- 1Java+Swing+mysql天气信息管理系统_java天气管理系统
- 2YoloV5 train.py 如何使用_yolov5中train.py中weights,cfy,data,hyp,怎么填
- 3MySQL之ACID实现原理
- 4【C++14算法】make_unique
- 5ati-driver在2.16.18-gentoo-r2内核编译有问题及解决方法!!!_uts_release
- 6使用Elasticsearch进行word,excel,PDF的全文检索 windows实现 超完整(ingest-attachment实现)_elasticsearch pdf
- 7uni-app开发多端之钉钉小程序_uniapp中如何获取corpid is required
- 8arcgis批量出图---批量输出结果为jpg_arcgis批量出图jpg步骤
- 9人工智能面试题
- 10【朝夕教育】2023年10月 WPF+上位机+工业互联 097-智能停车场项目专题(项目介绍)_朝夕智能停车场系统开发
Redis注解式开发结合SSM项目使用与Quartz框架介绍以及击穿、穿透、雪崩问题解决_com.zking.ssm
赞
踩
目录
一、SSM项目整合Redis
redis是nosql数据库,mysql是sql数据库,都是数据库因此可以参考mysql整合ssm项目的过程。
1.1 导入pom依赖
- <properties>
- <redis.version>2.9.0</redis.version>
- <redis.spring.version>1.7.1.RELEASE</redis.spring.version>
- </properties>
-
- <dependencies>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
- <artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
- <version>${redis.version}</version>
- </dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId>
- <version>${redis.spring.version}</version>
- </dependency>
- </dependencies>

1.2 spring-redis.xml
- 注册 redis.properties
- 配置数据源
- 连接工厂
- 配置序列化
- 配置redis的key生成策略
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
- xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache.xsd">
-
- <!-- 1. 引入properties配置文件 -->
- <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:redis.properties" />
-
- <!-- 2. redis连接池配置-->
- <bean id="poolConfig" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig">
- <!--最大空闲数-->
- <property name="maxIdle" value="300"/>
- <!--连接池的最大数据库连接数 -->
- <property name="maxTotal" value="${redis.maxTotal}"/>
- <!--最大建立连接等待时间-->
- <property name="maxWaitMillis" value="${redis.maxWaitMillis}"/>
- <!--逐出连接的最小空闲时间 默认1800000毫秒(30分钟)-->
- <property name="minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value="${redis.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis}"/>
- <!--每次逐出检查时 逐出的最大数目 如果为负数就是 : 1/abs(n), 默认3-->
- <property name="numTestsPerEvictionRun" value="${redis.numTestsPerEvictionRun}"/>
- <!--逐出扫描的时间间隔(毫秒) 如果为负数,则不运行逐出线程, 默认-1-->
- <property name="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" value="${redis.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis}"/>
- <!--是否在从池中取出连接前进行检验,如果检验失败,则从池中去除连接并尝试取出另一个-->
- <property name="testOnBorrow" value="${redis.testOnBorrow}"/>
- <!--在空闲时检查有效性, 默认false -->
- <property name="testWhileIdle" value="${redis.testWhileIdle}"/>
- </bean>
-
- <!-- 3. redis连接工厂 -->
- <bean id="connectionFactory" class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory"
- destroy-method="destroy">
- <property name="poolConfig" ref="poolConfig"/>
- <!--IP地址 -->
- <property name="hostName" value="${redis.hostName}"/>
- <!--端口号 -->
- <property name="port" value="${redis.port}"/>
- <!--如果Redis设置有密码 -->
- <property name="password" value="${redis.password}"/>
- <!--客户端超时时间单位是毫秒 -->
- <property name="timeout" value="${redis.timeout}"/>
- </bean>
-
- <!-- 4. redis操作模板,使用该对象可以操作redis
- hibernate课程中hibernatetemplete,相当于session,专门操作数据库。
- -->
- <bean id="redisTemplate" class="org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate">
- <property name="connectionFactory" ref="connectionFactory"/>
- <!--如果不配置Serializer,那么存储的时候缺省使用String,如果用User类型存储,那么会提示错误User can't cast to String!! -->
- <property name="keySerializer">
- <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer"/>
- </property>
- <property name="valueSerializer">
- <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer"/>
- </property>
- <property name="hashKeySerializer">
- <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer"/>
- </property>
- <property name="hashValueSerializer">
- <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer"/>
- </property>
- <!--开启事务 -->
- <property name="enableTransactionSupport" value="true"/>
- </bean>
- <!-- 5.配置缓存管理器 -->
- <bean id="redisCacheManager" class="org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager">
- <constructor-arg name="redisOperations" ref="redisTemplate"/>
- <!--redis缓存数据过期时间单位秒-->
- <property name="defaultExpiration" value="${redis.expiration}"/>
- <!--是否使用缓存前缀,与cachePrefix相关-->
- <property name="usePrefix" value="true"/>
- <!--配置缓存前缀名称-->
- <property name="cachePrefix">
- <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.cache.DefaultRedisCachePrefix">
- <constructor-arg index="0" value="-cache-"/>
- </bean>
- </property>
- </bean>
- <!--6.配置缓存生成键名的生成规则-->
- <bean id="cacheKeyGenerator" class="com.zking.ssm.redis.CacheKeyGenerator"></bean>
- <!--7.启用缓存注解功能-->
- <cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="redisCacheManager" key-generator="cacheKeyGenerator"/>
- </beans>

