- 1(过程超详细)适合新手的ATK-ESP8266+STM32F103系列单片机通过MQTT协议直连阿里云的教程_stm32f103rct6+8266
- 2OpenCV53:图像修补|Image Inpainting_image inpainting bertalmio, m
- 3unity3d显示c4d材质_C4D小白最常踩的9个坑,看看你中招了没?
- 4Android导入Gradle报错Could not install Gradle distribution......
- 5自用 | Latex常用(易忘)语法总结_latex {|c|} *
- 6Android知识体系总结之Android部分之Android系统版本特性篇_android4.4 android9.0特性对比分析
- 7unity的协程的用途_unity协程的作用
- 8老旗舰华为能用上鸿蒙吗,荣耀手机能升级鸿蒙吗?五款旗舰优先,老荣耀机主或有惊喜...
- 9除了ChatGPT,跨境电商必备的7个AI工具
- 10uni.chooseLocation报错:[JS Framework] 当前运行的基座不包含原生插件[mapSearch],请在manifest中配置该插件,重新制作包括该原生插件的自定义运行基座_当前运行的基座不包含原生插件[mapsearch],请在manifest中配置该插件,重新制作包
LangChain 58 深入理解LangChain 表达式语言21 Memory消息历史 LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)_runnablewithmessagehistory
赞
踩
LangChain系列文章
- LangChain 36 深入理解LangChain 表达式语言优势一 LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
- LangChain 37 深入理解LangChain 表达式语言二 实现prompt+model+output parser LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
- LangChain 38 深入理解LangChain 表达式语言三 实现RAG检索增强生成 LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
- LangChain 39 深入理解LangChain 表达式语言四 为什么要用LCEL LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
- LangChain 40 实战Langchain访问OpenAI ChatGPT API Account deactivated的另类方法,访问跳板机API
- LangChain 41 深入理解LangChain 表达式语言五 为什么要用LCEL调用大模型LLM LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
- LangChain 42 深入理解LangChain 表达式语言六 Runtime调用不同大模型LLM LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
- LangChain 43 深入理解LangChain 表达式语言七 日志和Fallbacks异常备选方案 LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
- LangChain 44 深入理解LangChain 表达式语言八 Runnable接口输入输出模式 LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
- LangChain 45 深入理解LangChain 表达式语言九 Runnable 调用、流输出、批量调用、异步处理 LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
- LangChain 46 深入理解LangChain 表达式语言十 Runnable 调用中间状态调试日志 LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
- LangChain 47 深入理解LangChain 表达式语言十一 Runnable 并行处理 LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
- LangChain 48 终极解决 实战Langchain访问OpenAI ChatGPT API Account deactivated的另类方法,访问跳板机API
- LangChain 49 深入理解LangChain 表达式语言十二 Runnable 透传数据保持输入不变 LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
- LangChain 50 深入理解LangChain 表达式语言十三 自定义pipeline函数 LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
- LangChain 51 深入理解LangChain 表达式语言十四 自动修复配置RunnableConfig LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
- LangChain 52 深入理解LangChain 表达式语言十五 Bind runtime args绑定运行时参数 LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
- LangChain 53 深入理解LangChain 表达式语言十六 Dynamically route动态路由 LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
- LangChain 54 深入理解LangChain 表达式语言十七 Chains Route动态路由 LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
- LangChain 55 深入理解LangChain 表达式语言十八 function Route自定义动态路由 LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
- LangChain 56 深入理解LangChain 表达式语言十九 config运行时选择大模型LLM LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
- LangChain 57 深入理解LangChain 表达式语言二十 LLM Fallbacks速率限制备份大模型 LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
1. 添加消息历史记录 memory
RunnableWithMessageHistory让我们可以向某些类型的链中添加消息历史记录。
具体来说,它可用于接受以下之一作为输入的任何可运行对象
- 一系列
BaseMessage - 一个带有以一系列
BaseMessage为值的键的字典 - 一个带有以字符串或一系列
BaseMessage为最新消息值的键和一个带有历史消息值的单独键的字典
并且以以下之一作为输出返回
- 可以被视为
AIMessage内容的字符串 - 一系列
BaseMessage - 一个带有包含一系列
BaseMessage的键的字典
让我们看一些示例来看看它是如何工作的。
2. 环境准备
我们将使用Redis来存储我们的聊天消息记录和ChatOpenAI模型,所以我们需要安装以下依赖项:
pip install -U langchain redis
- 1
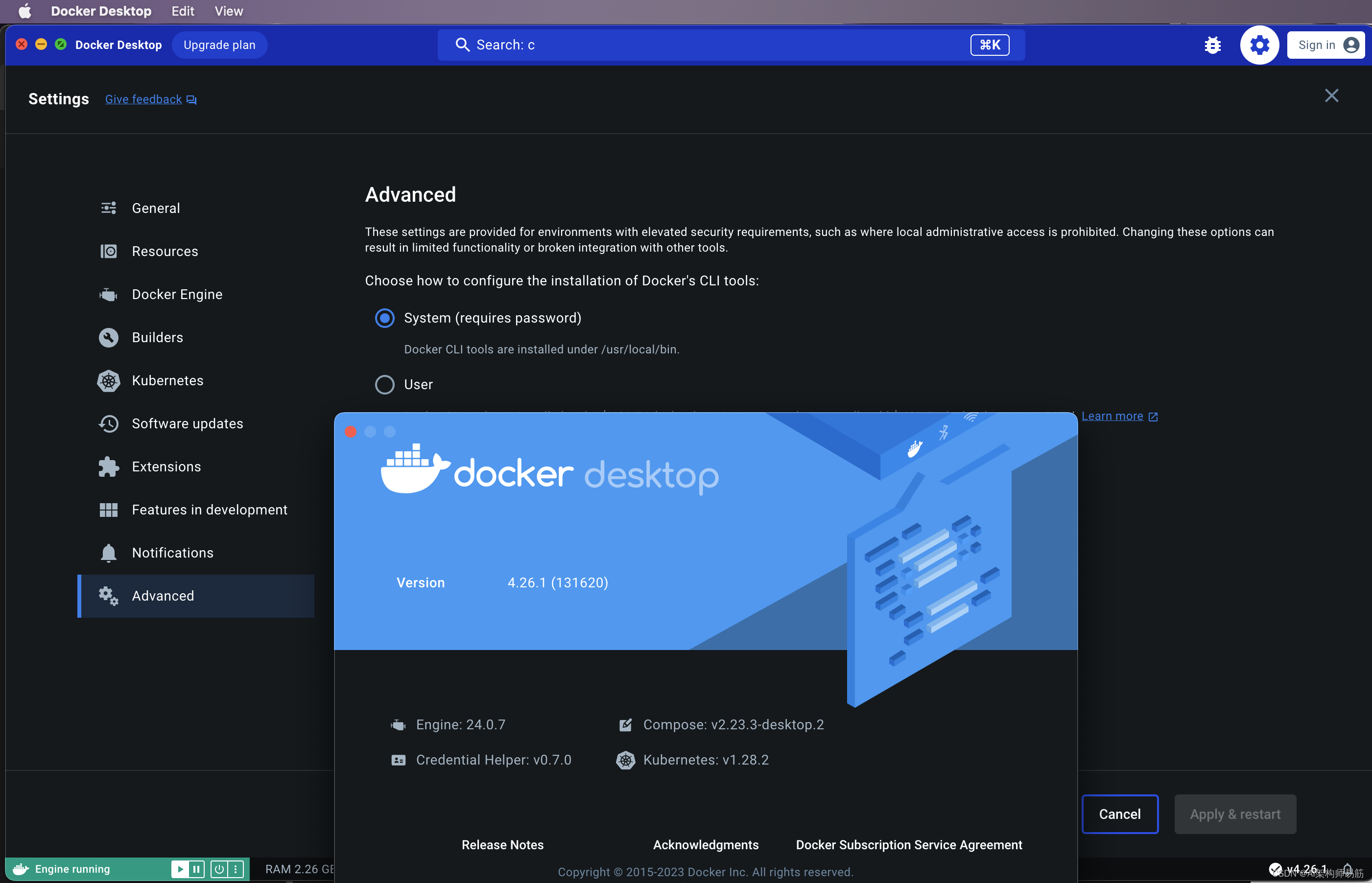
发现Docker Desktop version 4.26.1 需要设置 > Advanced > CLI tools 选择 System Docker CLI tools are install under /usr/local/bin. 才能在terminal中用docker命令
如果我们没有现有的Redis部署来连接,可以启动一个本地的Redis Stack服务器:
docker run -d -p 6379:6379 -p 8001:8001 redis/redis-stack:latest
- 1
REDIS_URL = "redis://localhost:6379/0"
- 1
3. 示例:字典输入Dict input,消息输出 message output
让我们创建一个简单的链,它以字典作为输入,并返回一个BaseMessage。
在这种情况下,输入中的“question”键代表我们的输入消息,“history”键是我们历史消息将被注入的地方。
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", "You're an assistant who's good at {ability}"),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="history"),
("human", "{question}"),
]
)
chain = prompt | ChatOpenAI()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
3.1 添加消息历史
要将消息历史添加到我们的原始链中,我们将其包装在RunnableWithMessageHistory类中。
至关重要的是,我们还需要定义一个方法,该方法接受一个session_id字符串,并基于它返回一个BaseChatMessageHistory。对于相同的输入,该方法应返回等效的输出。
在这种情况下,我们还需要指定input_messages_key(要视为最新输入消息的键)和history_messages_key(要将历史消息添加到的键)。
chain_with_history = RunnableWithMessageHistory(
chain,
lambda session_id: RedisChatMessageHistory(session_id, url=REDIS_URL),
input_messages_key="question",
history_messages_key="history",
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
3.2 调用配置config
每当我们使用消息历史记录调用我们的链时,我们需要包含一个包含session_id的配置。
config={"configurable": {"session_id": "<SESSION_ID>"}}
- 1
在相同的配置下,我们的链应该从相同的聊天消息记录中拉取。
chain_with_history.invoke(
{"ability": "math", "question": "What does cosine mean?"},
config={"configurable": {"session_id": "foobar"}},
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
输出
