热门标签
热门文章
- 1【极简版】一篇文章理解UGC、PGC、POI运营管理与O2O行业
- 2抓取静态网页数据
- 3免费期刊类表
- 42024最新Keilv5下载安装注册及添加ARM5编译器_mdk540
- 5【Python笔记-FastAPI】后台任务+WebSocket监控进度_fastapi list[websocket]
- 6数学建模大师手册:全国大学生数学建模竞赛模板(附Word模版)_数学建模模板csdn
- 7域内提权之CVE-2020-1472复现打域控_cve-2020-1472下载
- 8Python 3.x 学习:Python 简介、安装(一)_python官网python3.x安装包其中包括什么
- 9BIO、NIO、AIO你会用了吗,java高级技术经理面试题_byte[] bytes =new byte[1]; int value = socket.geti
- 10hadoop—haddop部署、yarn管理器使用、hdfs的高可用、yarn的高可用、Hbase分布式部署_哈道普分布式部署安装是什么原理
当前位置: article > 正文
Java并发编程之CompletableFuture详解_java completablefuture
作者:笔触狂放9 | 2024-07-14 10:03:15
赞
踩
java completablefuture
1、Futuru接口和Callable接口
- Future接口定义了操作异步任务执行的方法,如:获取异步任务的执行结果、取消任务的执行、判断任务是否被取消、是否执行完毕等
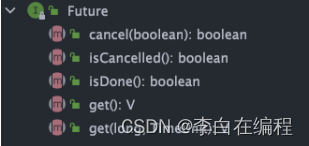
- Callable接口中定义了需要有返回结果的任务 要执行的方法,如:主线程让一个子线程去执行任务,子线程可能比较耗时,启动子线程开始执行任务后,主线程就去做其他事情了,过一段时间才会去获取子任务的执行结果
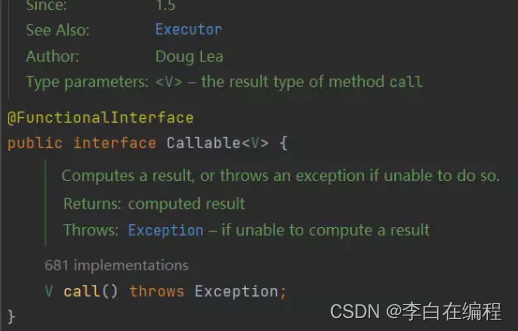
实现Callable接口中的call(),返回方法计算的结果,或抛出异常
2、FutureTask
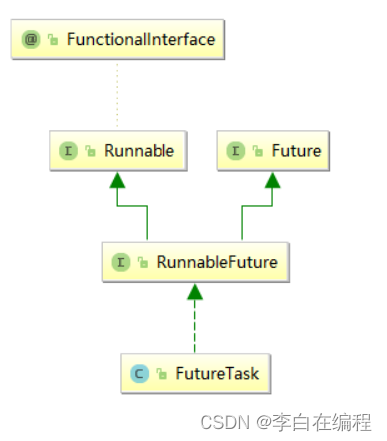
代码示例:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException{ FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(() -> { System.out.println("-----come in FutureTask"); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100); }); Thread t1 = new Thread(futureTask,"t1"); t1.start(); //3秒钟后才出来结果,还没有计算你提前来拿(只要一调用get方法,对于结果就是不见不散,会导致阻塞) //System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+futureTask.get()); //3秒钟后才出来结果,我只想等待1秒钟,过时不候 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+futureTask.get(1L,TimeUnit.SECONDS)); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+" run... here"); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- get(): 一旦调用get()方法,不管是否计算完成都会导致阻塞
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(() -> { System.out.println("-----come in FutureTask"); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return ""+ ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100); }); new Thread(futureTask,"t1").start(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"线程完成任务"); /** * 用于阻塞式获取结果,如果想要异步获取结果,通常都会以轮询的方式去获取结果 */ while (true){ if(futureTask.isDone()){ System.out.println(futureTask.get()); break; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- isDone()轮询
- 轮询的方式会耗费无谓的CPU资源,且未必能及时地得到计算结果.
