热门标签
热门文章
- 130天学会QT(进阶)--------------第二天(创建项目)
- 2嵌入式Linux开发环境搭建-(6)交叉编译QT4.8.7源码生成qmake工具
- 3【计算机网络】7. 网络基础5之详解以太网协议,ARP协议,NAT协议,DNS协议_arp和nat
- 4Mac 卸载重装 brew_mac 卸载brew
- 5$ionicView执行顺序_$scope.$on('$ionicview
- 6计算机启用远程桌面连接失败,开启局域网远程桌面连接不上怎么办
- 7Python文字识别_python识别文字
- 8flutter安卓模拟器不好使安卓每次打开android studio都下载并且download Importing ‘android“Gradle Project问题_importing android gradle project
- 9ARP协议,DNS协议,IP协议,TCP协议和IP路由原理
- 10几种使用了CNN(卷积神经网络)的文本分类模型_cnn文本分类模型是什么
当前位置: article > 正文
Java8 使用 stream().sorted()对List集合进行排序
作者:花生_TL007 | 2024-03-07 05:50:40
赞
踩
Java8 使用 stream().sorted()对List集合进行排序
集合对像定义
集合对象以学生类(StudentInfo)为例,有学生的基本信息,包括:姓名,性别,年龄,身高,生日几项。
使用stream().sorted()进行排序,需要该类实现 Comparable 接口,该接口只有一个方法需要实现,如下:
public int compareTo(T o);
有关compareTo方法的实现说明,请参考:Java 关于重写compareTo方法
我的学生类代码如下:
import java.time.LocalDate; import java.util.List; public class StudentInfo implements Comparable<StudentInfo> { //名称 private String name; //性别 true男 false女 private Boolean gender; //年龄 private Integer age; //身高 private Double height; //出生日期 private LocalDate birthday; public StudentInfo(String name, Boolean gender, Integer age, Double height, LocalDate birthday){ this.name = name; this.gender = gender; this.age = age; this.height = height; this.birthday = birthday; } public String toString(){ String info \= String.format("%s\\t\\t%s\\t\\t%s\\t\\t\\t%s\\t\\t%s",this.name,this.gender.toString(),this.age.toString(),this.height.toString(),birthday.toString()); return info; } public static void printStudents(List<StudentInfo> studentInfos){ System.out.println("\[姓名\]\\t\\t\[性别\]\\t\\t\[年龄\]\\t\\t\[身高\]\\t\\t\[生日\]"); System.out.println("----------------------------------------------------------"); studentInfos.forEach(s\->System.out.println(s.toString())); System.out.println(" "); } @Override public int compareTo(StudentInfo ob) { return this.age.compareTo(ob.getAge()); //return 1; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Boolean getGender() { return gender; } public void setGender(Boolean gender) { this.gender = gender; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public Double getHeight() { return height; } public void setHeight(Double height) { this.height = height; } public LocalDate getBirthday() { return birthday; } public void setBirthday(LocalDate birthday) { this.birthday = birthday; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
StudentInfo对象类
添加测试数据
下面来添加一些测试用的数据,代码如下:
//测试数据,请不要纠结数据的严谨性
List<StudentInfo> studentList = new ArrayList<>();
studentList.add(new StudentInfo("李小明",true,18,1.76,LocalDate.of(2001,3,23)));
studentList.add(new StudentInfo("张小丽",false,18,1.61,LocalDate.of(2001,6,3)));
studentList.add(new StudentInfo("王大朋",true,19,1.82,LocalDate.of(2000,3,11)));
studentList.add(new StudentInfo("陈小跑",false,17,1.67,LocalDate.of(2002,10,18)));
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
排序
使用年龄进行升序排序
//排序前输出
StudentInfo.printStudents(studentList);
//按年龄排序(Integer类型)
List<StudentInfo> studentsSortName = studentList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(StudentInfo::getAge)).collect(Collectors.toList());
//排序后输出
StudentInfo.printStudents(studentsSortName);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
结果如下图:

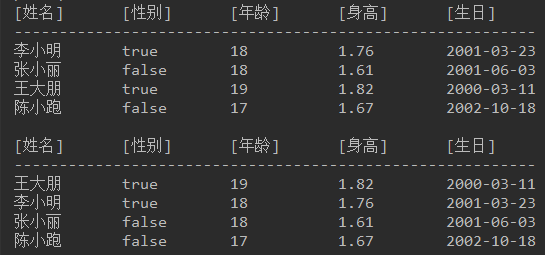
使用年龄进行降序排序(使用reversed()方法)
//排序前输出
StudentInfo.printStudents(studentList);
//按年龄排序(Integer类型)
List<StudentInfo> studentsSortName = studentList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(StudentInfo::getAge).reversed()).collect(Collectors.toList());
//排序后输出
StudentInfo.printStudents(studentsSortName);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
结果如下图:
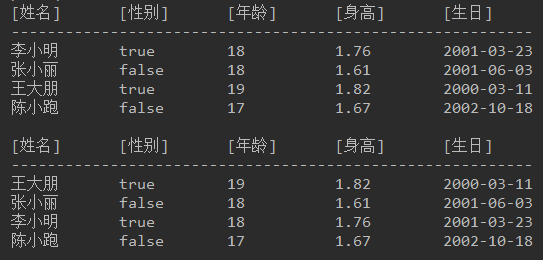
使用年龄进行降序排序,年龄相同再使用身高升序排序
//排序前输出
StudentInfo.printStudents(studentList);
//按年龄排序(Integer类型)
List<StudentInfo> studentsSortName = studentList.stream()
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(StudentInfo::getAge).reversed().thenComparing(StudentInfo::getHeight))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
//排序后输出
StudentInfo.printStudents(studentsSortName);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
结果如下图:
转至:https://www.cnblogs.com/codecat/p/10873757.html
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/花生_TL007/article/detail/203840
推荐阅读
相关标签



