- 1java判断日期前后_Java丨时间判断谁前谁后
- 2如何扩展 JPA Annotation 以更好的支持 OR Mapping_jpa annotation mappings require
- 32021-10-074号靶场转自y神的学习笔记(net渗透,sockcap,msf多重网段渗透,os-shell,验证码重放,C#解密,wfuzz穷举subdomain)_http-robots.txt: 1 disallowed entry
- 4update-alternatives: error: no alternatives for g++处理_update-alternatives: error: no alternatives for gc
- 5个人所得税 软件电脑上的安装路径和名字 如何在电脑上找到个人所得税软件程序名称 ServYou\EPPortal_DS3.0_V2.1\EPEvenue_SH.exe_file://d:\epportal_ds3.0\appmodules\itskhd\temp\pa
- 6一个比较完善的httpWebRequest 封装,适合网络爬取及暴力破解
- 7Android开发规范:API接口通用设计规范_安卓 api
- 8android字符串定义,android – 使用现有的字符串定义定义’resValue’
- 9Jetpack Compose入门详解(实时更新)
- 10有效突破的三三原则
鸿蒙HarmonyOS开发框架—ArkTS语言(状态管理 四)_鸿蒙开发状态管理框架
赞
踩
@Observed装饰器和@ObjectLink装饰器:嵌套类对象属性变化
上文所述的装饰器仅能观察到第一层的变化,但是在实际应用开发中,应用会根据开发需要,封装自己的数据模型。对于多层嵌套的情况,比如二维数组,或者数组项class,或者class的属性是class,他们的第二层的属性变化是无法观察到的。这就引出了@Observed/@ObjectLink装饰器。
概述
@ObjectLink和@Observed类装饰器用于在涉及嵌套对象或数组的场景中进行双向数据同步:
- 被@Observed装饰的类,可以被观察到属性的变化;
- 子组件中@ObjectLink装饰器装饰的状态变量用于接收@Observed装饰的类的实例,和父组件中对应的状态变量建立双向数据绑定。这个实例可以是数组中的被@Observed装饰的项,或者是class object中是属性,这个属性同样也需要被@Observed装饰。
- 单独使用@Observed是没有任何作用的,需要搭配@ObjectLink或者@Prop使用。
限制条件
使用@Observed装饰class会改变class原始的原型链,@Observed和其他类装饰器装饰同一个class可能会带来问题。
装饰器说明
| @Observed类装饰器 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 装饰器参数 | 无 |
| 类装饰器 | 装饰class。需要放在class的定义前,使用new创建类对象。 |
| @ObjectLink变量装饰器 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 装饰器参数 | 无 |
| 同步类型 | 不与父组件中的任何类型同步变量。 |
| 允许装饰的变量类型 | 必须为被@Observed装饰的class实例,必须指定类型。 不支持简单类型,可以使用@Prop。 @ObjectLink的属性是可以改变的,但是变量的分配是不允许的,也就是说这个装饰器装饰变量是只读的,不能被改变。 |
| 被装饰变量的初始值 | 不允许。 |
@ObjectLink装饰的数据为可读示例。
- // 允许@ObjectLink装饰的数据属性赋值
- this.objLink.a= ...
- // 不允许@ObjectLink装饰的数据自身赋值
- this.objLink= ...
复制
说明 @ObjectLink装饰的变量不能被赋值,如果要使用赋值操作,请使用@Prop。
- @Prop装饰的变量和数据源的关系是是单向同步,@Prop装饰的变量在本地拷贝了数据源,所以它允许本地更改,如果父组件中的数据源有更新,@Prop装饰的变量本地的修改将被覆盖;
- @ObjectLink装饰的变量和数据源的关系是双向同步,@ObjectLink装饰的变量相当于指向数据源的指针。如果一旦发生@ObjectLink装饰的变量的赋值,则同步链将被打断。
变量的传递/访问规则说明
| @ObjectLink传递/访问 | 说明 |
|---|---|
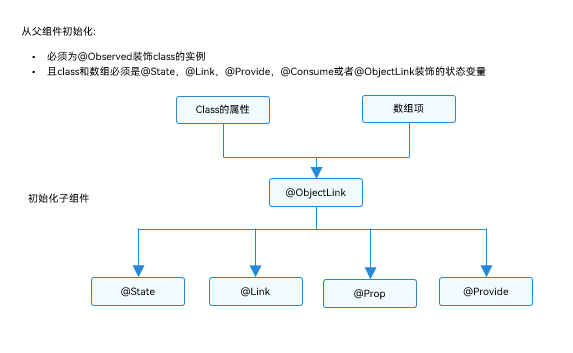
| 从父组件初始化 | 必须指定。 初始化@ObjectLink装饰的变量必须同时满足以下场景: 类型必须是@Observed装饰的class。初始化的数值需要是数组项,或者class的属性。同步源的class或者数组必须是@State,@Link,@Provide,@Consume或者@ObjectLink装饰的数据。 |
| 与源对象同步 | 双向。 |
| 可以初始化子组件 | 允许,可用于初始化常规变量、@State、@Link、@Prop、@Provide |
- 类型必须是@Observed装饰的class。
- 初始化的数值需要是数组项,或者class的属性。
- 同步源的class或者数组必须是@State,@Link,@Provide,@Consume或者@ObjectLink装饰的数据。
与源对象同步 双向。 可以初始化子组件 允许,可用于初始化常规变量、@State、@Link、@Prop、@Provide
图1 初始化规则图示
观察变化和行为表现
观察的变化
@Observed装饰的类,如果其属性为非简单类型,比如class、Object或者数组,也需要被@Observed装饰,否则将观察不到其属性的变化。
- class ClassA {
- public c: number;
-
- constructor(c: number) {
- this.c = c;
- }
- }
-
- @Observed
- class ClassB {
- public a: ClassA;
- public b: number;
-
- constructor(a: ClassA, b: number) {
- this.a = a;
- this.b = b;
- }
- }