- 如果想要异步获取结果,通常都会以轮询的方式去获取结果。尽量不要阻塞
3、CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture实现了Future,CompletionStage两个接口,故CompletableFuture功能更加强大
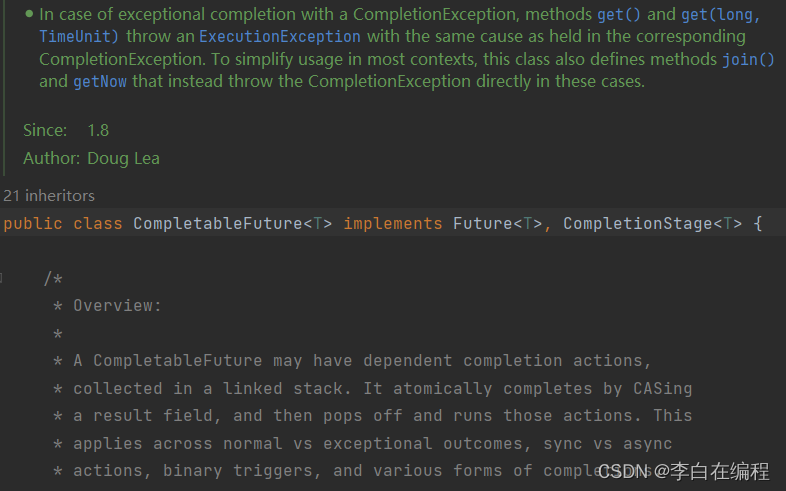
-
CompletableFuture

-
CompletionStage
- CompletionStage代表异步计算过程中的某个阶段,一个阶段完成以后可能会触发另外一个阶段,有些类似Linux系统的管道分隔符传参数
- 一个阶段的计算执行可以是一个Function,Consumer或者Runnable
- 一个阶段的执行可能是被单个阶段计算完成后触发,也可能是由多个阶段一起触发
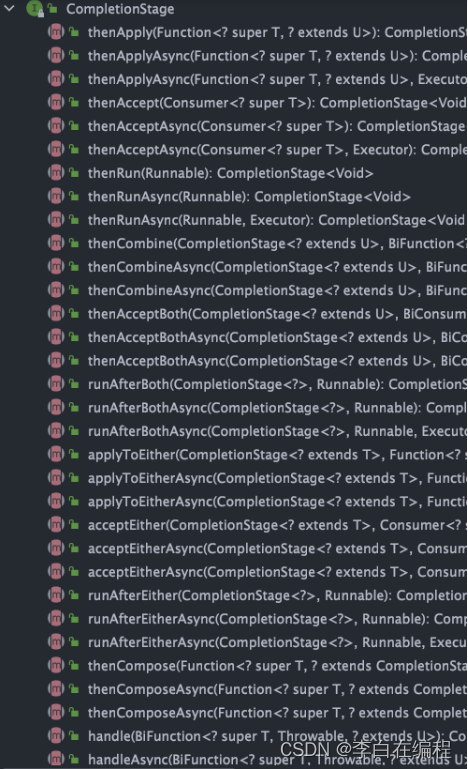
-
CompletionStage 接口中的方法比较多,CompletableFuture 的函数式能力就是这个接口赋予的。从这个接口的方法参数你就可以发现其大量使用了 Java8 引入的函数式编程。
4、CompletableFuture核心的四个静态方法
- runAsync 无 返回值
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable,Executor executor)
- 1
- 2
- supplyAsync 有 返回值
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier,Executor executor)
- 1
- 2
- 没有指定Executor的方法,直接使用默认的ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码
- 如果指定线程池,则使用我们自定义的或者特别指定的线程池执行异步代码
static ThreadPoolExecutor poolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 5, 10L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()); private static void testSimpleCompletableFuture() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t is coming in ..."); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t task was finished!"); }); // },poolExecutor); // 如果使用了自行创建的线程池,则使用自定义的或者特别指定的线程池执行异步代码 System.out.println(future.get()); // get方法返回null,因为runAsync方法无返回值 }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1 is coming in ...
ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1 task was finished!
null
- 1
- 2
- 3
同上,将runAsync方法改为supplyAsync方法,并返回一个整数类型的变量
static ThreadPoolExecutor poolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 5, 10L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()); private static void testSupplyAsync() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t is coming in ... supplyAsync"); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t task was finished!"); // return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100); return Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); }); // },poolExecutor); System.out.println(future.get()); // get方法返回null,因为runAsync方法无返回值 }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 输出结果:
ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1 is coming in ... supplyAsync
ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1 task was finished!
8
- 1
- 2
- 3
5、减少阻塞和轮询
- 从Java8开始引入了CompletableFuture,它是Future的功能增强版,可以传入回调对象,当异步任务完成或者发生异常时,自动调用回调对象的回调方法
private static void testWhenCompleteAndExceptionally() { CompletableFuture<Long> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { //主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭:暂停3秒钟线程 long result = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextLong(100); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } System.out.println("异步任务计算完成,结果为:" + result); if (result > 5) { int i = 1 / 0; } return result; }).whenComplete((res, err) -> { if (err == null) { System.out.println("异步任务执行正常,其结果为:" + res); } }).exceptionally(e -> { System.out.println("exceptionally,异步任务执行异常:" + e.getCause() + "< --- >" + e.getMessage()); return Runtime.getRuntime().freeMemory(); }); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " task was finished! ..."); // 主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭:暂停3秒钟线程 try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
输出结果:
main task was finished! ...
