- 1各种文字生成图片的AIGC模型_文本生成图像的模型
- 2依据pagesize和pageindex参数来进行分页出现重复数据问题解决方法
- 3目标检测系列(二)yolov1的全面讲解
- 4Mysql 启动错误:Error while setting value ‘STRICT_TRANS_TABLES, NO_ZERO_IN_DATE, NO_ZERO_DATE, ERROR_FOR_
- 5三星电视安装Jellyfin
- 6java比较字符串大小写_Java如何实现不区分字符串大小写进行比较
- 7python faiss 记录_faiss python 文档
- 8【2024最新版】超详细Kali安装保姆级教程,Kali Linux环境配置和使用指南,看完这一篇就够了(1)_kali2024默认密码
- 9Guitar Pro8永久破解版激活码2024专业音乐创作必备_guitarpro8 crack
- 10Hive笔记_hive对于主题、集市是如何理解的
Android 高德地图API(新版)_高德地图最新api
赞
踩
新版高德地图
前言
2020年的时候我写了关于高德地图的使用,在当时你按照文章是没有问题,然而现在到了2024年了,这几年高德的SDK发生了变化,Android Studio发生了变化,不变的是什么呢?就是学校的老师还是让一个没接触过Android的学生去完成相关的功能,定位地图之类的,然后不会怎么办呢?就搜索到我的文章了,一操作发现不对,几百个人问同样的问题,我是真的回答累了,因此我打算重新写一遍,根据最新的内容来写,从内容上和之前的文章大概相同,下面进入正文。
正文
在此之前呢,默认都没有账号,因此需要先注册一个账号才行,点击高德开放平台进入主页面。

完成账号的注册,注册的类型如果没有公司就选择个人开发者,注册完成之后登录,登录之后就创建应用。
一、创建应用
点击 控制台 → 应用管理 → 我的应用
然后点击右上角 创建新应用 按钮,会出现弹窗,输入内容。

点击创建按钮。完成之后我们需要添加Key。
点击 添加Key,出现弹窗,弹窗中需要我们配置Android工程中的内容,弹窗如下图所示:

你可以和我写的一样,这里选择Android平台,还有3个输入框需要我们填写值,其中有红色 * 号的是必填项,也就是说,这个调试版安全码SHA1我们可以不填,但是我还是会说明该怎么获取。这个网页先保留好,先别关了。
- ① 发布版安全码SHA1就是你的应用发布正式版本时的安全码,常规是使用jks秘钥来生成release包。
- ② 调试版安全码SHA1就是你的应用通过usb直接运行在手机或者虚拟机时的安全码,同一个项目在不同的电脑上运行,这个安全码各不相同。
- ③ PackageName 就是你的应用包名。
① 获取PackageName
要获取PackageName 就需要创建一个Android 项目,而这个项目创建也有很多细节可以说明,先看看我的Android Studio版本:

这个版本是属于比较新的,如果你还使用的老版本,那么参考老版本的文章,下面我们创建工程,这里要选择Empty Views Activity,别选错了。
点击Next,然后我们需要注意的地方就来了,首先是Package name也就是我们需要填到网页里的内容,也是项目的包名,然后项目的编程语言我们选择了Java,因为相比于不会Java的来说,不会Kotlin的更多,最后一点,就是配置文件所使用的语言,这里我使用了Groovy,默认是Kotlin。目前很多的SDK配置还是基于Groovy的,如果你使用了Kotlin,那么可能就会出现一些问题,这些问题我同样回答的烦了。
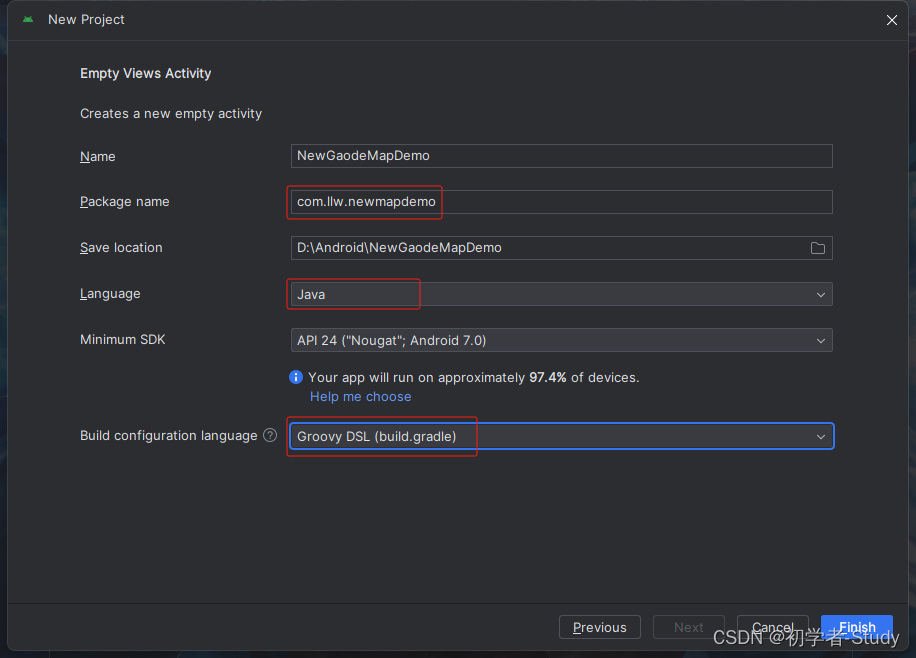
请对照我上面的配置去设置你的项目,包名你可以自行更改为自己习惯的,改好之后点击Finish,完成项目创建,与此同时我们将包名复制进行,如下图所示:

现在我们还差两个值需要填写,等项目创建完成之后我们就来获取。创建成功之后我们运行在真机上,什么是真机,就是Android手机,不要使用AS的虚拟机或者其他第三方虚拟机,为什么呢?因为你在使用SDK的时候会出现问题。没有真机的自己想办法,不要再问我虚拟机出现问题怎么办了。
OK ,真机上运行成功,我使用的是荣耀V40,Android 12的系统版本。下面我们来获取调试版安全码SHA1。
② 获取调试版安全码SHA1
Windows电脑,使用快捷键Win + R ,输入cmd,进入命令窗口。
输入cd .android
cd .android
- 1
先切换到.android目录下,然后输入如下指令:
keytool -list -v -keystore debug.keystore
- 1
然后回车,如下图所示:
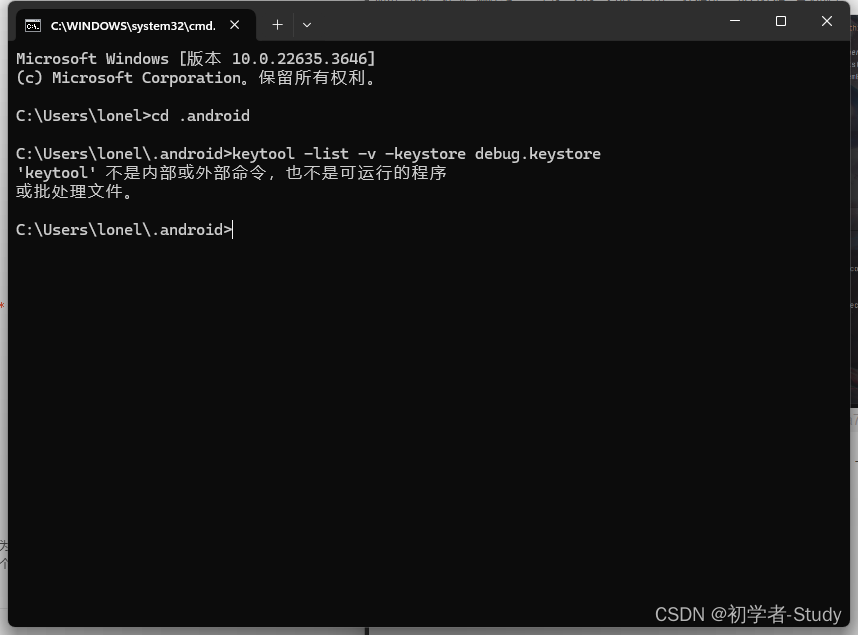
这里提示了keytool不是内部或外部命令,这说明我们没有配置JDK,下面我们配置一下,参考:JDK 安装与环境变量配置,配置之后我们重新走一下这个流程,如下图所示:
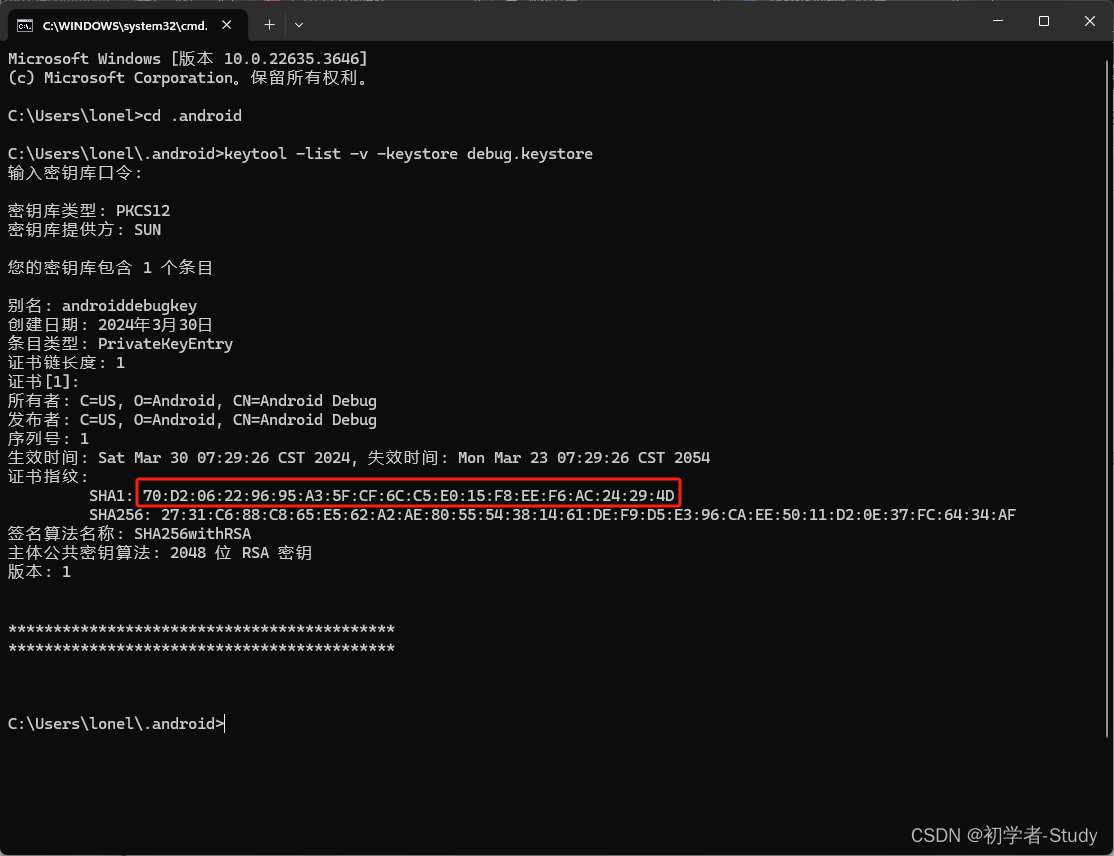
这里的密钥库口令是:android
输入的时候看不到内容,输入完成之后回车就可以了,如果你发现不是这样的话,就先运行一下项目,运行成功之后再尝试这一步。这里我们就拿到了调试版安全码SHA1,这里需要注意一点,调试版安全码SHA1会跟随电脑环境改变而改变,同一个项目在不同电脑上编译之后调试版安全码SHA1也会有变化,现在我们复制到那个网页里。

现在就只有一个发布版安全码SHA1需要获取了。
③ 获取发布版安全码SHA1
这个稍微有一些麻烦,因此需要先创建一个jks文件才行,首先我们点击这个菜单按钮。

然后点击Build 选择点击Generate Signed Bundle / APK…

这时候会出现一个弹窗,我们选择APK,Android App Bundle 打包的是aab格式,这种格式的包用于上传Google应用商店,国内都是apk格式。

点击Next。

在生成apk时需要一个jks文件,这里我们选择Create new...,创建一个新的jks文件。

首先指明生成的jks文件的路径,点击这个文件夹图标。

这里我选择将jks就生成在项目的根目录下,点击OK,然后我们输入一些其他的信息,实际上你只要输入商量密码和别名密码就可以了,但是还是都填好比较好。Confirm就是再输入一次密码,这里建议你把商店密码和别名密码设置成一样的。

点击OK,然后选择Remember passwords。

然后点击Next,然后选择release。

点击Create,当你看到右下角出现如下弹窗。

则说明这个Apk生成成功了,下面我们就可以来获取发布版安全码SHA1,还是之前那个窗口,我们输入:
keytool -list -v -keystore D:\Android\NewGaodeMapDemo\map.jks
- 1
这里需要注意地址是我项目的地址,你需要按照自己实际的地址填。
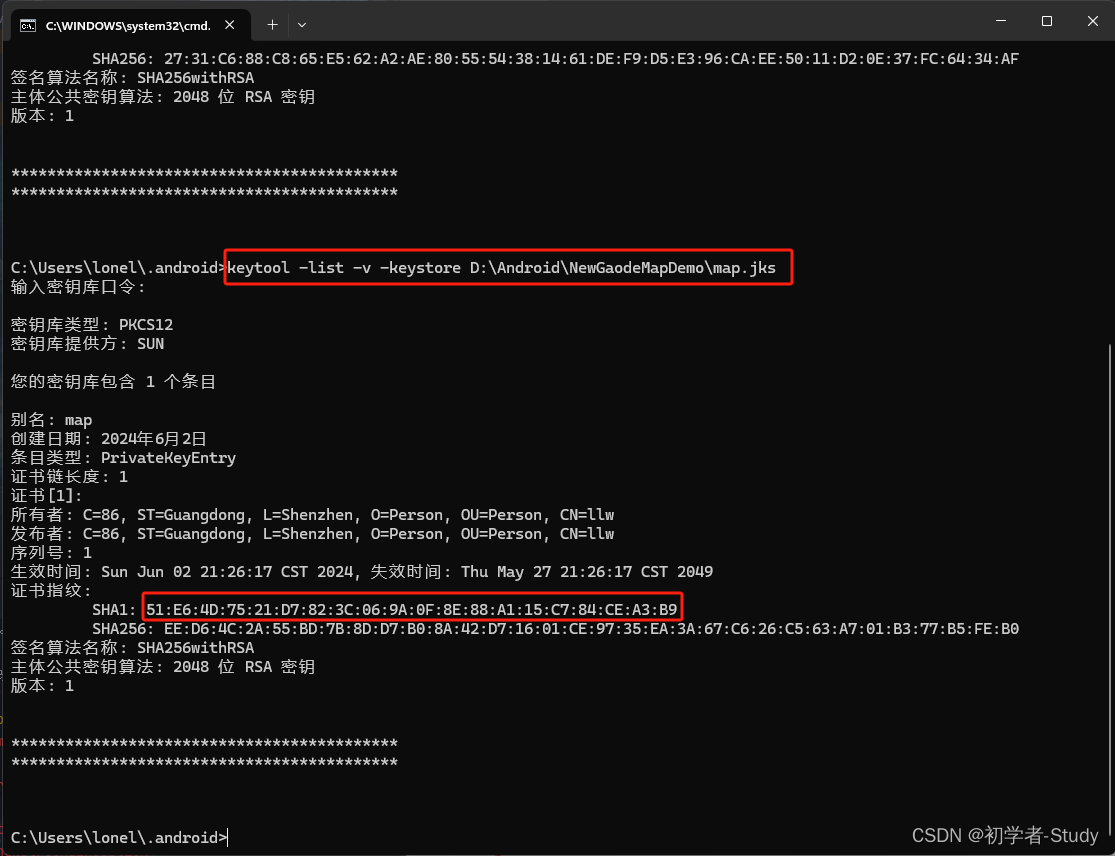
密钥口令,就是你刚才设置的jks密码,然后我们复制这个SHA1到那个网页里面。

