- 1gerrit submit撤回_Gerrit使用篇-提交代码,合并代码
- 2《图解密码技术》笔记_图解密码技术学习笔记
- 3算法体系-02第二 时间复杂分析(插入/冒泡/选择/二分)
- 4GitHub Actions入门教程
- 5基于neo4j的体育运动员问答问答系统_neo4j智慧问答
- 6体验文心一言AI大模型生成农行、苏行和南京银行报告_利用大模型生成报告
- 7Android中免root的hook框架Legend原理解析_simhook模块免root
- 8火狐浏览器firefox检测不到U盾证书
- 9C#程序变量统一管理例子 - 开源研究系列文章
- 10若依 验证码出不来 Fontconfig head is null, check your fonts or fonts configuration
【北邮国院大三下】Cybersecurity Law 网络安全法 Week1 Topic1-3_国院物联网大三
赞
踩
北邮国院大三电商在读,随课程进行整理知识点。仅整理PPT中相对重要的知识点,内容驳杂并不做期末突击复习用。个人认为相对不重要的细小的知识点不列在其中。如有错误请指出。转载请注明出处,祝您学习愉快。
编辑软件为Effie,如需要pdf/docx/effiesheet/markdown格式的文件请私信联系或微信联系
WEEK1
由于平台问题,重新导入md会自动生成新的文章,所以要看完整W1请移步
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_63759728/article/details/131098248?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
以下是一些比较定义性的东西,所以基本都是PPT内容翻译。如果考试是类似电商法的case式考法,这些就不用背只需要了解,大概知道什么是什么,有话说就可以。如果有其他变化和新理解,后续会修改这段话
在Week1中,很难总结出像电商法那种很有逻辑的东西,换句话说,PPT给的信息冗杂且无用,阅读下来完全不像电商法那种分几大块去介绍的感觉,法条的占比被拉得很低,对于这个课的更多想法还要在观察一周的课程。Week1的东西就挑着背背吧,毕竟往年题还没有
什么是Cybersecurity
Cyber security is the application of technologies, processes and controls to protect systems, networks, programs, devices and data from cyber attacks
网络安全是技术、流程和控制的应用,以保护系统、网络、程序、设备和数据免受网络攻击
It aims to reduce the risk of cyber attacks, and protect against the unauthorised exploitation of systems, networks and technologies
它旨在降低网络攻击的风险,防止系统、网络和技术受到未经授权的利用
Three distinct elements: information security, privacy and data protection and cybercrime
三个不同的要素:信息安全、隐私和数据保护以及网络犯罪
Information Security 信息安全
Seeks to protect all information assets, whether in hard copy or in digital form
力求保护所有信息资产,无论是纸质副本还是数字形式
Information is one of the most valuable assets
信息是最有价值的资产之一
Good business practice
Digital revolution changed how people communicate and conduct business
数字革命改变了人们沟通和开展业务的方式
New possibilities & challenges
Privacy and Data Protection 隐私与数据保护 (概念辨析)
Data privacy are the regulations, or policies, that governs the use of my data when shared with any entity
数据隐私是指在与任何实体共享时管理我的数据使用的法规或政策
Data protection is the mechanism — that is, the tools and procedures — to enforce the policy and regulation, including the prevention of unauthorized access or misuse of the data that I agreed to share
数据保护是一种机制,即工具和程序,用于执行政策和法规,包括防止未经授权的访问或滥用我同意共享的数据
- 这两个都是Control of personal data
- PPT给出了对control的定义,可以拿来凑字数。Control = the ability to specify the collection, use, and sharing of their data
Information Security x Privacy (概念辨析)
Privacy is an individual’s right to control the use and disclosure of their own personal information
隐私是个人控制使用和披露自己个人信息的权利
Information security is the process used to keep data private
信息安全是用来保持数据私密性的过程
- Security is the process; privacy is the result
Cybercrime 网络犯罪
Cybercrime is an act that violates the law, by using information and communication technology (ICT) to either target networks, systems, data, websites and/or technology or facilitate a crime
网络犯罪是一种违法行为,通过使用信息和通信技术(ICT)攻击网络、系统、数据、网站和/或技术,或为犯罪提供便利
Cybercrime knows no physical or geographic boundaries and can be conducted with less effort, greater ease, and at greater speed and scale than traditional crime
网络犯罪没有物理或地理的界限,与传统犯罪相比,可以更轻松、更轻松、更快、更大规模地进行
这门课我们会学到的三方面的Cybersecurity Law
- Information security obligations 信息安全义务
- Privacy and data protection laws 隐私和数据保护法
- Cybercrime substantive and procedural laws 网络犯罪实体法和程序法
网络安全遇到的Challenge
