- 1如何让知识图谱辅助多轮对话_知识图谱问答多轮对话实体的替换
- 2EHS管理系统避坑指南!这几个关键点需要注意!_ehs系统
- 3Tomcat服务安全加固和优化_tomcat加固使用安全的http请求(3)_linxu系统中tomcat安全加固日志开启
- 4困惑度:一种新的优化方法_困惑度的大小
- 5Stable Diffusion教程:4000字说清楚图生图_stable diffusion拉伸、裁剪、填充
- 6VSCode远程调试Linux程序
- 7刷题LeetCode第三天_leetcode listnode空指针问题
- 8对象加载JVM到GC清除的全过程分析
- 9【数学建模】——【A题 信用风险识别问题】全面解析
- 10Spring事务
SpringMVC系列三:SpringMVC的参数解析-HandlerMethodArgumentResolver处理流程
赞
踩
SpringMVC的http请求的参数解析HandlerMethodArgumentResolver流程
文章目录
- SpringMVC的http请求的参数解析HandlerMethodArgumentResolver流程
- 本文分析的HandlerMethodArgumentResolver
- 初始化解析映射关系
- 处理请求
- 总结
本文分析的HandlerMethodArgumentResolver

初始化解析映射关系
得到请求 url 与 RequestMappingInfo 的映射关系到 urlLookup 中;设置 RequestMappingInfo 与 HandlerMethod 的映射关系到 mappingLookup 中。得到 url -> HandlerMethod 的映射关系。
详见RequestMappingHandlerMapping的初始化
处理请求
调用DispatcherServlet#doService->DispatcherServlet#doDispatch方法
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null; Exception dispatchException = null; try { // processedRequest是经过checkMultipart方法处理过的request请求, // 如果不满足multipart条件,直接返回request,也就是request没有做任何处理, // 如果满足multipart基本条件将multipartRequest转换为StandardMultipartHttpServletRequest请求。 processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // Determine handler for the current request. // DispatcherServlet.getHandler方法会在底层调用HandlerMapping.getHandler方法 // 这个方法中会遍 历DispatcherServlet中的private List<HandlerMapping> // handlerMappings链表,找到能够处理当前 request请求的第一个HandlerMapping实例并返回: // DispatcherServlet接收到请求后,HandlerMapping将会把请求封装为HandlerExecutionChain, // 而HandlerExecutionChain包含请求的所有信息,包括拦截器、Handler处理器等。 // HandlerExecutionChain为真正的Handler对象与Interceptor的组合类 mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); if (mappedHandler == null) { // 如果没有找到对应的handler则抛出异常。 noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } // Determine handler adapter for the current request. // 通过getHandlerAdapter方法找到handler对应的HandlerAdapter // 则是遍历HandlerAdpaters,然后返回第一个支持handler的Adpater. // SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter是用来适配SimpleUrlHandlerMapping和BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping的映射的,也就是实现Controller接口的Handler。 // RequestMappingHandlerAdapter是用来适配RequestMappingHandlerMapping,也就是我们常用的RequestMapping注解。 // HttpRequestHandlerAdapter是用来适配远程调用的。 HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified); } if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } // 如果有拦截器,执行拦截器preHandler方法 // 如果拦截器preHandle返回false,那么请求终止。 if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } // Actually invoke the handler. // todo HandlerAdapter执行handle方法处理请求,返回ModelAndView mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } // 如果返回的ModelAndView不为null,并且没有设置view的话,这设置默认的view applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); // 如果有拦截器,执行拦截器postHandle方法 mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } catch (Throwable err) { // As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well, // making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios. dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err); } // 然后调用processDispatchResult方法处理请求结果,封装到response中 // DispatcherServlet会将ModelAndView对象传入View层进行渲染 processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Throwable err) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err)); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); } } else { // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. if (multipartRequestParsed) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception { ModelAndView mav; checkRequest(request); // Execute invokeHandlerMethod in synchronized block if required. // 判断当前是否需要支持在同一个session中只能线性地处理请求 if (this.synchronizeOnSession) { // 获取当前请求的session对象 HttpSession session = request.getSession(false); if (session != null) { // 为当前session生成一个唯一的可以用于锁定的key Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session); synchronized (mutex) { // 对HandlerMethod进行参数等的适配处理,并调用目标handler mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod); } } else { // No HttpSession available -> no mutex necessary // 如果当前不存在session,则直接对HandlerMethod进行适配 mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod); } } else { // No synchronization on session demanded at all... // 如果当前不需要对session进行同步处理,则直接对HandlerMethod进行适配 mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod); } ... return mav; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
之后调invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception { ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response); try { // 使用initBinderAdviceCache对@initBinder进行处理 // 获取容器中全局配置的InitBinder和当前HandlerMethod所对应的Controller中 // 配置的InitBinder,用于进行参数的绑定 WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod); // 使用modelAttributeAdviceCache对@ModelAttribute进行处理 // 获取容器中全局配置的ModelAttribute和当前当前HandlerMethod所对应的Controller // 中配置的ModelAttribute,这些配置的方法将会在目标方法调用之前进行调用 ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory); // 将handlerMethod封装为一个ServletInvocableHandlerMethod对象, // 该对象用于对当前request的整体调用流程进行了封装 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod); if (this.argumentResolvers != null) { // 设置当前容器中配置的所有ArgumentResolver invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers); } if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) { // 设置当前容器中配置的所有ReturnValueHandler invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers); } // 将前面创建的WebDataBinderFactory设置到ServletInvocableHandlerMethod中 invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory); // 设置ParameterNameDiscoverer,该对象将按照一定的规则获取当前参数的名称 invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer); ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer(); mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request)); // 这里initModel()方法主要作用是调用前面获取到的@ModelAttribute标注的方法, // 从而达到@ModelAttribute标注的方法能够在目标Handler调用之前调用的目的 modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod); // 获取当前的AsyncWebRequest,这里AsyncWebRequest的主要作用是用于判断目标 // handler的返回值是否为WebAsyncTask或DefferredResult,如果是这两种中的一种, // 则说明当前请求的处理应该是异步的。所谓的异步,指的是当前请求会将Controller中 // 封装的业务逻辑放到一个线程池中进行调用,待该调用有返回结果之后再返回到response中。 // 这种处理的优点在于用于请求分发的线程能够解放出来,从而处理更多的请求,只有待目标任务 // 完成之后才会回来将该异步任务的结果返回。 mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect); // 封装异步任务的线程池,request和interceptors到WebAsyncManager中 AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response); asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout); WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor); asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest); asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors); asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors); // 这里就是用于判断当前请求是否有异步任务结果的,如果存在,则对异步任务结果进行封装 if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) { Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult(); mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0]; asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Found concurrent result value [" + result + "]"); } // 封装异步任务的处理结果,虽然封装的是一个HandlerMethod,但只是Spring简单的封装 // 的一个Callable对象,该对象中直接将调用结果返回了。这样封装的目的在于能够统一的 // 进行右面的ServletInvocableHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle()方法的调用 invocableMethod = invocableMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result); } // 完成过程调用 // 对请求参数进行处理,调用目标HandlerMethod,并且将返回值封装为一个ModelAndView对象 invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return null; } //2 包装ModelAndView // 对封装的ModelAndView进行处理,主要是判断当前请求是否进行了重定向,如果进行了重定向, // 还会判断是否需要将FlashAttributes封装到新的请求中 return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest); } finally { // 调用request destruction callbacks和对SessionAttributes进行处理 webRequest.requestCompleted(); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
之后调用@ModelAttribute标注的方法
public void initModel(NativeWebRequest request, ModelAndViewContainer container, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception { // 在当前request中获取使用@SessionAttribute注解声明的参数 Map<String, ?> sessionAttributes = this.sessionAttributesHandler.retrieveAttributes(request); // 将@SessionAttribute声明的参数封装到ModelAndViewContainer中 container.mergeAttributes(sessionAttributes); // 调用前面获取的使用@ModelAttribute标注的方法 invokeModelAttributeMethods(request, container); // 这里首先获取目标handler执行所需的参数中与@SessionAttribute同名或同类型的参数, // 也就是handler想要直接从@SessionAttribute中声明的参数中获取的参数。然后对这些参数 // 进行遍历,首先判断request中是否包含该属性,如果不包含,则从之前的SessionAttribute缓存 // 中获取,如果两个都没有,则直接抛出异常 for (String name : findSessionAttributeArguments(handlerMethod)) { if (!container.containsAttribute(name)) { Object value = this.sessionAttributesHandler.retrieveAttribute(request, name); if (value == null) { throw new HttpSessionRequiredException("Expected session attribute '" + name + "'", name); } container.addAttribute(name, value); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
private void invokeModelAttributeMethods(NativeWebRequest request, ModelAndViewContainer container) throws Exception { while (!this.modelMethods.isEmpty()) { // 这里getNextModelMethod()方法始终会获取modelMethods中的第0号为的方法, // 后续该方法执行完了之后则会将该方法从modelMethods移除掉,因而这里while // 循环只需要判断modelMethods是否为空即可 InvocableHandlerMethod modelMethod = getNextModelMethod(container).getHandlerMethod(); // 获取当前方法中标注的ModelAttribute属性,然后判断当前request中是否有与该属性中name字段 // 标注的值相同的属性,如果存在,并且当前ModelAttribute设置了不对该属性进行绑定,那么 // 就直接略过当前方法的执行 ModelAttribute ann = modelMethod.getMethodAnnotation(ModelAttribute.class); Assert.state(ann != null, "No ModelAttribute annotation"); if (container.containsAttribute(ann.name())) { if (!ann.binding()) { container.setBindingDisabled(ann.name()); } continue; } // 通过ArgumentResolver对方法参数进行处理,并且调用目标方法 Object returnValue = modelMethod.invokeForRequest(request, container); // 如果当前方法的返回值不为空,则判断当前@ModelAttribute是否设置了需要绑定返回值, // 如果设置了,则将返回值绑定到请求中,后续handler可以直接使用该参数 if (!modelMethod.isVoid()){ String returnValueName = getNameForReturnValue(returnValue, modelMethod.getReturnType()); if (!ann.binding()) { container.setBindingDisabled(returnValueName); } // 如果request中不包含该参数,则将该返回值添加到ModelAndViewContainer中, // 供handler使用 if (!container.containsAttribute(returnValueName)) { container.addAttribute(returnValueName, returnValue); } } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception { // 处理方法的参数值 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("使用HandlerMethodArgumentResolver来处理方法的参数值"); } Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Invoking '" + ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(getMethod(), getBeanType()) + "' with arguments " + Arrays.toString(args)); } // 这里doInvoke()方法主要是结合处理后的参数,使用反射对目标方法进行调用 Object returnValue = doInvoke(args); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Method [" + ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(getMethod(), getBeanType()) + "] returned [" + returnValue + "]"); } return returnValue; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
