.parse(query).getTerms(); //用于存储去掉停用词后的分词结果 List<Term> termList=new ArrayList<>(); for(Term term:oldTerm){ if(stopWords.contains(term.getName())){ continue; } termList.add(term); } List<List<Weight>> allResultList=new ArrayList<>(); for(Term term:termList){ String s=term.getName(); List<Weight> temp=index.checkByInverted(s); if(temp==null){ continue; } allResultList.add(temp); } //进行权重合并 List<Weight> weightList=myselfMergeResult(allResultList); weightList.sort(new Comparator<Weight>() { @Override public int compare(Weight o1, Weight o2) { return o2.getWeight()-o1.getWeight(); } }); List<Result> resultList=new ArrayList<>(); for(Weight weight:weightList){ DocInfo docInfo=index.checkByForward(weight.getId()); Result result=new Result(); result.setTitle(docInfo.getTitle()); result.setUrl(docInfo.getUrl()); String content=updateContent(docInfo.getContent(),termList); result.setContent(content); resultList.add(result); } return resultList; } @Data static class Pos{ public int row; public int col; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
到此为止,我们的核心功能就以全部实现了。
四、全部代码
SpringBoot于前端进行交互的代码:
package com.example.searchproject.controller; import com.example.searchproject.Search.DocSearcher; import com.example.searchproject.Search.Result; import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; import jakarta.xml.ws.Action; import org.nlpcn.commons.lang.util.StringUtil; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import java.util.List; @RestController public class DocSearcherController { private DocSearcher docSearcher=new DocSearcher(); private ObjectMapper objectMapper=new ObjectMapper(); @RequestMapping(value = "/searcher",produces = "application/json;charset=utf-8") @ResponseBody public String search(@RequestParam("query") String query) throws JsonProcessingException { List<Result> resultList=docSearcher.search(query); return objectMapper.writeValueAsString(resultList); //return StringUtil.joiner(resultList,","); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
Parser解析文件类的代码如下:
package com.example.searchproject.Search; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import java.io.*; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; @Slf4j public class Parser { private Index index=new Index(); private final static String INPUT_FILE="C:\\Users\\xia\\IdeaProjects\\SearchProject\\docs"; public void run(){ List<File> fileList=new ArrayList<>(); //枚举所有以.html结尾的文件 enumFile(INPUT_FILE,fileList); //解析每一个html文件 for(File file:fileList){ //解析每一个html文件 parseHtml(file); } index.save(); } public void runByThread() throws InterruptedException { List<File> fileList=new ArrayList<>(); //枚举所有以.html结尾的文件 enumFile(INPUT_FILE,fileList); long start=System.currentTimeMillis(); //创建一个包含10个线程的线程池 ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10); //创建一个计数器来表示文件的数量 CountDownLatch countDownLatch=new CountDownLatch(fileList.size()); for(File file:fileList){ executorService.submit(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { parseHtml(file); log.info("文件名:"+file.getName()+"文件路径:"+file.getAbsolutePath()); countDownLatch.countDown(); } }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); index.save(); long