Technical
Growing number of devices
越来越多的设备
Every computer program, app or website are also software and software often has vulnerabilities
每一个电脑程序,应用程序或网站也是软件,软件往往有漏洞
A virtualized information technology infrastructure (cloud services)
虚拟化的信息技术基础设施(云服务)
Legal
Increasing number, scope and complexity of legal obligations in relation to information security, privacy and data protection, different approaches
与信息安全、隐私和数据保护有关的法律义务的数量、范围和复杂性不断增加,方法也有所不同
Different legal systems between countries, variations in national cybercrime laws, differences in the rules of evidence and criminal procedure, applicability of international treaties
各国法律体系不同,各国网络犯罪法律的差异,证据规则和刑事诉讼规则的差异,国际条约的适用性
网络安全的Trends
With the advent of new technologies (e.g., Internet of Things, drones, robots, self-driving cars), new cybercrime trends will be identified and therefore new information security and privacy measures will need to be developed
随着新技术(如物联网、无人机、机器人、自动驾驶汽车)的出现,将发现新的网络犯罪趋势,因此需要制定新的信息安全和隐私措施
Cyber attacks may involve:
- SPAM with the capacity to deliver range of malware
- 有能力传递各种恶意软件的垃圾邮件
- Spyware and keystroke loggers (3,7 million South Carolina tax records)
- 间谍软件和键盘记录(南卡罗来纳州3700万份税务记录)
- Worms, virus, Trojans
- 蠕虫病毒特洛伊木马
- Phishing / Spear Phishing / Whaling
- 钓鱼/鱼叉钓鱼/捕鲸
- DoS / DDoS
Drivers of Cybersecurity
- Legal
- Growing legal framework establishing safeguarding and information obligation
- 建立保护和信息义务的法律框架不断完善
- Regulatory
- Growing enforcement as a response to ineffective self-regulation
- 加强执法是对无效的自我监管的回应
- Commercial
- Growing awareness of risk, economic and legal consequences, trustworthiness of business transactions
- 对风险、经济和法律后果、商业交易可信度的意识不断增强
Information Security 是要保护什么
Processes, procedures and infrastructure to preserve:
- confidentiality 保密性
- integrity 完整性
- availability of information 信息的可用性
- 这三个简称CIA
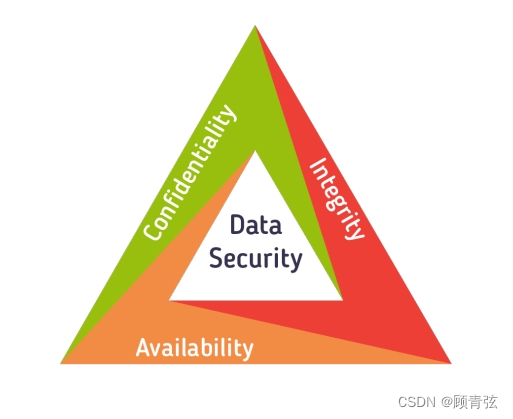
Confidentiality 保密性
Confidentiality means that only people with the right permission can access and use information
保密性意味着只有获得正确许可的人才能访问和使用信息
Protecting information from unauthorised access at all stages of its life cycle
保护信息在其生命周期的所有阶段不受未经授权的访问
Information must be created, used, stored, transmitted, and destroyed in ways that protect its confidentiality
信息的创建、使用、存储、传输和销毁必须以保护其保密性的方式进行
Ensuring confidentiality – encryption, access controls
确保机密性-加密,访问控制
Compromising confidentiality – (intentional) shoulder surfing, social engineering; (accidental) publication
泄露机密——(有意的)肩窥,社会工程;(偶然的)公之于众
It may result in identity theft, threats to public safety
这可能会导致身份盗窃,威胁公共安全
Integrity 完整性
Integrity means that information systems and their data are accurate
完整性意味着信息系统及其数据是准确的
Changes cannot be made to data without appropriate permission
没有适当的许可,不能对数据进行更改
Ensuring integrity – controls ensuring the correct entry of information, authorization, antivirus
确保完整性-控制确保信息、授权、防病毒的正确输入
Compromising integrity – (intentional) employee or external attacks; (accidental) employee error
损害诚信——(故意的)员工或外部攻击;(偶然的)员工失误
Authentication 身份验证
Specific to integrity and confidentiality considerations
具体到完整性和保密性的考虑
Ensuring that a machine or person is that which they purport to be
确保机器或人是他们所宣称的样子
- Creator/sender/signatory of record 记录的创建者/发送者/签署人
- Person who seeks access to it 寻求接近它的人
In analogue world, signatures, handwriting, in person attestation, witnesses, notary public, etc.
