- 1探索GameFi:区块链与游戏的未来融合_游戏+区块链
- 2从零开始制作STM32F103RCT6小车(一)
- 3DARPA加大拓扑量子投资!联合微软开发公用事业规模量子计算机
- 4Mac下常用命令_mac常用命令
- 5基于用户的协同过滤Movielens电影推荐系统简单实例_collaborative filtering和movielens的电影推荐系统
- 6FPGA自学教程 02 3-8译码器_小梅哥fpga自学教程
- 7✅从63%到10%‼️汉语同义句在线转换器_中文同义句在线转换器
- 81.triton镜像使用_triton inference server可以用在centos上吗
- 9【华为OD机试真题】159、星际篮球争霸赛 | 机试真题+思路参考+代码解析(C语言、C++、Java、Py、JS)
- 10MySQL中的存储过程详解(下篇)
C++使用Python/C API_python c++ api
赞
踩
目录
配置环境
环境:Windows10、Visual Studio 2019、Python3.x
打开VS,建立空项目。
第一步 导入Python3路径
1. 项目→属性→C/C++→常规→附加包含目录,添加Python3安装路径\include。
该文件夹下有Python.h,这就是C++调用Python的API前一定要include的库。
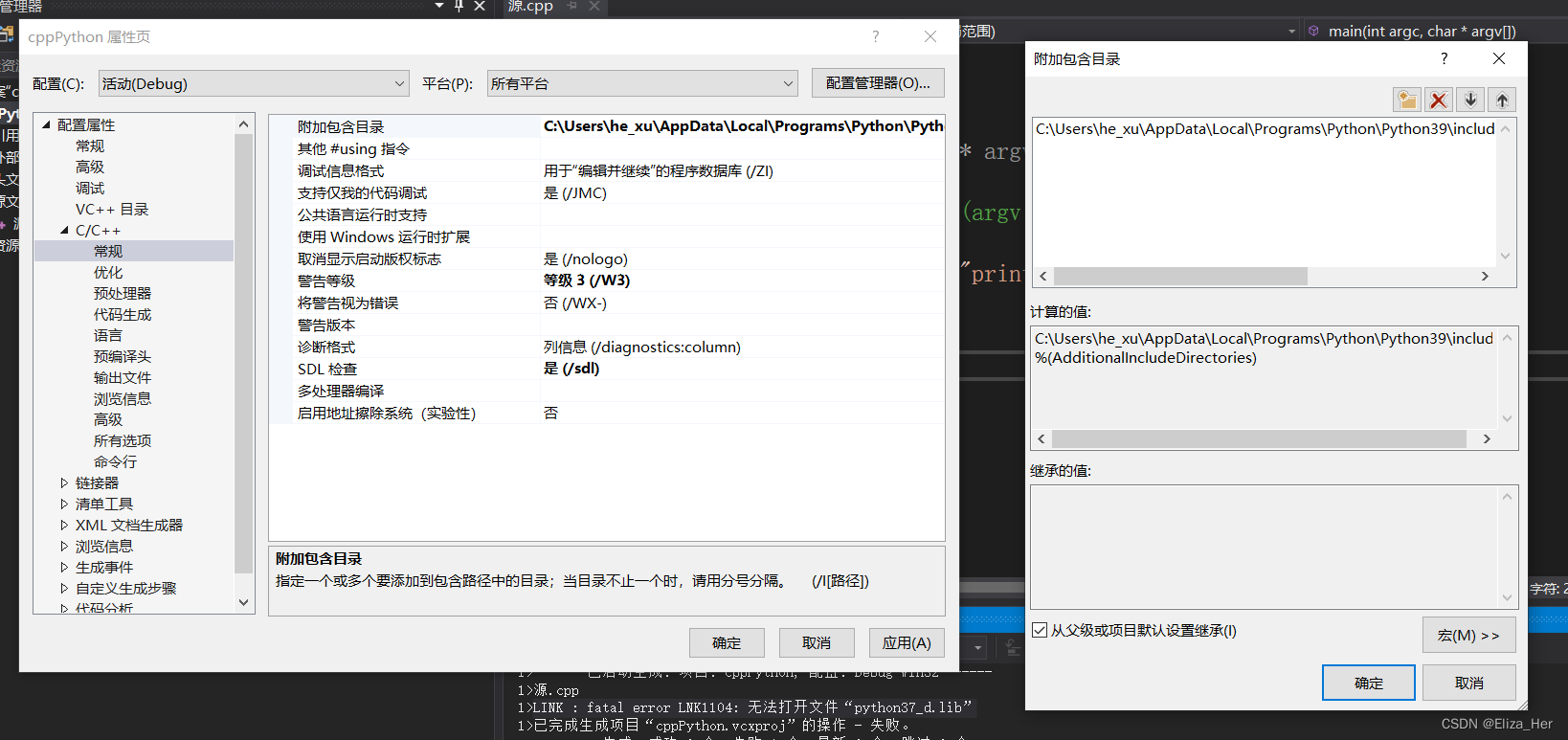
2. 项目→属性→VC++目录→库目录,添加Python3安装路径\libs。
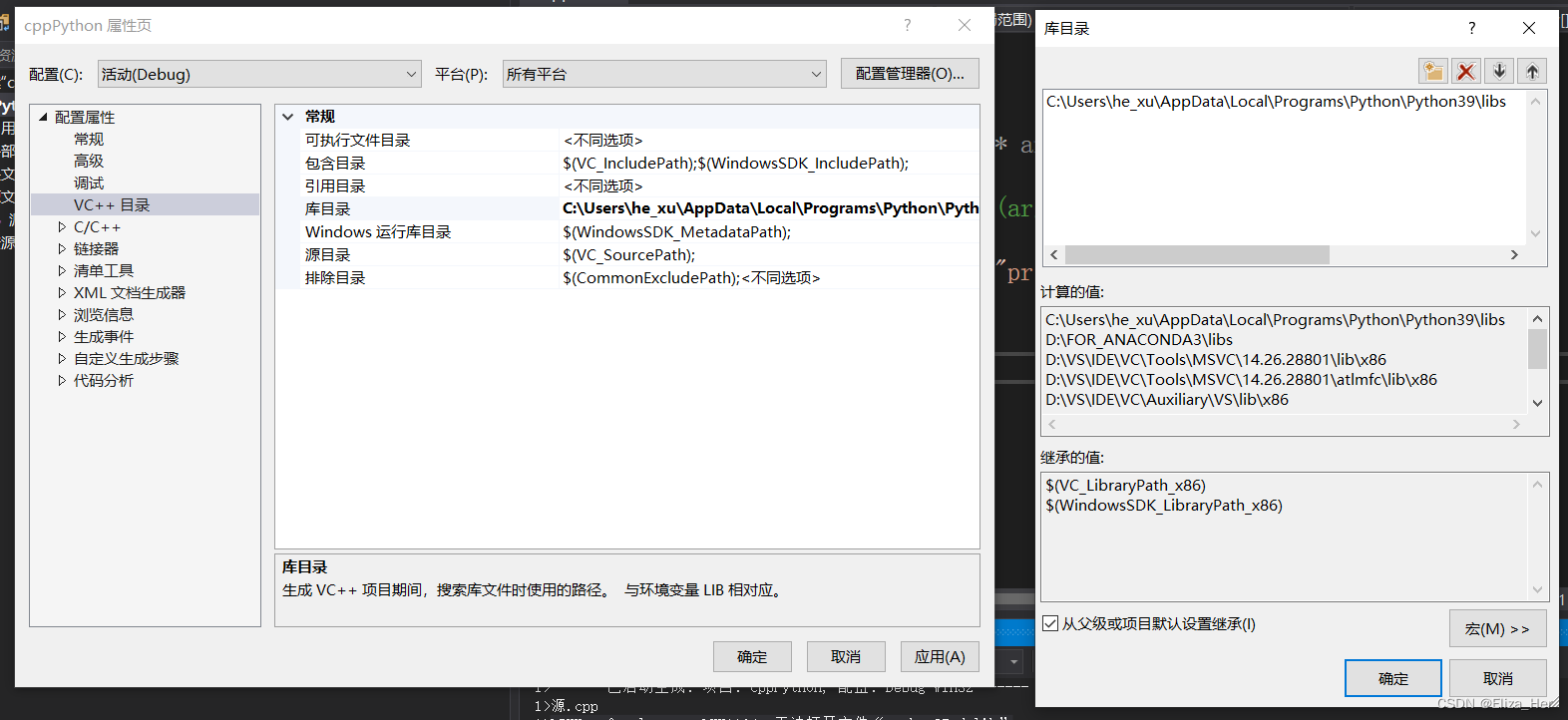
3. 项目→属性→链接器→输入→附加依赖项,添加Python3安装路径\libs\python39.lib。(如果Python版本是3.7则可以写python37.lib,以此类推)