现在需要的内容都有了,点击提交。
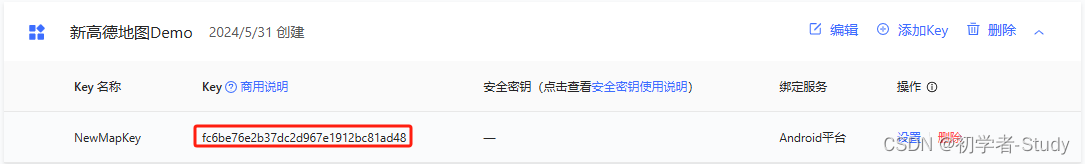
这里的Key我们需要到Android工程的AndroidManifest.xml中去配置,你需要使用自己的。到了这一步我们初期的应用创建就完成了,为自己点个赞吧,虽然这挺容易的。
二、配置项目
这里我们需要用到高德的SDK,点击 文档与支持 → Android 地图SDK。
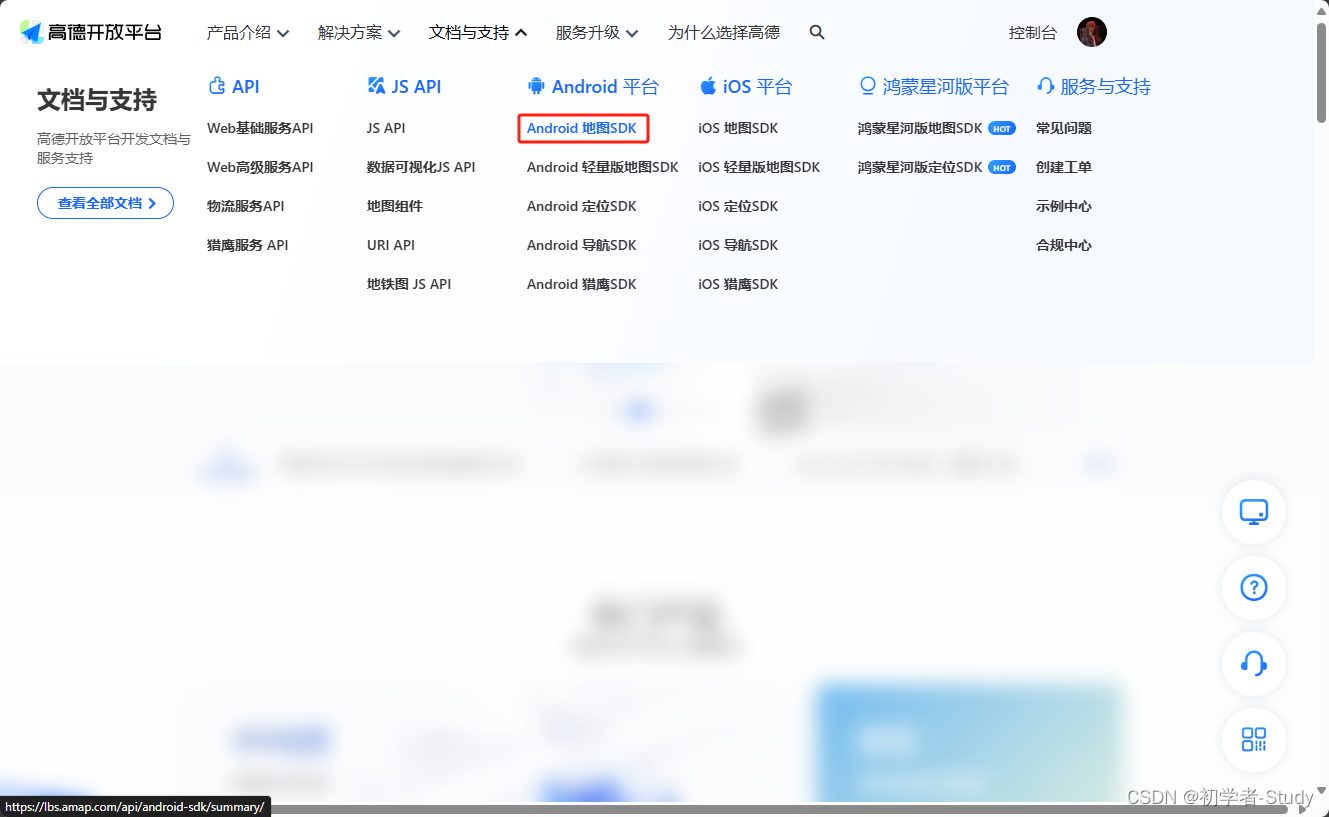
点击相关下载,然后向下滑动。
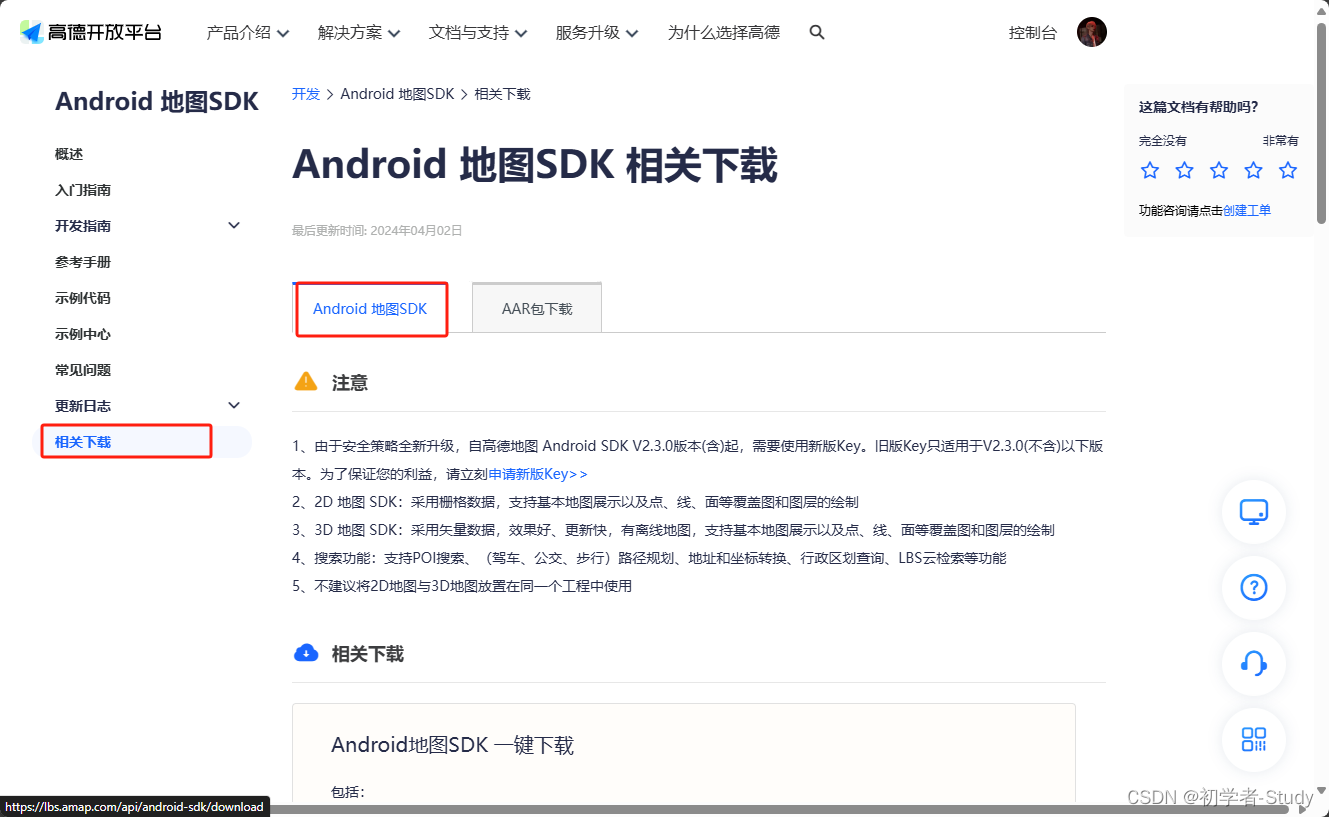
这里我们选择 3D地图合包,可以看到里面包含了,3D地图SDK、搜索SDK和定位SDK,点击下载。

下载之后解压,看到有一个Jar包和两个架构文件夹,里面都是so库。
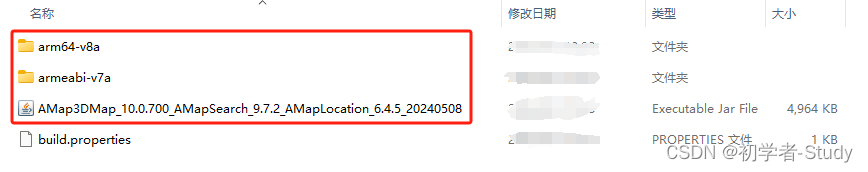
① 导入SDK
下面我们需要将她复制到Android项目的libs目录下,下面我们创建这个目录。这里默认是Android工程模式,我们先切换成Project工程模式,然后鼠标右键点击app → New → Directory。

出现弹窗输入libs,然后回车。

然后将解压包里的4个文件都复制进来,如下图所示:

只不过现在这个包现在还没有用起来,我们需要配置一下,在app模块下的build.gradle中添加如下代码:
ndk {
//设置支持的SO库架构(开发者可以根据需要,选择一个或多个平台的so)
abiFilters "armeabi", "armeabi-v7a", "arm64-v8a", "x86","x86_64"
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
sourceSets {
main {
jniLibs.srcDirs = ['libs']
}
debug.setRoot('build-types/debug')
release.setRoot('build-types/release')
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
buildFeatures {
viewBinding true
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
- 1
添加位置如下图所示:
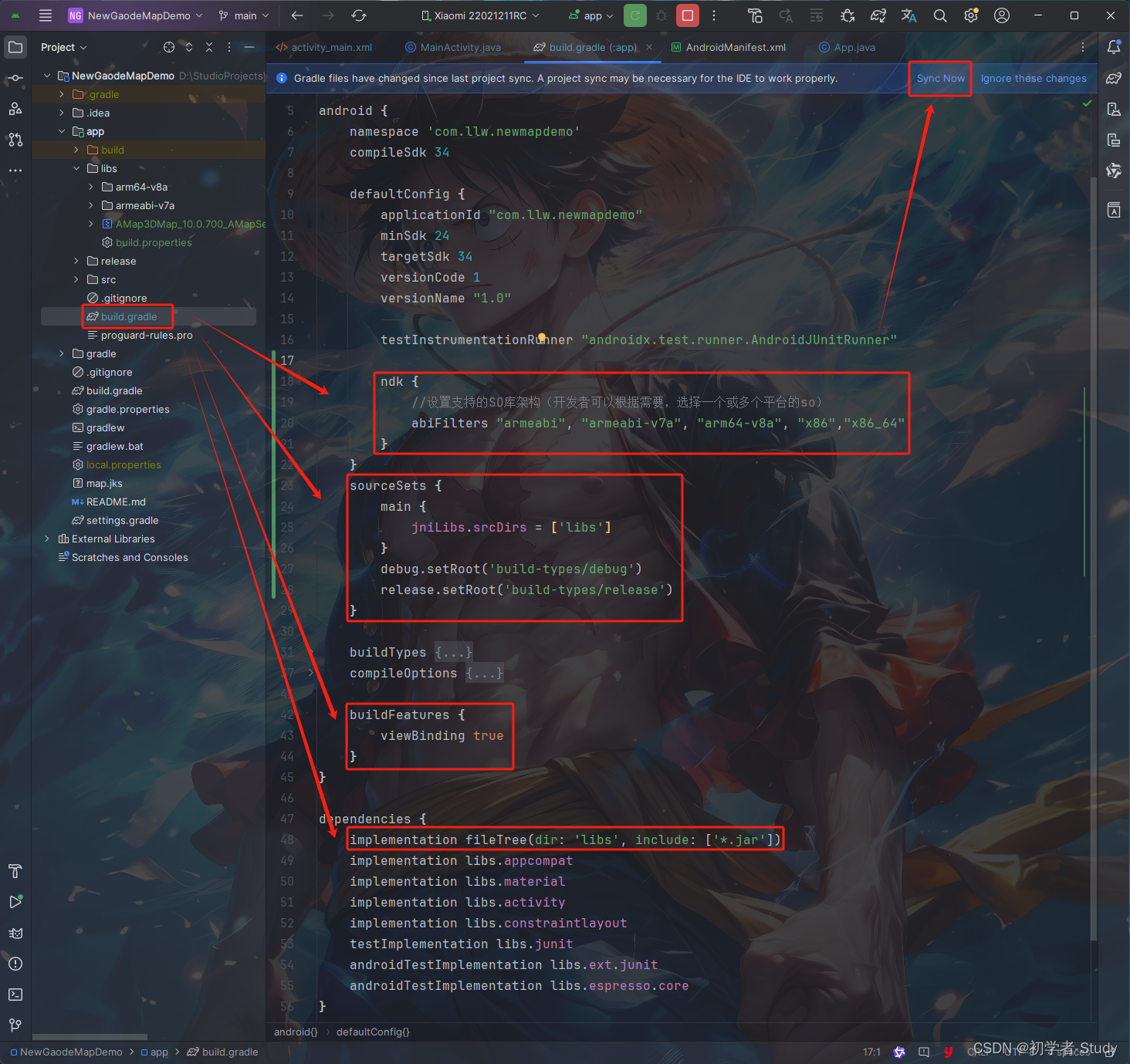
这里我除了添加配置代码,还配置了打开ViewBinding,记得点击Sync Now进行同步,同步完成之后就会发现Jar包前面就一个箭头,我们可以打开这个包,如下图所示:

这说明我们导入的SDK可以使用了。
② 配置AndroidManifest.xml
打开AndroidManifest.xml,首先在application标签下添加定位服务,添加代码如下:
<!--高德定位服务-->
<service android:name="com.amap.api.location.APSService" />
<!--高德的Key value里面的值请使用自己的Key-->
<meta-data
android:name="com.amap.api.v2.apikey"
android:value="key" />
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
添加位置如下图所示:
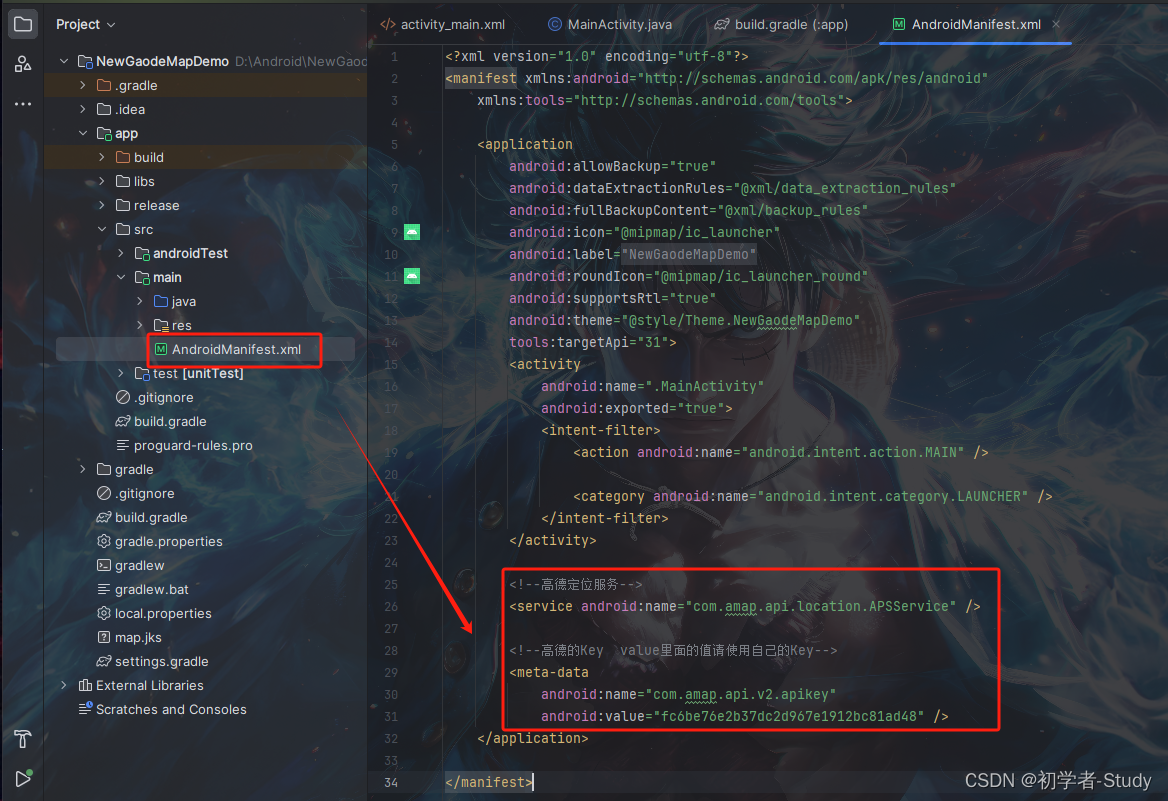
这里的value里面的值你就填写自己高德平台所创建的Key,我在前面提到过,这里不能错,请注意,下面我们添加权限。代码如下:
<!--用于进行网络定位--> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION"/> <!--用于访问GPS定位--> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION"/> <!--用于获取运营商信息,用于支持提供运营商信息相关的接口--> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE"/> <!--用于访问wifi网络信息,wifi信息会用于进行网络定位--> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE"/> <!--用于获取wifi的获取权限,wifi信息会用来进行网络定位--> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CHANGE_WIFI_STATE"/> <!--用于访问网络,网络定位需要上网--> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/> <!--用于写入缓存数据到扩展存储卡--> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/> <!--用于申请调用A-GPS模块--> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_LOCATION_EXTRA_COMMANDS"/> <!--如果设置了target >= 28 如果需要启动后台定位则必须声明这个权限--> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE"/> <!--如果您的应用需要后台定位权限,且有可能运行在Android Q设备上,并且设置了target>28,必须增加这个权限声明--> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_BACKGROUND_LOCATION"/> <!--允许写设备缓存,用于问题排查--> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_SETTINGS" tools:ignore="ProtectedPermissions" />
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
添加位置如下图所示:
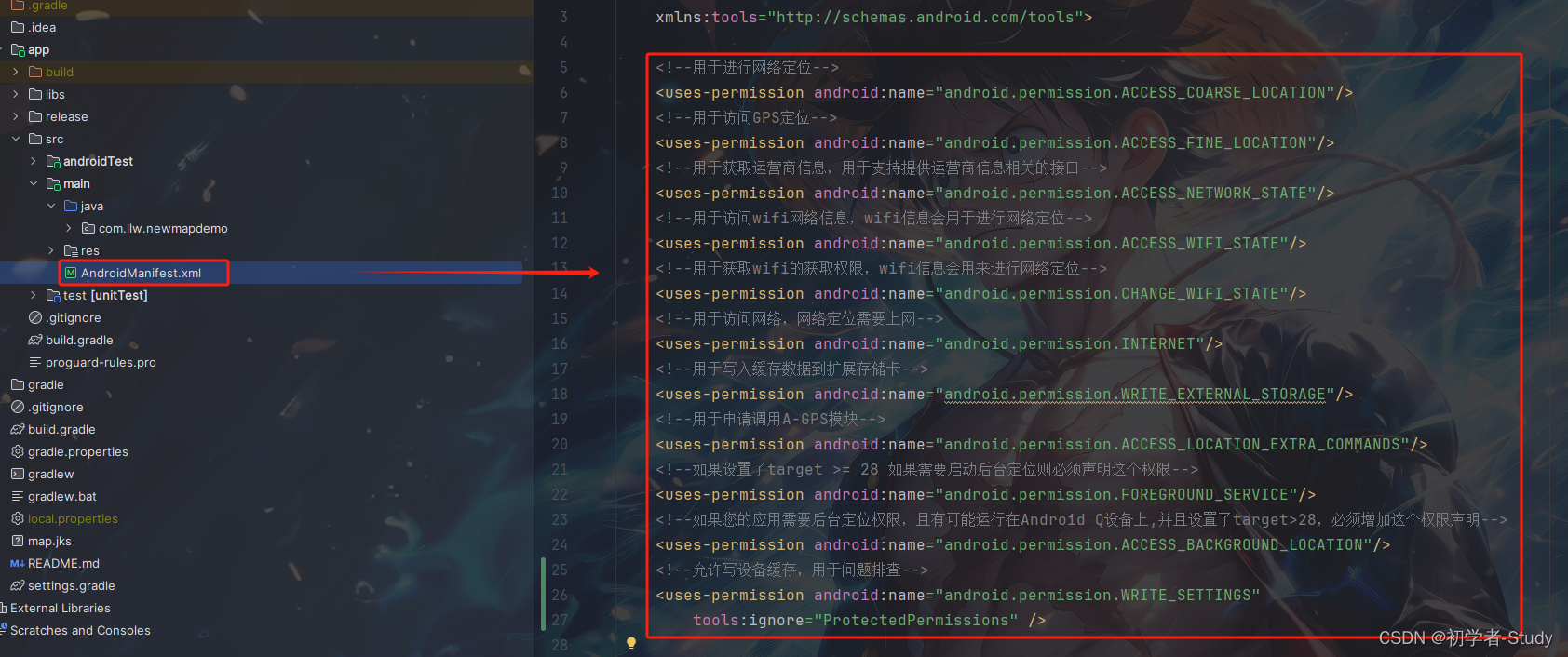
三、获取当前定位信息
获取定位信息之前我们需要先动态请求位置权限。
① ViewBinding使用和导包
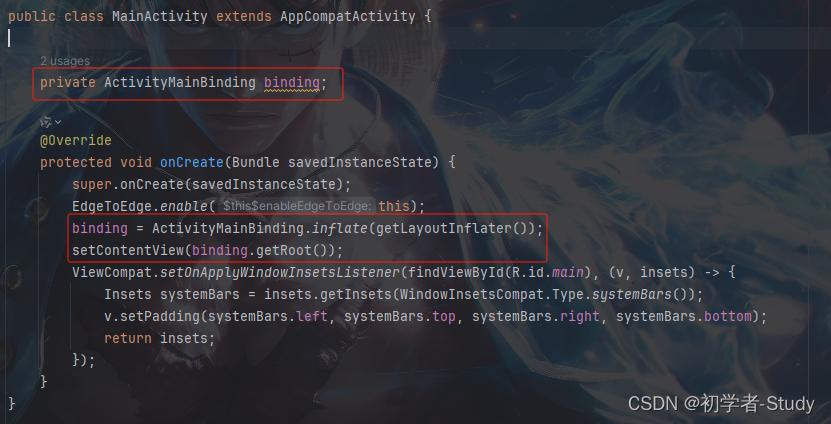
在此之前我们先了解一下ViewBinding的使用和导包,为什么我要说这个,因为确实别问我为什么报错的时候,我一看没有导包,那时候我的内心是相当复杂的,如果你是从事这个行业的你就会懂我的心情。
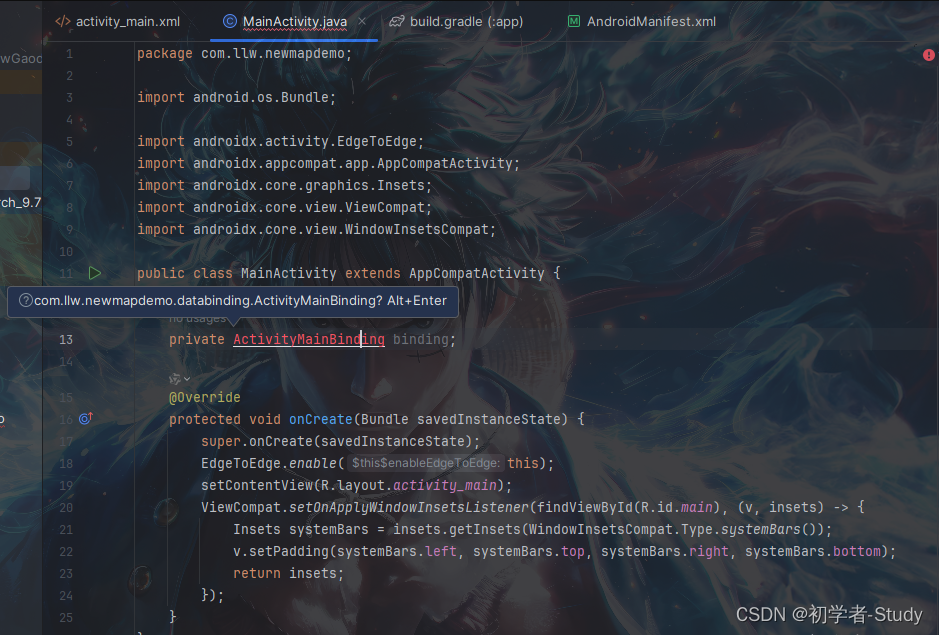
可以看到ActivityMainBinding是爆红的,这是因为使用了ViewBinding才有这个文件的生成,如果你想了解ViewBinding可以单独去了解。注意上面的一个小弹窗,有一个快捷键,Alt + Enter,使用之后就导了文件的包进来,就可以使用这个类了。

现在看到就不爆红了,后面你遇到这个情况的时候就知道怎么做了,为什么呢?因为很多人代码都不是一行行敲的,都是复制粘贴的,所以并不会自动导包,使用的方式如下图所示:
参考来就行了,汲取之前那篇文章的经验,我尽量每一行代码写在什么地方都截图,避免你不知道代码应该添加在哪里,又来问我怎么报错了。
② 隐私合规设置
随着工信部推行加强个人信息隐私的保护政策,各大SDK都需要相应增加一个API接口,确保用户是在知道会采集信息的情况下使用某一个功能,所以我们在使用高德的定位、地图、搜索功能时,需要先同意隐私政策,不通过则无法使用,一般是通过App启动之后出现一个弹窗,弹窗中你告知用户那些信息被采集,用到了那些SDK,作用是什么。并且要有隐私政策的链接地址,很麻烦。这里我们就简单一些,鼠标右键com.llw.newmapdemo包,然后选择New → Java Class。
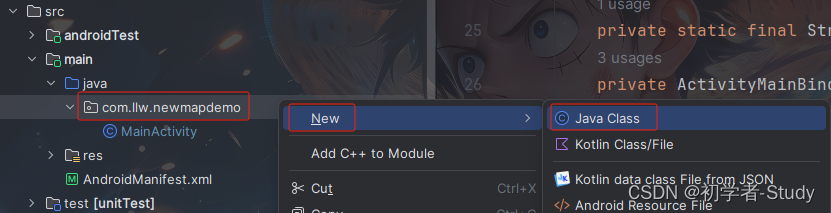
在出现的弹窗中输入App,然后回车。

里面的代码如下所示:
public class App extends Application { @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); Context mContext = this; // 定位隐私政策同意 AMapLocationClient.updatePrivacyShow(mContext,true,true); AMapLocationClient.updatePrivacyAgree(mContext,true); // 地图隐私政策同意 MapsInitializer.updatePrivacyShow(mContext,true,true); MapsInitializer.updatePrivacyAgree(mContext,true); // 搜索隐私政策同意 ServiceSettings.updatePrivacyShow(mContext,true,true); ServiceSettings.updatePrivacyAgree(mContext,true); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
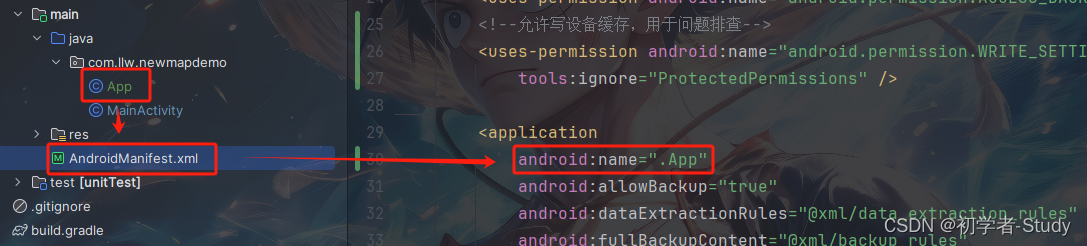
记得导包,后面我就不重复提醒,不要又来问我为什么没有这个AMapLocationClient和ServiceSettings,这里我们还需要将App配置到AndroidManifest.xml中的application标签里,如下图所示:
③ 权限请求
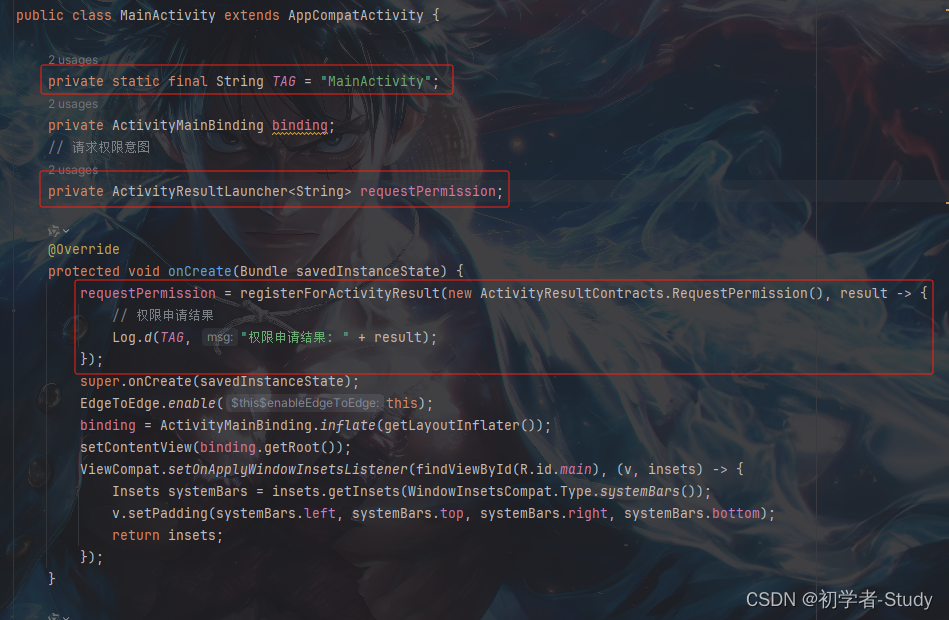
这里我们使用Android 原生的方式来请求动态权限,首先在MainActivity中添加如下代码:
private static final String TAG = "MainActivity";
// 请求权限意图
private ActivityResultLauncher<String> requestPermission;
- 1
- 2
- 3
然后再onCreate()方法中添加如下代码:
requestPermission = registerForActivityResult(new ActivityResultContracts.RequestPermission(), result -> {
// 权限申请结果
Log.d(TAG, "权限申请结果: " + result);
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
两处代码添加位置如下图所示:
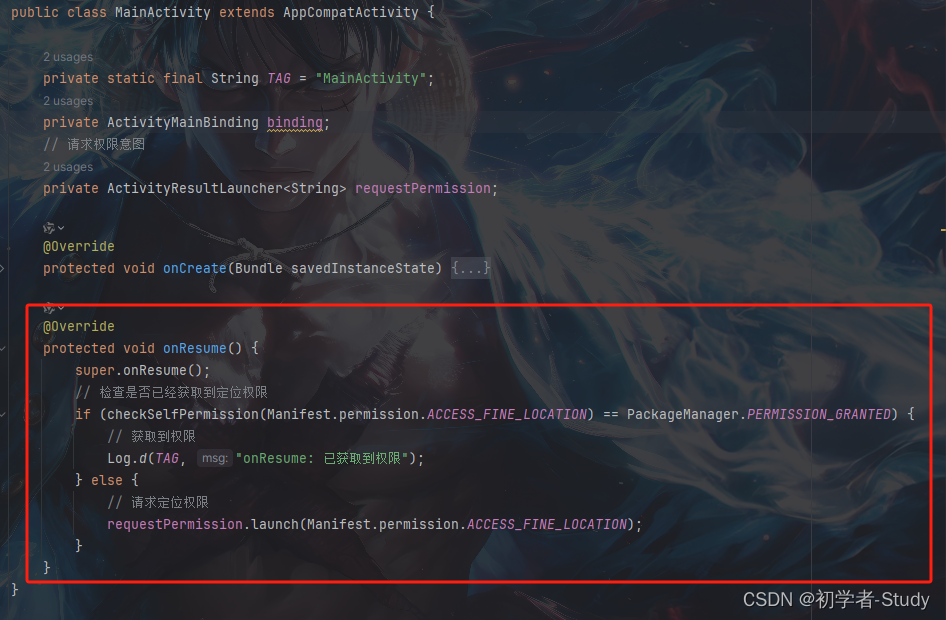
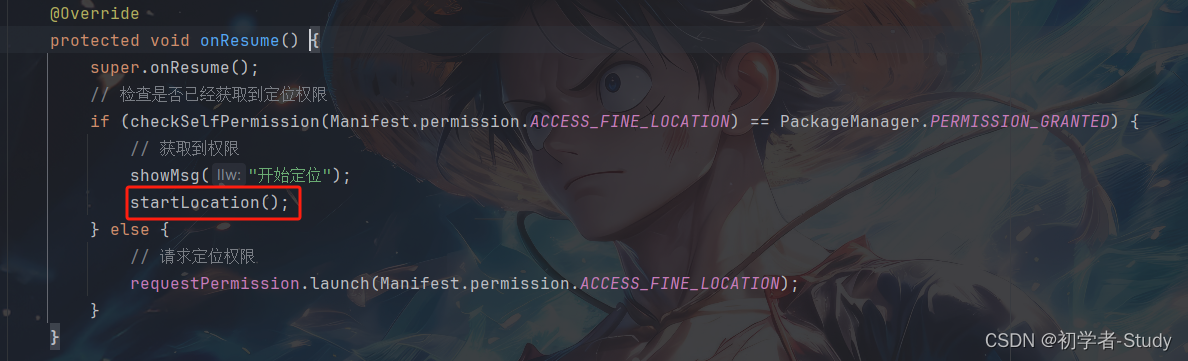
在权限申请结果处,我们打印了值,True就是授予了权限,False就是拒绝了权限,下面我们需要判断一下是否有权限,没有则请求权限,有则进入下一步。
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
// 检查是否已经获取到定位权限
if (checkSelfPermission(Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
// 获取到权限
Log.d(TAG, "onResume: 已获取到权限");
} else {
// 请求定位权限
requestPermission.launch(Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
这里添加了一个onResume()方法,它属于Activity的生命周期之一,通过注释你应该明白这个代码是什么意思。添加位置如下图所示:
下面我们运行一下看看。

