- 1异常检测(Anomaly Detection)
- 2Git常用配置与使用_git config username
- 3Git:远程分支----git pull和git push命令用法介绍_git pull 远程分支名:本地分支名
- 4ChatGPT 的结构:Encoder-Decoder_chatgpt decoder
- 5百度Easy_DL之模型训练_百度模型训练
- 6Kotlin:字符串(String,你值得拥有_kotlin截取字符串
- 7jmeter接口自动化
- 8当ChatGLM3能用搜索引擎时
- 9Mac M1 安装 nvm_now using node v18.12.1 (npm v8.19.2)
- 10Vue中Element的下载
C++初阶:vector类
赞
踩
vector的介绍及使用
vector(顺序表)的介绍
vector - C++ 参考 (cplusplus.com)
vector的使用
- void test_vector1()
- {
- /*vector<int> v;
- v.push_back(1);
- v.push_back(2);
- v.push_back(3);
- v.push_back(4);*/
- vector<int> v1;
- vector<int> v(10, 1);
- vector<int> x(v);
-
- for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
- {
- cout << v[i] << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
-
- for (size_t i = 0; i < x.size(); i++)
- {
- cout << x[i] << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
-
- vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();
- while (it != v.end())
- {
- cout << *it << " ";
- ++it;
- }
- cout << endl;
-
- for (auto e : v)
- {
- cout << e << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
Capacity:
// 测试vector的默认扩容机制
void TestVectorExpand()
{
size_t sz;
vector<int> v;
sz = v.capacity();
cout << "making v grow:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
{
v.push_back(i);
if (sz != v.capacity())
{
sz = v.capacity();
cout << "capacity changed: " << sz << '\n';
}
}
}
vs:运行结果:vs下使用的STL基本是按照1.5倍方式扩容
making foo grow :
capacity changed : 1
capacity changed : 2
capacity changed : 3
capacity changed : 4
capacity changed : 6
capacity changed : 9
capacity changed : 13
capacity changed : 19
capacity changed : 28
capacity changed : 42
capacity changed : 63
capacity changed : 94
capacity changed : 141
g++运行结果:linux下使用的STL基本是按照2倍方式扩容
making foo grow :
capacity changed : 1
capacity changed : 2
capacity changed : 4
capacity changed : 8
capacity changed : 16
capacity changed : 32
capacity changed : 64
capacity changed : 128
// 如果已经确定vector中要存储元素大概个数,可以提前将空间设置足够
// 就可以避免边插入边扩容导致效率低下的问题了
void TestVectorExpandOP()
{
vector<int> v;
size_t sz = v.capacity();