end=System.currentTimeMillis(); log.info("多线程所消耗的时间:"+(end-start)+"ms"); } private void parseHtml(File file) { //解析html的标题 String title=parseHtmlTitle(file); //解析html的url String url= parseHtmlUrl(file); //解析html的正文 //String content= parseHtmlContent(file); //解析html的正文通过正则表达式 String content=parseHtmlContentByRegex(file); //每解析一个文件就创造一个正排索引和倒排索引 index.createIndex(title,url,content); } private String readFile(File file) { StringBuilder stringBuilder=new StringBuilder(); try(BufferedReader bufferedReader=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file),1024*1024)){ while(true){ int c=bufferedReader.read(); if(c==-1){ break; } char ch=(char)c; if(ch=='\n'||ch=='\t'){ ch=' '; } stringBuilder.append(ch); } }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } return stringBuilder.toString(); } private String parseHtmlContentByRegex(File file ){ String content=readFile(file); //通过正则表达式去掉正文中的<script>标签 content=content.replaceAll("<script.*?>(.*?)</script>"," "); //通过正则表达式去掉正文中的其它标签 content=content.replaceAll("<.*?>"," "); 通过正则表达式合并多个空格 content = content.replaceAll("\\s+", " "); return content; } private String parseHtmlContent(File file) { StringBuilder stringBuilder=new StringBuilder(); try{ BufferedReader bufferedReader=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file),1024*1024); int flag=0; while (true){ int n=bufferedReader.read(); if(n==-1){ break; } char ch=(char)n; if(ch=='<'){ flag=1; }else { if(ch=='>'){ flag=0; continue; } if(ch=='\n'||ch=='\r'){ ch=' '; } stringBuilder.append(ch); } } }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } return stringBuilder.toString(); } private String parseHtmlUrl(File file) { //C:\Users\xia\IdeaProjects\SearchProject \docs\api\java.base\java\\util //file:///C:/Users/xia/IdeaProjects/SearchProject/docs/api/java.base/java/util/ArrayList.html //https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/22/docs/api/java.base/java/util/ArrayList.html String s=file.getAbsolutePath().substring("C:\\Users\\xia\\IdeaProjects\\SearchProject".length()); return "https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/22"+s; } private String parseHtmlTitle(File file) { return file.getName().replaceAll(".html",""); } private void enumFile(String inputFile, List<File> fileList) { File file=new File(inputFile); File[]files=file.listFiles(); for(File file1:files){ if(file1.isFile()){ if(file1.getAbsolutePath().endsWith(".html")){ fileList.add(file1); } }else{ enumFile(file1.getAbsolutePath(),fileList); } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Parser parser=new Parser(); parser.run(); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
index创建索引模块的代码如下:
package com.example.searchproject.Search; import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.type.TypeReference; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; import lombok.Synchronized; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.ansj.domain.Term; import org.ansj.splitWord.analysis.ToAnalysis; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.