在运行之后就会请求权限,点击仅使用期间允许,然后就可以看到权限通过了,如果你希望更明显一些,可以使用Toast,在MainActivity中添加一个方法。
private void showMsg(CharSequence llw) {
Toast.makeText(this, llw, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
再看看使用的地方,如下图所示:
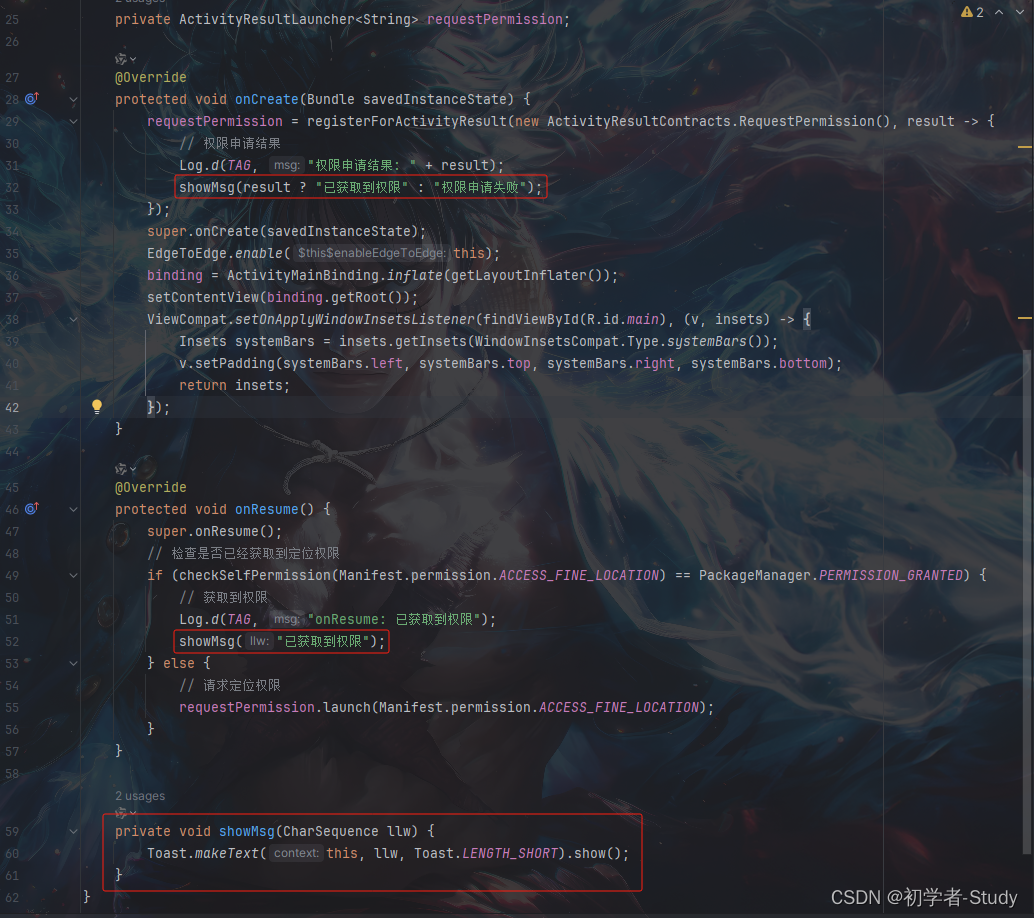
这里就是换成更明显的Toast。
④ 初始化定位
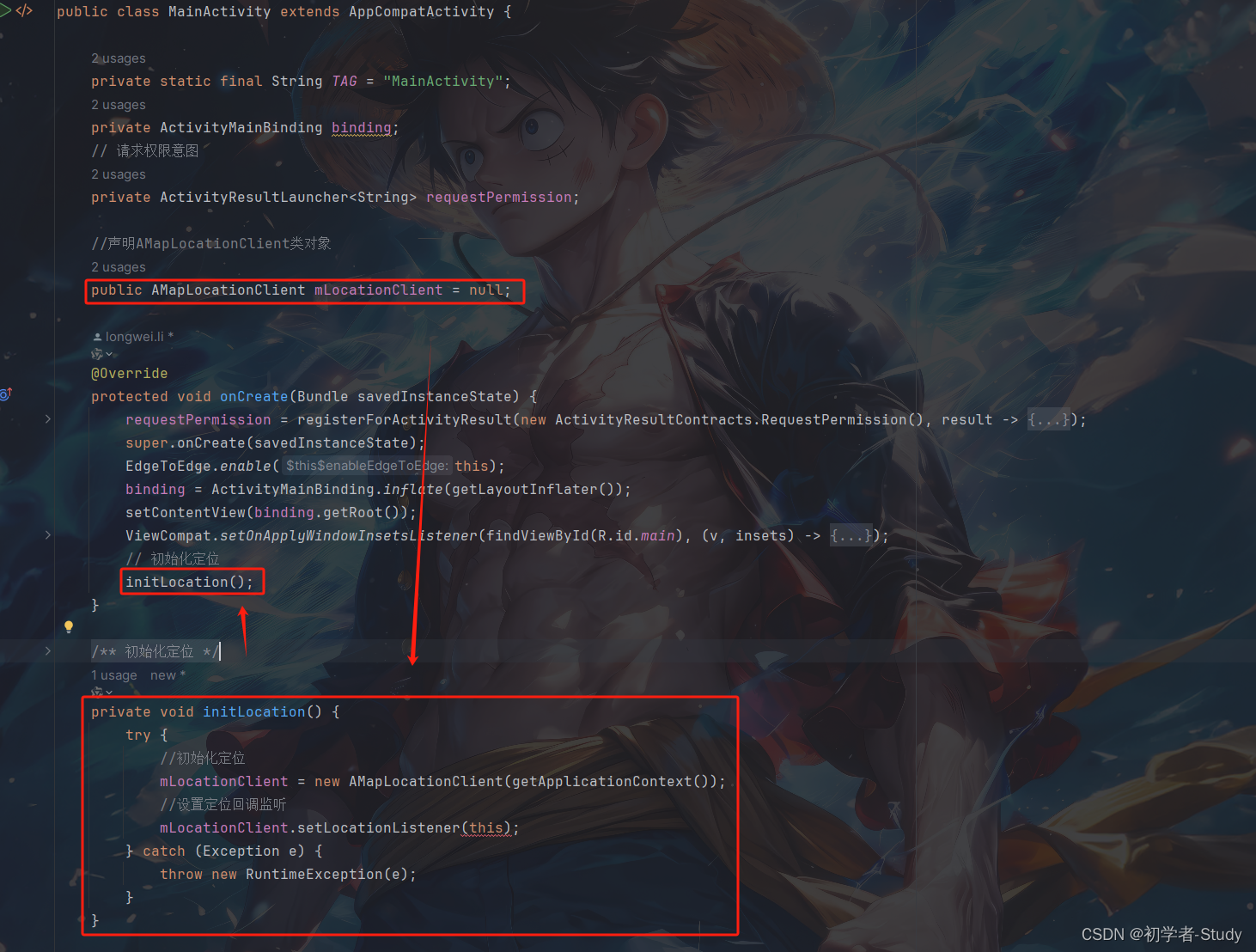
在获取到权限之后我们就需要进行定位了,在定位之前我们首先要初始化定位,首先声明一个变量,代码如下:
//声明AMapLocationClient类对象
public AMapLocationClient mLocationClient = null;
- 1
- 2
然后写一个方法去进行初始化,代码如下所示:
/**
* 初始化定位
*/
private void initLocation() {
try {
//初始化定位
mLocationClient = new AMapLocationClient(getApplicationContext());
//设置定位回调监听
mLocationClient.setLocationListener(this);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
最后我们需要在onCreate()方法中进行调用,以上代码及调用的地方如下图所示:
在initLocation()方法中设置了回调监听,这里用的是this,这表示在当前类,而下面有红线,说明我们没有实现里面的方法,鼠标点击这个this,然后使用快捷键Alt + Enter,会出现一个提示弹窗。
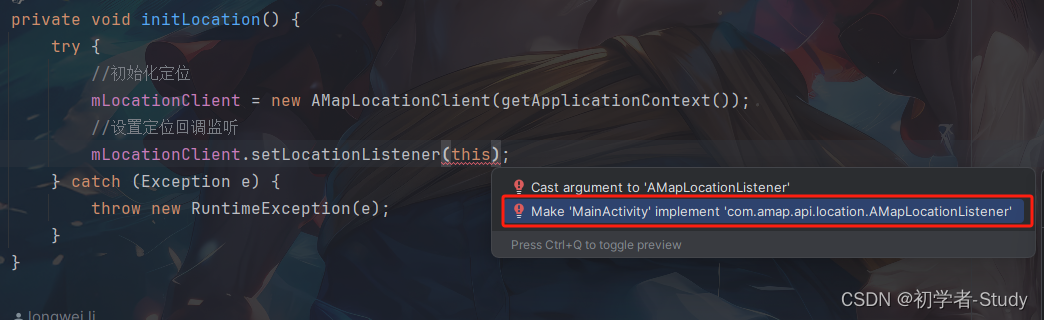
这里选择我标注的这一项进行回车,会再出现一个弹窗。