v.reserve(100); // 提前将容量设置好,可以避免一遍插入一遍扩容
cout << "making bar grow:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
{
v.push_back(i);
if (sz != v.capacity())
{
sz = v.capacity();
cout << "capacity changed: " << sz << '\n';
}
}
}
- void test_vector2()
- {
- size_t sz;
- vector<int> v;
- v.reserve(100);
- sz = v.capacity();
- cout << "making v grow:\n";
- for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
- {
- v.push_back(i);
- if (sz != v.capacity())
- {
- sz = v.capacity();
- cout << "capacity changed: " << sz << '\n';
- }
- }
-
- cout << v.size() << endl;
- cout << v.capacity() << endl;
- v.reserve(10);
- cout << v.size() << endl;
- cout << v.capacity() << endl;
-
- cout << "--------------" << endl;
-
- cout << v.size() << endl;
- cout << v.capacity() << endl;
- v.resize(10);
- cout << v.size() << endl;
- cout << v.capacity() << endl;
-
- cout << "--------------" << endl;
-
-
- v.shrink_to_fit();
- cout << v.size() << endl;
- cout << v.capacity() << endl;
-
- vector<int> a;
- a.resize(10, 1);
- for (auto e : a)
- {
- cout << e << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
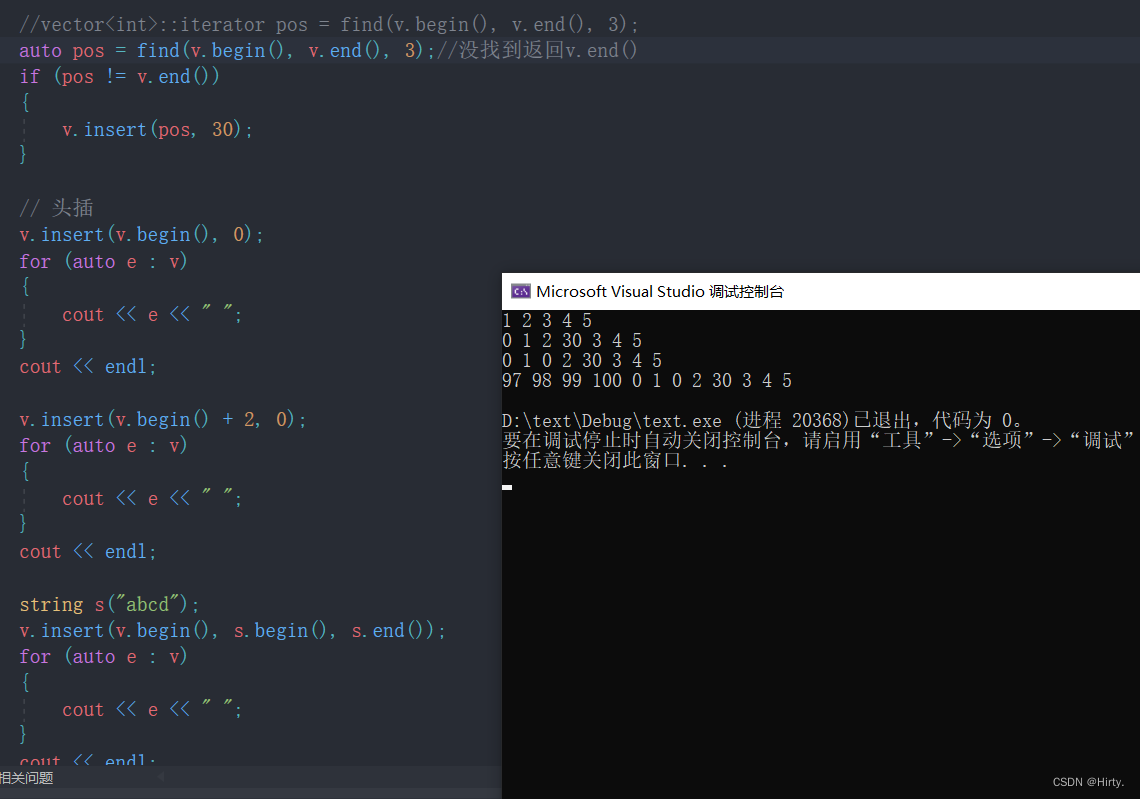
vector类中没有find函数,需要调用算法库(#include<algorithm>)中的find函数
vector::insert - C++ 参考 (cplusplus.com) 跟string类中的insert有些不同;不通过下标插入,用迭代器
- void test_vector3()
- {
- vector<int> v;
- v.push_back(1);
- v.push_back(2);
- v.push_back(3);
- v.push_back(4);
- v.push_back(5);
-
- for (auto e : v)
- {
- cout << e << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
-
- //vector<int>::iterator pos = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 3);
- auto pos = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 3);//没找到返回v.end()
- if (pos != v.end())
- {
- v.insert(pos, 30);
- }
-
- // 头插
- v.insert(v.begin(), 0);
- for (auto e : v)
- {
- cout << e << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
-
- v.insert(v.begin() + 2, 0);
- for (auto e : v)
- {
- cout << e << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
-
- string s("abcd");
- v.insert(v.begin(), s.begin(), s.end());
- for (auto e : v)
- {