*; @Slf4j public class Index { private static final String SAVE_LOAD_FILE="C:\\Users\\xia\\IdeaProjects\\SearchProject\\"; private ObjectMapper objectMapper=new ObjectMapper(); //正排索引 private List<DocInfo> forwardIndex=new ArrayList<>(); //倒排索引1 private Map<String,List<Weight>> invertedIndex=new HashMap<>(); private Object lock1=new Object(); private Object lock2=new Object(); public DocInfo checkByForward(Integer id){ return forwardIndex.get(id); } public List<Weight> checkByInverted(String query){ return invertedIndex.get(query); } /** * 创建正排索引和倒排索引 */ public void createIndex(String title,String url,String content){ //创建正排索引 DocInfo docInfo= CreateForwardIndex( title, url, content); //创建倒排索引 createInvertedIndex(docInfo); } private void createInvertedIndex(DocInfo docInfo) { class WordCount{ public int titleCount; public int contentCount; public WordCount(){}; } Map<String,WordCount> wordCountMap=new HashMap<>(); //先对标题进行分词 List<Term>terms=ToAnalysis.parse( docInfo.getTitle()).getTerms(); for(Term term:terms){ String temp=term.getName(); WordCount wordCount=wordCountMap.get(temp); if(wordCount==null){ WordCount newWordCount=new WordCount(); newWordCount.titleCount=10; newWordCount.contentCount=0; wordCountMap.put(temp,newWordCount); }else { wordCount.titleCount+=10; } } //对正文进行分词 List<Term>terms1=ToAnalysis.parse( docInfo.getContent()).getTerms(); for(Term term:terms1){ String temp=term.getName(); WordCount wordCount=wordCountMap.get(temp); if(wordCount==null){ WordCount newWordCount=new WordCount(); newWordCount.titleCount=0; newWordCount.contentCount=1; wordCountMap.put(temp,newWordCount); }else { wordCount.contentCount+=1; } } //统计完成,开始合并 Set<Map.Entry<String, WordCount>>entrySet= wordCountMap.entrySet(); for(Map.Entry<String, WordCount> entry:entrySet){ synchronized (lock2){ String s=entry.getKey(); Integer sum=entry.getValue().contentCount+entry.getValue().titleCount; Weight weight=new Weight(sum,docInfo.getId()); List<Weight>weightList=invertedIndex.get(s); if(weightList==null){ List<Weight>newList=new ArrayList<>(); newList.add(weight); invertedIndex.put(s,newList); }else { invertedIndex.get(s).add(weight); } } } } private DocInfo CreateForwardIndex(String title, String url, String content) { DocInfo docInfo=new DocInfo(); docInfo.setTitle(title); docInfo.setUrl(url); docInfo.setContent(content); synchronized (lock1){ docInfo.setId(forwardIndex.size()); forwardIndex.add(docInfo); } return docInfo; } ; /** * 加载到文件 */ public void save(){ long start=System.currentTimeMillis(); File indexPathFile=new File(SAVE_LOAD_FILE); if(!indexPathFile.exists()){ indexPathFile.mkdirs(); } File forwordFile=new File(SAVE_LOAD_FILE+"forword.txt"); File invertedFile=new File(SAVE_LOAD_FILE+"inverted.txt"); try{ objectMapper.writeValue(forwordFile,forwardIndex); objectMapper.writeValue(invertedFile,invertedIndex); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } long end=System.currentTimeMillis(); log.info("保存文件成功,消耗时间:"+(end-start)+"ms"); }; /** * 从文件中加载到idea */ public void load(){ long start=System.currentTimeMillis(); try { File forwordFile = new File(SAVE_LOAD_FILE + "forword.txt"); File invertedFile = new File(SAVE_LOAD_FILE + "inverted.txt"); forwardIndex= objectMapper.readValue(forwordFile, new TypeReference<List<DocInfo>>() { }); invertedIndex = objectMapper.readValue(invertedFile, new TypeReference<Map<String, List<Weight>>>() { }); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } long end=System.currentTimeMillis(); log.info("加载文件成功,消耗时间:"+(end-start)+"ms"); }; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