反射调用@ModelAttribute标注的方法
protected Object doInvoke(Object... args) throws Exception { ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(getBridgedMethod()); try { return getBridgedMethod().invoke(getBean(), args); } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { assertTargetBean(getBridgedMethod(), getBean(), args); String text = (ex.getMessage() != null ? ex.getMessage() : "Illegal argument"); throw new IllegalStateException(getInvocationErrorMessage(text, args), ex); } catch (InvocationTargetException ex) { // Unwrap for HandlerExceptionResolvers ... Throwable targetException = ex.getTargetException(); if (targetException instanceof RuntimeException) { throw (RuntimeException) targetException; } else if (targetException instanceof Error) { throw (Error) targetException; } else if (targetException instanceof Exception) { throw (Exception) targetException; } else { String text = getInvocationErrorMessage("Failed to invoke handler method", args); throw new IllegalStateException(text, targetException); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
解析请求参数
本次解析Model参数,@RequestBody标注参数,@RequestParam标注参数,@PathVariable标注参数,以及普通入参
在Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);里面解析请求参数
private Object[] getMethodArgumentValues(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception { // 获取当前handler所声明的所有参数,主要包括参数名,参数类型,参数位置,所标注的注解等等属性 MethodParameter[] parameters = getMethodParameters(); Object[] args = new Object[parameters.length]; for (int i = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) { MethodParameter parameter = parameters[i]; parameter.initParameterNameDiscovery(this.parameterNameDiscoverer); // providedArgs是调用方提供的参数,这里主要是判断这些参数中是否有当前类型 // 或其子类型的参数,如果有,则直接使用调用方提供的参数,对于请求处理而言,默认情况下, // 调用方提供的参数都是长度为0的数组 args[i] = resolveProvidedArgument(parameter, providedArgs); if (args[i] != null) { continue; } // 如果在调用方提供的参数中不能找到当前类型的参数值,则遍历Spring容器中所有的 // ArgumentResolver,判断哪种类型的Resolver支持对当前参数的解析,这里的判断 // 方式比较简单,比如RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver就是判断当前参数 // 是否使用@RequestParam注解进行了标注 if (this.argumentResolvers.supportsParameter(parameter)) { try { // 如果能够找到对当前参数进行处理的ArgumentResolver,则调用其 // resolveArgument()方法从request中获取对应的参数值,并且进行转换 args[i] = this.argumentResolvers.resolveArgument( parameter, mavContainer, request, this.dataBinderFactory); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("处理后参数值:"+args[i]); } continue; } catch (Exception ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug(getArgumentResolutionErrorMessage("Failed to resolve", i), ex); } throw ex; } } // 如果进行了参数处理之后当前参数还是为空,则抛出异常 if (args[i] == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("Could not resolve method parameter at index " + parameter.getParameterIndex() + " in " + parameter.getExecutable().toGenericString() + ": " + getArgumentResolutionErrorMessage("No suitable resolver for", i)); } } return args; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
public boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter) {
return getArgumentResolver(parameter) != null;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
private HandlerMethodArgumentResolver getArgumentResolver(MethodParameter parameter) {
HandlerMethodArgumentResolver result = this.argumentResolverCache.get(parameter);
if (result == null) {
for (HandlerMethodArgumentResolver resolver : this.argumentResolvers) {
if (resolver.supportsParameter(parameter)) {
result = resolver;
this.argumentResolverCache.put(parameter, result);
break;
}
}
}
return result;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
Model参数解析器是:ModelMethodProcessor
判断是否能解析
public boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter) {
return Model.class.isAssignableFrom(parameter.getParameterType());
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
处理参数
public Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception {
Assert.state(mavContainer != null, "ModelAndViewContainer is required for model exposure");
return mavContainer.getModel();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
@RequestBody标注参数的参数解析器是:RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor
前提是:必须要引入json解析相关的类,
例如:1.fastjson需要引入com.alibaba.fastjson并添加HttpMessageConverter