4. 检查版本: 检查一下自己下载的Python是x86还是x64版本的,如果与VS版本不一致,可以在VS窗口上方调整项目版本。

第二步 测试环境
这是一个简单的helloworld程序。如果能够成功运行,则可以直接进入下一节。
- #include <Python.h>
-
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
- Py_Initialize();
- PyRun_SimpleString("print('Hello, world!')");
- Py_Finalize();
- return 0;
- }
运行结果:

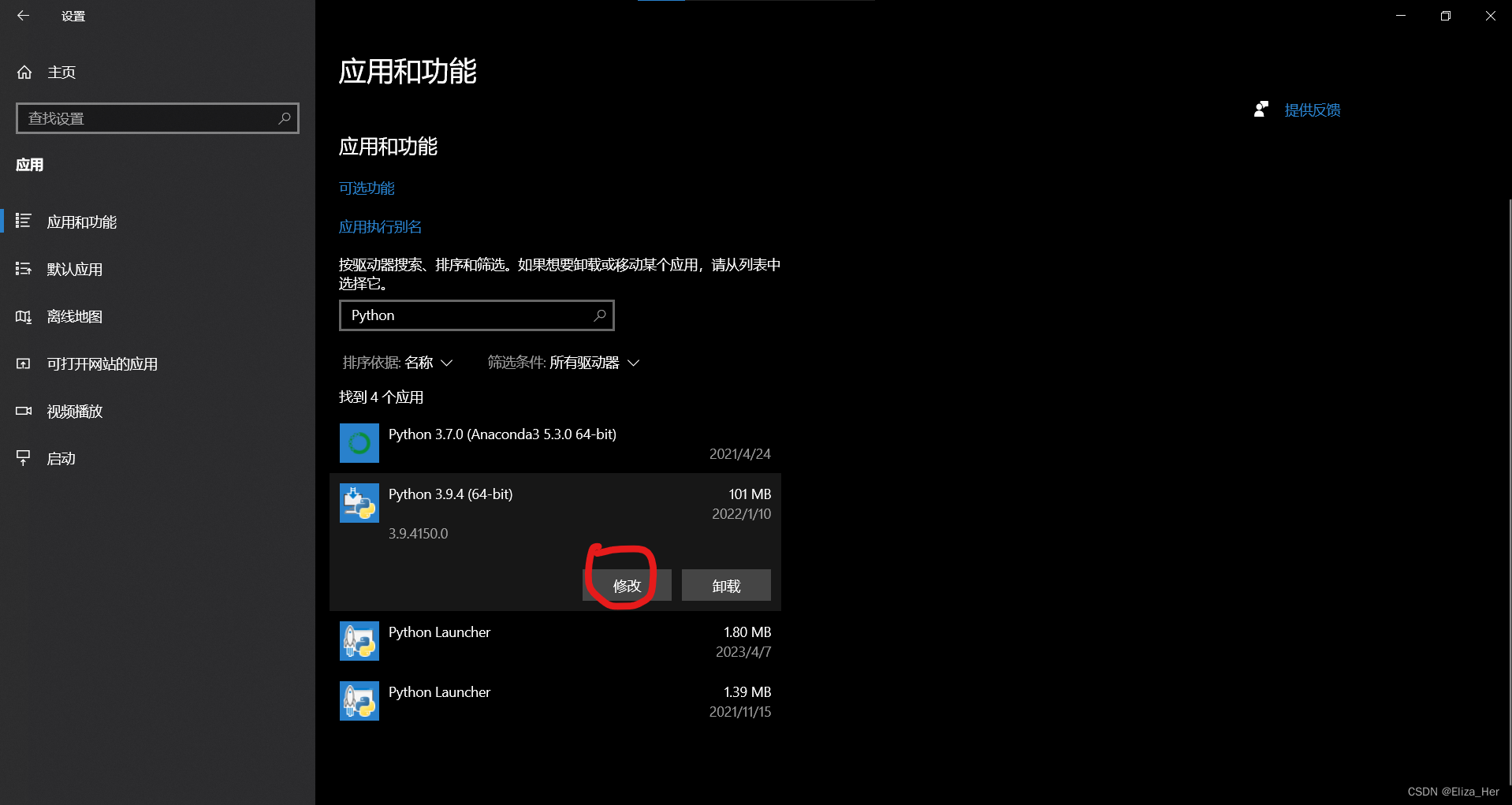