redis.properties 配置文件:
1.3 spring上下文配置
applicationContext.xml:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
- xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
- <!--1. 引入外部多文件方式 -->
- <bean id="propertyConfigurer"
- class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
- <property name="systemPropertiesModeName" value="SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_OVERRIDE" />
- <property name="ignoreResourceNotFound" value="true" />
- <property name="locations">
- <list>
- <value>classpath:jdbc.properties</value>
- <value>classpath:redis.properties</value>
- </list>
- </property>
- </bean>
-
- <!-- 随着后续学习,框架会越学越多,不能将所有的框架配置,放到同一个配制间,否者不便于管理 -->
- <import resource="applicationContext-mybatis.xml"></import>
- <import resource="spring-redis.xml"></import>
- <import resource="applicationContext-shiro.xml"></import>
- </beans>

二、Redis注解式开发
首先需要一个缓冲策略类,用于储存信息
- package com.ycxw.ssm.redis;
-
- import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
- import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator;
- import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
-
- import java.lang.reflect.Array;
- import java.lang.reflect.Method;
-
- @Slf4j
- public class CacheKeyGenerator implements KeyGenerator {
- // custom cache key
- public static final int NO_PARAM_KEY = 0;
- public static final int NULL_PARAM_KEY = 53;
-
- @Override
- public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) {
- StringBuilder key = new StringBuilder();
- key.append(target.getClass().getSimpleName()).append(".").append(method.getName()).append(":");
- if (params.length == 0) {
- key.append(NO_PARAM_KEY);
- } else {
- int count = 0;
- for (Object param : params) {
- if (0 != count) {//参数之间用,进行分隔
- key.append(',');
- }
- if (param == null) {
- key.append(NULL_PARAM_KEY);
- } else if (ClassUtils.isPrimitiveArray(param.getClass())) {
- int length = Array.getLength(param);
- for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
- key.append(Array.get(param, i));
- key.append(',');
- }
- } else if (ClassUtils.isPrimitiveOrWrapper(param.getClass()) || param instanceof String) {
- key.append(param);
- } else {//Java一定要重写hashCode和eqauls
- key.append(param.hashCode());
- }
- count++;
- }
- }
-
- String finalKey = key.toString();
- // IEDA要安装lombok插件
- log.debug("using cache key={}", finalKey);
- return finalKey;
- }
- }

2.1 Cacheable 注解
1、定义查询接口使用Cacheable注解
Spring会在其被调用后将其返回值缓存起来,以保证下次利用同样的参数来执行该方法时可以直接从缓存中获取结果,而不需要再次执行该方法。Spring在缓存方法的返回值时是以键值对进行缓存的,值就是方法的返回结果。
- package com.ycxw.ssm.biz;
-
- import com.zking.ssm.model.Clazz;
- import com.zking.ssm.util.PageBean;
-
- import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
-
- import java.util.List;
- import java.util.Map;
-
- public interface ClazzBiz {
-
- @Cacheable("clz")
- Clazz selectByPrimaryKey(Integer cid);
-
- }