DOSearcher搜索模块的代码如下:
package com.example.searchproject.Search; import lombok.Data; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.ansj.domain.Term; import org.ansj.splitWord.analysis.ToAnalysis; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.*; @Slf4j public class DocSearcher { private Index index=new Index(); public DocSearcher(){ index.load(); loadStopWords(STOP_WORD_PATH); log.info("文件加载成功"); } String STOP_WORD_PATH= "C:\\Users\\xia\\IdeaProjects\\SearchProject\\stop_word.txt" ; HashSet<String >stopWords=new HashSet<>(); public List<Result> search(String query){ List<Term> oldTerm=ToAnalysis.parse(query).getTerms(); //用于存储去掉停用词后的分词结果 List<Term> termList=new ArrayList<>(); for(Term term:oldTerm){ if(stopWords.contains(term.getName())){ continue; } termList.add(term); } List<List<Weight>> allResultList=new ArrayList<>(); for(Term term:termList){ String s=term.getName(); List<Weight> temp=index.checkByInverted(s); if(temp==null){ continue; } allResultList.add(temp); } //进行权重合并 List<Weight> weightList=myselfMergeResult(allResultList); weightList.sort(new Comparator<Weight>() { @Override public int compare(Weight o1, Weight o2) { return o2.getWeight()-o1.getWeight(); } }); List<Result> resultList=new ArrayList<>(); for(Weight weight:weightList){ DocInfo docInfo=index.checkByForward(weight.getId()); Result result=new Result(); result.setTitle(docInfo.getTitle()); result.setUrl(docInfo.getUrl()); String content=updateContent(docInfo.getContent(),termList); result.setContent(content); resultList.add(result); } return resultList; } @Data static class Pos{ public int row; public int col; } private List<Weight> myselfMergeResult(List<List<Weight>> source) { PriorityQueue<Weight> queue=new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Weight>() { @Override public int compare(Weight o1, Weight o2) { return o1.getId()-o2.getId(); } }); for(List<Weight> list:source){ for(Weight weight:list){ queue.offer(weight); } } List<Weight> target=new ArrayList<>(); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ Weight curWeight=queue.poll(); if(!target.isEmpty()){ Weight oldWeight=target.get(target.size()-1); if(curWeight.getId()==oldWeight.getId()){ oldWeight.setWeight(oldWeight.getWeight()+curWeight.getWeight()); }else { target.add(curWeight); } }else { target.add(curWeight); } } return target; } private void loadStopWords(String stopWordPath) { try { BufferedReader bufferedReader=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(stopWordPath)); while (true){ String line=bufferedReader.readLine(); if(line==null){ break; } stopWords.add(line); } } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } private String updateContent(String content, List<Term> termList) { int index=-1; for(Term term:termList){ String word=term.getName(); index=content.toLowerCase().indexOf(" "+word+" "); if(index>=0){ break; } } if(index==-1){ if(content.length()<160){ return content; } return