在模拟世界中,签名、笔迹、亲自认证、证人、公证人等。
In digital world, may not only be a person but also machine we are seeking to authenticate
在数字世界中,我们要验证的可能不仅是人,还有机器
- Digital Signatures – electronic PKI, other certificates of trust 数字签名-电子PKI,其他信任证书
Availability
Availability is the security goal of making sure information systems are reliable
可用性是确保信息系统可靠的安全目标
Data is accessible
数据是可访问的
Individuals with proper permission can use systems and retrieve data in a dependable and timely manner
获得适当许可的个人可以可靠和及时地使用系统和检索数据
Ensuring availability – recovery plans, backup systems
确保可用性-恢复计划,备份系统
Compromising availability – (intentional) denial of service (DoS) attack, (accidental) outage
影响可用性-(故意的)拒绝服务(DoS)攻击,(意外的)停机
Mitigating risks to the trustworthiness of information of corporations and governments 降低企业和政府信息可信度的风险的方法
- Development of strategies and 制定策略
- Implementation to technologies and procedures in order to preserve its 实施以技术和程序为主,以保存其
- confidentiality
- integrity, and
- availability
Risk management 风险管理
Risk management as means to justify information security laws
风险管理作为证明信息安全法律合理性的手段
= process of listing the risks that an organization faces and taking steps to control them
列出组织面临的风险并采取措施控制这些风险的过程
- Vulnerabilities 缺陷
- Threats 威胁
- Risks 风险
- Safeguards 保障措施
Vulnerabilities 缺陷
- weakness or flaw in the information system that can be exploited 信息系统中可以被利用的弱点或缺陷
- Construction, design mistake 结构、设计错误
- Flaws how internal safeguards is used/not used 内部安全措施使用/不使用的缺陷
Successful attacks take place when vulnerability is exploited
当漏洞被利用时,就会发生成功的攻击
Vulnerabilities的四方面
-
People
- separation of duties principle 职责分离原则
- two or more people need to split a critical task functions 两个或两个以上的人需要拆分一个关键任务的职能
- separation of duties principle 职责分离原则
-
Process
- flaws in organization’s procedures 组织程序上的缺陷
- missing step in a checklist/no checklist, failure to apply hardware and software patches 检查表中缺少步骤/没有检查表,未能应用硬件和软件补丁
- flaws in organization’s procedures 组织程序上的缺陷
-
Facility 设备
- flaws in physical infrastructure 物理基础设施缺陷
- fences, locks, CCTV cameras 围栏,门锁,监控摄像头
- flaws in physical infrastructure 物理基础设施缺陷
-
Technology
- design flaws 设计缺陷
- unpatched applications, improperly configured equipment 未打补丁的应用程序,配置不当的设备
- design flaws 设计缺陷
Threats
Anything that can cause harm to an information system – successful exploits of vulnerabilities
任何可能对信息系统造成伤害的东西——成功地利用漏洞
- Threats to information, networks, systems have increased 对信息、网络和系统的威胁有所增加
- More devices, more use, more ‘always on’ 更多的设备,更多的使用,更多的“总是开启”
- More complex networks with greater ‘attack surface’ 具有更大“攻击面”的更复杂网络
- More devices with IoT; smart watches possibly not connected to enterprise authentication systems 更多物联网设备;智能手表可能没有连接到企业认证系统.