异步任务计算完成,结果为:39
exceptionally,异步任务执行异常:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero< --- >java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 小总结
- 异步任务不管是正常结束,还是出现异常,都会自动回调某个方法
- 主线程设置好回调函数后,不再关心异步任务的执行,异步任务之间可以顺序执行
6、电商网站的比价需求案例
- 对于分布式微服务的调用,按照实际业务,如果是无关联step by step的业务,可以尝试是否可以多箭齐发,同时调用。我们去比同一个商品在各个平台上的价格,要求获得一个清单列表,分别同时或异步查询某个商品在各大商城中的价格,查完京东查淘宝,查完淘宝查天猫…
- 实现方法如下:
代码实现1(逐个查询):
class Emall { @Getter private String emallName; public Emall(String emallName) { this.emallName = emallName; } // 生成随机数,模拟价格计算 public double computePrice(String productName) { try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextDouble() * 2 + productName.charAt(0); } } static List<Emall> list = Arrays.asList( new Emall("jdong"), new Emall("dangdang"), new Emall("taobao"), new Emall("pdd"), new Emall("tmall") ); // 实现基本的功能需求 // List<Emall> --> map --> List<String> public static List<String> getPrice(List<Emall> list, String productName) { return list.stream().map(emall -> String.format(productName + " in %s price is %.2f", emall.getEmallName(), emall.computePrice(productName)) ).collect(Collectors.toList()); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 代码实现2(一口气查询):
public static List<String> getPriceByCompletableFuture(List<Emall> list, String productName) {
List<String> collect = list.stream().map(emall -> // 将每个商城对象emall映射成一个CompletableFuture异步任务,即将每个emall放到异步任务的线程中
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->
String.format(productName + " in %s price is %.2f",
emall.getEmallName(), emall.computePrice(productName))))
.collect(Collectors.toList())
.stream()
.map(s -> s.join())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return collect;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 两种实现方式的性能对比:
public static void main(String[] args) { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); List<String> list2 = getPriceByCompletableFuture(list, "mysql"); for (String element : list2) { System.out.println(element); } long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("异步处理任务 ----costTime: "+(endTime - startTime) +" 毫秒"); long startTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); List<String> ansList = getPrice(list, "mysql"); for (String ele : ansList) { System.out.println(ele); } long endTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("同步处理任务 ----costTime: "+(endTime2 - startTime2) +" 毫秒"); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
输出结果:
mysql in jdong price is 110.77
mysql in dangdang price is 110.44
mysql in taobao price is 109.06
mysql in pdd price is 109.14
mysql in tmall price is 109.60
异步处理任务 ----costTime: 1220 毫秒
mysql in jdong price is 110.81
mysql in dangdang price is 110.86
mysql in taobao price is 110.08
mysql in pdd price is 109.36
mysql in tmall price is 109.12
同步处理任务 ----costTime: 5050 毫秒
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
7、CompletableFuture常用方法
7.1、获得结果和触发计算
// 不见不散
public T get()
// 过时不候
public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
// 没有计算完成的情况下,给我一个替代结果
// 立即获取结果不阻塞 计算完,返回计算完成后的结果 没算完,返回设定的valueIfAbsent值
public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent)
// 和get方法功能类似,但join方法不需要抛出异常
public T join()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
private static void testGetAndGetNow() { CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "111"; }); // try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // 注释掉如上的Sleep方法,getNow返回的结果是方法中设置的值"2222" // 不注释如上的sleep方法,getNow方法的结果是future返回的结果值"111" System.out.println(future.getNow("2222")); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "abc").thenApply(r -> r + "123").join());
// abc123
- 1
- 2
7.2、处理计算结果
- thenApply方法: 计算结果存在依赖关系,这两个线程串行化,当前步骤有异常的话就停止执行
public static void main(String[] args) { // 注意: 这里最好不要使用 ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);的方式来创建线程池(见阿里开发手册) ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(3, 5, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(2), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy() //new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy() //new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy() //new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy() ); // 当一个线程依赖另一个线程时用 thenApply 方法来把这两个线程串行化, CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } System.out.println("异步任务操作步骤 111"); return 1; },threadPool).thenApply(res ->{ System.out.println("异步任务操作步骤 222"); return res + 2; }).thenApply(res ->{ System.out.println("异步任务操作步骤 