@Override protected void extendMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) { converters.clear(); converters.add(stringHttpMessageConverter()); converters.add(fastJsonHttpMessageConverter()); } @Bean public FastJsonHttpMessageConverter fastJsonHttpMessageConverter() { FastJsonHttpMessageConverter fastJsonHttpMessageConverter = new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter(); FastJsonConfig fastJsonConfig = new FastJsonConfig(); fastJsonConfig.setSerializerFeatures( SerializerFeature.QuoteFieldNames, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue,//保留空的字段 SerializerFeature.WriteNullListAsEmpty,//List null-> [] SerializerFeature.WriteDateUseDateFormat,// 日期格式化 SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty);//String null -> "" List<MediaType> mediaTypeList = new ArrayList<>(); mediaTypeList.add(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8); mediaTypeList.add(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON); fastJsonHttpMessageConverter.setSupportedMediaTypes(mediaTypeList); fastJsonHttpMessageConverter.setFastJsonConfig(fastJsonConfig); return fastJsonHttpMessageConverter; } /** * 在ResponseBody注解下,Spring处理返回值为String时会用到StringHttpMessageConverter * */ @Bean public StringHttpMessageConverter stringHttpMessageConverter() { StringHttpMessageConverter httpMessageConverter = new StringHttpMessageConverter(); httpMessageConverter.setDefaultCharset(Charset.forName("UTF-8")); return httpMessageConverter; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
2.如果使用jackson需要pom引入:com.fasterxml.jackson.core.jackson-databind
下面以fastjson为例进行解析
判断是否能解析
public boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter) {
return parameter.hasParameterAnnotation(RequestBody.class);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
处理参数
public Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception { parameter = parameter.nestedIfOptional(); // 使用 HttpMessageConverter 将 请求body 中数据解析出来 Object arg = readWithMessageConverters(webRequest, parameter, parameter.getNestedGenericParameterType()); String name = Conventions.getVariableNameForParameter(parameter); if (binderFactory != null) { WebDataBinder binder = binderFactory.createBinder(webRequest, arg, name); if (arg != null) { validateIfApplicable(binder, parameter); if (binder.getBindingResult().hasErrors() && isBindExceptionRequired(binder, parameter)) { throw new MethodArgumentNotValidException(parameter, binder.getBindingResult()); } } if (mavContainer != null) { mavContainer.addAttribute(BindingResult.MODEL_KEY_PREFIX + name, binder.getBindingResult()); } } return adaptArgumentIfNecessary(arg, parameter); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
protected <T> Object readWithMessageConverters(NativeWebRequest webRequest, MethodParameter parameter,
Type paramType) throws IOException, HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException, HttpMessageNotReadableException {
HttpServletRequest servletRequest = webRequest.getNativeRequest(HttpServletRequest.class);
Assert.state(servletRequest != null, "No HttpServletRequest");
ServletServerHttpRequest inputMessage = new ServletServerHttpRequest(servletRequest);
// 使用 HttpMessageConverter 将 请求body 中数据解析出来
Object arg = readWithMessageConverters(inputMessage, parameter, paramType);
if (arg == null && checkRequired(parameter)) {
throw new HttpMessageNotReadableException("Required request body is missing: " +
parameter.getExecutable().toGenericString());
}
return arg;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
protected <T> Object readWithMessageConverters(HttpInputMessage inputMessage, MethodParameter parameter, Type targetType) throws IOException, HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException, HttpMessageNotReadableException { MediaType contentType; boolean noContentType = false; try { // 获取 ContentType contentType = inputMessage.getHeaders().getContentType(); } catch (InvalidMediaTypeException ex) { throw new HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException(ex.getMessage()); } if (contentType == null) { noContentType = true; contentType = MediaType.APPLICATION_OCTET_STREAM; } Class<?> contextClass = parameter.getContainingClass(); // 获取 method 的参数的类型 Class<T> targetClass = (targetType instanceof Class ? (Class<T>) targetType : null); if (targetClass == null) { ResolvableType resolvableType = ResolvableType.forMethodParameter(parameter); targetClass = (Class<T>) resolvableType.resolve(); } HttpMethod httpMethod = (inputMessage instanceof HttpRequest ? ((HttpRequest) inputMessage).getMethod() : null); Object body = NO_VALUE; EmptyBodyCheckingHttpInputMessage message; try { message = new EmptyBodyCheckingHttpInputMessage(inputMessage); // 使用一个 HttpMessageConverter 将 请求body 中数据解析出来 for (HttpMessageConverter<?> converter : this.messageConverters) { Class<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converterType = (Class<HttpMessageConverter<?>>) converter.getClass(); GenericHttpMessageConverter<?> genericConverter = (converter instanceof GenericHttpMessageConverter ? (GenericHttpMessageConverter<?