- cout << e << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
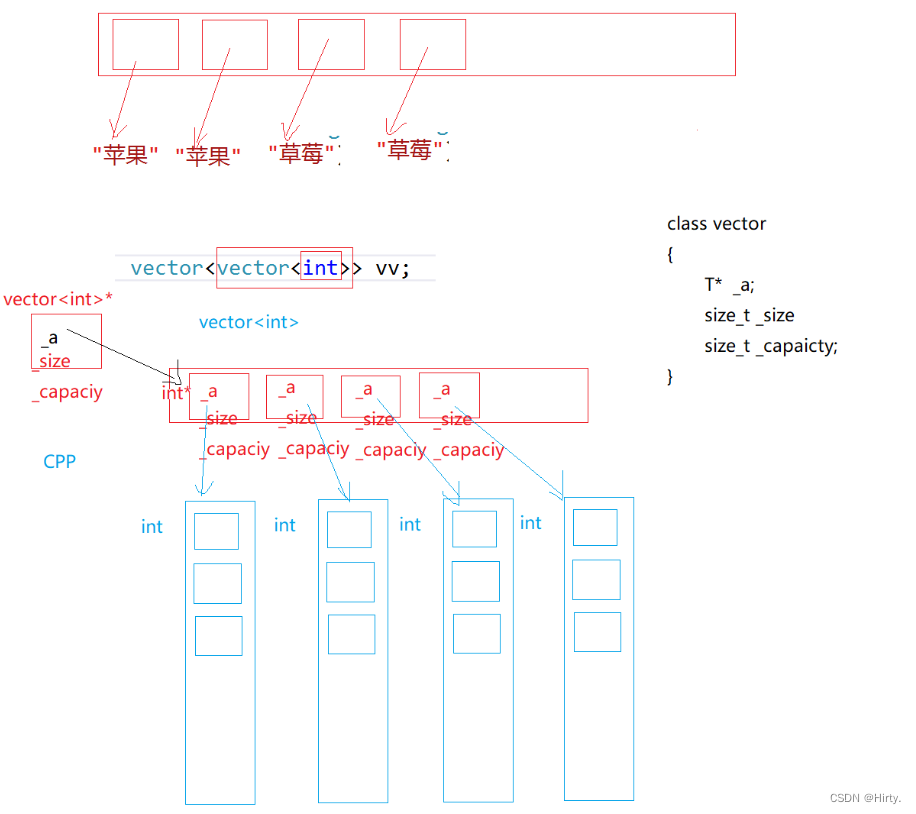
对象数组:
- void test_vector()
- {
- // 对象数组
- vector<string> v;
- string s1("苹果");
- v.push_back(s1);
- v.push_back(string("香蕉"));
- v.push_back("草莓");
-
- vector<vector<int>> vv;//二维数组
- }
vector 迭代器失效问题。(重点)
1. 会引起其底层空间改变的操作,都有可能是迭代器失效
- #include <iostream>
- using namespace std;
- #include <vector>
- int main()
- {
- vector<int> v{1,2,3,4,5,6};
-
- auto it = v.begin();
-
- // 将有效元素个数增加到100个,多出的位置使用8填充,操作期间底层会扩容
- // v.resize(100, 8);
-
- // reserve的作用就是改变扩容大小但不改变有效元素个数,操作期间可能会引起底层容量改变
- // v.reserve(100);
-
- // 插入元素期间,可能会引起扩容,而导致原空间被释放
- // v.insert(v.begin(), 0);
- // v.push_back(8);
-
- // 给vector重新赋值,可能会引起底层容量改变
- v.assign(100, 8);
-
- /*
- 出错原因:以上操作,都有可能会导致vector扩容,也就是说vector底层原理旧空间被释放掉,
- 而在打印时,it还使用的是释放之间的旧空间,在对it迭代器操作时,实际操作的是一块已经被释放的
- 空间,而引起代码运行时崩溃。
- 解决方式:在以上操作完成之后,如果想要继续通过迭代器操作vector中的元素,只需给it重新
- 赋值即可。
- */
- while(it != v.end())
- {
- cout<< *it << " " ;
- ++it;
- }
- cout<<endl;
- return 0;
- }
2. 指定位置元素的删除操作--erase
- #include <iostream>
- using namespace std;
- #include <vector>
- int main()
- {
- int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
- vector<int> v(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(int));
- // 使用find查找3所在位置的iterator
- vector<int>::iterator pos = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 3);
- // 删除pos位置的数据,导致pos迭代器失效。
- v.erase(pos);
- cout << *pos << endl; // 此处会导致非法访问
- return 0;
- }
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
int main()
{
vector<int> v{ 1, 2, 3, 4 };
auto it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end()) //导致it错过判断条件,永远大于v.end()
{
if (*it % 2 == 0)
v.erase(it);
++it;
}return 0;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v{ 1, 2, 3, 4 };
auto it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
if (*it % 2 == 0)
it = v.erase(it);
else
++it;
}
return 0;
}
3.注意:Linux下,g++编译器对迭代器失效的检测并不是非常严格,处理也没有vs下极端。
// 1. 扩容之后,迭代器已经失效了,程序虽然可以运行,但是运行结果已经不对了
int main()
{
vector<int> v{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i)