AIMessage(content=' Cosine is one of the basic trigonometric functions in mathematics. It is defined as the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse in a right triangle.\n\nSome key properties and facts about cosine:\n\n- It is denoted by cos(θ), where θ is the angle in a right triangle. \n\n- The cosine of an acute angle is always positive. For angles greater than 90 degrees, cosine can be negative.\n\n- Cosine is one of the three main trig functions along with sine and tangent.\n\n- The cosine of 0 degrees is 1. As the angle increases towards 90 degrees, the cosine value decreases towards 0.\n\n- The range of values for cosine is -1 to 1.\n\n- The cosine function maps angles in a circle to the x-coordinate on the unit circle.\n\n- Cosine is used to find adjacent side lengths in right triangles, and has many other applications in mathematics, physics, engineering and more.\n\n- Key cosine identities include: cos(A+B) = cosAcosB − sinAsinB and cos(2A) = cos^2(A) − sin^2(A)\n\nSo in summary, cosine is a fundamental trig')
- 1
这里的its 就表示history的cosine
chain_with_history.invoke(
{"ability": "math", "question": "What's its inverse"},
config={"configurable": {"session_id": "foobar"}},
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
输出
AIMessage(content=' The inverse of the cosine function is called the arccosine or inverse cosine, often denoted as cos-1(x) or arccos(x).\n\nThe key properties and facts about arccosine:\n\n- It is defined as the angle θ between 0 and π radians whose cosine is x. So arccos(x) = θ such that cos(θ) = x.\n\n- The range of arccosine is 0 to π radians (0 to 180 degrees).\n\n- The domain of arccosine is -1 to 1. \n\n- arccos(cos(θ)) = θ for values of θ from 0 to π radians.\n\n- arccos(x) is the angle in a right triangle whose adjacent side is x and hypotenuse is 1.\n\n- arccos(0) = 90 degrees. As x increases from 0 to 1, arccos(x) decreases from 90 to 0 degrees.\n\n- arccos(1) = 0 degrees. arccos(-1) = 180 degrees.\n\n- The graph of y = arccos(x) is part of the unit circle, restricted to x')
- 1
4. 完整代码
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate from langchain_community.chat_models import ChatOpenAI from langchain_core.runnables import ConfigurableField # We add in a string output parser here so the outputs between the two are the same type from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate # Now lets create a chain with the normal OpenAI model from langchain_community.llms import OpenAI from typing import Optional from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder from langchain_community.chat_message_histories import RedisChatMessageHistory from langchain_community.chat_models import ChatAnthropic from langchain_core.chat_history import BaseChatMessageHistory from langchain_core.runnables.history import RunnableWithMessageHistory from dotenv import load_dotenv # 导入从 .env 文件加载环境变量的函数 load_dotenv() # 调用函数实际加载环境变量 from langchain.globals import set_debug # 导入在 langchain 中设置调试模式的函数 set_debug(True) # 启用 langchain 的调试模式 prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages( [ ("system", "You're an assistant who's good at {ability}"), MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="history"), ("human", "{question}"), ] ) chain = prompt | ChatOpenAI() REDIS_URL = "redis://localhost:6379/0" chain_with_history = RunnableWithMessageHistory( chain, lambda session_id: RedisChatMessageHistory(session_id, url=REDIS_URL), input_messages_key="question", history_messages_key="history", ) # config={"configurable": {"session_id": "<SESSION_ID>"}} cosine_response = chain_with_history.invoke( {"ability": "math", "question": "What does cosine mean?"}, config={"configurable": {"session_id": "foobar"}}, ) print('cosine_response >> ', cosine_response) inverse_response = chain_with_history.invoke( {"ability": "math", "question": "What's its inverse"}, config={"configurable": {"session_id": "foobar"}}, ) print('inverse_response >> ', inverse_response)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
debug 输出如下
"id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What does cosine mean?", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "human", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "I apologize for any confusion. In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that relates the angle of a right triangle to the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. It is defined as the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. In more general terms, cosine is a mathematical function that maps angles to real numbers. The cosine function has many applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and signal processing. It is commonly used to analyze periodic phenomena and to solve problems involving angles and distances.", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "ai", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What's its inverse", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "human", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "The inverse of the cosine function is called the arccosine function (abbreviated as arccos or acos). It is denoted as acos(x) or arccos(x), where x is a real number between -1 and 1. The arccosine function returns the angle whose cosine is equal to the given value. In other words, if y = arccos(x), then cos(y) = x. The output of the arccosine function is always an angle in the range of 0 to 180 degrees (or 0 to π radians), inclusive. It is important to note that the arccosine function is the inverse of the cosine function only within this restricted range.", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "ai", "example": false } } ] } [chain/end] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory > 2:chain:insert_history > 3:chain:RunnableParallel<history>] [12ms] Exiting Chain run with output: [outputs] [chain/end] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory > 2:chain:insert_history] [27ms] Exiting