复制
以上示例中,ClassB被@Observed装饰,其成员变量的赋值的变化是可以被观察到的,但对于ClassA,没有被@Observed装饰,其属性的修改不能被观察到。
- @ObjectLink b: ClassB
-
- // 赋值变化可以被观察到
- this.b.a = new ClassA(5)
- this.b.b = 5
-
- // ClassA没有被@Observed装饰,其属性的变化观察不到
- this.b.a.c = 5
复制
@ObjectLink:@ObjectLink只能接收被@Observed装饰class的实例,可以观察到:
- 其属性的数值的变化,其中属性是指Object.keys(observedObject)返回的所有属性。
- 如果数据源是数组,则可以观察到数组item的替换,如果数据源是class,可观察到class的属性的变化。
框架行为
- 初始渲染:
- @Observed装饰的class的实例会被不透明的代理对象包装,代理了class上的属性的setter和getter方法
- 子组件中@ObjectLink装饰的从父组件初始化,接收被@Observed装饰的class的实例,@ObjectLink的包装类会将自己注册给@Observed class。
- 属性更新:当@Observed装饰的class属性改变时,会走到代理的setter和getter,然后遍历依赖它的@ObjectLink包装类,通知数据更新。
使用场景
嵌套对象
以下是嵌套类对象的数据结构。
- // objectLinkNestedObjects.ets
- let NextID: number = 1;
-
- @Observed
- class ClassA {
- public id: number;
- public c: number;
-
- constructor(c: number) {
- this.id = NextID++;
- this.c = c;
- }
- }
-
- @Observed
- class ClassB {
- public a: ClassA;
-
- constructor(a: ClassA) {
- this.a = a;
- }
- }

复制
以下组件层次结构呈现的是此数据结构
- @Component
- struct ViewA {
- label: string = 'ViewA1';
- @ObjectLink a: ClassA;
-
- build() {
- Row() {
- Button(`ViewA [${this.label}] this.a.c=${this.a.c} +1`)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.a.c += 1;
- })
- }
- }
- }
-
- @Entry
- @Component
- struct ViewB {
- @State b: ClassB = new ClassB(new ClassA(0));
-
- build() {
- Column() {
- ViewA({ label: 'ViewA #1', a: this.b.a })
- ViewA({ label: 'ViewA #2', a: this.b.a })
-
- Button(`ViewB: this.b.a.c+= 1`)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.b.a.c += 1;
- })
- Button(`ViewB: this.b.a = new ClassA(0)`)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.b.a = new ClassA(0);
- })
- Button(`ViewB: this.b = new ClassB(ClassA(0))`)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.b = new ClassB(new ClassA(0));
- })
- }
- }
- }