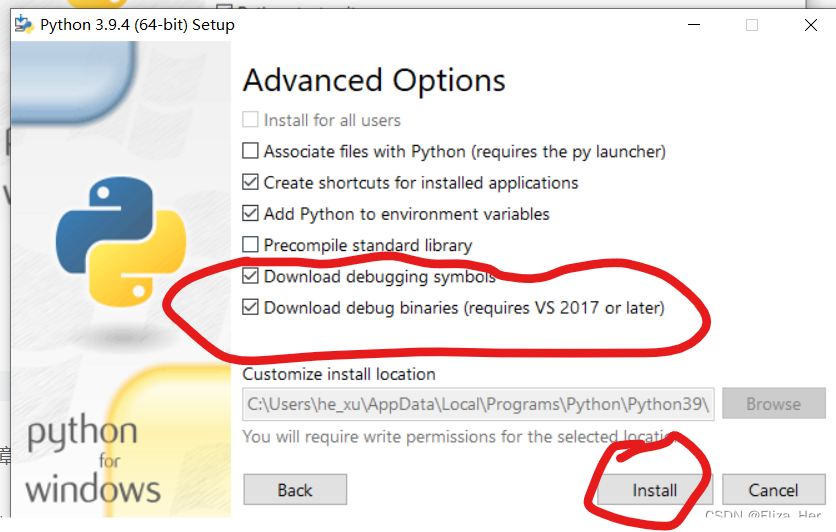
如果出现错误:LINK : fatal error LNK1104: 无法打开文件“python39_d.lib”,则说明没有安装Python的Debug功能,需要为Python增加Debug功能。增加方法如下图:
(注:针对该错误,除了本文中提到的方法,网上还有其它办法可供选择:扩展Python模块系列(一)----开发环境配置 - 建木 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)。)


运行例程
C++调用Python的结构都如下:
- #include <Python.h>
-
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
- Py_Initialize(); //初始化
-
- //... ...