Chain run with output: { "ability": "math", "question": "What does cosine mean?", "history": [ { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What does cosine mean?", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "human", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that represents the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle. It is defined for all real numbers and is commonly used in geometry, physics, and engineering to solve problems involving angles and distances. The cosine function oscillates between -1 and 1, with its maximum value of 1 occurring at 0 degrees (or 360 degrees) and the minimum value of -1 occurring at 180 degrees.", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "ai", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What does cosine mean?", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "human", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "I apologize for any confusion. In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that relates the angle of a right triangle to the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. It is defined as the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. In more general terms, cosine is a mathematical function that maps angles to real numbers. The cosine function has many applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and signal processing. It is commonly used to analyze periodic phenomena and to solve problems involving angles and distances.", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "ai", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What's its inverse", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "human", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "The inverse of the cosine function is called the arccosine function (abbreviated as arccos or acos). It is denoted as acos(x) or arccos(x), where x is a real number between -1 and 1. The arccosine function returns the angle whose cosine is equal to the given value. In other words, if y = arccos(x), then cos(y) = x. The output of the arccosine function is always an angle in the range of 0 to 180 degrees (or 0 to π radians), inclusive. It is important to note that the arccosine function is the inverse of the cosine function only within this restricted range.", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "ai", "example": false } } ] } [chain/start] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory > 5:chain:RunnableSequence] Entering Chain run with input: [inputs] [chain/start] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory > 5:chain:RunnableSequence > 6:prompt:ChatPromptTemplate] Entering Prompt run with input: [inputs] [chain/end] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory > 5:chain:RunnableSequence > 6:prompt:ChatPromptTemplate] [16ms] Exiting Prompt run with output: { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "prompts", "chat", "ChatPromptValue" ], "kwargs": { "messages": [ { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "SystemMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "You're an assistant who's good at math", "additional_kwargs": {} } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What does cosine mean?", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "human", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that represents the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle. It is defined for all real numbers and is commonly used in geometry, physics, and engineering to solve problems involving angles and distances. The cosine function oscillates between -1 and 1, with its maximum value of 1 occurring at 0 degrees (or 360 degrees) and the minimum value of -1 occurring at 180 degrees.", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "ai", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What does cosine mean?", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "human", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "I apologize for any confusion. In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that relates the angle of a right triangle to the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. It is defined as the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. In more general terms, cosine is a mathematical function that maps angles to real numbers. The cosine function has many applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and signal processing. It is commonly used to analyze periodic phenomena and to solve problems involving angles and distances.", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "ai", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What's its inverse", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "human", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "The inverse of the cosine function is called the arccosine function (abbreviated as arccos or acos). It is denoted as acos(x) or arccos(x), where x is a real number between -1 and 1. The arccosine function returns the angle whose cosine is equal to the given value. In other words, if y = arccos(x), then cos(y) = x. The output of the arccosine function is always an angle in the range of 0 to 180 degrees (or 0 to π radians), inclusive. It is important to note that the arccosine function is the inverse of the cosine function only within this restricted range.", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "ai", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What does cosine mean?", "additional_kwargs": {} } } ] } } [llm/start] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory > 5:chain:RunnableSequence > 7:llm:ChatOpenAI] Entering LLM run with input: { "prompts": [ "System: You're an assistant who's good at math\nHuman: What does cosine mean?