- Attacks have grown more sophisticated 攻击变得更加复杂
- Attacks that take months to achieve goals; undetected
- ‘Ransomware’ = threat to encrypt data unless paid “勒索软件”=威胁加密数据,除非付费
- Attacks that take months to achieve goals; undetected
Relationship between a vulnerability and a threat
An organization does not have sufficient controls to prevent an employee from deleting critical computer files (lack of controls – vulnerability). An employee could delete files by mistake (employee – source of threat) (deleting critical files – threat). If the files are deleted, successful exploit of the vulnerability has taken place. If the file is not recoverable, the incident harms the organizations and its security. Availability is compromised.
组织没有足够的控制来防止员工删除关键的计算机文件(缺乏控制-漏洞)。员工可能误删文件(员工-威胁来源)(删除关键文件-威胁)。如果文件被删除,则表明该漏洞已被成功利用。如果文件不可恢复,则该事件将损害组织及其安全。可用性受到影响。
【简而言之,threat是利用了vulnerability达到的结果,是一个“事件”,而vulnerability是可以利用的漏洞,是一个“东西”】
Threats的四方面
-
Human
- internal and external, includes well-meaning employees and external attackers 内部和外部,包括善意的员工和外部攻击者
-
Natural
- uncontrollable events (fire, flood) 不可控制事件(火灾、洪水)
-
Technology and operational
- operate inside information systems (malicious code, hardware and software failures) 在信息系统内部操作(恶意代码、硬件和软件故障)
-
Physical and environmental
- lack of physical security 缺乏人身安全保障
- Accidental or intentional 意外或故意
- Internal or external attackers 内部或外部攻击者
- lack of physical security 缺乏人身安全保障
Risks
a likelihood that a threat will exploit a vulnerability and cause harm, where the harm is the impact to organization
威胁利用漏洞并造成危害的可能性,其中危害是对组织的影响
** Risk = vulnerability + threat **
Risks can occur at any layer of the information system:
- At the physical hardware or device layer, e.g. when a flood renders servers stored in a basement unavailable; 在物理硬件或设备层,例如当洪水导致存储在地下室的服务器不可用;
- At the various software layers, e.g. when hackers exploit a vulnerability in software; 在各个软件层,例如当黑客利用软件中的漏洞时;
- At the network layer, e.g. when a hacker intercepts data packets as they pass through the network from sender, via routers, to receiver; or, 在网络层,例如,当数据包从发送方通过路由器通过网络传递到接收方时,黑客会拦截数据包
- At the user layer, e.g. through ‘social engineering’, such as convincing users to share their passwords through ‘phishing’ emails 在用户层,例如通过“社会工程”,例如说服用户通过“网络钓鱼”电子邮件分享他们的密码
Risk analysis and management to classify and respond to risks
风险分析和管理,对风险进行分类和应对
Probability a threat will exploit a vulnerability – high, medium, low
威胁利用漏洞的概率-高,中,低
Information security impact – loss of confidentiality, integrity and availability
信息安全影响-机密性、完整性和可用性的损失
Other impacts – loss of life, productivity or profit, property and reputation
其他影响-生命、生产力或利润、财产和声誉的损失
Assessment of impact – address risks that have large impact on information security
影响评估-解决对信息安全有重大影响的风险
Types of responses: risk avoidance, risk mitigation, risk transfer, risk acceptance
反应类型:风险规避、风险缓解、风险转移、风险接受
Safeguards
safeguard reduces the harm posed by information security vulnerabilities or threats
保障措施降低信息安全漏洞或威胁带来的危害
Safeguards can be put in place at all layers of the system:
- At the physical hardware or device layer, e.g. by physically securing server rooms against flooding; 在物理硬件或设备层,例如通过物理保护服务器机房免受水浸;
- At the various software layers, e.g. by installing the latest patches; 在不同的软件层面,例如安装最新的补丁;
- At the network layer, e.g. by using virtual private networks (‘VPN’); and, 在网络层,例如使用虚拟专用网络(VPN)
- At the user layer, by ensuring that all personnel receive appropriate training to recognise phishing emails and other forms of social engineering. 在用户层,通过确保所有人员接受适当的培训,以识别网络钓鱼电子邮件和其他形式的社会工程
Safeguards的三方面
- Administrative 管理
- actions and rules implemented to protect information (need to know rule) 为保护信息而实施的操作和规则(需要了解规则)