-
- Py_Finalize(); //结束,释放资源
-
- return 0;
- }
注:下文仅包含C++运行或调用Python代码段、脚本、函数、类的基本方法,不包含进阶用法。
考虑到便利性,也由于其在 Python 解释器中被广泛使用, "Python.h" 还包含了一些标准头文件: <stdio.h> , <string.h> , <errno.h> 和 <stdlib.h> 。 如果后面的头文件在你的系统上不存在,它还会直接声明函数 malloc () , free () 和 realloc () 。
——Python官方文档
1. 直接运行Python代码段
- #include <Python.h>
-
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
- Py_Initialize();
-
- PyRun_SimpleString("print('Hello from Python string')");
-
- Py_Finalize();
- return 0;
- }
2. 运行Python脚本
源目录下helloScript.py:
print("Hello from Python script")C++:
- //my_python.c
- #include <Python.h>
-
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
- Py_Initialize();
-
- PyObject* obj = Py_BuildValue("s", "helloScript.py");
- FILE* file = _Py_fopen_obj(obj, "r+");
- if (file != NULL)
- {
- PyRun_SimpleFile(file, "helloScript.py");
- }
-
- Py_Finalize();
- return 0;
- }

3. 导入Python模块,调用Python函数
源目录下hello.py:
- def Hello():
- print("Hello from Python module")
-
- def Add(a, b):
- print ("Add function: ", end="")
- print (str(a) + " + " + str(b) + " = " + str(a+b))
- return a + b
C++:
- #include <Python.h>
-
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
- Py_Initialize();
-
- //必须修改Python路径,否则会找不到Python模块
- PyRun_SimpleString("import sys");
- PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('./')");
-
- PyObject* pModule = NULL;
- PyObject* pFunc = NULL;
-
- //import模块
- pModule = PyImport_ImportModule("hello");//模块文件名
- //找不到模块则报错
- if (pModule == nullptr) {
- PyErr_Print();
- Py_Finalize();
- return 0;
- }
-
- //1. 调用不带参数的函数 Hello()
- pFunc = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "Hello");//函数名
- PyObject_CallFunction(pFunc, NULL);//调用函数
-
- //2. 调用带参数的函数 Add(a, b)
- PyObject* pAdd = NULL;
- PyObject* args = NULL;
- pAdd = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "Add");
- args = Py_BuildValue("(ii)", 123, 456); //设置传入Add的参数
- PyObject* pRet = PyObject_CallObject(pAdd, args); //pRet = Add(123, 456)
-
- //输出返回值
- int ans = 0;
- PyArg_Parse(pRet, "i", &ans);//返回类型转换
- printf("Return C++: ans = %d\n", ans);
-
- Py_Finalize();
-
- return 0;
- }

4. 调用Python类
注:调用类中方法的API不止一套,建议去官网看看,并且建议使用Python3.9版本以上才支持的API,那些API对类的支持更好,不容易出现需要手动加入Python类的self参数的问题。
源目录下helloClass.py:
- class myClass:
- welcome = "Hello from Python class attribute"
-
- def hello(self):
- print("Hello from Python class method")
-
- def minus(self, a, b):
- print(str(a) + " - " + str(b) + " = " + str(a-b))
- return a-b
C++:
(1)Python3.9以下可用:
- #include <Python.h>
-
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
- Py_Initialize();
-
- //必须修改Python路径,否则会找不到Python模块
- PyRun_SimpleString("import sys");
- PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('./')");
-
- PyObject* pModule2 = NULL;
- PyObject* pFunc2 = NULL;
- PyObject* pClass = NULL;
- PyObject* pInstance = NULL;
- PyObject* args2 = NULL;
-
- pModule2 = PyImport_ImportModule("helloClass");//这里是要调用的文件名helloClass.py
- if (pModule2 == NULL)
- {
- PyErr_Print();
- Py_Finalize();
- return 0;
- }