\nAI: In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that represents the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle. It is defined for all real numbers and is commonly used in geometry, physics, and engineering to solve problems involving angles and distances. The cosine function oscillates between -1 and 1, with its maximum value of 1 occurring at 0 degrees (or 360 degrees) and the minimum value of -1 occurring at 180 degrees.\nHuman: What does cosine mean?\nAI: I apologize for any confusion. In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that relates the angle of a right triangle to the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. It is defined as the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. In more general terms, cosine is a mathematical function that maps angles to real numbers. The cosine function has many applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and signal processing. It is commonly used to analyze periodic phenomena and to solve problems involving angles and distances.\nHuman: What's its inverse\nAI: The inverse of the cosine function is called the arccosine function (abbreviated as arccos or acos). It is denoted as acos(x) or arccos(x), where x is a real number between -1 and 1. The arccosine function returns the angle whose cosine is equal to the given value. In other words, if y = arccos(x), then cos(y) = x. The output of the arccosine function is always an angle in the range of 0 to 180 degrees (or 0 to π radians), inclusive. It is important to note that the arccosine function is the inverse of the cosine function only within this restricted range.\nHuman: What does cosine mean?" ] } [llm/end] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory > 5:chain:RunnableSequence > 7:llm:ChatOpenAI] [8.96s] Exiting LLM run with output: { "generations": [ [ { "text": "I apologize for the confusion earlier. In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that relates the angle of a right triangle to the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. It is defined as the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. In simpler terms, cosine represents the horizontal component of a unit vector in a given direction. The cosine function has values that range between -1 and 1, where -1 represents a negative direction, 0 represents perpendicularity, and 1 represents a positive direction. Cosine is widely used in various fields of science, engineering, and mathematics to analyze and solve problems involving angles, distances, and periodic phenomena.", "generation_info": { "finish_reason": "stop", "logprobs": null }, "type": "ChatGeneration", "message": { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "I apologize for the confusion earlier. In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that relates the angle of a right triangle to the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. It is defined as the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. In simpler terms, cosine represents the horizontal component of a unit vector in a given direction. The cosine function has values that range between -1 and 1, where -1 represents a negative direction, 0 represents perpendicularity, and 1 represents a positive direction. Cosine is widely used in various fields of science, engineering, and mathematics to analyze and solve problems involving angles, distances, and periodic phenomena.", "additional_kwargs": {} } } } ] ], "llm_output": { "token_usage": { "completion_tokens": 155, "prompt_tokens": 433, "total_tokens": 588 }, "model_name": "gpt-3.5-turbo", "system_fingerprint": null }, "run": null } [chain/end] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory > 5:chain:RunnableSequence] [9.02s] Exiting Chain run with output: [outputs] [chain/end] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory] [9.07s] Exiting Chain run with output: [outputs] cosine_response >> content='I apologize for the confusion earlier. In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that relates the angle of a right triangle to the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. It is defined as the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. In simpler terms, cosine represents the horizontal component of a unit vector in a given direction. The cosine function has values that range between -1 and 1, where -1 represents a negative direction, 0 represents perpendicularity, and 1 represents a positive direction. Cosine is widely used in various fields of science, engineering, and mathematics to analyze and solve problems involving angles, distances, and periodic phenomena.' [chain/start] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory] Entering Chain run with input: { "ability": "math", "question": "What's its inverse" } [chain/start] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory > 2:chain:insert_history] Entering Chain run with input: { "ability": "math", "question": "What's its inverse" } [chain/start] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory > 2:chain:insert_history > 3:chain:RunnableParallel<history>] Entering Chain run with input: { "ability": "math", "question": "What's its inverse" } [chain/start] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory > 2:chain:insert_history > 3:chain:RunnableParallel<history> > 4:chain:load_history] Entering Chain run with input: { "ability": "math", "question": "What's its inverse" } [chain/end] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory > 2:chain:insert_history > 3:chain:RunnableParallel<history> > 4:chain:load_history] [3ms] Exiting Chain run with output: { "output": [ { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What does cosine mean?", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "human", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that represents the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle. It is defined for all real numbers and is commonly used in geometry, physics, and engineering to solve problems involving angles and distances. The cosine function oscillates between -1 and 1, with its maximum value of 1 occurring at 0 degrees (or 360 degrees) and the minimum value of -1 occurring at 180 degrees.", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "ai", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What does cosine mean?", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "human", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "I apologize for any confusion. In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that relates the angle of a right triangle to the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. It is defined as the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. In more general terms, cosine is a mathematical function that maps angles to real numbers. The cosine function has many applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and signal processing. It is commonly used to analyze periodic phenomena and to solve problems involving angles and distances.", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "ai", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What's its inverse", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "human", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "The inverse of the cosine function is called the arccosine function (abbreviated as arccos or acos). It is denoted as acos(x) or arccos(x), where x is a real number between -1 and 1. The arccosine function returns the angle whose cosine is equal to the given value. In other words, if y = arccos(x), then cos(y) = x. The output of the arccosine function is always an angle in the range of 0 to 180 degrees (or 0 to π radians), inclusive. It is important to note that the arccosine function is the inverse of the cosine function only within this restricted range.", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "ai", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What does cosine mean?", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "human", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "I apologize for the confusion earlier. In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that relates the angle of a right triangle to the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. It is defined as the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. In simpler terms, cosine represents the horizontal component of a unit vector in a given direction. The cosine function has values that range between -1 and 1, where -1 represents a negative direction, 0 represents perpendicularity, and 1 represents a positive direction. Cosine is widely used in various fields of science, engineering, and mathematics to analyze and solve problems involving angles, distances, and periodic phenomena.", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "ai", "example": false } } ] } [chain/end] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory > 2:chain:insert_history > 3:chain:RunnableParallel<history>] [9ms] Exiting Chain run with output: [outputs] [chain/end] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory > 2:chain:insert_history] [12ms] Exiting Chain run with output: { "ability": "math", "question": "What's its inverse", "history": [ { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What does cosine mean?", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "human", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that represents the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle. It is defined for all real numbers and is commonly used in geometry, physics, and engineering to solve problems involving angles and distances. The cosine function oscillates between -1 and 1, with its maximum value of 1 occurring at 0 degrees (or 360 degrees) and the minimum value of -1 occurring at 180 degrees.", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "ai", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What does cosine mean?", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "human", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "I apologize for any confusion. In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that relates the angle of a right triangle to the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. It is defined as the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. In more general terms, cosine is a mathematical function that maps angles to real numbers. The cosine function has many applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and signal processing. It is commonly used to analyze periodic phenomena and to solve problems involving angles and distances.", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "ai", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What's its