>) converter : null); // 选出一个 HttpMessageConverter if (genericConverter != null ? genericConverter.canRead(targetType, contextClass, contentType) : (targetClass != null && converter.canRead(targetClass, contentType))) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Read [" + targetType + "] as \"" + contentType + "\" with [" + converter + "]"); } // 使用 HttpMessageConverter 解析数据 if (message.hasBody()) { HttpInputMessage msgToUse = getAdvice().beforeBodyRead(message, parameter, targetType, converterType); body = (genericConverter != null ? genericConverter.read(targetType, contextClass, msgToUse) : ((HttpMessageConverter<T>) converter).read(targetClass, msgToUse)); body = getAdvice().afterBodyRead(body, msgToUse, parameter, targetType, converterType); } else { body = getAdvice().handleEmptyBody(null, message, parameter, targetType, converterType); } break; } } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new HttpMessageNotReadableException("I/O error while reading input message", ex); } if (body == NO_VALUE) { if (httpMethod == null || !SUPPORTED_METHODS.contains(httpMethod) || (noContentType && !message.hasBody())) { return null; } throw new HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException(contentType, this.allSupportedMediaTypes); } return body; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
public boolean canRead(Class<?> clazz, @Nullable MediaType mediaType) {
return supports(clazz) && canRead(mediaType);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
FastJsonHttpMessageConverter的supports方法:
protected boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) {
return true;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
FastJsonHttpMessageConverter支持两种类型的MediaType:application/json;charset=UTF-8, application/json
protected boolean canRead(@Nullable MediaType mediaType) {
if (mediaType == null) {
return true;
}
for (MediaType supportedMediaType : getSupportedMediaTypes()) {
if (supportedMediaType.includes(mediaType)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
使用FastJsonHttpMessageConverter读取数据并反序列化成对象
public Object read(Type type, //
Class<?> contextClass, //
HttpInputMessage inputMessage //
) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException {
return readType(getType(type, contextClass), inputMessage);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
private Object readType(Type type, HttpInputMessage inputMessage) { try { InputStream in = inputMessage.getBody(); return JSON.parseObject(in, fastJsonConfig.getCharset(), type, fastJsonConfig.getParserConfig(), fastJsonConfig.getParseProcess(), JSON.DEFAULT_PARSER_FEATURE, fastJsonConfig.getFeatures()); } catch (JSONException ex) { throw new HttpMessageNotReadableException("JSON parse error: " + ex.getMessage(), ex); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new HttpMessageNotReadableException("I/O error while reading input message", ex); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
StringHttpMessageConverter的supports方法:
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) {
return String.class == clazz;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
StringHttpMessageConverter支持的MediaType是MediaType.ALL,所以String类型且加@RequestBody标注的参数的都能处理。
使用StringHttpMessageConverter读取数据
public final T read(Class<? extends T> clazz, HttpInputMessage inputMessage)
throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException {
return readInternal(clazz, inputMessage);
}
protected String readInternal(Class<? extends String> clazz, HttpInputMessage inputMessage) throws IOException {
Charset charset = getContentTypeCharset(inputMessage.getHeaders().getContentType());
return StreamUtils.copyToString(inputMessage.getBody(), charset);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
@RequestParam标注参数以及没有注解的简单参数的参数解析器是:RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver
判断是否能解析
public boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter) { // 有 @RequestParam 注解 if (parameter.hasParameterAnnotation(RequestParam.class)) { if (Map.class.isAssignableFrom(parameter.nestedIfOptional().getNestedParameterType())) { RequestParam requestParam = parameter.getParameterAnnotation(RequestParam.class); return (requestParam != null && StringUtils.hasText(requestParam.name())); } else { return true; } } else { if (parameter.hasParameterAnnotation(RequestPart.class)) { return false; } parameter = parameter.nestedIfOptional(); if (MultipartResolutionDelegate.isMultipartArgument(parameter)) { return true; } else if (this.useDefaultResolution) { // 是简单参数 return BeanUtils.isSimpleProperty(parameter.getNestedParameterType()); } else { return false; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
处理参数
org.springframework.web.method.annotation.AbstractNamedValueMethodArgumentResolver#resolveArgument
public final Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception { // 底层使用 asm 来获取方法中的参数的名称 NamedValueInfo namedValueInfo = getNamedValueInfo(parameter); MethodParameter nestedParameter = parameter.nestedIfOptional(); // 获取方法的参数名称 Object resolvedName = resolveStringValue(namedValueInfo.name); if (resolvedName == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Specified name must not resolve to null: [" + namedValueInfo.name + "]"); } // 根据方法的参数名称获取 http请求的参数值 Object arg = resolveName(resolvedName.toString(), nestedParameter, webRequest); if (arg == null) { if (namedValueInfo.defaultValue != null) { arg = resolveStringValue(namedValueInfo.defaultValue); } else if (namedValueInfo.required && !nestedParameter.isOptional()) { handleMissingValue(namedValueInfo.name, nestedParameter, webRequest); } arg = handleNullValue(namedValueInfo.name, arg, nestedParameter.getNestedParameterType()); } else if ("".equals(arg) && namedValueInfo.defaultValue != null) { arg = resolveStringValue(namedValueInfo.defaultValue); } if (binderFactory != null) { // 创建 WebDataBinder,并调用 @InitBinder 标注的方法 WebDataBinder binder = binderFactory.createBinder(webRequest, null, namedValueInfo.name); try { // 使用 SimpleTypeConverter 转换,其中 conversionService 都是从 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 中获取 // conversionService 中含有大量默认的 Converter arg = binder.convertIfNecessary(arg, parameter.getParameterType(), parameter); } catch (ConversionNotSupportedException ex) { throw new MethodArgumentConversionNotSupportedException(arg, ex.getRequiredType(), namedValueInfo.name, parameter, ex.getCause()); } catch (TypeMismatchException ex) { throw new MethodArgumentTypeMismatchException(arg, ex.getRequiredType(), namedValueInfo.name, parameter, ex.getCause()); } } handleResolvedValue(arg, namedValueInfo.name, parameter, mavContainer, webRequest); return arg; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
调用AbstractNamedValueMethodArgumentResolver#resolveStringValue 来解析参数名
private Object resolveStringValue(String value) {
if (this.configurableBeanFactory == null) {
return value;
}
// ${} 解析处理
String placeholdersResolved = this.configurableBeanFactory.resolveEmbeddedValue(value);
BeanExpressionResolver exprResolver = this.configurableBeanFactory.getBeanExpressionResolver();
if (exprResolver == null || this.expressionContext == null) {
return value;
}
// #{} 解析处理
return exprResolver.evaluate(placeholdersResolved, this.expressionContext);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
org.springframework.web.bind.support.DefaultDataBinderFactory#createBinder创建 WebDataBinder,并调用 @InitBinder 标注的方法,在这个方法里面通常registerCustomEditor来注册用户自定义的转换器提供string->指定类的能力
public final WebDataBinder createBinder(
NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable Object target, String objectName) throws Exception {
WebDataBinder dataBinder = createBinderInstance(target, objectName, webRequest);
if (this.initializer != null) {
// 初始化 WebDataBinder, 设置一些重要属性
this.initializer.initBinder(dataBinder, webRequest);
}
// 调用 @InitBinder 标注的方法
initBinder(dataBinder, webRequest);
return dataBinder;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
org.springframework.validation.DataBinder#convertIfNecessary(java.lang.Object, java.lang.Class, org.springframework.core.MethodParameter)
public <T> T convertIfNecessary(@Nullable Object value, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType,
@Nullable MethodParameter methodParam) throws TypeMismatchException {
// 使用 SimpleTypeConverter 转换,其中 conversionService 都是从 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 中获取
// conversionService 中含有大量默认的 Converter
return getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(value, requiredType, methodParam);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
public <T> T convertIfNecessary(@Nullable Object value, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable MethodParameter methodParam)
throws TypeMismatchException {
return doConvert(value, requiredType, methodParam, null);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
调用org.springframework.beans.TypeConverterSupport#doConvert来进行参数转换,支持用户自定义的转换器以及内置的Converter
private <T> T doConvert(@Nullable Object value,@Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable MethodParameter methodParam, @Nullable Field field) throws TypeMismatchException { Assert.state(this.typeConverterDelegate != null, "No TypeConverterDelegate"); try { if (field != null) { return this.typeConverterDelegate.convertIfNecessary(value, requiredType, field); } else { return this.typeConverterDelegate.convertIfNecessary(value, requiredType, methodParam); } } catch (ConverterNotFoundException | IllegalStateException ex) { throw new ConversionNotSupportedException(value, requiredType, ex); } catch (ConversionException | IllegalArgumentException ex) { throw new TypeMismatchException(value, requiredType, ex); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
真正进行类型转换
public <T> T convertIfNecessary(@Nullable String propertyName, @Nullable Object oldValue, @Nullable Object newValue, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable TypeDescriptor typeDescriptor) throws IllegalArgumentException { // 获取客户自定义的 PropertyEditor, 在调用 @InitBinder 标注的方法的时候,在registerCustomEditor注册的用户自定义的转换器 PropertyEditor editor = this.propertyEditorRegistry.findCustomEditor(requiredType, propertyName); ConversionFailedException conversionAttemptEx = null; // No custom editor but custom ConversionService specified? // conversionService 包含着所有的转换器 ConversionService conversionService = this.propertyEditorRegistry.getConversionService(); if (editor == null && conversionService != null && newValue != null && typeDescriptor != null) { TypeDescriptor sourceTypeDesc = TypeDescriptor.forObject(newValue); if (conversionService.canConvert(sourceTypeDesc, typeDescriptor)) { try { return (T) conversionService.convert(newValue, sourceTypeDesc, typeDescriptor); } catch (ConversionFailedException ex) { // fallback to default conversion logic below conversionAttemptEx = ex; } } } Object convertedValue = newValue; // Value not of required type? if (editor != null || (requiredType != null && !ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(requiredType, convertedValue))) { if (typeDescriptor != null && requiredType != null && Collection.class.isAssignableFrom(requiredType) && convertedValue instanceof String) { TypeDescriptor elementTypeDesc = typeDescriptor.getElementTypeDescriptor(); if (elementTypeDesc != null) { Class<?> elementType = elementTypeDesc.getType(); if (Class.class == elementType || Enum.class.isAssignableFrom(elementType)) { convertedValue = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) convertedValue); } } } if (editor == null) { editor = findDefaultEditor(requiredType); } // 使用客户自定义的 PropertyEditor 进行转换 convertedValue = doConvertValue(oldValue, convertedValue, requiredType, editor); } 。。。 return (T) convertedValue; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
小结
- 调用@InitBinder 标注的方法,在这个方法里面通常registerCustomEditor来注册用户自定义的转换器提供string->指定类的能力
- 绑定http请求参数到入参参数(简单参数)中,支持类型转换
@PathVariable标注参数的参数解析器是:PathVariableMethodArgumentResolver
判断是否能解析
public boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter) {
if (!parameter.hasParameterAnnotation(PathVariable.class)) {
return false;
}
if (Map.class.isAssignableFrom(parameter.nestedIfOptional().getNestedParameterType())) {
PathVariable pathVariable = parameter.getParameterAnnotation(PathVariable.class);
return (pathVariable != null && StringUtils.hasText(pathVariable.value()));
}
return true;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
处理参数
调用AbstractNamedValueMethodArgumentResolver#resolveArgument方法同上,之后调resolveName方法
protected Object resolveName(String name, MethodParameter parameter, NativeWebRequest request) throws Exception {
Map<String, String> uriTemplateVars = (Map<String, String>) request.getAttribute(
HandlerMapping.URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE, RequestAttributes.SCOPE_REQUEST);
return (uriTemplateVars != null ? uriTemplateVars.get(name) : null);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
在根据路径获取 HandlerMethod 的时候设置了HandlerMapping.URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE属性,详见org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#getHandlerInternal方法
小结
- 调用@InitBinder 标注的方法,在这个方法里面通常registerCustomEditor来注册用户自定义的转换器提供string->指定类的能力
- 绑定http请求参数到入参参数(简单参数)中,支持类型转换
处理复杂类型的参数解析器是:ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor
判断是否能解析:只能处理复杂类型,通常是用户自定义类
public boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter) {
return (parameter.hasParameterAnnotation(ModelAttribute.class) ||
(this.annotationNotRequired && !BeanUtils.isSimpleProperty(parameter.getParameterType())));
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
处理参数
public final Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception { Assert.state(mavContainer != null, "ModelAttributeMethodProcessor requires ModelAndViewContainer"); Assert.state(binderFactory != null, "ModelAttributeMethodProcessor requires WebDataBinderFactory"); // 根据@ModelAttribute参数注释(如果存在) // 或根据方法参数的 简单类名,第一个字母小写 String name = ModelFactory.getNameForParameter(parameter); ModelAttribute ann = parameter.getParameterAnnotation(ModelAttribute.class); if (ann != null) { mavContainer.setBinding(name, ann.binding()); } Object attribute = null; BindingResult bindingResult = null; // 从mavContainer.getModel() 中获取 方法参数简单名称,即要写入参数中的属性 if (mavContainer.containsAttribute(name)) { attribute = mavContainer.getModel().get(name); } else { // 反射创建方法入参中的类 try { attribute = createAttribute(name, parameter, binderFactory, webRequest); } catch (BindException ex) { if (isBindExceptionRequired(parameter)) { // No BindingResult parameter -> fail with BindException throw ex; } // Otherwise, expose null/empty value and associated BindingResult if (parameter.getParameterType() == Optional.class) { attribute = Optional.empty(); } bindingResult = ex.getBindingResult(); } } if (bindingResult == null) { // Bean property binding and validation; // skipped in case of binding failure on construction. // 创建 WebDataBinder,并调用 @InitBinder 标注的方法 WebDataBinder binder = binderFactory.createBinder(webRequest, attribute, name); if (binder.getTarget() != null) { if (!mavContainer.isBindingDisabled(name)) { // 将请求绑定至目标binder的target对象,也就是刚刚创建的attribute对象。 bindRequestParameters(binder, webRequest); } // 如果有验证,则验证参数 validateIfApplicable(binder, parameter); if (binder.getBindingResult().hasErrors() && isBindExceptionRequired(binder, parameter)) { throw new BindException(binder.getBindingResult()); } } // Value type adaptation, also covering java.util.Optional if (!parameter.getParameterType().isInstance(attribute)) { // 使用 SimpleTypeConverter 转换,其中 conversionService 都是从 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 中获取 // conversionService 中含有大量默认的 Converter attribute = binder.convertIfNecessary(binder.getTarget(), parameter.getParameterType(), parameter); } bindingResult = binder.getBindingResult(); } // Add resolved attribute and BindingResult at the end of the model Map<String, Object> bindingResultModel = bindingResult.getModel(); mavContainer.removeAttributes(bindingResultModel); mavContainer.addAllAttributes(bindingResultModel); return attribute; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