-
- // 模块的字典列表
- PyObject* pDict = PyModule_GetDict(pModule2);
- if (!pDict) {
- PyErr_Print();
- Py_Finalize();
- return 0;
- }
-
- //从字典中获取myClass类
- PyObject* pClassCalc = PyDict_GetItemString(pDict, "myClass");
- if (!pClassCalc) {
- PyErr_Print();
- Py_Finalize();
- return 0;
- }
-
- //构造实例
- PyObject* pInstanceCalc = PyInstanceMethod_New(pClassCalc);
- if (!pInstanceCalc) {
- PyErr_Print();
- Py_Finalize();
- return 0;
- }
-
- //获取pInstanceCalc实例的属性,转换成字符串并输出
- PyObject* obj2 = PyObject_GetAttrString(pInstanceCalc, "welcome");
- PyObject* str = PyUnicode_AsEncodedString(obj2, "utf-8", "strict");
- char* result = PyBytes_AsString(str);
- printf("%s\n", result);
-
- //如果属性是int型,可用下面这句转换属性:
- //int qwq;
- //PyArg_Parse(obj2, "i", &qwq);
-
- //调用无参数Python方法,s和pInstanceCalc对应Python中的self
- PyObject_CallMethod(pClassCalc, "hello", "s", pInstanceCalc);
-
- //调用多参数Python方法,(s,i,i)和pInstanceCalc、12、22 分别对应Python方法中的 self、a、b
- pRet = PyObject_CallMethod(pClassCalc, "minus","(s,i,i)",pInstanceCalc, 12, 22);
- if (!pRet)
- {
- PyErr_Print();
- Py_Finalize();
- return 0;
- }
-
- int res = 0;
- PyArg_Parse(pRet, "i", &res);//转换返回类型
-
- printf("Return C++: ans = %d\n", res);
-
-
- Py_Finalize();
-
- return 0;
- }

(2)Python3.9以上可用:
- PyObject* getClass(const char* fileName, const char* className) {
- //必须修改Python路径,否则会找不到Python模块
- PyRun_SimpleString("import sys");
- PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('./')");
-
- PyObject* pModule = NULL;
- PyObject* pClass = NULL;
- PyObject* pInstance = NULL;
-
-
- pModule = PyImport_ImportModule(fileName);
- if (pModule == NULL)
- {
- PyErr_Print();
- Py_Finalize();
- return NULL;
- //return 0;
- }
-
- // 模块的字典列表
- PyObject* pDict = PyModule_GetDict(pModule);
- if (!pDict) {
- PyErr_Print();
- Py_Finalize();
- return NULL;
- //return 0;
- }
-
- //从字典中获取myClass类
- pClass = PyDict_GetItemString(pDict, className);
- if (!pClass) {
- PyErr_Print();
- Py_Finalize();
- return NULL;
- //return 0;
- }
- //实例化
- pInstance = PyObject_CallObject(pClass, NULL);
-
- return pInstance;
- }
-
-
- int main(){
- Py_Initialize();
-
- PyObject* pInstance = getClass("sarsaScript", "RL");
-
- //调用多参数Python类方法
- //cjoose_action是方法名
- PyObject* pAction = PyUnicode_FromString("choose_action");
- std::string state = "state1";
- PyObject* pState = PyUnicode_FromString(state.c_str());
-
- //参数以NULL结尾
- PyObject* pRet = PyObject_CallMethodObjArgs(pInstance, pAction, pState, NULL);
- if (!pRet)
- {
- PyErr_Print();
- Py_Finalize();
- return -1;
- }
-
- int res = 0;
- PyArg_Parse(pRet, "i", &res);//转换返回类型为int
-
- //调用无参数Python类方法
- //qwq是方法名
- PyObject* pQWQ = PyUnicode_FromString("qwq");
- PyObject_CallMethodNoArgs(pInstance, pQWQ);
-
- Py_Finalize();
- return 0;
- }

把上面的四段代码整合到一起运行,控制台输出为:

参考资料
文档:
- 官方API文档:The Very High Level Layer — Python 3.10.11 documentation
- API文档中文版本:C++调用Python浅析_pyeval_callobject_magictong的博客-CSDN博客
- 官方使用教程:1. 在其它应用程序嵌入 Python — Python 3.7.13 文档
- 官方API手册:Python 中文文档 - Python/C API 参考手册 | Docs4dev
博客:


