- 1Flutter正在被悄悄放弃?浅析Flutter的未来_flutter框架为什么凉了
- 2CPU也能运行ChatGLM_chatglm cpu
- 3Ubuntu服务器端口放行没有用_ubuntu端口开放后不通
- 4Postman和Jmeter的区别
- 5云起实验室:云上开发Serverless SSR应用
- 6java home should_NB: JAVA_HOME should point to a JDK not a JRE
- 7一天一个 Linux 命令(40):vmstat 命令_vmstat us sy id wa st
- 8NGINX动态DNS解析原理及源码分析_nginx配置dns
- 9【Linux】Vmware虚拟机安装教程_linux安装vmware虚拟机
- 10Zabbix故障集——图形界面报错Unsupported charset or collation for tables_unsupported charset or collation for tables: ackno
BOM 和 DOM_bom dom
赞
踩
BOM 和 DOM
一、介绍
到目前为止,我们已经学过了JavaScript的一些简单的语法。但是这些简单的语法,并没有和浏览器有任何交互。
也就是我们还不能制作一些我们经常看到的网页的一些交互,我们需要继续学习BOM和DOM相关知识。
JavaScript分为 ECMAScript,DOM,BOM。
BOM(Browser Object Model)是指浏览器对象模型 ,作用是通过js代码操作浏览器
DOM ( Document Object Model)是指文档对象模型,作用是通过js代码操作标签。通过它访问HTML文档的所有元素。
Window对象是客户端JavaScript最高层对象之一,由于window对象是其它大部分对象的共同祖先,在调用window对象的方法和属性时,可以省略window对象的引用。例如:window.document.write()可以简写成:document.write()。
BOM结构图
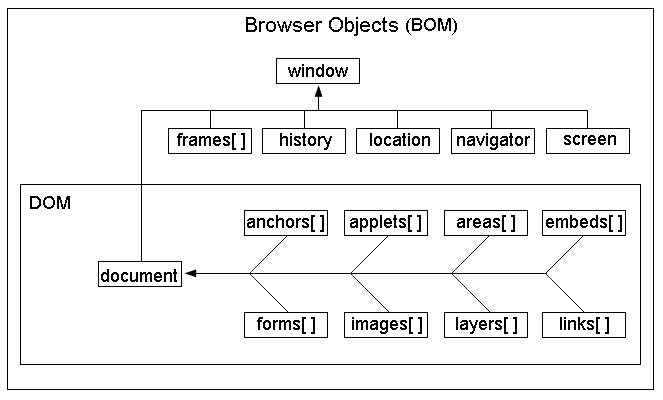
从上图可以看出来:
- DOM对象也是BOM的一部分
- window对象是BOM的顶层(核心)对象
window对象是BOM的顶层(核心)对象
#1、在调用window对象的方法和属性时,可以省略window,例如:window.document.location可以简写为document.location
#2、全局变量也是windows对象的属性,全局的函数时window对象的方法
- 1
- 2
- 3
二、BOM
1. window对象
window对象指代的就是浏览器窗口
console.log(window.innerHeight); // 927 (浏览器窗口内的高度) console.log(window.innerWidth); // 1918 (浏览器窗口内的宽度) // window.open('https://www.baidu.com', '', 'height=400px, width=400px, top=400px, left=400px'); // 新建窗口打开页面 第二个参数写空即可 第三个参数写新建的窗口的大小和位置 // window.close(); // 关闭当前页面 // window.opener(); // 扩展父子页面通信(了解) // 总结 /* window.innerHeight(); 浏览器内部高度 window.innerWidth(); 浏览器内部宽度 window.open(url, '', '宽高+位置'); window.close(); 关闭当前页面 window.opener(); */
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
2. window的子对象
提示: 如果是window的子对象 那么window可以省略不写, 下面写是为了更加见名知意.
2.1 navigator对象
console.log(window.navigator.appName); // Netscape (浏览器名称) console.log(window.navigator.appVersion); // 5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/75.0.3770.100 Safari/537.36 (返回浏览器版本) console.log(window.navigator.userAgent); // Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/75.0.3770.100 Safari/537.36 (掌握: 解析出用户信息) // 扩展:仿爬措施 /* 1.最简单最常用的一个就是校验当前请求的发起者是否是一个浏览器 userAgent user-agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_14_6) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/81.0.4044.138 Safari/537.36 如何破解该措施 在你的代码中加上上面的user-agent配置即可 */ console.log(window.navigator.platform); // Win32 (平台) // 总结 /* window.navigator.appName; 浏览器名称 window.navigator.appVersion; 返回浏览器版本 window.navigator.userAgent; 解析出用户信息 window.navigator.platform; 平台 */
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
2.2 history对象
// 对应的就是你浏览器左上方的两个的箭头
window.history.back(); // 回退到上一页
window.history.forward(); // 前进到下一页
- 1
- 2
- 3
2.3 location对象(掌握)
// 一. location对象的浏览器的位置操作 // 1. href属性: 获取url地址栏的,整个url(统一资源定位器) console.log(location.href); // 2. host属性: 获取url地址栏的,IP和端口号 console.log(location.host); // 3. hostname属性: 获取url地址栏的,IP console.log(location.hostname); // 4. port属性: 获取url地址栏的,端口号 console.log(location.port); // 5. protocol属性: 获取url地址栏的,协议名称 console.log(location.protocol); // 6. search属性: 获取url地址栏的,?后面查询的内容 console.log(location.search); // 7. pathname属性: 获取url地址栏的,html文件路径地址 console.log(location.pathname); // 二. location对象的浏览器的位置操作 // 1. location.href = 'url', 当前页面跳转新的网址,保留历史记录 location.href = 'https://www.baidu.com'; // 2. location.replace('url'), 当前页面跳转新的网址,不保留历史记录 location.replace('https://www.baidu.com'); // 3. location.reload(), 重载当前网页(用的少) location.reload();
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
2.4 弹出框
alert('警告框');
console.log(confirm('确认框')); // 返回布尔值
console.log(prompt('提示框')); // 返回输入值
- 1
- 2
- 3
2.5 定时器
function func1() { alert('111'); } let t1 = setTimeout(func1, 3000); // 毫秒为单位 3秒之后自动执行func1函数 // clearTimeout(t1); // 取消定时任务 如果你想要清除定时任务 需要提前前用变量(t1)指代定时任务 // cleatTimeout(setTimeout(func1, 3000)); // 简写 function func2() { alert('222'); } function show() { let t2 = setInterval(func2, 3000); function inner() { clearInterval(t2); } setTimeout(inner, 9000); // 9秒中之后触发inner清除定时器t2 } show(); // 总结: /* 一次性定时器: let t = setTimeout(func, 毫秒); clearTimeout(t); 多次性定时器: function show() { let t = setInterval(func, 毫秒); function inner() { clearInterval(t); } setTimeout(inner, 毫秒); } */
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
3.小结
Browser Object Model
window对象 innerHeight; 浏览器内高 innerWidth; 浏览器内宽 open(url, '', '宽高+位置'); close(); window子对象: navigator navigator.appName; 浏览器名 navigator.appVersion; 浏览器版本 navigator.userAgent; 解析用户信息 navigator.platform; 平台 history: history.back(); 回退 history.forward(); 前进 location: location.href 获取url location.href=url 跳转url location.reload 重载 弹出框: 警告框: alert(value); 确认框: confirm(value); 返回布尔 提示框: prompt(value); 返回输入内容 定时器: 一次性: let t = setTimeout(func, 3000); clearTimeout(t); 多次性: function show() { let t = setInterval(func, 3000); function inner() { clearInterval(t); } setTimeout(inner, 9000); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
4.练习
练习:上一页下一页
================page11.html <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <p>第一个页</p> <a href="page22.html">点我进入下一页</a> </body> </html> ================page22.html <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <p>第二个页</p> <a href="page33.html">点我进入下一页</a> </body> </html> ================page33.html <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script> function back() { window.history.back() } </script> </head> <body> <p>第三个页</p> <input type="button" value="点我进入上一页" onclick="back()"> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
location.href练习2:3s后,自动跳转页面
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div>这天下,本就是大争之世,孤的儿子,不仅要争,而且要争的光芒万丈</div> <script> setTimeout(function () { location.href = 'https://www.cnblogs.com/linhaifeng'; }, 3000) </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
location.href练习3:3s后让网页整个刷新
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>这天下,本就是大争之世,孤的儿子,不仅要争,而且要争的光芒万丈</div>
<script>
setTimeout(function () {
location.reload();
}, 3000)
</script>
</body>
</html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
三、DOM
DOM(Document Object Model)是一套对文档的内容进行抽象和概念化的方法。
当网页被加载时,浏览器会创建页面的文档对象模型(Document Object Model)。DOM标准规定HTML文档中的每个成员都是一个节点(node)
HTML DOM 模型被构造为对象的树,HTML DOM树如下图:
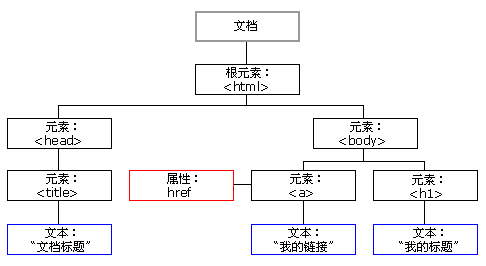
""" DOM树的概念 所有的标签都可以称之为是节点 JavaScript 可以通过DOM创建动态的 HTML: JavaScript 能够改变页面中的所有 HTML 元素 JavaScript 能够改变页面中的所有 HTML 属性 JavaScript 能够改变页面中的所有 CSS 样式 JavaScript 能够对页面中的所有事件做出反应 DOM操作操作的是标签 而一个html页面上的标签有很多 1.先学如何查找标签 2.再学DOM操作标签 DOM操作需要用关键字document起手 """
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
1. 查找标签之直接查找
三种查找标签方法: id查找, 类查找, 标签查找
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div>div上面的div</div> <div>div上面的div</div> <div id="d1">div <div>div>div</div> <p>div>p <span class="c1">div>p>span <span>div>p>span>span</span> </span> <span class="c1">div>p>span+span</span> </p> <p>div>p</p> </div> <div>div下面的div</div> <div>div下面的div</div> <script> // 三种查找标签方法: id查找, 类查找, 标签查找 /*直接查找*/ let divEle = document.getElementById('d1'); console.log(divEle); // 返回#d1自己+所有后代元素 /* <div id="d1">div <div>div>div</div> <p>div>p <span class="c1">div>p>span</span> </p> <p>div>p</p> </div> */ let spanEle = document.getElementsByClassName('c1'); console.log(spanEle); // 返回所有的.c1(数组) /* HTMLCollection [span.c1] 0: span.c1 length: 1 __proto__: HTMLCollection */ console.log(spanEle[0]); /* <span class="c1">div>p>span <span>div>p>span>span</span> </span> */ let pEle = document.getElementsByTagName('p'); console.log(pEle); // 返回所有的p(数组) /* HTMLCollection(2) [p, p] 0: p 1: p length: 2 __proto__: HTMLCollection */ console.log(pEle[0]); /* <p>div>p <span class="c1">div>p>span <span>div>p>span>span</span> </span> <span class="c1">div>p>span+span</span> </p> */ </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
总结:
id查找 document.getElementById();
返回对象. 可以拿到自己+后代所有
类查找 document.getElementsByClassName();
返回数组对象. 通过索引取值可以拿到自己+后代所有
元素查找 document.getElementsByTagName();
返回数组对象. 通过索引取值可以拿到自己+后代所有
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
2.间接查找
| 语法 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| childNodes | 获取所有的子节点,除了元素还有文本等 |
| children | 获取所有元素子节点,不包含文本 |
| parentNode | 获取父节点 |
| previousSibling | 获取上一个兄弟节点,包含文本 |
| previousElementSibling | 获取上一个兄弟元素节点,不包含文本 |
| nextSibling | 获取下一个兄弟节点,包含文本 |
| nextElementSibling | 获取下一个兄弟元素节点,不包含文本 |
| firstChild | 获取第一个子节点,包含文本 |
| firstElementChild | 获取第一个子节点,不包含文本 |
| lastChild | 获取最后一个子节点,包含文本 |
| lastElementChild | 获取父元素最后一个元素节点。不包含文本 |
代码示例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div>div上面的div</div> <div>div上面的div</div> <div id="d1">div <div>div>div</div> <p>div>p <span class="c1">div>p>span <span>div>p>span>span</span> </span> <span class="c1">div>p>span+span</span> </p> <p>div>p</p> </div> <div>div下面的div</div> <div>div下面的div</div> <script> /*间接查找*/ let divEle = document.getElementById('d1'); console.log(divEle.parentElement); // 拿父节点 console.log(divEle.parentElement.parentElement); // 拿父节点的父节点 console.log(divEle.parentElement.parentElement.parentElement); // 拿父节点的拿父节点的拿父节点(没有返回null) console.log(divEle.children); // 获取所有的子标签(返回数组对象) console.log(divEle.children[0]); // 通过索引取值第一个子标签 console.log(divEle.firstElementChild); // 与上面等同 console.log(divEle.children[divEle.children.length-1]); // 通过索引获取最后一个子标签 console.log(divEle.lastElementChild); // 与上面等同 console.log(divEle.nextElementSibling); // 同级别下面第一个 console.log(divEle.previousElementSibling); // 同级别上面第一个 // 总结 /* 注意: 下面所有拿到的标签如果没有后代标签则就是单个. 如果有那么后代标签对象也会被包含, 只是以当前拿到的标签作为起始. 拿父标签: 没有父标签返回null nodeEle.parentElement 拿所有子标签: nodeEle.children 返回所有子标签, 以数组的形式呈现. 可以通过索引取值获取其内部的子标签. 拿子标签第一个: nodeEle.firstElementChild nodeEle.children[0] 拿子标签最后一个: nodeEle.lastElementChild nodeEle.children[nodeEle.children.length-1] 拿同级别上一个: nodeEle.nextElementSibling 拿同级别下一个: nodeEle.previousElementSibling */ </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
3.节点操作
涵盖了: 创建标签, 为创建的标签添加属性, 为创建的标签添加文本, 对创建的标签进行追加, 对创建的标签进行插入.
以及补充的获取标签属性, 删除标签属性. 删除标签, 替换标签
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div id="d1"> <p id="d2">div>p</p> <span>div>span</span> </div> <script> /* 通过DOM操作动态的创建img标签 并且给标签加属性 最后将标签添加到文本中 */ /*创建标签*/ let imgEle = document.createElement('img'); // 创建标签 imgEle.src = 'https://img2020.cnblogs.com/blog/1402974/202005/1402974-20200518221931333-1731690860.png'; // 给标签设置默认的属性 imgEle.useranme = 'jsaon'; // 自定义的属性没办法点的方式直接设置 console.log(imgEle); /* <img src="https://img2020.cnblogs.com/blog/1402974/202005/1402974-20200518221931333-1731690860.png"> */ imgEle.setAttribute('username', 'jsaon'); // 既可以设置自定义的属性也可以设置默认的书写 console.log(imgEle); /* <img src="https://img2020.cnblogs.com/blog/1402974/202005/1402974-20200518221931333-1731690860.png" username="jsaon"> */ /*标签内部添加元素*/ let divEle = document.getElementById('d1'); divEle.appendChild(imgEle); // 尾部追加 console.log(divEle); /* <div id="d1"> <p id="d2">div>p</p> <span>div>span</span> <img src="https://img2020.cnblogs.com/blog/1402974/202005/1402974-20200518221931333-1731690860.png" username="jsaon"> </div> */ /* 创建a标签 设置属性 设置文本 添加到标签内部 添加到指定的标签的上面 */ let aEle = document.createElement('a'); // 创建a标签 aEle.href = 'https://www.baidu.com'; // 设置属性 aEle.innerText = '点我有你好看!'; // 给标签设置文本内容 // let divEle = document.getElementById('d1'); let pEle = divEle.firstElementChild; // let pEle = document.getElementById('d2'); divEle.insertBefore(aEle, pEle); // 添加标签内容指定位置添加 console.log(divEle); /* <div id="d1"> <a href="https://www.baidu.com">点我有你好看!</a><p id="d2">div>p</p> <span>div>span</span> <img src="https://img2020.cnblogs.com/blog/1402974/202005/1402974-20200518221931333-1731690860.png" username="jsaon"> </div> */ // innerText与innerHTML // let divEle = document.getElementById('d1'); console.log(divEle.innerText); // 获取标签内部所有的文本 /* 点我有你好看! div>p div>span */ console.log(divEle.innerHTML); // 内部文本和标签都拿到 /* 点我有你好看! div>p div>span <a href="https://www.baidu.com">点我有你好看!</a><p id="d2">div>p</p> <span>div>span</span> <img src="https://img2020.cnblogs.com/blog/1402974/202005/1402974-20200518221931333-1731690860.png" username="jsaon"> */ divEle.innerText = '哈哈哈'; console.log(divEle.innerText); // 哈哈哈 divEle.innerHTML = '嘻嘻嘻'; console.log(divEle.innerHTML); // 嘻嘻嘻 divEle.innerText = '<h1>哈哈哈</h1>'; // 不识别html标签 console.log(divEle.innerText); // <h1>哈哈哈</h1> divEle.innerHTML = '<h1>嘻嘻嘻</h1>'; // 识别html标签 console.log(divEle.innerText); // 嘻嘻嘻 // 额外补充 /* appendChild() removeChild() replaceChild() setAttribute() 设置属性 getAttribute() 获取属性 removeAttribute() 移除属性 */ </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
总结:
创建标签: let imgEle = document.createElement('img'); 设置属性: 只能设置内置属性: imgEle.src=''; 内置属性+自定义属性: imgEle.setAttribute('username', 'jason'); 追加标签: let divEle = document.getElementById('d1'); divEle.appendChild(imgEle); 插入标签: let divEle = document.getElementById('d1'); let pEle = divEle.firstElementChild(); let aEle = document.creatElement('a'); divEle.insertBefore(aEle, pEle) // 将aEle插入到divEle中的第一个子标签pEle之前.(第一个参数始是要插入的元素, 第二个参数是插入的位置. 还需要明确是在那个标签中插.) innerText 和 innerHTML 访问内容: 访问内容所有文本: divEle.innerText 访问内容所有文本+标签: divEle.innerHTML 设置内容: let aEle = document.createElement('a'); 只设置文本内容: aEle.innerText = '哈哈哈'; 文本内容+标签: aEle.innerHTML = '<h1>哈哈哈</h1>';
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
4.获取值操作
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <input type="text" id="d1" value="111"> <select name="" id="d2"> <option value="haha" selected>哈哈</option> <option value="heihei">嘿嘿</option> <option value="momo">摸摸</option> </select> <input type="file" id="d3" multiple> <script> /*获取用户数据标签内部的数据*/ var inputEle = document.getElementById('d1'); console.log(inputEle.value); // 111 var seEle = document.getElementById('d2'); console.log(seEle.value); // haha var fileEle = document.getElementById('d3'); console.log(fileEle.value); // C:\fakepath\2sCode.zip (只能获取到文件的本地路径, 无法获取到文件数据) console.log(fileEle.files); /* FileList {0: File, 1: File, length: 2} 0: File {name: "2sCode.zip", lastModified: 1588031367082, lastModifiedDate: Tue Apr 28 2020 07:49:27 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间), webkitRelativePath: "", size: 8192, …} 1: File {name: "6组发布内容.txt", lastModified: 1587516178144, lastModifiedDate: Wed Apr 22 2020 08:42:58 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间), webkitRelativePath: "", size: 2553, …} length: 2 __proto__: FileList */ console.log(fileEle.files[0]); // 获取文件数据 /* File {name: "2sCode.zip", lastModified: 1588031367082, lastModifiedDate: Tue Apr 28 2020 07:49:27 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间), webkitRelativePath: "", size: 8192, …} */ // 总结: /* 非文件获取值: var inputEle = document.getElementById('d1'); inputEle.value 针对文件: var fileEle = document.getElementById('d3'); 获取本地上传路径: fileEle.value 获取文件对象们: fileEle.files 获取文件对象: fileEle.files[0] 补充: 如果想重置某标签下的所有值使用inputEle.value=''; */ </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
5.class、css操作
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> #d1 { height: 400px; width: 400px; border-radius: 50%; } .bg_green { background-color: green; } .bg_red { background-color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="d1" class="c1 bg_green bg_red"></div> <p>呼呼哈哈哈哈哈哈</p> <script> let divEle = document.getElementById('d1'); console.log(divEle.classList); // 获取标签所有的类属性 /* DOMTokenList(3) ["c1", "bg_green", "bg_red", value: "c1 bg_green bg_red"] 0: "c1" 1: "bg_green" length: 2 value: "c1 bg_green" __proto__: DOMTokenList */ divEle.classList.remove('bg_red'); console.log(divEle.classList); // 移除某个类属性 /* DOMTokenList(2) ["c1", "bg_green", value: "c1 bg_green"] 0: "c1" 1: "bg_green" length: 2 value: "c1 bg_green" __proto__: DOMTokenList */ divEle.classList.add('bg_red'); console.log(divEle.classList); // 添加类属性 /* DOMTokenList(3) ["c1", "bg_green", "bg_red", value: "c1 bg_green bg_red"] 0: "c1" 1: "bg_green" length: 2 value: "c1 bg_green" __proto__: DOMTokenList */ console.log(divEle.classList.contains('c1')); // true console.log(divEle.classList.contains('c99')); // false console.log(divEle.classList.toggle('bg_red')); // false (有则删除无则添加. 执行之前是有的, 执行之后发现有就删除了, 所以打印是false) // console.log(divEle.classList.toggle('bg_red')); // true // console.log(divEle.classList.toggle('bg_red')); // false // console.log(divEle.classList.toggle('bg_red')); // true /*DOM操作操作标签样式 统一先用style起手*/ let pEle = document.getElementsByTagName('p')[0]; pEle.style.color = 'red'; pEle.style.fontSize = '28px'; pEle.style.backgroundColor = 'yellow'; pEle.style.border = '3px solid red'; // 总结: /* 属性操作: 获取标签所有类属性 divEle.classList; --> 返回数组对象 获取标签所有类属性中的某个属性: divEle.classList[0]; 删除获取的标签所有类属性中的某个属性: divEle.classList.remove('bg_red'); 往获取的标签所有类属性中添加某个属性: divEle.classList.add('bg_red'); 对获取的标签所有类属性中判断某个属性是否存在: divEle.classList.contains('c1'); --> 返回布尔值 对获取的标签所有类属性中如果属性存在则删除,不存在则添加: divEle.classList.toggle('bg_red'); --> 之前有布尔值为true, 执行了以后删除了它, 布尔值就是false 样式设置: pEle.style.属性名 = 属性值; */ </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
6.事件
6.1 什么是事件?
事件就是达到某一特定的条件自动触发的某种功能
HTML 4.0 的新特性之一是有能力使 HTML 事件触发浏览器中的动作(action),比如当用户点击某个 HTML 元素时执行一段JavaScript。下面是一个属性列表,这些属性可插入 HTML 标签来定义事件动作。
6.2 常用事件
onclick 鼠标单击 ondblclick 双击后激活事件 onfocus 获得焦点时触发 onblur 失去焦点时触发 应用场景:用于表单验证,用户离开某个输入框时,代表已经输入完了,我们可以对它进行验证. onchange 域的内容被改变。 应用场景:通常用于表单元素,当元素内容被改变时触发.(select联动) onkeydown 某个键盘按键被按下。 应用场景: 当用户在最后一个输入框按下回车按键时,表单提交 onkeypress 某个键盘按键被按下并松开。 onkeyup 某个键盘按键被松开。 onload 载入网页时 onmousedown 鼠标按钮被按下。 onmousemove 鼠标被移动。 onmouseout 鼠标从某元素移开。 onmouseover 鼠标移到某元素之上。 onselect 在文本框中的文本被选中时发生。 onsubmit 确认按钮被点击,使用的对象是form。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
6.3 事件之导入js的2种方式 和 绑定事件的2种方式
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script> /*导入js的第二种方式实现: 使用window.onload预加载, 等待以下标签都加载完毕以后才执行以下代码*/ // 注意: onload事件只能声明一个,声明多个会出现事件覆盖现象,下面的定义的事件覆盖上面的事件 window.onload = function () { // 第一种绑定事件的方式: 这种方式的缺点就是无法执行οnclick="func1()"这种绑定方式, 所以还是推荐使用第一种方式将js代码写在body标签底部 function func1() { prompt('提示框'); } // 第二种绑定事件的方式:: 推荐 let btnEle = document.getElementById('d1'); btnEle.onclick = function () { confirm(navigator.userAgent); } } </script> </head> <body> <button onclick="func1()">点我</button> <button id="d1">点我</button> <script> /*导入js的第一种方式实现: 在以上标签都加载完毕以后才执行以下代码*/ // function func1() { // prompt('提示框'); // } // // // let btnEle = document.getElementById('d1'); // btnEle.onclick = function () { // confirm(navigator.userAgent); // } </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
6.4 事件之onclick实例: 开关灯
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> #d1 { height: 400px; width: 400px; border-radius: 50%; } .bg_green { background-color: green; } .bg_red { background-color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="d1" class="c1 bg_red bg_green"></div> <button id="d2">变色</button> <script> // onclick: 鼠标单击触发 let divEle = document.getElementById('d1'); let btnEle = document.getElementById('d2'); btnEle.onclick = function () { divEle.classList.toggle('bg_red'); }; </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
6.5 事件之onfoucs+onblur实例: input框
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <input type="text" value="老板去吗?" id="d1"> <script> /* onfocus: 获得焦点时触发 onblur: 失去焦点时触发. 应用场景:用于表单验证,用户离开某个输入框时,代表已经输入完了,我们可以对它进行验证. */ /* 解题思路: 1. 当鼠标获取inputEle焦点时, 内容被清空 2. 当鼠标移开inputEle焦点时, 内容又展示 */ let inputEle = document.getElementById('d1'); inputEle.onfocus = function () { inputEle.value=''; // 点value就是获取 等号赋值就是设置 }; inputEle.onblur = function () { inputEle.value='不去, 没钱!'; // 给input标签重写赋值 }; </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
6.6 事件之onclick+定时器实例: 展示当前时间
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <input type="text" id="d1"> <button id="d2">开始</button> <button id="d3">结束</button> <script> let t; // 3. 那么定义一个全局存储定时器的变量, 提供清除定时器能够访问到这个变量 let inputEle = document.getElementById('d1'); let startBtnEle = document.getElementById('d2'); let endBtnEle = document.getElementById('d3'); function showTime() { let currentTime = new Date(); inputEle.value = currentTime.toLocaleString(); } startBtnEle.onclick = function () { if (!t) { // 2. 所以限制定时器只能开一个 t = setInterval(showTime, 1000); // 1. 每点击一次就会开设一个定时器 而t只指代最后一个 } }; endBtnEle.onclick = function () { clearInterval(t); t = null; // 4. 清除完了定时器, 还应该将t重置为空, 如果不置位空, 下次点击!t布尔值位true } </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
6.7 事件之onchange实例: 省市联动
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <select name="" id="d1"></select> <select name="" id="d2"></select> <script> // onchange: 文本域变化事件. 应用场景:通常用于表单元素,当元素内容被改变时触发. let proEle = document.getElementById('d1'); let cityEle = document.getElementById('d2'); let data = { "河北省": ["廊坊", "邯郸"], "北京": ["朝阳区", "海淀区"], "山东": ["威海市", "烟台市"] }; // 1. 为proEle和cityEle初始化提示option proEle.innerHTML = "<option disabled selected>--请选择省--</option>"; cityEle.innerHTML = '<option disabled selected>--请选择市--</option>'; // 2. for循环取值获取省, 并将获取到的省添加到proEle内 for (let key in data) { let optEle = document.createElement('option'); optEle.value = key; optEle.innerText = key; proEle.appendChild(optEle); } // 3. 当proEle被改变了自动触发绑定的onchange事件, 准备为cityEle添加对应的市区提供选择 proEle.onchange = function () { cityEle.innerHTML = ''; // 关键: 一上来就清空市区optEle, 为了防止下面多次选择触发appendChild出现一直追加的情况. let cityArray = data[proEle.value]; // 4. 循环所有的市 渲染到第二个select中 // // 方法一: 使用for循环. (提示: for循环取值争对数组取出来的是索引. 争对对象{}取出来的是key) // for (let index in cityArray) { // let optEle = document.createElement('option'); // optEle.value = cityArray[index]; // optEle.innerText = cityArray[index]; // cityEle.appendChild(optEle); // } // 方法二: 使用forEach cityArray.forEach(function (city) { let optEle = document.createElement('option'); optEle.value = city; optEle.innerText = city; cityEle.appendChild(optEle); }, this); }; </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
7.练习
案例一:模态框
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } html, body { height: 100%; } #bg { height: 100%; background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3); } #content { position: relative; top: 150px; width: 400px; height: 200px; line-height: 200px; text-align: center; color: red; background-color: white; margin: 0 auto; } #cancel { position: absolute; top: 0; right: 0; color: white; width: 30px; height: 30px; line-height: 30px; text-align: center; background-color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <input type="button" value="弹出模态框" id="btn"> <script> var oBtn = document.getElementById('btn'); var oDiv = document.createElement('div'); var oP = document.createElement('p'); var oSpan = document.createElement('span'); oDiv.id = 'bg'; oP.id = 'content'; oSpan.id = 'cancel'; oP.innerHTML = '弹出模态框'; oSpan.innerHTML = 'X'; oDiv.appendChild(oP); oP.appendChild(oSpan); oBtn.onclick = function () { this.parentNode.replaceChild(oDiv, this); }; oSpan.onclick =function () { oDiv.parentNode.replaceChild(oBtn,oDiv); } </script> </body> </html> <!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } html,body { height: 100%; } #bg { position: absolute; top: 0; left: 0; right: 0; bottom: 0; background-color: rgba(0,0,0,0.3); display: none; } #content { position: absolute; top: 100px; left: 50%; margin-left: -150px; background-color: white; width: 300px; height: 200px; } #content p:nth-child(3) { position: absolute; top: 100px; } </style> </head> <body> <input type="button" value="弹出" id="btn"> <div id="bg"> <div id="content"> <p> <label for="inp-username">用户名: </label><input type="text" name="username" id="inp-username"> </p> <p> <label for="inp-password">密码: </label><input type="text" name="username" id="inp-password"> </p> <p> <input type="button" value="提交" > <input type="button" value="取消" id="cancel"> </p> </div> </div> <script> var oBtn = document.getElementById('btn'); var oBg = document.getElementById('bg'); var oInpUsername=document.getElementById('inp-username'); var oInpPwd=document.getElementById('inp-password'); var oInp=document.getElementById('cancel'); oBtn.onclick=function () { oBg.style.display='block'; } oInp.onclick=function () { oInpUsername.value=''; oInpPwd.value=''; oBg.style.display='none' } </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
案例二:点击有惊喜
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } .box { width: 200px; height: 200px; background: red; text-align: center; color: white; line-height: 200px; font-size: 23px; font-weight: bold; margin: 20px auto; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box">点击有惊喜!!!</div> <script> var oBox = document.getElementsByClassName('box')[0]; //初始化点击的次数。通过次数的增加来改变DOM的样式 var a = 0; oBox.onclick = function () { a++; console.log(a % 4); if (a % 4 === 1) { this.style.background = 'green'; this.innerText = '继续点击哦!!!'; } else if (a % 4 == 2) { this.style.background = 'blue'; this.innerText = '骗你的,傻逼'; } else if (a % 4 == 3) { this.style.background = 'transparent'; this.innerText = ''; } else { this.style.background = 'red'; this.innerText = '点击有惊喜!!!'; } } </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
案例三:简易评论板
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } #comment { background-color: #b0b0b0; width: 500px; } #comment ul li { list-style: none; background-color: wheat; border: 1px dashed #000; margin: 0px 10px 10px; word-break: break-all; word-wrap: break-word; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="comment"> <p>评论内容:</p> </div> <div id="box"> <p>留言内容:</p> <textarea name="" id="content" cols="30" rows="10"></textarea> <p> <input type="button" value="提交" id="btn"> <input type="button" value="统计" id="calculate"> </p> </div> <script> var comment = document.getElementById('comment'); var box = document.getElementById('box'); var submit = document.getElementById('submit'); var content = document.getElementById('content'); var btn = document.getElementById('btn'); var calculate=document.getElementById('calculate'); var ul = document.createElement('ul'); comment.appendChild(ul); var count=0; btn.onclick = function () { var val = content.value; if (val.length != 0) { var date = new Date(); var subTime = date.toLocaleString(); var li = document.createElement('li'); var p1 = document.createElement('h3'); var p2 = document.createElement('p'); var spans = document.getElementsByClassName('del'); count=spans.length+1; p1.innerHTML = '#'+'<span class="num">'+count+'</span>'+'楼'+' '+subTime + '<span class="del"> 删除</span>'; p2.innerHTML = val; li.appendChild(p1); li.appendChild(p2); ul.appendChild(li); content.value = ''; } function aa() { var spans = document.getElementsByClassName('del'); for (var i = 0; i < spans.length; i++) { spans[i].onclick=function (currentIndex) { function bb() { ul.removeChild(this.parentNode.parentNode); count--; var ss=document.getElementsByClassName('num'); for (var j=currentIndex;j<ss.length;j++){ ss[j].innerHTML=parseInt(ss[j].innerHTML)-1; } aa(); } return bb; }(i); } } aa() }; calculate.onclick = function () { alert('一共发布了'+count+'条评论'); } </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
案例四:选项卡