- Technical
- logical rules that state how systems will operate (least privilege rule) 描述系统如何运行的逻辑规则(最小特权规则)
- Physical
- actions to protect actual physical resources 保护实际物理资源的行动
Mechanisms Ensuring Information Security 保障信息安全的机制
No single information security law – no single definition
没有单一的信息安全法律,没有单一的定义
Different potential sources of liability: statutes, regulations, contracts, organizational governance, voluntary organizations, private law tort
不同的潜在责任来源:法规、规章、合同、组织治理、自愿组织、私法侵权
Different kinds of information often sought to be protected:
- personal data under data protection laws 数据保护法下的个人数据
- corporate financial information 企业财务信息
- health information 健康信息
- credit card information 信用卡信息
No such thing as perfect information security 没有完美的信息安全
Sources of Obligations
- Laws – rules – regulations
- Common law
- body of law that developed through legal tradition and court cases (case law/judge-made law) – impact on torts, contract, and property law 通过法律传统和法庭案件(判例法/法官制定的法律)发展起来的法律体系——对侵权法、合同法和财产法的影响
- Statutory law 成文法
- written law that is adopted by the governments 政府通过的成文法
- 【关于这两个法律的不同:(以下斜体答案来自newBing)The main difference between common law and statutory law is that common law is based on precedent, or previous court decisions, while statutory law is based on written laws passed by a legislature or other government agency. Common law is also procedural, meaning it regulates how lawsuits are conducted, while statutory law is substantive, meaning it defines rights and duties of citizens 普通法和成文法之间的主要区别在于普通法是基于先例或以前的法院判决,而成文法是基于立法机关或其他政府机构通过的成文法。普通法也是程序法,这意味着它规定了诉讼如何进行,而成文法是实体法,这意味着它规定了公民的权利和义务】
- Rules
- governments delegate power to agencies to create rules, enforce rules, and review rules 政府授权各机构制定规则、执行规则和审查规则
- Regulations
- regulatory authorities have the power to create and enforce regulations 监管机构有权制定和执行法规
- Common law
- Standards
Common Law
Tort law
- A tort, in common law jurisdictions, is a civil wrong that unfairly causes someone else to suffer loss or harm resulting in legal liability for the person who commits the tortious act 侵权行为,在普通法司法管辖区,是一种民事错误,不公平地导致他人遭受损失或伤害,并导致实施侵权行为的人承担法律责任
- Duty – breach – causation – harm elements
Contract Law
- A contract is an agreement, giving rise to obligations, which are enforced or recognised by law 合同是一种协议,产生了由法律强制执行或承认的义务
Regulations 规则
Sector regulators are increasingly auditing companies for their information security management and also issuing ‘regulatory guidance’ or ‘best practice advisories’ on information security
行业监管机构越来越多地对公司的信息安全管理进行审计,并发布关于信息安全的“监管指导”或“最佳实践建议”
Standard
Emerging guidance in form of ‘standards’
以“标准”形式出现的指导
These standards determine how to comply with a legal duty or self-imposedobligation for adequate/reasonable/appropriate information security
这些标准确定如何遵守充分/合理/适当的信息安全的法定义务或自我强制义务
- Standards bodies (ISO; PCI Council)
- International organizations (OECD Guidelines)
- Recent legislation with regulations detailing the necessary steps to the process that will meet the duty of care (GLBA, HIPAA)
Statutes 议会立法,章程
都是一些例子,直接看图得了


Scope of Obligations
These legal obligations specify a duty:
这些法律义务规定了一种义务:
- For example, to provide adequate or reasonable or appropriate security 例如,提供充分的、合理的或适当的保障
They don’t usually give specific guidance as to what that means or how it is to be accomplished
他们通常不会给出具体的指导,说明这意味着什么或如何实现
Issues
The duty to keep information secure is not further specified in the statutes
保护信息安全的义务在法规中没有进一步规定
The GDPR indicates: ‘Having regard to the state of the art and the cost of their implementation, such measures shall ensure a level of security appropriate to the risks represented by the processing and the nature of the data to be protected.’
GDPR指出:“考虑到技术水平和实施成本,此类措施应确保与处理所代表的风险和被保护数据的性质相适应的安全水平。”
A cost/risk analysis qualifies an appropriate level of security
成本/风险分析确定了适当的安全级别
【上面这些东西确实没有一条主逻辑链,所以ppt很乱,我整理的也很乱,将就看吧,也没啥内容】
什么是cybersecurity中的cyber
It might potentially include any device that has the ability to communicate
它可能包括任何具有通信能力的设备
- Cybersecurity refers to the systems, contracts and policies we put in place to manage risk with regards to Cyberspace 网络安全是指我们为管理网络空间风险而制定的系统、合同和政策
网络安全的main risk areas
- Threats to corporate files 公司文件威胁
- Loss of files 文件丢失
- Email attacks and theft 电子邮件攻击和盗窃
- Threats to industrial control systems 对工业控制系统的威胁
- Threats to confidential information 对机密信息的威胁
- Other commercial risks
网络安全的main vulnerabilities
- Password and policy issues 密码和策略问题
- BYOD and shadow IT BYOD和影子IT
- Loss or theft of devices 设备丢失或被盗
- Technical flaws 技术的缺陷
- Out-of-date applications 过时的应用程序
- Insider threats 内部威胁
- Data storage issues 数据存储问题
- SQL injections, cryptographic flaws SQL注入,密码漏洞
- Cloud-based storage and systems 基于云的存储和系统
接下来要谈的是EU的information security相关问题
Conclusions of EU
【为什么把conclusion放前面,因为PPT的东西太乱了,conclusion给的应该都是重点,带着这些重点再往后看】
- No single source of Information Security obligations – no single definition 没有单一来源的信息安全义务-没有单一的定义
- Different types of information – different level of protection –different mechanisms 不同类型的信息——不同级别的保护——不同的机制
- EU approach is a principle-based regulation 欧盟的做法是基于原则的监管
Directives / Regulations 指示/规例
- Privacy
- EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) 欧盟的通用数据保护条例
- Telecommunications networks/services
- ePrivacy Directive (regulates the use of electronic communications services) 电子资料私隐指引(规管电子通讯服务的使用)
- Critical Infrastructure 关键基础设施
- Network and Information Systems Directive (NIS Directive) 网络和信息系统指令(NIS指令)
GDPR
Introduction
Organisations that decide to collect and process personal data for their own purposes are known as controllers
决定为自己的目的收集和处理个人数据的组织被称为控制者
A controller may engage a service provider or processor to process personal data on behalf of the controller
控制者可以聘请服务提供者或处理者代表控制者处理个人数据
A processor is an individual or legal person or other body that processes personal data on behalf of the controller
处理者是指代表控制者处理个人数据的个人、法人或其他团体
Scope
The GDPR regulates the processing of personal data
GDPR规范了个人数据的处理
Personal data is any information relating to an identified or identifiable natural person (‘data subject’)
个人数据是指与已识别或可识别自然人(“数据主体”)有关的任何信息。
Identifiable natural person is one who can be identified, directly or indirectly, in particular by reference to an identifier such as a name, an identification number, location data, an online identifier or to one or more factors specific to the physical, physiological, genetic, mental, economic, cultural or social identity of that natural person
可识别自然人是指可以直接或间接识别的自然人,特别是通过参考一个标识符,如姓名、识别号码、位置数据、在线标识符,或参考该自然人的身体、生理、遗传、心理、经济、文化或社会身份的一个或多个特定因素
Relates to living individuals only
只涉及活着的个人
Special categories of personal data is subject to a stricter regime
特殊类别的个人资料受到更严格的制度管制
- Racial or ethnic origin 种族或民族起源
- Political opinions 政治意见
- Religious or philosophical beliefs 宗教或哲学信仰
- Trade union membership 工会会员资格
- Genetic data 遗传学数据
- Biometric data for the purpose of uniquely identifying a natural person 用于唯一识别自然人的生物特征数据
- Data concerning health 关于健康的数据
- Data concerning a natural person’s sex life or sexual orientation 有关自然人性生活或性取向的资料
Principles
- Principles-based regulation 基于原则的监管