content.substring(0,160)+"..."; } int start=index<60?0:index-60; String desc=""; if(start+160>content.length()){ desc=content.substring(start); }else{ desc=content.substring(start,start+160)+"..."; } for(Term term:termList){ String word=term.getName(); //(?i)表示不区分大小写进行替换 desc=desc.replaceAll("(?i) "+word+" ","<i> "+word+" </i>"); //自己加的 desc=desc.replaceAll("\\s"," "); } return desc; } public static void main(String[] args) { DocSearcher docSearcher=new DocSearcher(); List<Result> resultList=docSearcher.search("arraylist"); for(Result result:resultList){ System.out.println(result.toString()); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
正排索引中包含DOInfo类的代码:
package com.example.searchproject.Search;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class DocInfo {
private Integer id;
private String title;
private String url;
private String content;
public DocInfo(){};
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
每个文件的基本构成的Rusult类的代码:
package com.example.searchproject.Search; import lombok.Data; @Data public class Result { private String title; private String url; private String content; public Result(){}; public Result(String title, String url, String content) { this.title = title; this.url = url; this.content = content; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
权重类的代码:
package com.example.searchproject.Search;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Weight {
private Integer weight;
private Integer id;
public Weight(){};
public Weight(Integer weight, Integer id) {
this.weight = weight;
this.id = id;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
遇到的困难
在本次项目中遇到的这个困难困扰了我整整一天,最后终于在电脑仅剩10%电量时给解决了,说多了都是泪…
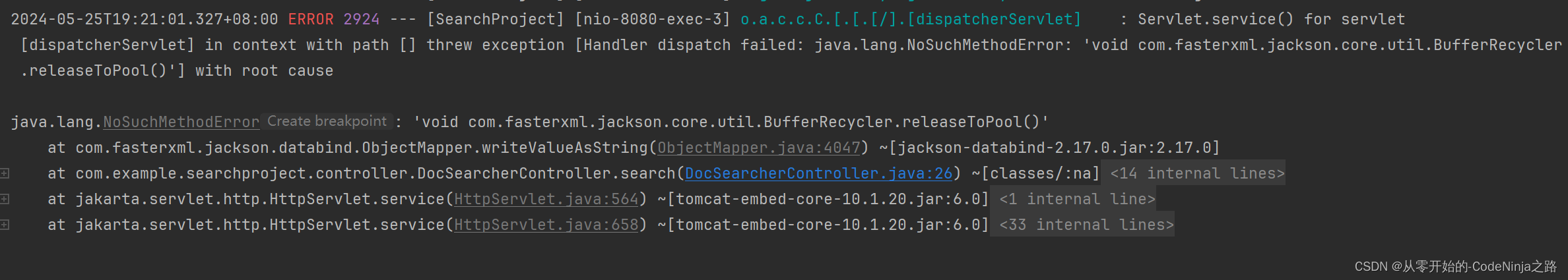
刚开始fiddle抓包试了,postman试了,前端就是有响应内容但是不显示页面,而且报的不是平时那种一眼就知道的异常
然后就是上网查看文章,有的说这时运行时异常,就是编译时有这个方法运行时由于版本不同就无法调用这个方法体,应该是idea运行时的版本和我下载的版本不一样,我就去上网查如何看两个版本,简单学了使用命令框看版本和端口号,最后发现我的版本是一样的

又有文章说方法调用的包名不同,这也不是我那个错误,那时认为错误出在了前端代码的页面渲染上,又硬着头皮把copy过来的前端代码给看了,里面有好多在资源上没有的,又去自己查这个代码有啥作用,然后发现简单看懂了前端代码,但是我的前端是渲染有问题
然后受不了了,在csdn上把代码贴给了一起写文章的大佬们,让他们看看,然后他们说让我去调试前端代码,那时我也认为是前端代码的错,可我又不会前端的调试啊,平时都是搞后端的,然后去csdn上查如何调试,他们说用浏览器提供的有说用vs code的,我学了一下调试浏览器感觉不习惯,又去学了vs code 如何调试,然后就是没有问题
最后我有把objectMapper方法换成了StringUtils方法,然后就是不报错了但是前端还是不显示页面,最后没办法了,又去看了一遍报错日志,用翻译软件给它全翻译过来,还是不明白,然后晚上看csdn常见出错的地方后,文章突然提到了还有一个细小且不容易发现的地方就是依赖冲突,但是pom.xml里没有报错,日志里只显示了引用的依赖,我就想,算了试着注掉试试,注释掉后用maven更新以后跑了一遍,发现突然显示出来了,当时电脑还剩有10%的电量差点就回寝了,那一刻感觉值了,成就感拉满了
总结
-
在使用ObjectMapper的方法时,将文件或字符串等类型转为类对象或包含类对象时,该类必须包含无参构造方法,若写的有含参的构造方法则Spring就不会在提供无参构造方法,会导致程序报错
-
应为Spring MVC中以内置了Object Mapper方法,在使用时直接创建调用即可,调用后生成一个JSON类型的字符串, 再在RequestMpping中添加Produces来指定返回数据的类型,这样传递出去的是JSON对象格式,传递结果图片如下:
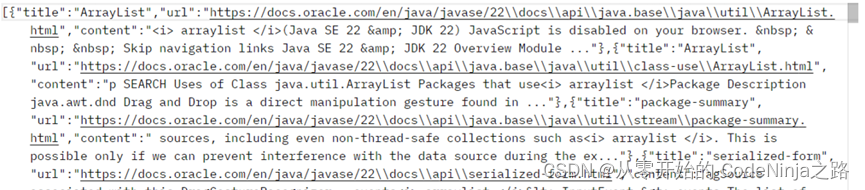
然而若是引入该依赖
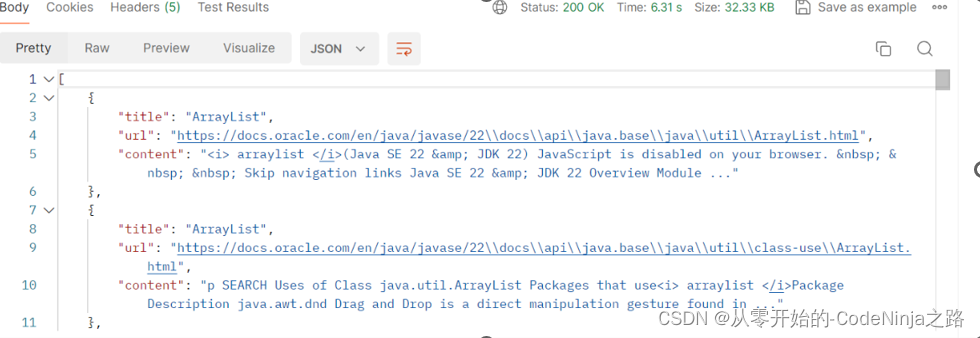
则会发生依赖冲突,当我引入SpringWeb(Spring Web MVC)框架时就已经引入了ObjectMapper,在次引入依赖就是多此一举,我再次引入的依赖和SpringWeb框架内置的依赖版本不同,在运行加载配置文件时从我引入的低版本依赖中找objectMapper方法,发现找不到就报异常
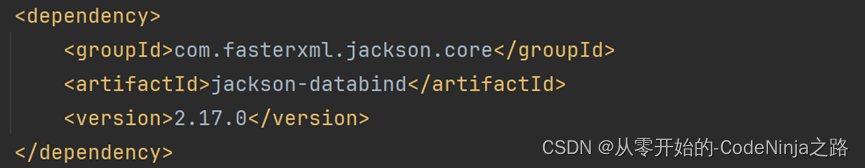
StringUtils则是生成字符串,在不指定返回类型时默认的是text/html格式
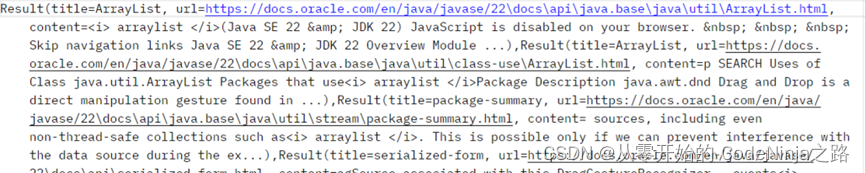
在指定返回类型是json后,因为不是json字符串转json对象,而是由字符串转json对象,则结果如下:
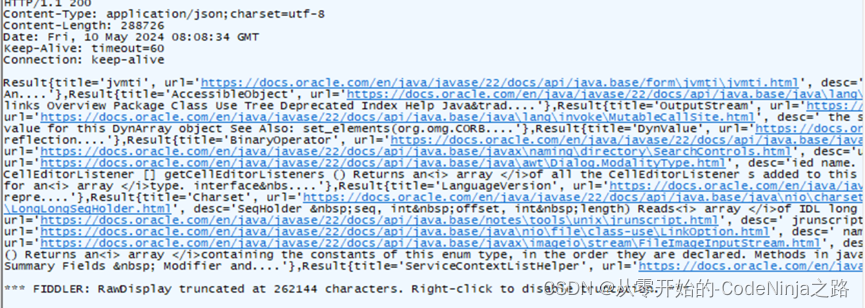
此时看前端接收处理数据对应的格式了,如不同则报错,例:搜索引擎中前端接收JSON对象而我引入了jackson依赖则导致类型不同,前端无法解析数据而报错