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } .tab { width: 480px; height: 200px; border: 1px solid red; margin: 0 auto; } ul li { list-style: none; width: 160px; height: 60px; line-height: 60px; text-align: center; background-color: #b0b0b0; float: left; } li.active { background-color: #55BBBB; } p { display: none; height: 200px; text-align: center; line-height: 200px; background-color: white; } p.active { display: block; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="tab"> <ul> <li class="active">首页</li> <li>新闻</li> <li>图片</li> </ul> <p class="active">首页内容</p> <p>新闻内容</p> <p>图片内容</p> </div> <script> var aLi=document.getElementsByTagName('li'); var aP=document.getElementsByTagName('p'); for (var i=0;i<aLi.length;i++){ aLi[i].index=i; aLi[i].onclick=function () { for (var j=0;j<aLi.length;j++){ aLi[j].className=''; aP[j].className=''; } this.className='active'; aP[this.index].className='active'; } } </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
案例五:仿淘宝搜索框
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } #search { position: relative; } input { outline: none; display: block; border: 2px solid #f2a83c; border-radius: 10px; width: 490px; height: 50px; margin-top: 20px; } label { position: absolute; top: 20px; left: 10px; font-size: 8px; color: gray; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="search"> <input type="text" id="text"> <label for="text" id="msg">老男孩上海校区</label> </div> <script> var txt = document.getElementById('text'); var msg = document.getElementById('msg'); //检测用户表单输入的时候 txt.oninput = function () { //控制元素显示隐藏 if (this.value == '') { msg.style.display = 'block'; } else { msg.style.display = 'none'; } } </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
案例六:获取当前时间
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <script> setInterval(function () { var date = new Date(); var y = date.getFullYear(); var m = date.getMonth(); var d = date.getDate(); var h = date.getHours(); var min = date.getMinutes(); var s = date.getSeconds(); //今天是2018年2月23日 8:23:09 document.body.innerHTML = "今天是" + y + '年' + num(m + 1) + "月" + num(d) + "日" + num(h) + ":" + num(min) + ":" + num(s) }, 1000) function num(n) { if (n < 10) { return "0" + n; } return n } </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
案例七:匀速运动
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> * { padding: 0; margin: 0; } .box { width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: #FF0000; position: absolute; top: 50px; left: 0px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="wrap"> <button id="btn1">前进</button> <button id="btn2">后退</button> <div class="box" id="box1"> </div> </div> <script> var btn1 = document.getElementById('btn1'); var btn2 = document.getElementById('btn2'); var box1 = document.getElementById('box1') var count = 0; var time1 = null; var time2 = null; btn1.onclick = function () { clearInterval(time2); time1 = setInterval(function () { count += 10; if (count > 1000) { box1.style.left = '1000px'; box1.style.borderRadius = '50%'; clearInterval(time1); } else { box1.style.left = count + 'px'; box1.style.borderRadius = count / 2000 * 100 + '%'; } }, 10) }; btn2.onclick = function () { clearInterval(time1); time2 = setInterval(function () { count -= 10; if (count <= 0) { box1.style.left = '0px'; box1.style.borderRadius = ''; clearInterval(time2); } else { box1.style.left = count + 'px'; box1.style.borderRadius = count / 2000 * 100 + '%'; ; } }, 10) } </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
案例八:5s后关闭广告
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> * { padding: 0; margin: 0; } img { position: fixed; width: 300px; } ul { list-style: none; } #left { left: 0; } #right { right: 0; } ul li { font-size: 25px; } </style> </head> <body> <img src="images/1.jpg" id="left"> <img src="images/1.jpg" id="right"> <ul> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> <li>屠龙宝刀,点击就送</li> </ul> <script> window.onload = function () { var left = document.getElementById('left'); var right = document.getElementById('right'); setTimeout(function () { left.style.display = 'none'; right.style.display = 'none'; }, 5000) } </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
案例九:小米滚动
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> * { padding: 0; margin: 0; } .wrap { width: 512px; height: 400px; border: 3px solid #808080; position: relative; overflow: hidden; margin: 100px auto; } .wrap span { width: 100%; height: 200px; position: absolute; background-color: transparent; border: 1px solid #000; } .up { top: 0; } .down { bottom: 0; } img { position: absolute; top: 0; left: 0; height: 200px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="box" class="wrap"> <img src="images/mi.png" id="xiaomi"> <span class="up" id="picUp">11111</span> <span class="down" id="picDown">22222</span> </div> <script> var up = document.getElementById('picUp'); var down = document.getElementById('picDown'); var img = document.getElementById('xiaomi'); var count = 0; var time = null; //鼠标移入的时候吧 up.onmouseover = function () { //不管怎样 上来先清定时器 clearInterval(time); time = setInterval(function () { count -= 3; count >= -1070 ? img.style.top = count + 'px' : clearInterval(time); }, 30) }; down.onmouseover = function () { clearInterval(time); time = setInterval(function () { count += 1; count < 0 ? img.style.top = count + 'px' : clearInterval(time); }, 30) } </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
案例十:无缝轮播