- The EU has adopted similar risk-based safeguarding and information obligations in respect of telecommunication networks and payment services, as well as under the NIS Directive and the e-Privacy Directive 欧盟在电信网络和支付服务方面,以及在NIS指令和电子隐私指令下,也采取了类似的基于风险的保障和信息义务
- Lawfulness, fairness and transparency 依法、公平、透明
- Purpose limitation 目的限制
- Data minimisation 数据最小化
- Accuracy 准确性
- Storage limitation 储存限量
- Integrity and Confidentiality 数据完整性和隐私保护
- ensures appropriate security of personal data, including protection against unauthorised or unlawful processing and against accidental loss, destruction or damage, using appropriate technical or organisational measures 使用适当的技术或组织措施,确保个人资料的适当安全,包括防止未经授权或非法处理,以及防止意外遗失、破坏或损坏
- Accountability 责任
Information Security Obligation 信息安全义务
- Safeguarding obligations, which require organisations to put in place ‘appropriate and proportionate’ security measures, and 保护义务,要求组织实施“适当和相称的”安全措施
- Information obligations, which require the sharing or disclosure of information 信息义务,即要求分享或披露信息
- Article 32 requires that the controller:
- Taking into account the state of the art, the costs of implementation and the nature, scope, context and purposes of processing as well as the risk of varying likelihood and severity for the rights and freedoms of natural persons, the controller and the processor shall implement appropriate technical and organisational measures to ensure a level of security appropriate to the risk 考虑到技术水平、实施成本、处理的性质、范围、背景和目的,以及对自然人的权利和自由具有不同可能性和严重程度的风险,控制者和处理者应实施适当的技术和组织措施,以确保与风险相适应的安全水平
- This includes, inter alia: 其中包括:
- the pseudonymisation and encryption of personal data; 个人资料的假名化和加密;
- the ability to ensure the ongoing confidentiality, integrity, availability and resilience of processing systems and services; 确保处理系统和服务的持续保密性、完整性、可用性和弹性的能力;
- the ability to restore the availability and access to personal data in a timely manner in the event of a physical or technical incident; 在发生物理或技术事件时,及时恢复个人数据的可用性和访问的能力;
- a process for regularly testing, assessing and evaluating the effectiveness of technical and organisational measures for ensuring the security of the processing 定期测试、评估和评价确保处理安全的技术和组织措施的有效性的过程
- 【关于inter alia,详情可以看interalia在法律文件中的使用及译法 (baidu.com),拉丁语,可以理解为“其中”的意思】
Information Obligation
- Article 33 creates a legal a duty on all organisations to report certain types of personal data breach to the relevant supervisory authority 第33条规定,所有组织都有法律义务向相关监管机构报告某些类型的个人数据泄露
- within 72 hours of becoming aware of the breach, where feasible 在可能的情况下,在72小时内发现该漏洞
- Article 34 requires the controller to notify data subjects affected or potentially affected by breach 第34条要求控制者通知受违约影响或可能受违约影响的数据主体
Data Breach 数据外泄
Data breach is a breach of security leading to the accidental or unlawful destruction, loss, alteration, unauthorised disclosure of, or access to, personal data
数据泄露是指违反安全导致意外或非法破坏、丢失、更改、未经授权披露或访问个人数据
- This includes breaches that are the result of both accidental and deliberate causes 这包括意外和故意原因造成的违约
- A security incident that has affected the confidentiality, integrity or availability of personal data 影响个人资料的机密性、完整性或可用性的安全事件
When a personal data breach has occurred, organisations need to establish the likelihood and severity of the resulting risk to people’s rights and freedoms
当发生个人数据泄露时,组织需要确定由此对人们的权利和自由造成风险的可能性和严重程度
- Likelihood of risk –> need to report it 有风险的可能性- >需要报告
- No likelihood of risk –> no need to report it 风险的可能性- >需要报告
The adverse affect of a security incident on individuals may include emotional distress, and physical and material damage