这里什么都不用改,点击OK即可,然后我们看看当前的MainActivity有什么变化。
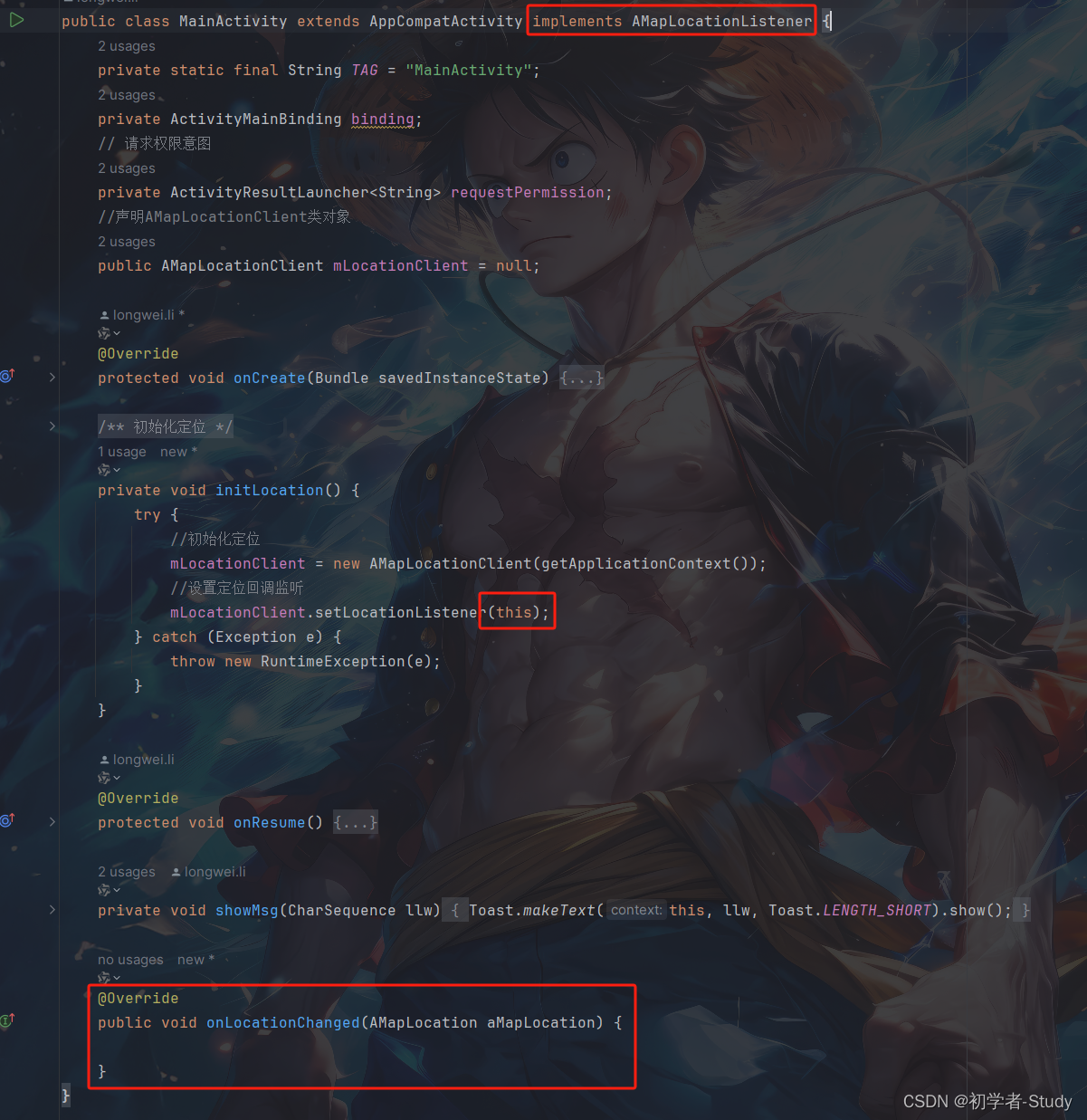
我们实现了AMapLocationListener接口,重写了里面onLocationChanged()方法,同时this也没有红线了,此时代码是正常的。但是我们的定位配置还没有完成,再声明一个变量:
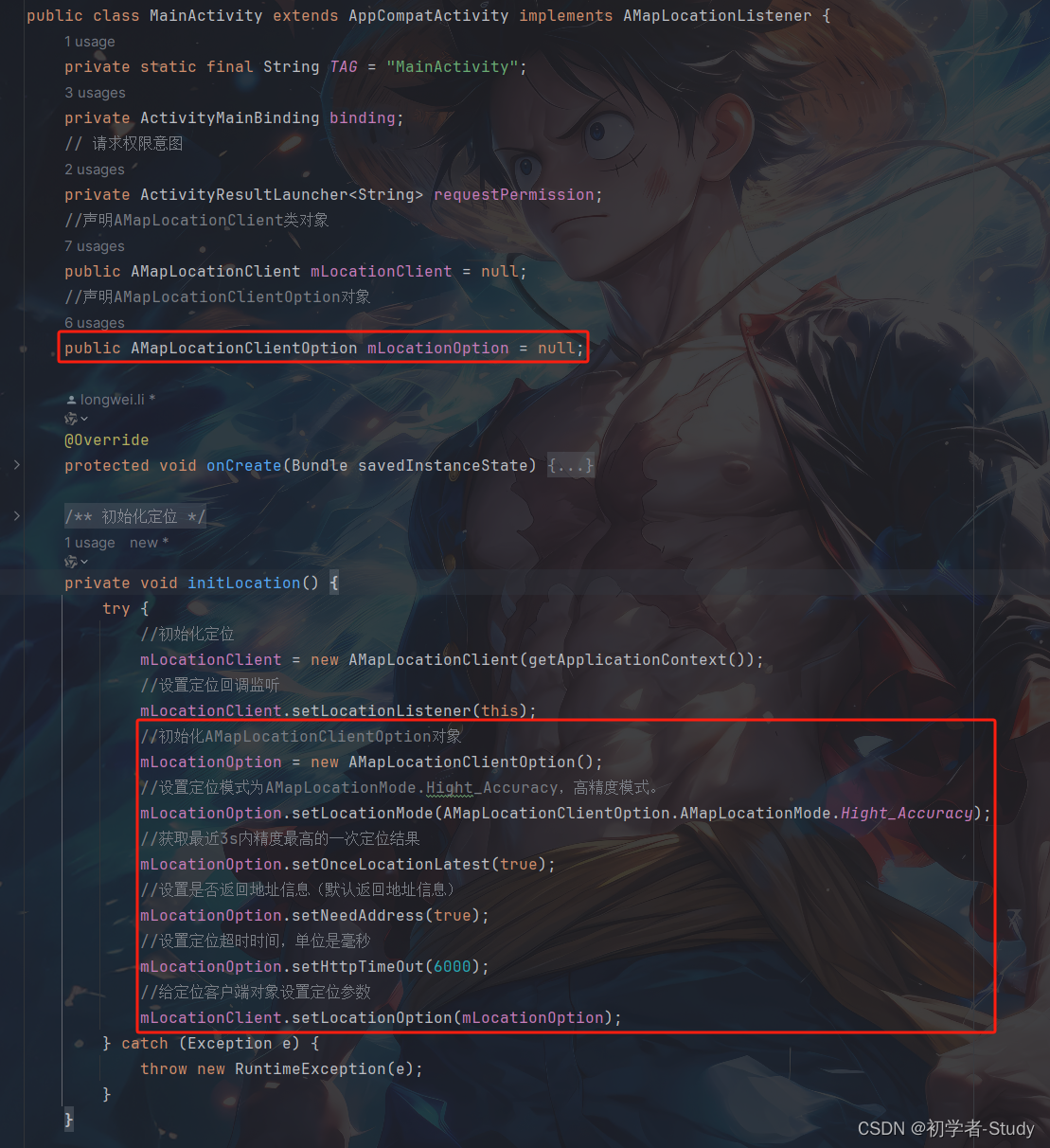
//声明AMapLocationClientOption对象
public AMapLocationClientOption mLocationOption = null;
- 1
- 2
然后在initLocation()方法中进行配置,代码如下所示:
//初始化AMapLocationClientOption对象
mLocationOption = new AMapLocationClientOption();
//设置定位模式为AMapLocationMode.Hight_Accuracy,高精度模式。
mLocationOption.setLocationMode(AMapLocationClientOption.AMapLocationMode.Hight_Accuracy);
//获取最近3s内精度最高的一次定位结果
mLocationOption.setOnceLocationLatest(true);
//设置是否返回地址信息(默认返回地址信息)
mLocationOption.setNeedAddress(true);
//设置定位超时时间,单位是毫秒
mLocationOption.setHttpTimeOut(6000);
//给定位客户端对象设置定位参数
mLocationClient.setLocationOption(mLocationOption);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
添加位置如下图所示:
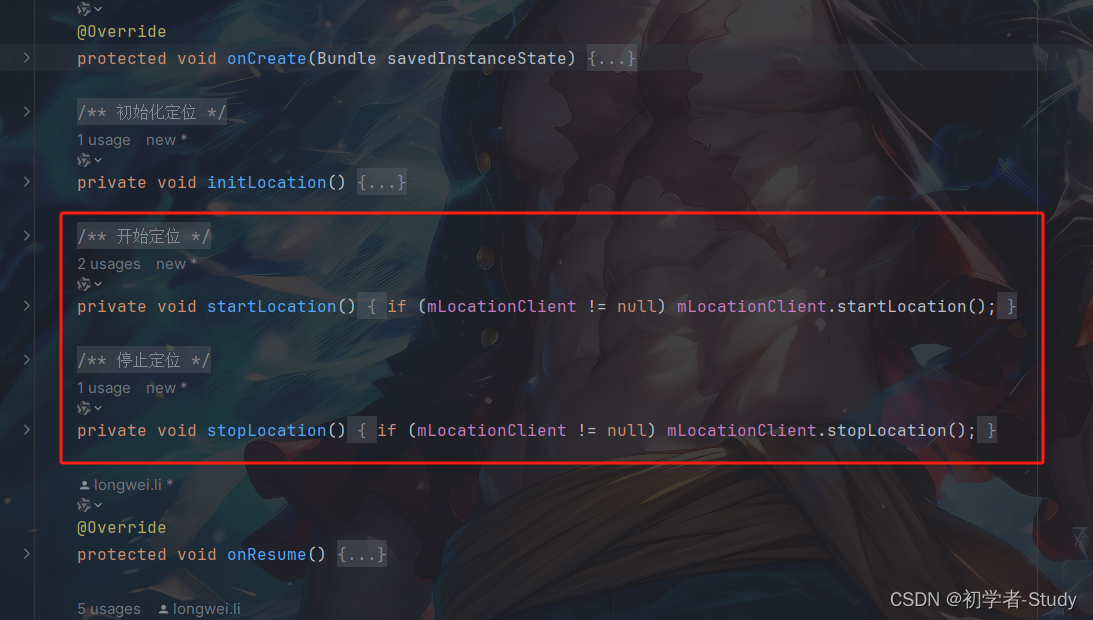
下一步我们写开始和停止定位的方法,在MainActivity中增加如下代码:
/**
* 开始定位
*/
private void startLocation() {
if (mLocationClient != null) mLocationClient.startLocation();
}
/**
* 停止定位
*/
private void stopLocation() {
if (mLocationClient != null) mLocationClient.stopLocation();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
添加位置如下所示:
⑤ 获取定位信息
然后就是这两个方法的调用位置了,首先看开始定位,首先我们在获取权限之后就要开始定位,增加代码如下图所示:
至于停止定位的使用,我们需要在拿到定位结果之后,同时我们需要将定位结果显示在页面,那么我们先修改一下activity_main.xml中的代码,为TextView控件增加一个为tv_address的id,代码如下所示:
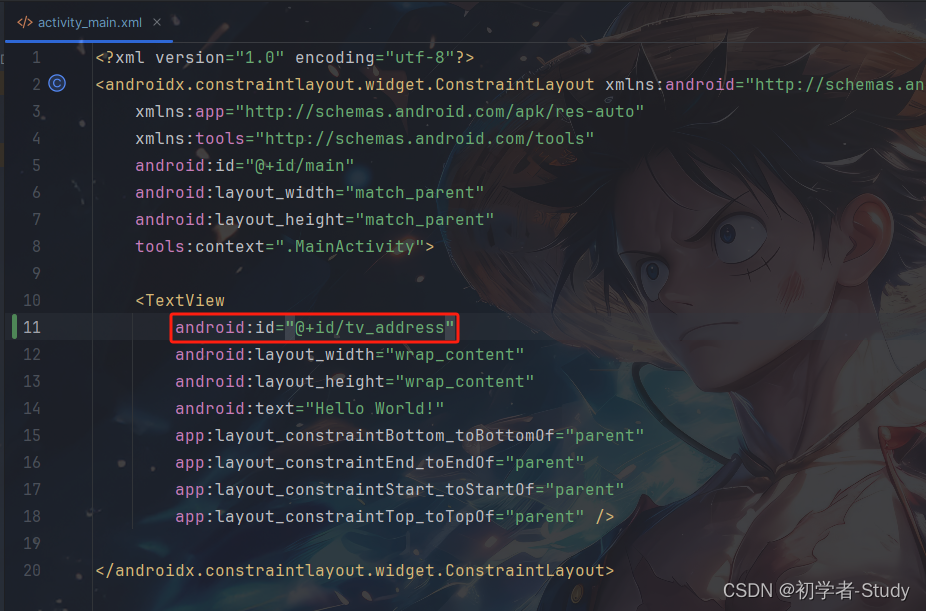
然后我们再回到MainActivity中,修改onLocationChanged()方法中的代码,如下所示:
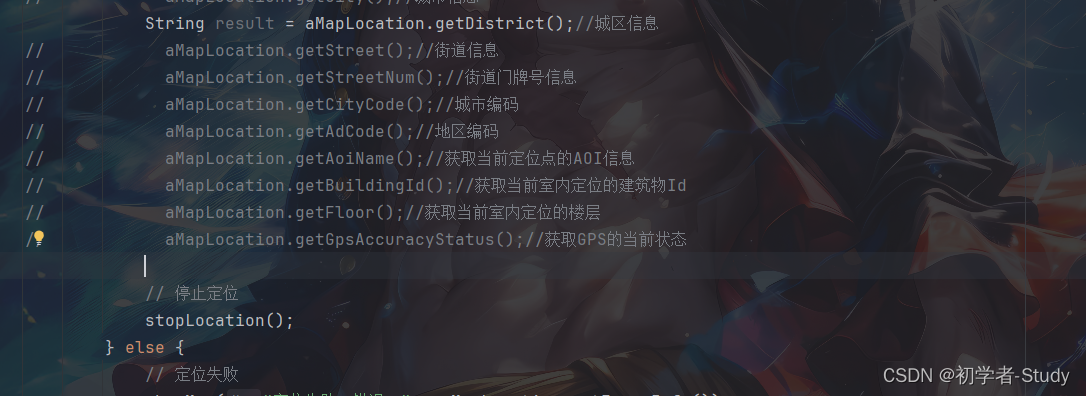
/** * 定位回调结果 */ @Override public void onLocationChanged(AMapLocation aMapLocation) { if (aMapLocation == null) { showMsg("定位失败,aMapLocation 为空"); return; } // 获取定位结果 if (aMapLocation.getErrorCode() == 0) { // 定位成功 showMsg("定位成功"); // aMapLocation.getLocationType();//获取当前定位结果来源,如网络定位结果,详见定位类型表 // aMapLocation.getLatitude();//获取纬度 // aMapLocation.getLongitude();//获取经度 // aMapLocation.getAccuracy();//获取精度信息 // aMapLocation.getAddress();//详细地址,如果option中设置isNeedAddress为false,则没有此结果,网络定位结果中会有地址信息,GPS定位不返回地址信息。 // aMapLocation.getCountry();//国家信息 // aMapLocation.getProvince();//省信息 // aMapLocation.getCity();//城市信息 String result = aMapLocation.getDistrict();//城区信息 // aMapLocation.getStreet();//街道信息 // aMapLocation.getStreetNum();//街道门牌号信息 // aMapLocation.getCityCode();//城市编码 // aMapLocation.getAdCode();//地区编码 // aMapLocation.getAoiName();//获取当前定位点的AOI信息 // aMapLocation.getBuildingId();//获取当前室内定位的建筑物Id // aMapLocation.getFloor();//获取当前室内定位的楼层 // aMapLocation.getGpsAccuracyStatus();//获取GPS的当前状态 binding.tvAddress.setText(result); // 停止定位 stopLocation(); } else { // 定位失败 showMsg("定位失败,错误:" + aMapLocation.getErrorInfo()); Log.e(TAG,"location Error, ErrCode:" + aMapLocation.getErrorCode() + ", errInfo:" + aMapLocation.getErrorInfo()); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
这里我只在页面上显示了所在的城区信息,其他的信息我先注释了,你可以根据自己的需求拿相应的数据进行显示,下面我们就可以开始运行了。