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> * { padding: 0; margin: 0; } ul { list-style: none; } .box { width: 600px; height: 700px; margin: 50px auto; overflow: hidden; position: relative; border: 1px solid #000; } ul li { float: left; } .box ul { width: 500%; position: absolute; top: 0; left: 0; } img { width: 600px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"> <ul> <li><img src="https://images2018.cnblogs.com/blog/1036857/201805/1036857-20180516225816920-580320384.jpg"/></li> <li><img src="https://images2018.cnblogs.com/blog/1036857/201805/1036857-20180516225809591-1990809146.jpg"/></li> <li><img src="https://images2018.cnblogs.com/blog/1036857/201805/1036857-20180516225724530-539090864.jpg"/></li> <li><img src="https://images2018.cnblogs.com/blog/1036857/201805/1036857-20180516225751362-1832630751.jpg"/></li> <li><img src="https://images2018.cnblogs.com/blog/1036857/201805/1036857-20180516225816920-580320384.jpg"/></li> </ul> </div> <script> var box = document.getElementsByClassName('box')[0]; var ul = box.children[0]; var num = 0; var timer = null; timer = setInterval(autoPlay, 3); //函数的声明 function autoPlay() { num--; num <= -2400? num = 0: num; ul.style.left = num + 'px' } //鼠标移动上去 box.onmouseover = function () { clearInterval(timer) }; box.onmouseout = function () { timer = setInterval(autoPlay, 3); } </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
案例十一:用户名和密码校验
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> <style> span { background-color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <form> <p> <input type="text" name="username"> <span></span> </p> <p> <input type="password" name="password"> <span></span> </p> <p> <input type="button" value="提交" id="btn"> </p> </form> <script> var isOk1=false var reg1=new RegExp('(?!^[0-9]+$)(?!^[a-zA-Z]+$)^[0-9A-Za-z]{4}$') var inp1 = document.getElementsByName("username")[0] inp1.onblur=function () { var res=reg1.test(this.value) this.style.border="1px solid red" if (!res) { this.nextElementSibling.innerText="用户名必须由4位字母和数字组成" setTimeout(function () { inp1.nextElementSibling.innerText="" inp1.value="" },3000) }else { this.style.border="1px solid green" isOk1=true } } var isOk2=false var reg2=new RegExp('(?!^[0-9]+$)(?!^[a-zA-Z]+$)^[0-9A-Za-z]{6}$') var inp2 = document.getElementsByName("password")[0] inp2.onblur=function () { var res=reg2.test(this.value) this.style.border="1px solid red" if (!res) { this.nextElementSibling.innerText="密码必须由6位字母和数字组成" setTimeout(function () { inp2.nextElementSibling.innerText="" inp2.value="" },3000) }else { this.style.border="1px solid green" isOk2=true } } var btn=document.getElementById("btn") btn.onclick=function () { if(isOk1 && isOk2) { alert("提交成功") }else { alert("请重新填写") } } </script> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
四、总结:
/* 查找标签: 直接查找: id查找 document.getElementById() 返回对象 类名查找 document.getElementsByClassName() 返回数组对象 标签名查找 document.getElementByTagName() 返回数组对象 间接查找: 查找父标签: 没有父标签则返回null divEle.parentElement 查找所有子标签: 返回数组对象, 通过索引取值获取对应子标签 divEle.children 查找第一个子标签: divEle.firstElementChild divEle.children[0] 查找最后一个子标签: divEle.lastElementChild divEle.children[divEle.children.length-1] 查找同级别上一个: divEle.nextElementSibling 查找同级别下一个: divEle.previousElementSibling 节点操作: 创建标签: let aEle = document.createElement('a'); 添加属性: 添加内置: aEle.alt=''; 添加内置+自定义: aEle.setAttribute('username', 'egon'); 拓展: getAttribute('username') removeAttribute('username') 文本操作: 获取所有文本: aEle.innerText; 获取所有文本+标签: aEle.innerHTML; 添加文本: aEle.innerText='xxx'; 添加文本+标签: aEle.innerHTML='<h1>xxx</h1>; 追加标签: let divEle = document.getElementById('d1'); divEle.appendChild(aEle); 拓展: removeChild(aEle) replaceChild(src, dst) 插入标签: let pEle = divEle.children[0]; divEle.inertBefore(aEle, pEle) 获取值操作: 获取非文件: inputEle.value 获取文件: 获取文件本次上传路径: inputEle.value 获取文件对象集合: inputEle.files 返回格式{0: 文件对象, 1: 文件对象1} 获取某一个文件对象: inputEle.files[0] 拓展: 值清空 inputEle.value='' class, css操作: class操作: 获取所有类属性: divEle.classList 返回数组对象 获取某一个类属性: divEle.classList[0] 返回数组对象中按照索引取值的类名 对获取到的所有类属性进行追加: divEle.classList.add('bg_red') 对获取到的所有类属性进行删除: divEle.classList.remove('bg_red') 对获取到的所有类属性判断是否存在某个类: divEle.classList.contains('bg_red') 返回布尔值 对获取到的所有类属性判断有则删除,无则添加: divEle.classList.toggle('bg_red') 之前有布尔值为true, 执行了以后删除了它, 布尔值就是false css操作: 统一style起手, 将css中的横杆换成驼峰体 divEle.style.backgroundColor = 'red'; divEle.style.fontSize = '28px'; 事件: 满足某种条件自动触发的功能 导入js的2种方式: head中绑定预加载事件window.onload. 预加载无法执行以下的绑定事件的第一种方式. 且不能多次声明, 多次绑定, 下面会覆盖上面 body中底部 绑定事件的2种方式: 标签中定义属性οnclick='func()' 通过DOM操作获取标签对象, 再通过标签对象绑定事件. 例如: aEle.onclick = function () {} onclick 鼠标单击事件. 实例1: 开关灯. 主要利用nodeEle.classList.toggle实现 实例2: 展示当前时间. 主要利用创建时间对象new Date() + 循环定时器实现 onfocus 获得焦点时触发事件 + onblur 失去焦点时触发事件. 实例: input框的焦点获取与失去. 主要利用inputEle.value实现 onchange 文本域变化事件 实例: 省市联动. 主要利用节点操(创建标签, 为标签添加属性, 为标签添加文本内容, 找到需要添加的位置添加) 常用事件总结: onclick 鼠标单击 ondblclick 双击后激活事件 onfocus 获得焦点时触发 onblur 失去焦点时触发 应用场景:用于表单验证,用户离开某个输入框时,代表已经输入完了,我们可以对它进行验证. onchange 域的内容被改变。 应用场景:通常用于表单元素,当元素内容被改变时触发.(select联动) onkeydown 某个键盘按键被按下。 应用场景: 当用户在最后一个输入框按下回车按键时,表单提交 onkeypress 某个键盘按键被按下并松开。 onkeyup 某个键盘按键被松开。 onload 载入网页时 onmousedown 鼠标按钮被按下。 onmousemove 鼠标被移动。 onmouseout 鼠标从某元素移开。 onmouseover 鼠标移到某元素之上。 onselect 在文本框中的文本被选中时发生。 onsubmit 确认按钮被点击,使用的对象是form。 */
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109