2、编写测试类
- package com.ycxw.shiro;
-
- import com.zking.ssm.biz.ClazzBiz;
- import org.junit.Test;
- import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
- import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
- import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
- import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
-
-
- @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
- @ContextConfiguration(locations={"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
- public class ClazzBizTest {
- @Autowired
- private ClazzBiz clazzBiz;
-
- @Test
- public void test1(){
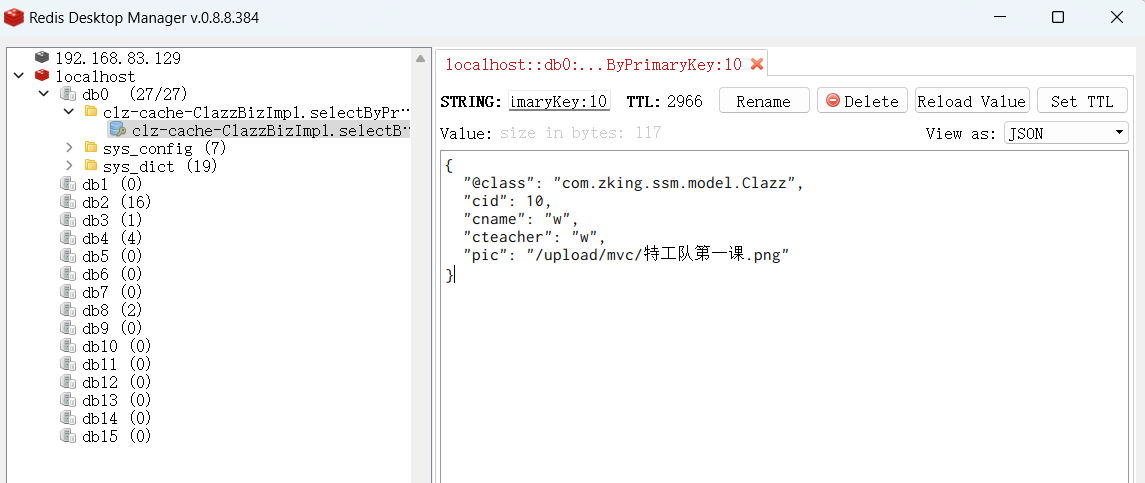
- System.out.println(clazzBiz.selectByPrimaryKey(10));
- System.out.println(clazzBiz.selectByPrimaryKey(10));
- }
-
- }

第一次运行时:(查询两次)
第二次运行时:(无查询语句)
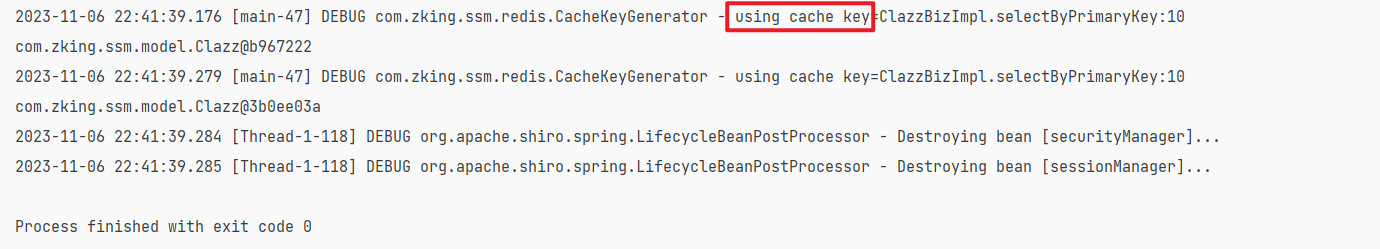
再次运行相同的数据时不再查询了,直接从缓冲中拿取数据:
2.2 自定义策略
@Cacheable可以指定三个属性,value、key和condition。
我可定义key值来修改我们保存到redis缓冲的key值,并且可通过condition来制定什么时候需要缓冲,进一步优化性能。
自定义策略,如果查询的cid大于6才进行缓冲
- package com.ycxw.ssm.biz;
-
- import com.zking.ssm.model.Clazz;
- import com.zking.ssm.util.PageBean;
-
- import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
-
- import java.util.List;
- import java.util.Map;
-
- public interface ClazzBiz {
-
- @Cacheable(value = "clz",key = "'cid:'+#cid",condition = "#cid > 6")
- Clazz selectByPrimaryKey(Integer cid);
-
- }