安全事件对个人的不利影响可能包括情绪困扰、身体和物质损害
Contract Law相关
GDPR Article 28 states that controllers must include in contracts with processors
GDPR第28条规定,控制者必须在与处理者的合同中包括
- The processor shall not engage another processor without prior specific or general written authorisation of the controller 未经控制者事先明确或一般书面授权,处理者不得与其他处理者接触
- Processing by a processor shall be governed by a contract or other legal act 处理者的处理应受合同或其他法律行为的约束
- Sets out the subject-matter and duration of the processing, the nature and purpose of the processing, the type of personal data and categories of data subjects and the obligations and rights of the controller 列明处理的主题事项和持续时间、处理的性质和目的、个人数据的类型和数据主体的类别,以及控制者的义务和权利
NIS Directive 2
Introduction
NIS Directive 2 regulates the cybersecurity of critical national infrastructure, and updates the previous version
NIS指令2规范了关键国家基础设施的网络安全,并更新了之前的版本
- It covers more sectors and activities than before, streamlines reporting obligations and addresses supply chain security 它涵盖了比以前更多的部门和活动,简化了报告义务,并解决了供应链安全问题
It applies to providers of critical national infrastructure (CNI):
它适用于关键国家基础设施(CNI)的提供商:
- Operators of essential services (OES), which are directly responsible for CNI 直接负责CNI的基本服务(OES)运营商
- Digital service providers (DSPs), which provide services upon which others, including OES, are reliant 数字服务提供商(dsp),提供其他人(包括OES)依赖的服务
Scope
Operators of essential services (OES) provide a listed service in one of seven critical infrastructure sectors, and energy, transport, banking, financial markets, health, drinking water, and digital infrastructure
基本服务(OES)运营商在能源、交通、银行、金融市场、卫生、饮用水和数字基础设施等七个关键基础设施领域之一提供所列服务
they operate on such a scale that their service is “essential for the maintenance of critical societal and economic activities”
它们的运作规模如此之大,以至于它们的服务“对于维持关键的社会和经济活动至关重要”。
Digital service is a new subset of the category of service known as ‘information society services’ which is any service normally provided for remuneration, at a distance, by electronic means and at the individual request of a recipient of services
数字服务是被称为“信息社会服务”的服务类别的一个新子集,它是指通常通过电子手段并应服务接受者的个人要求提供的有偿服务
Digital service providers (DSPs) are: 数码服务供应商包括:
- an online marketplace; 在线市场
- an online search engine; or 在线搜索引擎
- a cloud computing service 云计算服务
Tort Law
A private law mechanism
私法机制
Data controllers can be held liable under the tort of negligence for damages caused by cybersecurity incidents that they should have reasonably foreseen and prevented or mitigated
根据过失侵权法,数据控制者可能对他们本应合理预见、预防或减轻的网络安全事件造成的损害承担责任
To hold data controllers liable, a court would have to find that (i) the operator had a duty of care to the person(s) who suffered harm which (ii) the operator failed to fulfil
为了让数据控制者承担责任,法院必须认定(i)运营者对遭受伤害的人负有注意义务,而(ii)运营者未能履行
Requirement
Duty – breach – causation – harm
义务-违约-因果-损害
A duty of care may arise from:
- common law principles governing negligence 管辖过失的普通法原则
- a special / contractual relationship between the defendant and the claimant 被告与索赔人之间的特殊/合同关系
- from a statute or regulation governing a specific activity 来自管理某一特定活动的法令或规章
There must be a proximity between the parties for a duty of care to exist
为了注意义务的存在,当事人之间必须有接近性
Foreseeability means that a person can be held liable only when they should reasonably have foreseen that their negligent act would imperil others
可预见性意味着只有当一个人合理地预见到自己的过失行为会危及他人时,他才能承担责任
Damage needs to be proven by claimants – economic loss or emotional harm
损害需要由索赔人证明——经济损失或精神伤害