333"); // int i = 10 / 0; // 异常情况:哪步出错就停在哪步 return res + 3; }).whenComplete((result,err)->{ if (err == null){ System.out.println("异步任务处理正常,计算结果为:" + result); // result = 1 + 2 + 3 = 6 } }).exceptionally(e->{ e.getStackTrace(); System.out.println(e.getMessage()); return 404; }); // 主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭,即主线程执行太快,导致异步任务无法执行,可以让主线程Sleep几秒 // 除了sleep的方法,还可以使用线程池来处理,注意,最后一定关闭线程池 threadPool.shutdown(); 否则,程序会一直处于运行状态 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + " --- 主线程先去忙其他任务"); // try { // TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); // } catch (InterruptedException e) { // throw new RuntimeException(e); // } threadPool.shutdown(); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- handle方法: 出现异常也可以继续执行,根据带的异常参数可以进一步处理
// 当一个线程依赖另一个线程时用 handle 方法来把这两个线程串行化, // 异常情况:有异常也可以往下一步走,handle会根据异常参数在最后抛出对应的异常 CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { //暂停几秒钟线程 try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("111"); return 1024; }).handle((f,e) -> { // int age = 10/0; System.out.println("222"); return f + 1; }).handle((f,e) -> { System.out.println("333"); return f + 1; }).whenCompleteAsync((res,e) -> { System.out.println("任务处理的结果为: "+res); }).exceptionally(e -> { e.printStackTrace(); return null; }); System.out.println("-----主线程结束, END"); // 主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭: try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
7.3、消费计算结果
- thenRun:thenRun(Runnable runnable),任务A和B依次先后执行,并且B不需要A的结果
- thenAccept:thenAccept(Consumer action),任务A和B依次先后执行,B需要A的结果任务A和B依次先后执行,B需要A的结果,但是任务B无返回值
- thenApply:thenApply(Function fn),任务A和B依次先后执行**,B需要A的结果,同时任务B有返回值**
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
return 1;
}).thenApply(num ->{
return num + 2;
}).thenApply(num ->{
return num + 3;
}).thenAccept(num -> System.out.println(num));
System.out.println("--------------------");
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()-> "the resultA of thenRun").thenRun(()->{
System.out.println("thenRun,B不需要A的结果");
}).join());
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()-> "任务A和B依次先后执行,B需要A的结果,thenAccept").thenAccept(res -> System.out.println(res + ",任务B无返回值")).join());
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()-> "任务A和B先后执行,B需要A的结果").thenApply(str -> str + " --> 任务B有返回值").join());
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 线程池运行选择
- 如果没有传入自定义的线程池,则使用默认线程池ForkJoinPool
- 如果执行第一个任务,传入了一个自定义线程池,调用thenRun方法执行第二个任务时,则第二个任务和第一个任务共用一个线程池,调用thenRunAsync方法执行第二个任务时,则第一个任务使用的是传入的自定义线程池,第二个任务使用的是ForkJoinPool
- 可能存在程序处理太快的情况,系统会优化切换原则,直接使用主线程处理
7.4、计算速度选用
applyToEither方法:任务谁执行快,就用谁(选用执行速度最快的任务 返回的结果作为最后的总结果)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> applyToEither(
CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Function<? super T, U> fn)
- 1
- 2
使用实例:
CompletableFuture<String> planA = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { System.out.println("A coming in..."); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } return "planA"; }); CompletableFuture<String> planB = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { System.out.println("B coming in..."); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); // TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } return "planB"; }); CompletableFuture<String> result = planA.applyToEither(planB, p -> { return p + " is winner!"; // 两个任务planA和planB,谁执行得更快,p就是对应的返回结果 }); // 补充: // join()和get()方法类似,其不同在于使用get方法需要抛出异常 或 进行异常捕获, // join()则不需要抛出异常,也不用进行异常捕获,但出现异常时,会直接抛异常 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" +result.join());
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
7.5、合并计算结果
- 两个CompletionStage任务都完成后,最终能把两个任务的结果一起交给thenCombine来处理,
先完成的任务需要等待其他分支任务完成,最后合并任务的计算结果 - thenCombine:将两个异步任务的返回结果进行合并,再返回最后的结果值
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t --- 开始执行任务1..."); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } return 20; }); CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t -- 开始执行任务2.."); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } return 30; }); CompletableFuture<Integer> result = future1.thenCombine(future2, (x, y) -> { System.out.println("---> 合并两个任务的计算结果"); return x * y; }); System.out.println(result.join()); //System.out.println(result.get()); // get方法需要抛出异常或进行异常捕获
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
参考资料:尚硅谷2022版JUC并发编程
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/笔触狂放9/article/detail/824276
推荐阅读
相关标签