2.3 CachePut 注解
它的使用与Cacheable的使用一致,它们的区别:
- Cacheable:会在redis中存储数据,同时也会读取数据
- CachePut:只会在redis储存数据,不会进行读取操作
- package com.ycxw.ssm.biz;
-
- import com.zking.ssm.model.Clazz;
- import com.zking.ssm.util.PageBean;
-
- import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
-
- import java.util.List;
- import java.util.Map;
-
- public interface ClazzBiz {
-
- @CachePut(value = "clz",key = "'cid:'+#cid",condition = "#cid > 6")
- Clazz selectByPrimaryKey(Integer cid);
-
- }

测试:
- public class ClazzBizTest {
- @Autowired
- private ClazzBiz clazzBiz;
-
- @Test
- public void test1(){
- System.out.println(clazzBiz.selectByPrimaryKey(9));
- System.out.println(clazzBiz.selectByPrimaryKey(9));
- }
-
- }

不管运行多少次,它还是会查询数据库,即便已经将数据存储到redis中
三、Redis中缓冲、击穿、穿透、雪崩问题解决
3.1 缓冲问题 —— Quartz 框架
现在模拟一个场景:我在某系统中增加了一条数据,在主界面中会显示该条数据。而数据是从缓冲中拿取的,而新增的数据并没有立即添加到缓冲中。那我们如何保证redis数据与数据库数据的一致性呢?
方案一:手动刷新数据同步策略
这样我们每次添加了新的数据,需要手动点击刷新缓冲键,显然这个对管理者不便的。
方案二:利用Quartz作业调度框架,定时刷新任务
Quartz是一个开源的作业调度框架,用于在Java应用程序中实现任务调度和定时任务管理。它提供了一种简单而强大的方式来安排和执行各种类型的作业,包括定时任务、周期性任务和异步任务。
Quartz框架的核心概念是作业(Job)和触发器(Trigger)。作业是要执行的任务,而触发器定义了作业执行的时间和频率。通过配置作业和触发器,可以实现灵活的任务调度和执行。
在Redis中,它本身并没有直接使用Quartz框架。然而,我们可以结合使用Quartz和Redis来实现一些特定的功能,例如:
- 使用Quartz调度任务,将任务的执行结果存储到Redis中,以便其他系统或模块可以读取和处理。
- 使用Quartz定时清理Redis中的过期数据,以确保Redis的存储空间得到有效利用。
- 使用Quartz定时刷新Redis中的缓存数据,以保持数据的最新性。
- 使用Quartz和Redis实现分布式锁机制,确保在多个节点上的任务调度不会发生冲突。
3.2 常见的三种问题解决方案
1、击穿(Cache Miss) 击穿指的是在高并发情况下,当一个缓存键(key)不存在于缓存中,但是被大量请求同时查询时,这些请求会直接访问数据库,导致数据库压力过大。这种情况下,缓存无法发挥作用,而且数据库可能会因此而崩溃。
解决方案:
- 使用互斥锁(Mutex Lock)或分布式锁(Distributed Lock)来保护数据库访问,确保只有一个请求能够访问数据库,其他请求等待结果。
- 在缓存中设置短暂的空值(Null Value),以防止大量请求同时查询同一个缓存键。
2、穿透(Cache Penetration) 穿透指的是当一个缓存键不存在于缓存中,并且被大量请求同时查询时,这些请求都会直接访问数据库,导致数据库压力过大。与击穿不同的是,穿透是因为查询的键根本不存在于缓存中。
解决方案:
- 在查询数据库之前,可以添加一个布隆过滤器(Bloom Filter)来快速判断查询的键是否存在于缓存中。如果不存在,可以直接返回空结果,而不是访问数据库。
- 对于查询结果为空的情况,也可以将空结果缓存一段时间,以避免频繁查询数据库。
3、雪崩(Cache Avalanche) 雪崩指的是在缓存中大量的缓存键同时过期或失效,导致大量请求直接访问数据库,造成数据库压力过大,甚至崩溃。
解决方案:
- 设置缓存键的过期时间时,可以引入随机值,使得缓存键的过期时间分散开来,避免大量缓存键同时过期。
- 使用热点数据预加载(Cache Pre-warming)策略,提前加载热门数据到缓存中,减少缓存键同时失效的可能性。
- 使用多级缓存架构,将缓存分为多个层级,以降低整体缓存失效的风险。
总结: 在解决这些问题时,我们需要综合考虑系统的并发性、可用性和性能。通过合理的缓存策略、锁机制、预加载与使用调度框架等手段,可以有效地解决Redis中的击穿、穿透和雪崩问题,提高系统的稳定性和性能。