inverse", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "human", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "The inverse of the cosine function is called the arccosine function (abbreviated as arccos or acos). It is denoted as acos(x) or arccos(x), where x is a real number between -1 and 1. The arccosine function returns the angle whose cosine is equal to the given value. In other words, if y = arccos(x), then cos(y) = x. The output of the arccosine function is always an angle in the range of 0 to 180 degrees (or 0 to π radians), inclusive. It is important to note that the arccosine function is the inverse of the cosine function only within this restricted range.", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "ai", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What does cosine mean?", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "human", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "I apologize for the confusion earlier. In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that relates the angle of a right triangle to the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. It is defined as the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. In simpler terms, cosine represents the horizontal component of a unit vector in a given direction. The cosine function has values that range between -1 and 1, where -1 represents a negative direction, 0 represents perpendicularity, and 1 represents a positive direction. Cosine is widely used in various fields of science, engineering, and mathematics to analyze and solve problems involving angles, distances, and periodic phenomena.", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "ai", "example": false } } ] } [chain/start] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory > 5:chain:RunnableSequence] Entering Chain run with input: [inputs] [chain/start] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory > 5:chain:RunnableSequence > 6:prompt:ChatPromptTemplate] Entering Prompt run with input: [inputs] [chain/end] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory > 5:chain:RunnableSequence > 6:prompt:ChatPromptTemplate] [3ms] Exiting Prompt run with output: { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "prompts", "chat", "ChatPromptValue" ], "kwargs": { "messages": [ { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "SystemMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "You're an assistant who's good at math", "additional_kwargs": {} } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What does cosine mean?", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "human", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that represents the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle. It is defined for all real numbers and is commonly used in geometry, physics, and engineering to solve problems involving angles and distances. The cosine function oscillates between -1 and 1, with its maximum value of 1 occurring at 0 degrees (or 360 degrees) and the minimum value of -1 occurring at 180 degrees.", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "ai", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What does cosine mean?", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "human", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "I apologize for any confusion. In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that relates the angle of a right triangle to the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. It is defined as the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. In more general terms, cosine is a mathematical function that maps angles to real numbers. The cosine function has many applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and signal processing. It is commonly used to analyze periodic phenomena and to solve problems involving angles and distances.", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "ai", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What's its inverse", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "human", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "The inverse of the cosine function is called the arccosine function (abbreviated as arccos or acos). It is denoted as acos(x) or arccos(x), where x is a real number between -1 and 1. The arccosine function returns the angle whose cosine is equal to the given value. In other words, if y = arccos(x), then cos(y) = x. The output of the arccosine function is always an angle in the range of 0 to 180 degrees (or 0 to π radians), inclusive. It is important to note that the arccosine function is the inverse of the cosine function only within this restricted range.", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "ai", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What does cosine mean?", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "human", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "I apologize for the confusion earlier. In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that relates the angle of a right triangle to the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. It is defined as the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. In simpler terms, cosine represents the horizontal component of a unit vector in a given direction. The cosine function has values that range between -1 and 1, where -1 represents a negative direction, 0 represents perpendicularity, and 1 represents a positive direction. Cosine is widely used in various fields of science, engineering, and mathematics to analyze and solve problems involving angles, distances, and periodic phenomena.", "additional_kwargs": {}, "type": "ai", "example": false } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "What's its inverse", "additional_kwargs": {} } } ] } } [llm/start] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory > 5:chain:RunnableSequence > 7:llm:ChatOpenAI] Entering LLM run with input: { "prompts": [ "System: You're an assistant who's good at math\nHuman: What does cosine mean?