复制
ViewB中的事件句柄:
- this.b.a = new ClassA(0) 和this.b = new ClassB(new ClassA(0)): 对@State装饰的变量b和其属性的修改。
- this.b.a.c = ... :该变化属于第二次的变化,@State无法观察到第二层的变化,但是ClassA被@Observed装饰,ClassA的属性c的变化可以被@ObjectLink观察到。
ViewA中的事件句柄:
- this.a.c += 1:对@ObjectLink变量a的修改,将触发Button组件的刷新。@ObjectLink和@Prop不同,@ObjectLink不拷贝来自父组件的数据源,而是在本地构建了指向其数据源的引用。
- @ObjectLink变量是只读的,this.a = new ClassA(...)是不允许的,因为一旦赋值操作发生,指向数据源的引用将被重置,同步将被打断。
对象数组
对象数组是一种常用的数据结构。以下示例展示了数组对象的用法。
- @Component
- struct ViewA {
- // 子组件ViewA的@ObjectLink的类型是ClassA
- @ObjectLink a: ClassA;
- label: string = 'ViewA1';
-
- build() {
- Row() {
- Button(`ViewA [${this.label}] this.a.c = ${this.a.c} +1`)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.a.c += 1;
- })
- }
- }
- }
-
- @Entry
- @Component
- struct ViewB {
- // ViewB中有@State装饰的ClassA[]
- @State arrA: ClassA[] = [new ClassA(0), new ClassA(0)];
-
- build() {
- Column() {
- ForEach(this.arrA,
- (item) => {
- ViewA({ label: `#${item.id}`, a: item })
- },
- (item) => item.id.toString()
- )
- // 使用@State装饰的数组的数组项初始化@ObjectLink,其中数组项是被@Observed装饰的ClassA的实例
- ViewA({ label: `ViewA this.arrA[first]`, a: this.arrA[0] })
- ViewA({ label: `ViewA this.arrA[last]`, a: this.arrA[this.arrA.length-1] })
-
- Button(`ViewB: reset array`)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.arrA = [new ClassA(0), new ClassA(0)];
- })
- Button(`ViewB: push`)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.arrA.push(new ClassA(0))
- })
- Button(`ViewB: shift`)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.arrA.shift()
- })
- Button(`ViewB: chg item property in middle`)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.arrA[Math.floor(this.arrA.length / 2)].c = 10;
- })
- Button(`ViewB: chg item property in middle`)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.arrA[Math.floor(this.arrA.length / 2)] = new ClassA(11);
- })
- }
- }
- }