将请求绑定至目标binder的target对象,也就是刚刚创建的attribute对象最终调到
protected void applyPropertyValues(MutablePropertyValues mpvs) {
try {
// Bind request parameters onto target object.
getPropertyAccessor().setPropertyValues(mpvs, isIgnoreUnknownFields(), isIgnoreInvalidFields());
}
catch (PropertyBatchUpdateException ex) {
// Use bind error processor to create FieldErrors.
for (PropertyAccessException pae : ex.getPropertyAccessExceptions()) {
getBindingErrorProcessor().processPropertyAccessException(pae, getInternalBindingResult());
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
public void setPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, boolean ignoreUnknown, boolean ignoreInvalid) throws BeansException { List<PropertyAccessException> propertyAccessExceptions = null; List<PropertyValue> propertyValues = (pvs instanceof MutablePropertyValues ? ((MutablePropertyValues) pvs).getPropertyValueList() : Arrays.asList(pvs.getPropertyValues())); for (PropertyValue pv : propertyValues) { try { // This method may throw any BeansException, which won't be caught // here, if there is a critical failure such as no matching field. // We can attempt to deal only with less serious exceptions. // 将请求参数中的属性赋值到方法的入参中 setPropertyValue(pv); } catch (NotWritablePropertyException ex) { if (!ignoreUnknown) { throw ex; } // Otherwise, just ignore it and continue... } catch (NullValueInNestedPathException ex) { if (!ignoreInvalid) { throw ex; } // Otherwise, just ignore it and continue... } catch (PropertyAccessException ex) { if (propertyAccessExceptions == null) { propertyAccessExceptions = new ArrayList<>(); } propertyAccessExceptions.add(ex); } } // If we encountered individual exceptions, throw the composite exception. if (propertyAccessExceptions != null) { PropertyAccessException[] paeArray = propertyAccessExceptions.toArray(new PropertyAccessException[0]); throw new PropertyBatchUpdateException(paeArray); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
public void setPropertyValue(PropertyValue pv) throws BeansException { PropertyTokenHolder tokens = (PropertyTokenHolder) pv.resolvedTokens; if (tokens == null) { String propertyName = pv.getName(); AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor nestedPa; try { //根据属性名获取BeanWrapImpl对象,支持多重属性的递归分析处理 nestedPa = getPropertyAccessorForPropertyPath(propertyName); } catch (NotReadablePropertyException ex) { throw new NotWritablePropertyException(getRootClass(), this.nestedPath + propertyName, "Nested property in path '" + propertyName + "' does not exist", ex); } // 经过上面的递归后,获取到最终需要操作的属性的对象,下面将根据该属性对象,获取最终要操作的内嵌对象的属性, // 生成PropertyTokenHolder,内省设置属性值 tokens = getPropertyNameTokens(getFinalPath(nestedPa, propertyName)); if (nestedPa == this) { pv.getOriginalPropertyValue().resolvedTokens = tokens; } nestedPa.setPropertyValue(tokens, pv); } else { setPropertyValue(tokens, pv); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
递归处理比较复杂,不展开分析
小结
- 先从model中根据类的简单名称(第一个字母小写)获取入参参数类或者反射创建入参参数类
- 调用@InitBinder 标注的方法,在这个方法里面通常registerCustomEditor来注册用户自定义的转换器提供string->指定类的能力
- 绑定http请求参数到入参参数类的属性中,支持类型转换,支持递归处理
总结
类关系图:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-EzHq68LL-1684591466071)(assets/image-20221017204656903.png)]
- Model参数的参数解析器是:ModelMethodProcessor
- @RequestBody标注参数的参数解析器是:RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor
- @RequestParam标注以及没有注解的简单参数的参数解析器是:RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver
- @PathVariable标注参数的简单参数的参数解析器是:PathVariableMethodArgumentResolver
- 普通入参(非简单参数)即兜底的参数解析器是:ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor
- 需要使用 spring 进行类型转换的都会调用@InitBinder 标注的方法
RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver和PathVariableMethodArgumentResolver都使用父类的org.springframework.web.method.annotation.AbstractNamedValueMethodArgumentResolver#resolveArgument方法进行参数解析。
);
}
// 经过上面的递归后,获取到最终需要操作的属性的对象,下面将根据该属性对象,获取最终要操作的内嵌对象的属性,
// 生成PropertyTokenHolder,内省设置属性值
tokens = getPropertyNameTokens(getFinalPath(nestedPa, propertyName));
if (nestedPa == this) {
pv.getOriginalPropertyValue().resolvedTokens = tokens;
}
nestedPa.setPropertyValue(tokens, pv);
}
else {
setPropertyValue(tokens, pv);
}
}
递归处理比较复杂,不展开分析 ##### 小结 1. 先从model中根据类的简单名称(第一个字母小写)获取入参参数类或者反射创建入参参数类 2. 调用@InitBinder 标注的方法,在这个方法里面通常registerCustomEditor来注册用户自定义的转换器提供string->指定类的能力 3. 绑定http请求参数到入参参数类的属性中,支持类型转换,支持递归处理 ## 总结 类关系图: 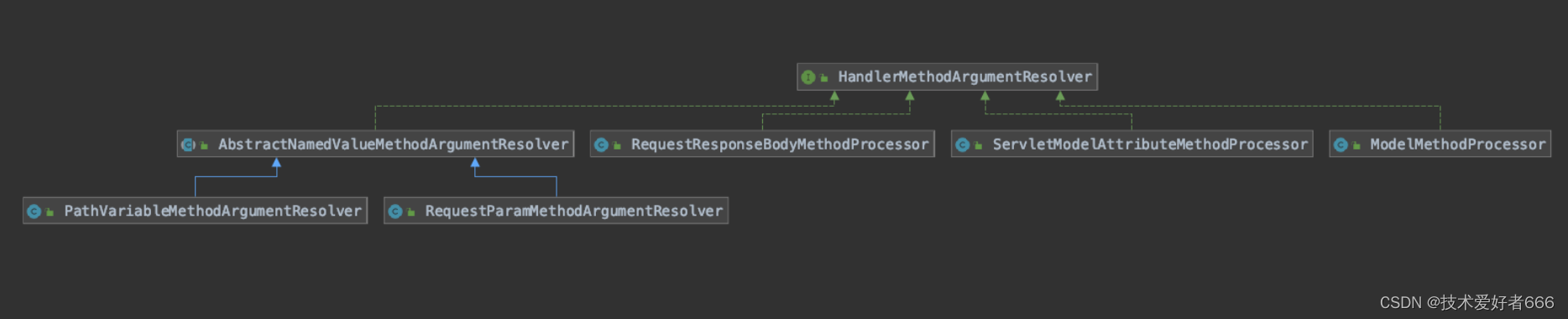 1. Model参数的参数解析器是:ModelMethodProcessor 2. @RequestBody标注参数的参数解析器是:RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor 3. @RequestParam标注以及没有注解的**简单参数**的参数解析器是:RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver 4. @PathVariable标注参数的**简单参数**的参数解析器是:PathVariableMethodArgumentResolver 5. 普通入参(**非简单参数**)即兜底的参数解析器是:ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor 6. 需要使用 spring 进行类型转换的都会调用@InitBinder 标注的方法 RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver和PathVariableMethodArgumentResolver都使用父类的org.springframework.web.method.annotation.AbstractNamedValueMethodArgumentResolver#resolveArgument方法进行参数解析。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25