\nAI: In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that represents the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle. It is defined for all real numbers and is commonly used in geometry, physics, and engineering to solve problems involving angles and distances. The cosine function oscillates between -1 and 1, with its maximum value of 1 occurring at 0 degrees (or 360 degrees) and the minimum value of -1 occurring at 180 degrees.\nHuman: What does cosine mean?\nAI: I apologize for any confusion. In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that relates the angle of a right triangle to the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. It is defined as the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. In more general terms, cosine is a mathematical function that maps angles to real numbers. The cosine function has many applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and signal processing. It is commonly used to analyze periodic phenomena and to solve problems involving angles and distances.\nHuman: What's its inverse\nAI: The inverse of the cosine function is called the arccosine function (abbreviated as arccos or acos). It is denoted as acos(x) or arccos(x), where x is a real number between -1 and 1. The arccosine function returns the angle whose cosine is equal to the given value. In other words, if y = arccos(x), then cos(y) = x. The output of the arccosine function is always an angle in the range of 0 to 180 degrees (or 0 to π radians), inclusive. It is important to note that the arccosine function is the inverse of the cosine function only within this restricted range.\nHuman: What does cosine mean?\nAI: I apologize for the confusion earlier. In mathematics, cosine (abbreviated as cos) is a trigonometric function that relates the angle of a right triangle to the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. It is defined as the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. In simpler terms, cosine represents the horizontal component of a unit vector in a given direction. The cosine function has values that range between -1 and 1, where -1 represents a negative direction, 0 represents perpendicularity, and 1 represents a positive direction. Cosine is widely used in various fields of science, engineering, and mathematics to analyze and solve problems involving angles, distances, and periodic phenomena.\nHuman: What's its inverse" ] } [llm/end] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory > 5:chain:RunnableSequence > 7:llm:ChatOpenAI] [4.45s] Exiting LLM run with output: { "generations": [ [ { "text": "The inverse of the cosine function is called the arccosine function (abbreviated as arccos or acos). It is denoted as acos(x) or arccos(x), where x is a real number between -1 and 1. The arccosine function returns the angle whose cosine is equal to the given value. In other words, if y = arccos(x), then cos(y) = x. The output of the arccosine function is always an angle in the range of 0 to 180 degrees (or 0 to π radians), inclusive. It is important to note that the arccosine function is the inverse of the cosine function only within this restricted range.", "generation_info": { "finish_reason": "stop", "logprobs": null }, "type": "ChatGeneration", "message": { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "messages", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "The inverse of the cosine function is called the arccosine function (abbreviated as arccos or acos). It is denoted as acos(x) or arccos(x), where x is a real number between -1 and 1. The arccosine function returns the angle whose cosine is equal to the given value. In other words, if y = arccos(x), then cos(y) = x. The output of the arccosine function is always an angle in the range of 0 to 180 degrees (or 0 to π radians), inclusive. It is important to note that the arccosine function is the inverse of the cosine function only within this restricted range.", "additional_kwargs": {} } } } ] ], "llm_output": { "token_usage": { "completion_tokens": 146, "prompt_tokens": 600, "total_tokens": 746 }, "model_name": "gpt-3.5-turbo", "system_fingerprint": null }, "run": null } [chain/end] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory > 5:chain:RunnableSequence] [4.46s] Exiting Chain run with output: [outputs] [chain/end] [1:chain:RunnableWithMessageHistory] [4.49s] Exiting Chain run with output: [outputs] inverse_response >> content='The inverse of the cosine function is called the arccosine function (abbreviated as arccos or acos). It is denoted as acos(x) or arccos(x), where x is a real number between -1 and 1. The arccosine function returns the angle whose cosine is equal to the given value. In other words, if y = arccos(x), then cos(y) = x. The output of the arccosine function is always an angle in the range of 0 to 180 degrees (or 0 to π radians), inclusive. It is important to note that the arccosine function is the inverse of the cosine function only within this restricted range.'