复制
- this.arrA[Math.floor(this.arrA.length/2)] = new ClassA(..) :该状态变量的改变触发2次更新:
- ForEach:数组项的赋值导致ForEach的itemGenerator被修改,因此数组项被识别为有更改,ForEach的item builder将执行,创建新的ViewA组件实例。
- ViewA({ label: `ViewA this.arrA[first]`, a: this.arrA[0] }):上述更改改变了数组中第一个元素,所以绑定this.arrA[0]的ViewA将被更新;
- this.arrA.push(new ClassA(0)) : 将触发2次不同效果的更新:
- ForEach:新添加的ClassA对象对于ForEach是未知的itemGenerator,ForEach的item builder将执行,创建新的ViewA组件实例。
- ViewA({ label: `ViewA this.arrA[last]`, a: this.arrA[this.arrA.length-1] }):数组的最后一项有更改,因此引起第二个ViewA的实例的更改。对于ViewA({ label: `ViewA this.arrA[first]`, a: this.arrA[0] }),数组的更改并没有触发一个数组项更改的改变,所以第一个ViewA不会刷新。
- this.arrA[Math.floor(this.arrA.length/2)].c:@State无法观察到第二层的变化,但是ClassA被@Observed装饰,ClassA的属性的变化将被@ObjectLink观察到。
二维数组
使用@Observed观察二维数组的变化。可以声明一个被@Observed装饰的继承Array的子类。
- @Observed
- class StringArray extends Array<String> {
- }
复制
使用new StringArray()来构造StringArray的实例,new运算符使得@Observed生效,@Observed观察到StringArray的属性变化。
声明一个从Array扩展的类class StringArray extends Array<String> {},并创建StringArray的实例。@Observed装饰的类需要使用new运算符来构建class实例。
- @Observed
- class StringArray extends Array<String> {
- }
-
- @Component
- struct ItemPage {
- @ObjectLink itemArr: StringArray;
-
- build() {
- Row() {
- Text('ItemPage')
- .width(100).height(100)
-
- ForEach(this.itemArr,
- item => {
- Text(item)
- .width(100).height(100)
- },
- item => item
- )
- }
- }
- }
-
- @Entry
- @Component
- struct IndexPage {
- @State arr: Array<StringArray> = [new StringArray(), new StringArray(), new StringArray()];
-
- build() {
- Column() {
- ItemPage({ itemArr: this.arr[0] })
- ItemPage({ itemArr: this.arr[1] })
- ItemPage({ itemArr: this.arr[2] })
-
- Divider()
-
- ForEach(this.arr,
- itemArr => {
- ItemPage({ itemArr: itemArr })
- },
- itemArr => itemArr[0]
- )
-
- Divider()
-
- Button('update')
- .onClick(() => {
- console.error('Update all items in arr');
- if (this.arr[0][0] !== undefined) {
- // 正常情况下需要有一个真实的ID来与ForEach一起使用,但此处没有
- // 因此需要确保推送的字符串是唯一的。
- this.arr[0].push(`${this.arr[0].slice(-1).pop()}${this.arr[0].slice(-1).pop()}`);
- this.arr[1].push(`${this.arr[1].slice(-1).pop()}${this.arr[1].slice(-1).pop()}`);
- this.arr[2].push(`${this.arr[2].slice(-1).pop()}${this.arr[2].slice(-1).pop()}`);
- } else {
- this.arr[0].push('Hello');
- this.arr[1].push('World');
- this.arr[2].push('!');
- }
- })
- }
- }
- }

最后,为了能让大家更好的去学习提升鸿蒙 (Harmony OS) 开发技术,小编连夜整理了一份30个G纯血版学习资料(含视频、电子书、学习文档等)以及一份在Github上持续爆火霸榜的《纯血版华为鸿蒙 (Harmony OS)开发手册》(共计890页),希望对大家有所帮助。
纯血版鸿蒙 HarmonyOS 4.0 视频学习资料


需要以上视频学习资料小伙伴
《纯血版华为鸿蒙 (Harmony OS)开发手册》
这份手册涵盖了当前鸿蒙 (Harmony OS) 开发技术必掌握的核心知识点
纯血版鸿蒙 (Harmony OS)开发手册部分精彩内容
HarmonyOS 概念:
- 系统定义
- 技术架构
- 技术特性
- 系统安全

如何快速入门?
- 基本概念
- 构建第一个ArkTS应用
- 构建第一个JS应用
- ……

开发基础知识:
- 应用基础知识
- 配置文件
- 应用数据管理
- 应用安全管理
- 应用隐私保护
- 三方应用调用管控机制
- 资源分类与访问
- 学习ArkTS语言
- ……
基于ArkTS 开发:
- Ability开发
- UI开发
- 公共事件与通知
- 窗口管理
- 媒体
- 安全
- 网络与链接
- 电话服务
- 数据管理
- 后台任务(Background Task)管理
- 设备管理
- 设备使用信息统计
- DFX
- 国际化开发
- 折叠屏系列
- .……

获取以上文中提到的这份纯血版鸿蒙 (Harmony OS) 开发资料的小伙伴
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/花生_TL007/article/detail/288937
Copyright © 2003-2013 www.wpsshop.cn 版权所有,并保留所有权利。