cout << v[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
auto it = v.begin();
cout << "扩容之前,vector的容量为: " << v.capacity() << endl;
// 通过reserve将底层空间设置为100,目的是为了让vector的迭代器失效
v.reserve(100);
cout << "扩容之后,vector的容量为: " << v.capacity() << endl;// 经过上述reserve之后,it迭代器肯定会失效,在vs下程序就直接崩溃了,但是linux下不会
// 虽然可能运行,但是输出的结果是不对的
while (it != v.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
程序输出:
1 2 3 4 5
扩容之前,vector的容量为: 5
扩容之后,vector的容量为 : 100
0 2 3 4 5 409 1 2 3 4 5
// 2. erase删除任意位置代码后,linux下迭代器并没有失效
// 因为空间还是原来的空间,后序元素往前搬移了,it的位置还是有效的
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
int main()
{
vector<int> v{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
vector<int>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 3);
v.erase(it);
cout << *it << endl;
while (it != v.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
程序可以正常运行,并打印:
4
4 5// 3: erase删除的迭代器如果是最后一个元素,删除之后it已经超过end
// 此时迭代器是无效的,++it导致程序崩溃
int main()
{
vector<int> v{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
// vector<int> v{1,2,3,4,5,6};
auto it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
if (*it % 2 == 0)
v.erase(it);
++it;
}
for (auto e : v)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
========================================================
// 使用第一组数据时,程序可以运行
[sly@VM - 0 - 3 - centos 20220114]$ g++ testVector.cpp - std = c++11
[sly@VM - 0 - 3 - centos 20220114]$ . / a.out
1 3 5
======================================================== =
// 使用第二组数据时,程序最终会崩溃
[sly@VM - 0 - 3 - centos 20220114]$ vim testVector.cpp
[sly@VM - 0 - 3 - centos 20220114]$ g++ testVector.cpp - std = c++11
[sly@VM - 0 - 3 - centos 20220114]$ . / a.out
Segmentation fault
4.与vector类似,string在插入+扩容操作+erase之后,迭代器也会失效
#include <string>
void TestString()
{
string s("hello");
auto it = s.begin();
// 放开之后代码会崩溃,因为resize到20会string会进行扩容
// 扩容之后,it指向之前旧空间已经被释放了,该迭代器就失效了
// 后序打印时,再访问it指向的空间程序就会崩溃
//s.resize(20, '!');
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
it = s.erase(it);
// 按照下面方式写,运行时程序会崩溃,因为erase(it)之后
// it位置的迭代器就失效了
// s.erase(it);
++it;
}
}