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
- 294
- 295
- 296
- 297
- 298
- 299
- 300
- 301
- 302
- 303
- 304
- 305
- 306
- 307
- 308
- 309
- 310
- 311
- 312
- 313
- 314
- 315
- 316
- 317
- 318
- 319
- 320
- 321
- 322
- 323
- 324
- 325
- 326
- 327
- 328
- 329
- 330
- 331
- 332
- 333
- 334
- 335
- 336
- 337
- 338
- 339
- 340
- 341
- 342
- 343
- 344
- 345
- 346
- 347
- 348
- 349
- 350
- 351
- 352
- 353
- 354
- 355
- 356
- 357
- 358
- 359
- 360
- 361
- 362
- 363
- 364
- 365
- 366
- 367
- 368
- 369
- 370
- 371
- 372
- 373
- 374
- 375
- 376
- 377
- 378
- 379
- 380
- 381
- 382
- 383
- 384
- 385
- 386
- 387
- 388
- 389
- 390
- 391
- 392
- 393
- 394
- 395
- 396
- 397
- 398
- 399
- 400
- 401
- 402
- 403
- 404
- 405
- 406
- 407
- 408
- 409
- 410
- 411
- 412
- 413
- 414
- 415
- 416
- 417
- 418
- 419
- 420
- 421
- 422
- 423
- 424
- 425
- 426
- 427
- 428
- 429
- 430
- 431
- 432
- 433
- 434
- 435
- 436
- 437
- 438
- 439
- 440
- 441
- 442
- 443
- 444
- 445
- 446
- 447
- 448
- 449
- 450
- 451
- 452
- 453
- 454
- 455
- 456
- 457
- 458
- 459
- 460
- 461
- 462
- 463
- 464
- 465
- 466
- 467
- 468
- 469
- 470
- 471
- 472
- 473
- 474
- 475
- 476
- 477
- 478
- 479
- 480
- 481
- 482
- 483
- 484
- 485
- 486
- 487
- 488
- 489
- 490
- 491
- 492
- 493
- 494
- 495
- 496
- 497
- 498
- 499
- 500
- 501
- 502
- 503
- 504
- 505
- 506
- 507
- 508
- 509
- 510
- 511
- 512
- 513
- 514
- 515
- 516
- 517
- 518
- 519
- 520
- 521
- 522
- 523
- 524
- 525
- 526
- 527
- 528
- 529
- 530
- 531
- 532
- 533
- 534
- 535
- 536
- 537
- 538
- 539
- 540
- 541
- 542
- 543
- 544
- 545
- 546
- 547
- 548
- 549
- 550
- 551
- 552
- 553
- 554
- 555
- 556
- 557
- 558
- 559
- 560
- 561
- 562
- 563
- 564
- 565
- 566
- 567
- 568
- 569
- 570
- 571
- 572
- 573
- 574
- 575
- 576
- 577
- 578
- 579
- 580
- 581
- 582
- 583
- 584
- 585
- 586
- 587
- 588
- 589
- 590
- 591
- 592
- 593
- 594
- 595
- 596
- 597
- 598
- 599
- 600
- 601
- 602
- 603
- 604
- 605
- 606
- 607
- 608
- 609
- 610
- 611
- 612
- 613
- 614
- 615
- 616
- 617
- 618
- 619
- 620
- 621
- 622
- 623
- 624
- 625
- 626
- 627
- 628
- 629
- 630
- 631
- 632
- 633
- 634
- 635
- 636
- 637
- 638
- 639
- 640
- 641
- 642
- 643
- 644
- 645
- 646
- 647
- 648
- 649
- 650
- 651
- 652
- 653
- 654
- 655
- 656
- 657
- 658
- 659
- 660
- 661
- 662
- 663
- 664
- 665
- 666
- 667
- 668
- 669
- 670
- 671
- 672
- 673
- 674
- 675
- 676
- 677
- 678
- 679
- 680
- 681
- 682
- 683
- 684
- 685
- 686
- 687
- 688
- 689
- 690
- 691
- 692
- 693
- 694
- 695
- 696
- 697
- 698
- 699
- 700
- 701
- 702
- 703
- 704
- 705
- 706
- 707
- 708
- 709
- 710
- 711
- 712
- 713
- 714
- 715
- 716
- 717
- 718
- 719
- 720
- 721
- 722
- 723
- 724
- 725
- 726
- 727
- 728
- 729
- 730
- 731
- 732
- 733
- 734
- 735
- 736
- 737
- 738
- 739
- 740
- 741
- 742
- 743
- 744
- 745
- 746
- 747
- 748
- 749
- 750
- 751
- 752
- 753
- 754
- 755
- 756
- 757
- 758
- 759
- 760
- 761
- 762
- 763
- 764
- 765
- 766
- 767
- 768
- 769
- 770
- 771
- 772
- 773
- 774
- 775
- 776
- 777
- 778
- 779
- 780
- 781
- 782
- 783
- 784
- 785
- 786
- 787
- 788
- 789
- 790
- 791
- 792
- 793
- 794
- 795
- 796
- 797
- 798
- 799
- 800
- 801
- 802
- 803
- 804
- 805
- 806
- 807
- 808
- 809
- 810
- 811
- 812
- 813
- 814
- 815
- 816
- 817
- 818
- 819
- 820
- 821
- 822
- 823
- 824
- 825
- 826
- 827
- 828
- 829
- 830
- 831
- 832
- 833
- 834
- 835
- 836
- 837
- 838
- 839
- 840
- 841
- 842
- 843
- 844
- 845
- 846
- 847
- 848
- 849
- 850
- 851
- 852
- 853
- 854
- 855
- 856
- 857
- 858
- 859
- 860
- 861
- 862
- 863
- 864
- 865
- 866
- 867
- 868
- 869
- 870
- 871
- 872
- 873
- 874
- 875
- 876
代码
https://github.com/zgpeace/pets-name-langchain/tree/develop
参考
https://python.langchain.com/docs/expression_language/how_to/message_history