无论你是第一次进来时获取权限还是后面已经拿到权限再进来都是会获取定位信息,需要注意的是使用真机,同时需要联网。
四、显示地图
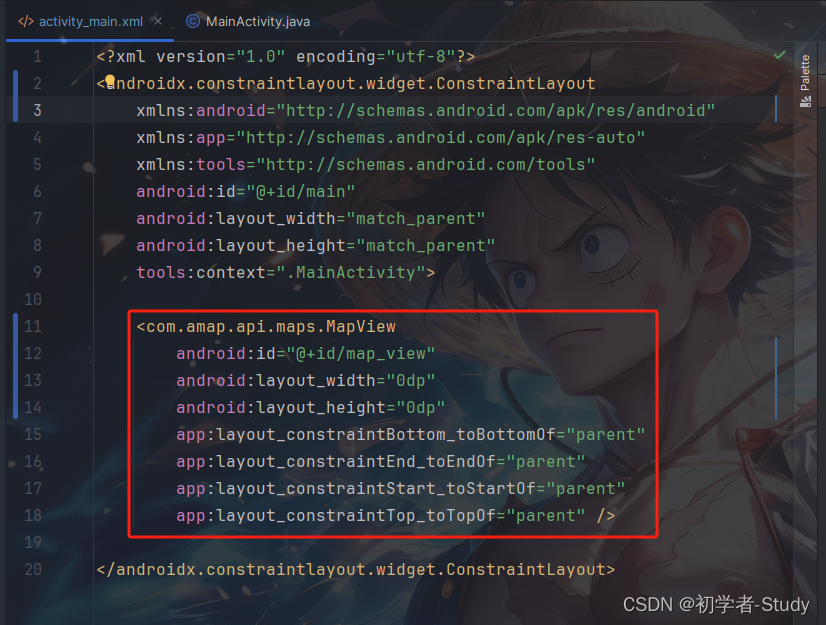
现在我们开始显示地图,首先我们需要修改一下activity_main.xml中的代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/main" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <com.amap.api.maps.MapView android:id="@+id/map_view" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="0dp" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" /> </androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
这里主要的改动就是去掉TextView,然后使用了MapView,因为根布局使用的约束布局,如果不了解的话尽量代码跟我一样,避免不必要的错误出现。
好了,下面我们回到MainActivity中,首先我们删除掉onLocationChanged()方法中之前显示定位结果在TextView上的一行代码,删除后如下图所示:
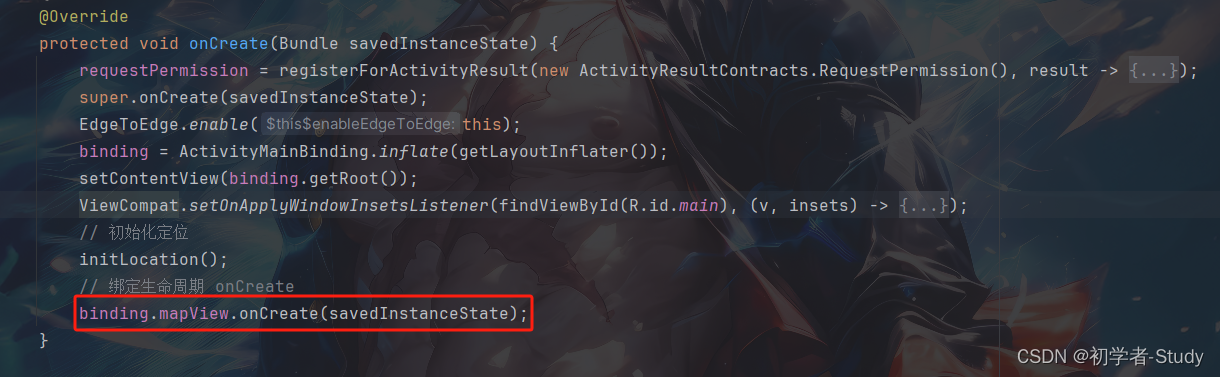
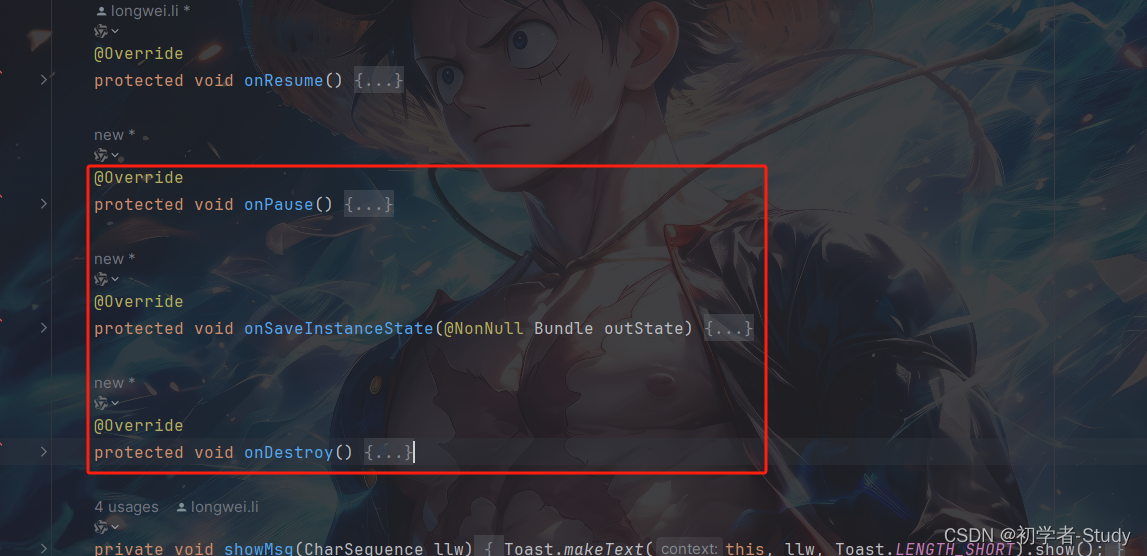
然后我们需要去配置MapView,将MapView和Activity的声明周期绑定起来,首先是onCreate(),如下图所示:
然后是onResume()
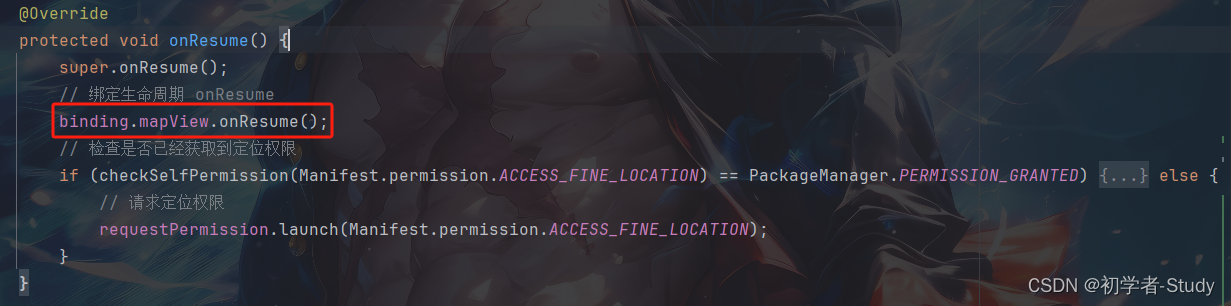
之后是onPause()、onSaveInstanceState()和onDestroy(),这三个方法当前没有所以我们需要增加,代码如下所示:
@Override protected void onPause() { super.onPause(); // 绑定生命周期 onPause binding.mapView.onPause(); } @Override protected void onSaveInstanceState(@NonNull Bundle outState) { super.onSaveInstanceState(outState); // 绑定生命周期 onSaveInstanceState binding.mapView.onSaveInstanceState(outState); } @Override protected void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); // 绑定生命周期 onDestroy binding.mapView.onDestroy(); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
添加位置如下图所示:
好了,下面我们运行一下看看:

地图是显示出来了,但是很明显,不是我当前的位置,那么如果我想显示当前的位置呢?比如我在广东省深圳市南山区,我要定位到我这里。
五、显示当前定位地图
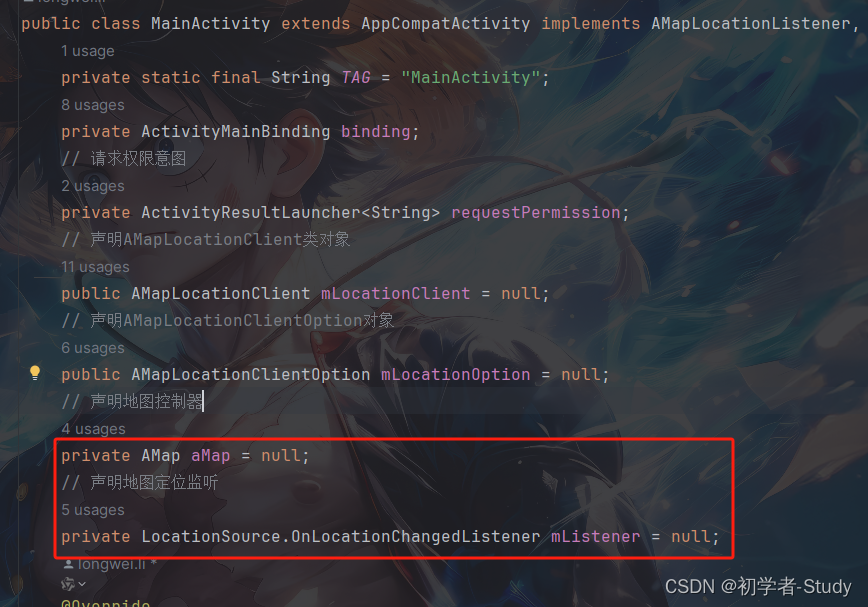
要显示当前定位地图,首先我们需要将位置在地图上进行设置,从而使地图中心点移动到我们所在的位置,首先我们声明两个变量。
// 声明地图控制器
private AMap aMap = null;
// 声明地图定位监听
private LocationSource.OnLocationChangedListener mListener = null;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
添加位置如下图所示:
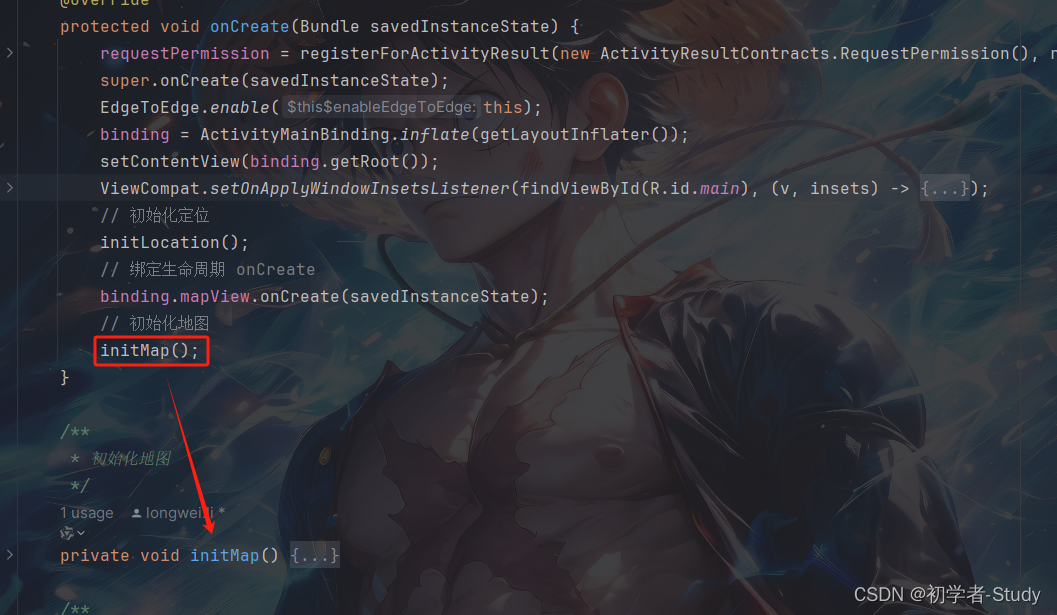
然后我们新增一个方法,代码如下所示:
/**
* 初始化地图
*/
private void initMap() {
if (aMap == null) {
aMap = binding.mapView.getMap();
// 设置定位监听
aMap.setLocationSource(this);
// 设置为true表示启动显示定位蓝点,false表示隐藏定位蓝点并不进行定位,默认是false。
aMap.setMyLocationEnabled(true);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
这里的this同样会有红线,我们依然使用之前的方式去实现接口,会有两个方法,如下图所示:

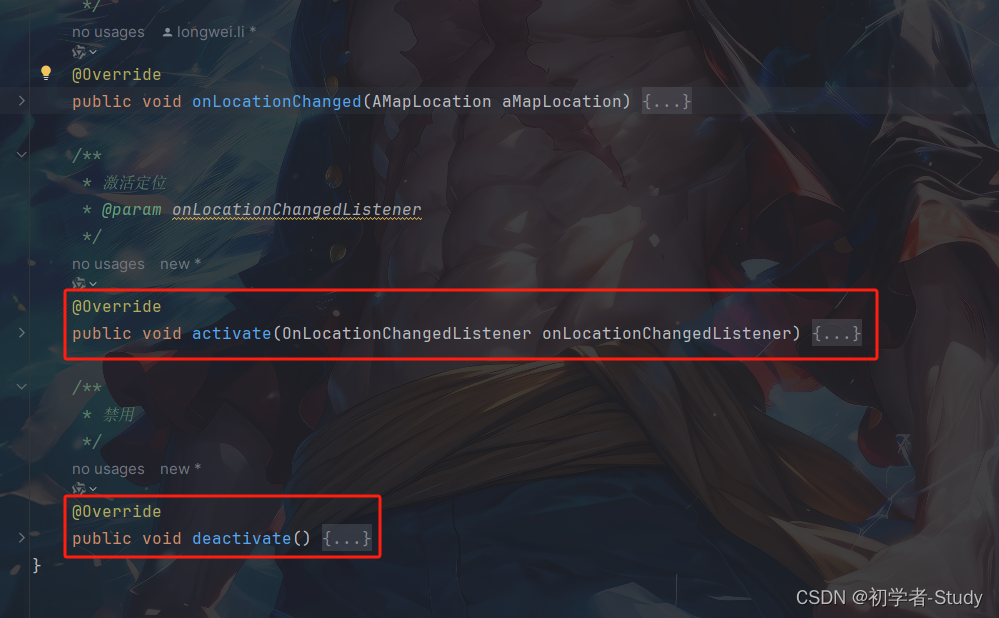
实现那两个方法之后,我们修改里面的代码如下所示:
/** * 激活定位 * @param onLocationChangedListener */ @Override public void activate(OnLocationChangedListener onLocationChangedListener) { if (mListener == null) { mListener = onLocationChangedListener; } startLocation(); } /** * 禁用 */ @Override public void deactivate() { mListener = null; if (mLocationClient != null) { mLocationClient.stopLocation(); mLocationClient.onDestroy(); } mLocationClient = null; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
两个方法,激活和禁止,在地图上激活定位后,我们开始定位,在定位的回调中,我们需要显示地图定位结果onLocationChanged()方法中增加如下代码:
// 显示地图定位结果
if (mListener != null) {
mListener.onLocationChanged(aMapLocation);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
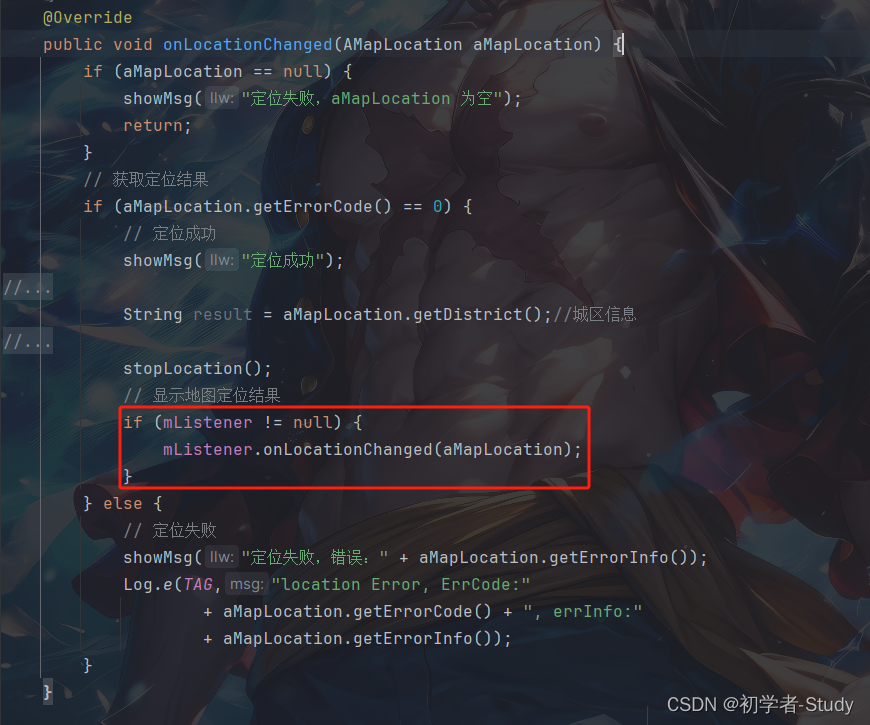
两个方法的位置如下图所示:
最后我们要做的就是在onCreate()方法中调用initMap()方法,使我们的配置生效,如下图所示:
下面我们运行一下看看效果:

六、地图设置
① 修改定位图标样式
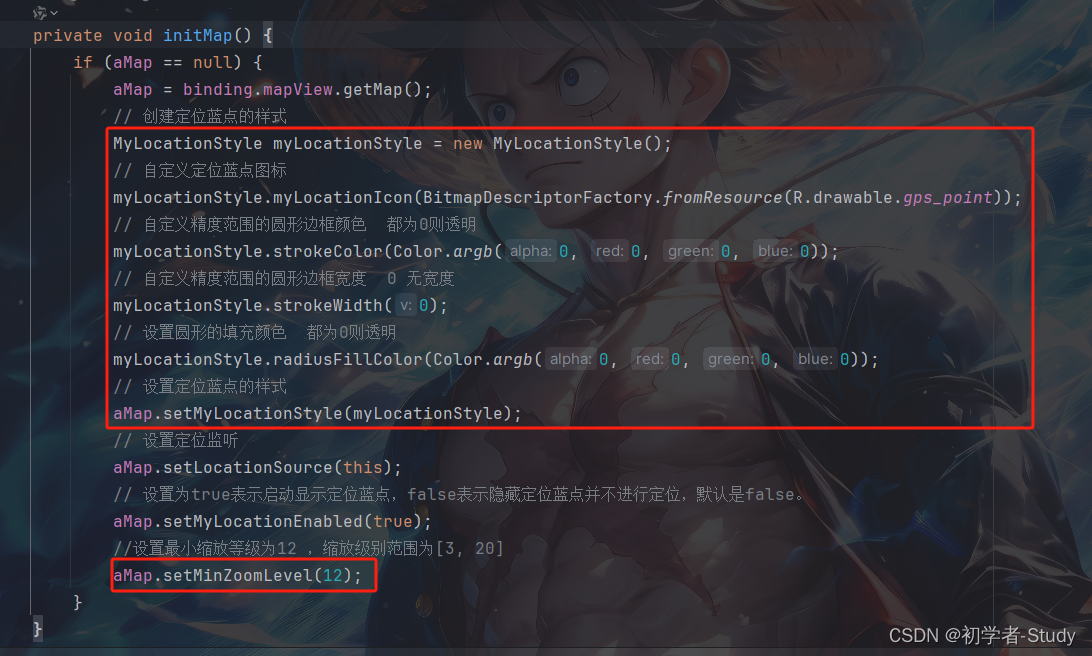
我们可以直接在initMap()方法中完成,增加如下代码:
// 创建定位蓝点的样式
MyLocationStyle myLocationStyle = new MyLocationStyle();
// 自定义定位蓝点图标
myLocationStyle.myLocationIcon(BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.gps_point));
// 自定义精度范围的圆形边框颜色 都为0则透明
myLocationStyle.strokeColor(Color.argb(0, 0, 0, 0));
// 自定义精度范围的圆形边框宽度 0 无宽度
myLocationStyle.strokeWidth(0);
// 设置圆形的填充颜色 都为0则透明
myLocationStyle.radiusFillColor(Color.argb(0, 0, 0, 0));
// 设置定位蓝点的样式
aMap.setMyLocationStyle(myLocationStyle);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
这里如果你没有这个图标,不修改自定义图标,或者去我的代码中获取这个R.drawable.gps_point图标。
② 设置缩放等级
//设置最小缩放等级为12 ,缩放级别范围为[3, 20]
aMap.setMinZoomLevel(12);
- 1
- 2
最终设置如下图所示:
下面运行一下:

③ 开启室内地图
// 开启室内地图
aMap.showIndoorMap(true);
- 1
- 2
这里你就在initMap()中添加即可,然后加载地图出来后,不断放大,直到你看到3D的建筑,添加位置如下图所示:

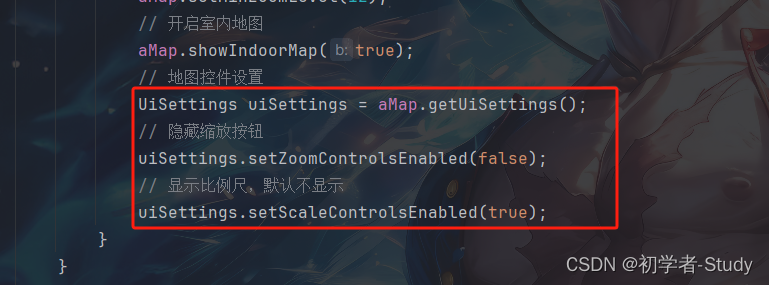
④ 地图控件设置
// 地图控件设置
UiSettings uiSettings = aMap.getUiSettings();
// 隐藏缩放按钮
uiSettings.setZoomControlsEnabled(false);
// 显示比例尺,默认不显示
uiSettings.setScaleControlsEnabled(true);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
添加位置如下图所示:
运行一下看看:

七、获取POI数据
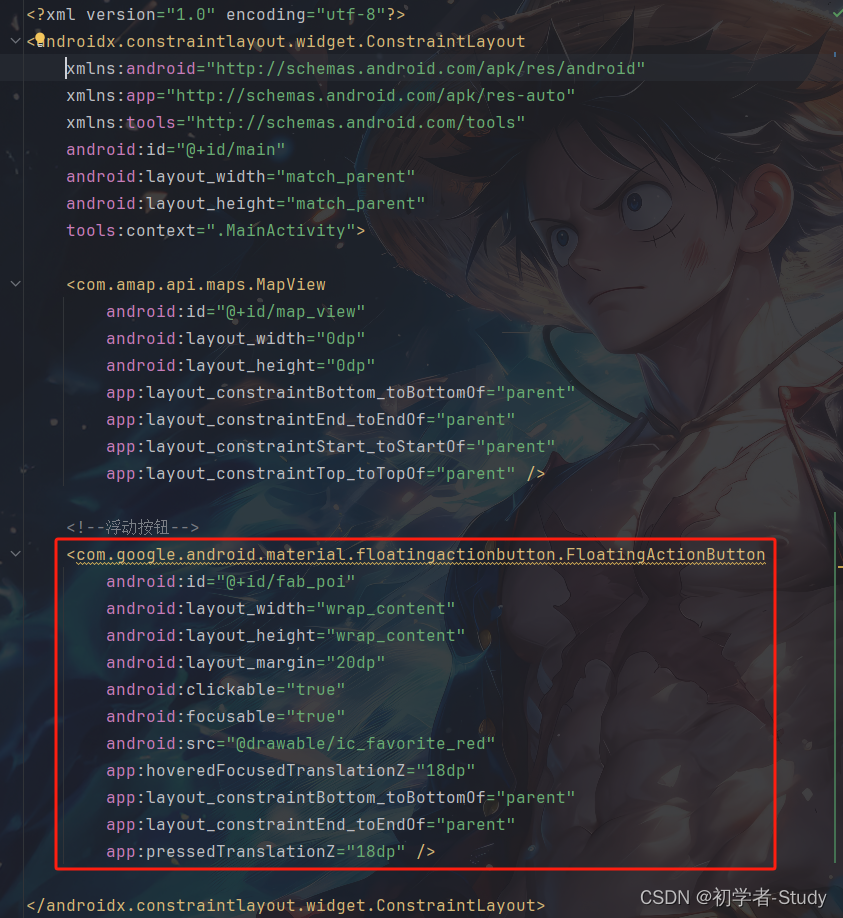
POI (Point of Interest,兴趣点)。在地图表达中,一个 POI 可代表一栋大厦、一家商铺、一处景点等等。通过POI搜索,完成找餐馆、找景点、找厕所等等的功能,首先我们修改一下activity_main.xml中的代码:
<!--浮动按钮-->
<com.google.android.material.floatingactionbutton.FloatingActionButton
android:id="@+id/fab_poi"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="20dp"
android:clickable="true"
android:focusable="true"
android:src="@drawable/ic_favorite_red"
app:hoveredFocusedTranslationZ="18dp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:pressedTranslationZ="18dp" />
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
添加位置如下图所示:
然后回到MainActivity中,我们声明变量,代码如下所示:
//POI查询对象
private PoiSearch.Query query;
//POI搜索对象
private PoiSearch poiSearch;
//城市码
private String cityCode = null;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
添加位置如下图所示:

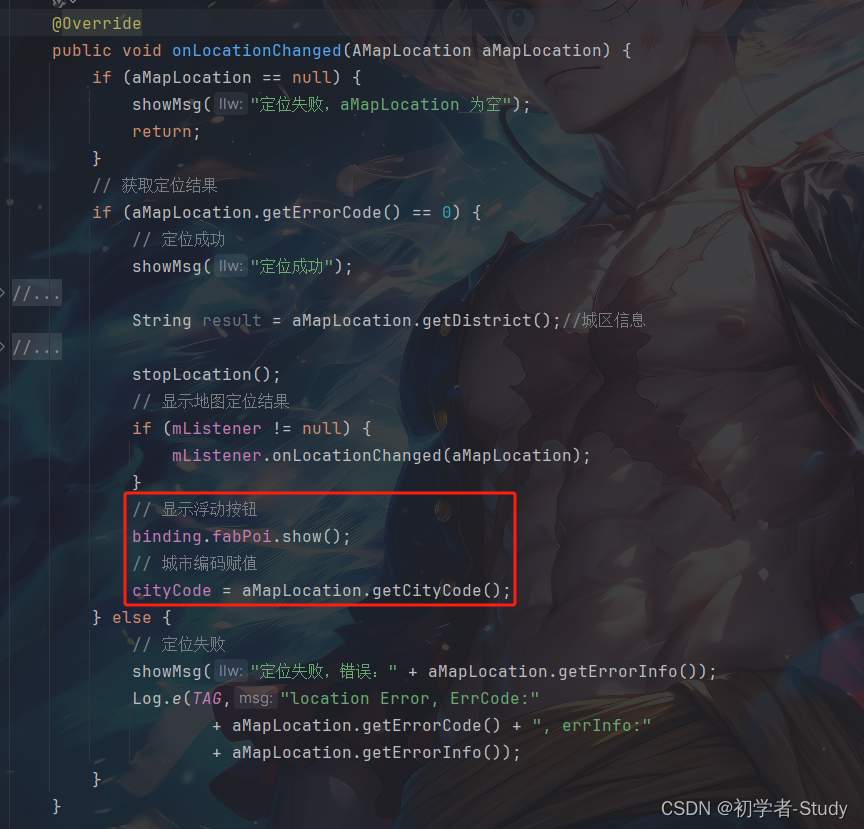
然后在onLocationChanged()方法中显示这个浮动按钮,添加代码如下:
// 显示浮动按钮
binding.fabPoi.show();
// 城市编码赋值
cityCode = aMapLocation.getCityCode();
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
添加位置如下图所示:
下面我们添加一个initView()方法,处理点击浮动按钮事件,代码如下所示:
/** * 初始化控件 */ private void initView() { // Poi搜索按钮点击事件 binding.fabPoi.setOnClickListener(v -> { //构造query对象 query = new PoiSearch.Query("购物", "", cityCode); // 设置每页最多返回多少条poiItem query.setPageSize(10); //设置查询页码 query.setPageNum(1); //构造 PoiSearch 对象 try { poiSearch = new PoiSearch(this, query); //设置搜索回调监听 poiSearch.setOnPoiSearchListener(this); //发起搜索附近POI异步请求 poiSearch.searchPOIAsyn(); } catch (AMapException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
这里同样this会报错,实现接口,出现弹窗如下所示:

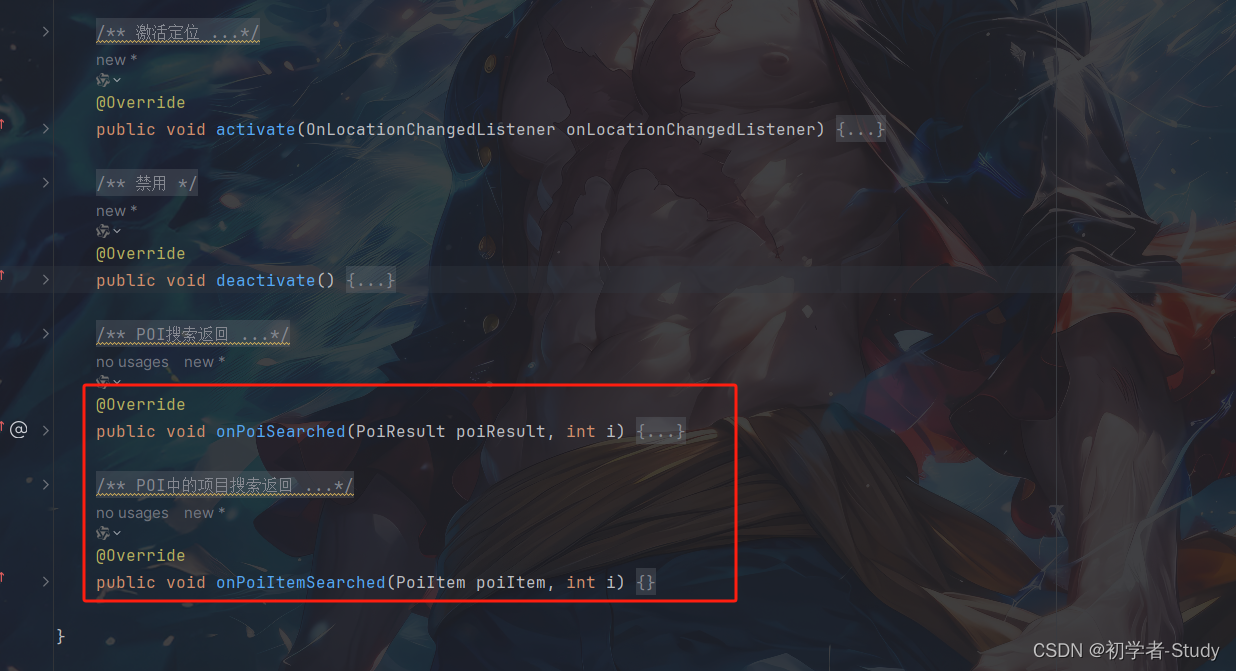
现在代码如下所示:
/** * POI搜索返回 * * @param poiResult POI所有数据 * @param i */ @Override public void onPoiSearched(PoiResult poiResult, int i) { //解析result获取POI信息 //获取POI组数列表 ArrayList<PoiItem> poiItems = poiResult.getPois(); for (PoiItem poiItem : poiItems) { Log.d("MainActivity", " Title:" + poiItem.getTitle() + " Snippet:" + poiItem.getSnippet()); } } /** * POI中的项目搜索返回 * * @param poiItem 获取POI item * @param i */ @Override public void onPoiItemSearched(PoiItem poiItem, int i) { }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
添加位置如下图所示:
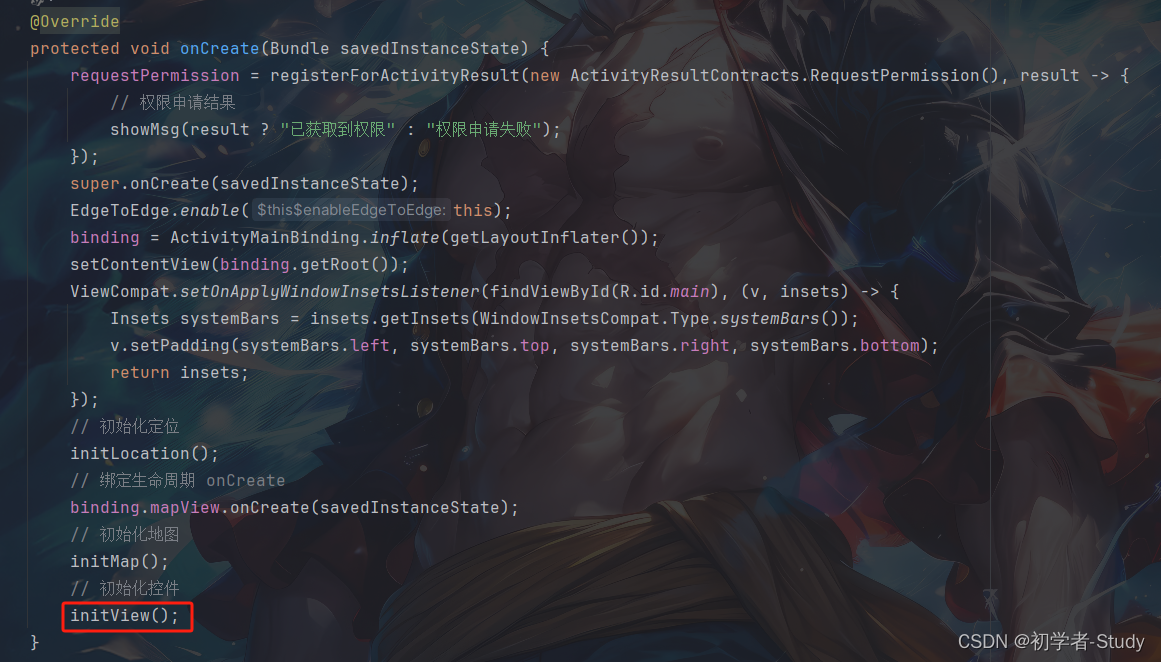
最后在onCreate()方法中调用initView()。
下面运行一下,然后点击页面右下角的浮动按钮,查看控制台,你会看到有打印,如下图所示:
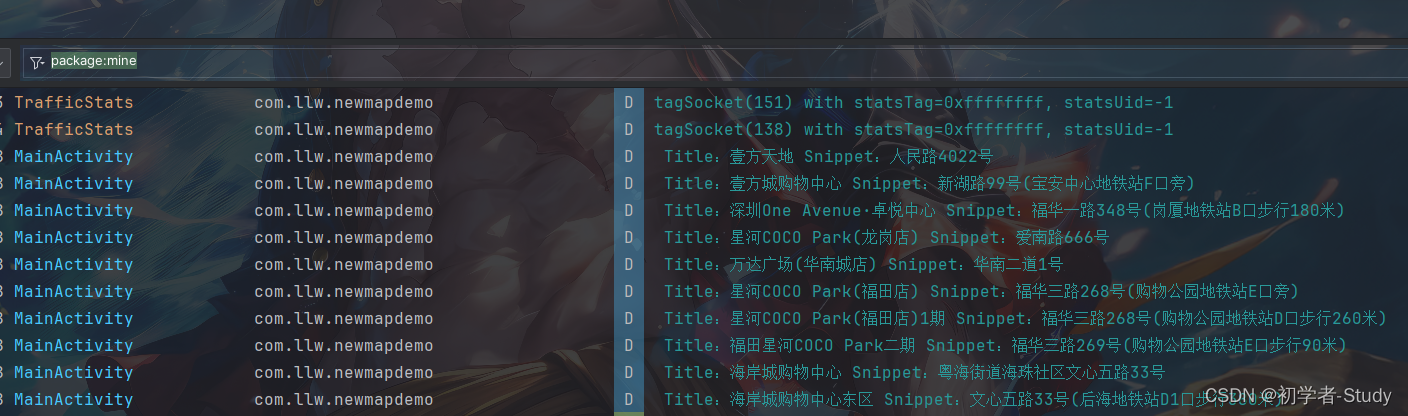
八、地图点击长按事件
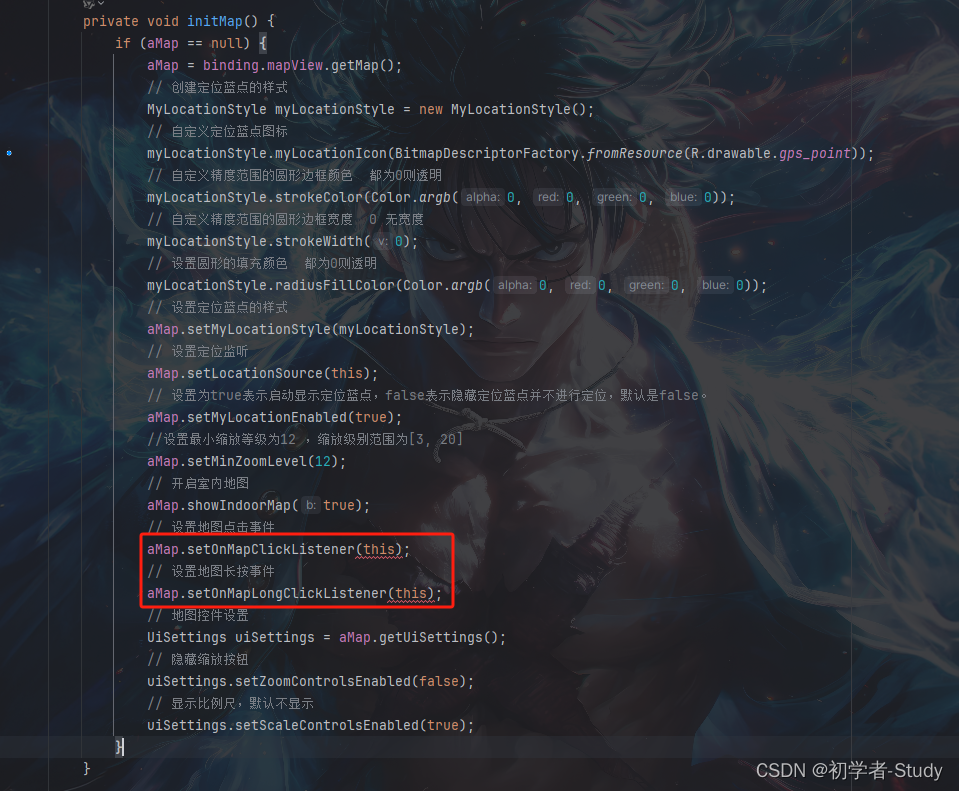
实际开发中都会对地图的点击和长按做处理,比如点击某一个地方获取经纬度,下面来操作一下吧,首先我们在initMap()方法中添加如下代码:
// 设置地图点击事件
aMap.setOnMapClickListener(this);
// 设置地图长按事件
aMap.setOnMapLongClickListener(this);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
添加位置如下图所示:
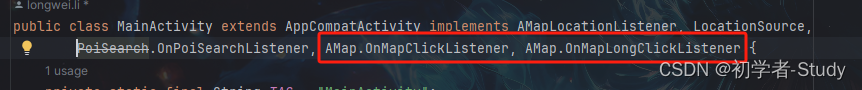
然后实现接口的点击和长按的回调,在MainActivity中添加代码如下所示:
/** * 地图点击事件 * @param latLng */ @Override public void onMapClick(LatLng latLng) { showMsg("点击了地图,经度:"+latLng.longitude+",纬度:"+latLng.latitude); } /** * 地图长按事件 * @param latLng */ @Override public void onMapLongClick(LatLng latLng) { showMsg("长按了地图,经度:"+latLng.longitude+",纬度:"+latLng.latitude); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
注意一下,MainActivity实现这两个接口
看看运行效果:

可看到成功获取到了经纬度,但是这就够了吗?用户又看不懂,那么怎么样让用户知道自己点击的是那里呢?那就是要把经纬度进行一次转换,转换成实际的地址描述。在高德中这种坐标转地址称之为逆地理编码。
① 逆地理编码
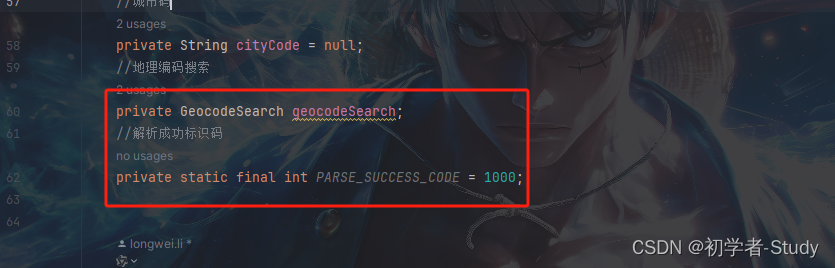
上面已经说过了,逆地理编码就是将坐标转为地址,坐标刚才已经拿到了,就是经纬度,下面来转换一下吧,首先在MainActivity中创建两个对象。
//地理编码搜索
private GeocodeSearch geocodeSearch;
//解析成功标识码
private static final int PARSE_SUCCESS_CODE = 1000;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
添加位置如下所示:
然后我们写一个initSearch()方法,在onCreate()调用,代码如下所示:
/**
* 初始化搜索
*/
private void initSearch() {
// 构造 GeocodeSearch 对象
try {
geocodeSearch = new GeocodeSearch(this);
// 设置监听
geocodeSearch.setOnGeocodeSearchListener(this);
} catch (AMapException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
添加位置如下图所示:

这里同样需要实现监听,会出现弹窗

实现代码如下所示:
/** * 坐标转地址 * @param regeocodeResult * @param rCode */ @Override public void onRegeocodeSearched(RegeocodeResult regeocodeResult, int rCode) { } /** * 地址转坐标 * @param geocodeResult * @param rCode */ @Override public void onGeocodeSearched(GeocodeResult geocodeResult, int rCode) { }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
一个是地址转坐标,一个是坐标转地址。当前我们需要将坐标转地址,所以目前重点关注这个onRegeocodeSearched方法。
既然是坐标转地址,那么肯定要先拿到坐标,刚才的地图点击的监听中我们已经拿到了坐标,于是你就可以写出这样的一个方法:
/**
* 通过经纬度获取地址
* @param latLng
*/
private void latLonToAddress(LatLng latLng) {
//位置点 通过经纬度进行构建
LatLonPoint latLonPoint = new LatLonPoint(latLng.latitude, latLng.longitude);
//逆编码查询 第一个参数表示一个Latlng,第二参数表示范围多少米,第三个参数表示是火系坐标系还是GPS原生坐标系
RegeocodeQuery query = new RegeocodeQuery(latLonPoint, 20, GeocodeSearch.AMAP);
//异步获取地址信息
geocodeSearch.getFromLocationAsyn(query);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
这个方法我们可以在地图点击和长按的时候调用,如下图所示:

通过经纬度构建LatLonPoint对象,然后构建RegeocodeQuery时,传入,并且输入另外两个参数,范围和坐标系。最后通过geocodeSearch发起一个异步的地址获取请求,下面修改一下onRegeocodeSearched()方法。
@Override
public void onRegeocodeSearched(RegeocodeResult regeocodeResult, int rCode) {
//解析result获取地址描述信息
if(rCode == PARSE_SUCCESS_CODE){
RegeocodeAddress regeocodeAddress = regeocodeResult.getRegeocodeAddress();
//显示解析后的地址
showMsg("地址:"+regeocodeAddress.getFormatAddress());
}else {
showMsg("获取地址失败");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
这就可以了,下面运行一下看看。

② 地理编码
上面说了逆地理编码,下面来说说地理编码,地理编码就是地址转坐标,那么它的使用场景是怎么样的呢?比如说你到一个景点去游玩,不知道路线只知道景点名,那么这个时候通常你会在导航软件中输入这个景点名,然后搜索出前往的路线及搭乘的交通工具。此时,导航软件会将你输入的地址转成经纬度坐标,然后通过你当前的所在地坐标计算距离,获取两点之间的交通情况,然后规划路线,是不是脑瓜子嗡嗡的,怎么导航还有这么多门道吗?其实我说的还算简单了,里面的步骤还会有很多的细化过程,好了,当前的重点不是这个地理编码吗?下面我也模仿一下,通过输入框输入地址,然后得出它的经纬度坐标。下面修改一下activity_main.xml中的代码,如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/main" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <com.google.android.material.appbar.MaterialToolbar android:id="@+id/toolbar" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize" android:background="@color/white" android:paddingTop="8dp" android:paddingEnd="12dp" android:paddingBottom="8dp" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"> <EditText android:id="@+id/et_address" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="@drawable/et_bg" android:hint="请输入地址" android:imeOptions="actionSearch" android:paddingStart="12dp" android:singleLine="true" android:textColor="#000" android:textSize="14sp" /> </com.google.android.material.appbar.MaterialToolbar> <com.amap.api.maps.MapView android:id="@+id/map_view" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="0dp" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/toolbar" /> <!--浮动按钮--> <com.google.android.material.floatingactionbutton.FloatingActionButton android:id="@+id/fab_poi" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_margin="20dp" android:clickable="true" android:focusable="true" android:src="@drawable/ic_favorite_red" app:hoveredFocusedTranslationZ="18dp" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:pressedTranslationZ="18dp" /> </androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
这里你就直接复制粘贴就好了,这里有一个输入框背景et_bg,在drawable下创建et_bg.xml,代码如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<corners android:radius="8dp"/>
<solid android:color="#E4E4E4"/>
</shape>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
好了,现在就不报错了,下面我们回到MainActivity中,首先声明一个变量
//城市
private String city;
- 1
- 2
在定位回调中我们需要对这个变量进行赋值,如下图所示:

输入框输入地址,我们通过点击输入框弹出输入法,因为涉及到输入法的点击事件,我们就在initView()方法中增加如下代码:
// 键盘按键监听 binding.etAddress.setOnKeyListener((v, keyCode, event) -> { if (keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_ENTER && event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_UP) { //获取输入框的值 String address = binding.etAddress.getText().toString().trim(); if (address.isEmpty()) { showMsg("请输入地址"); } else { InputMethodManager imm = (InputMethodManager) getSystemService(Context.INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE); //隐藏软键盘 imm.hideSoftInputFromWindow(getWindow().getDecorView().getWindowToken(), 0); // name表示地址,第二个参数表示查询城市,中文或者中文全拼,citycode、adcode GeocodeQuery query = new GeocodeQuery(address, city); geocodeSearch.getFromLocationNameAsyn(query); } return true; } return false; });
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
添加位置如下图所示:

下面进入到onGeocodeSearched()方法,在这个方法中进行解析后的坐标显示代码如下所示:
@Override
public void onGeocodeSearched(GeocodeResult geocodeResult, int rCode) {
if (rCode != PARSE_SUCCESS_CODE) {
showMsg("获取坐标失败");
return;
}
List<GeocodeAddress> geocodeAddressList = geocodeResult.getGeocodeAddressList();
if (geocodeAddressList != null && !geocodeAddressList.isEmpty()) {
LatLonPoint latLonPoint = geocodeAddressList.get(0).getLatLonPoint();
//显示解析后的坐标
showMsg("坐标:" + latLonPoint.getLongitude() + "," + latLonPoint.getLatitude());
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
通过返回值获取编码地址列表,判断不为空并且大于0则取第一条数据,然后获取经纬度的值显示出来。运行效果图如下所示:

③ 添加标点Marker
通常使用地图是会对地图进行标注,添加标点。刚才通过点击地图获取到了经纬度,那么同样可以根据这个经纬度在地图上绘制标点。
那么其实也很简单,下面在onMapClick方法中添加如下代码:
aMap.addMarker(new MarkerOptions().position(latLng).snippet("DefaultMarker"));
- 1
添加位置如下图所示:
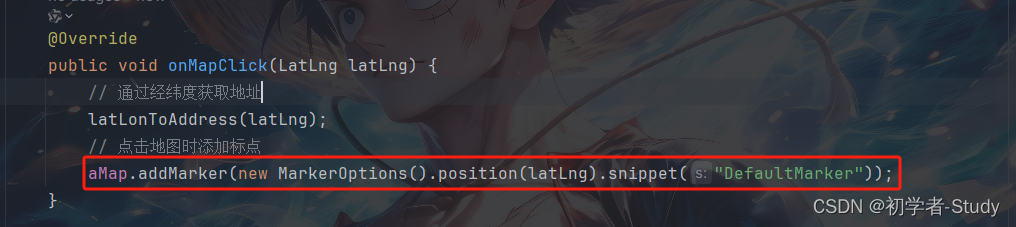
运行效果如下图所示:

④ 删除标点Marker
那么我们怎么去删除标点Marker呢,我们可以在页面上再增加一个浮动按钮,默认隐藏,当添加标点之后我们显示出按钮,点击该按钮之后就清除地图上的所有添加的标点,同时隐藏这个按钮。针对这个需求,首先我们修改activity_main.xml中代码,添加一个按钮,代码如下所示:
<!--浮动按钮 清空marker-->
<com.google.android.material.floatingactionbutton.FloatingActionButton
android:id="@+id/fab_clear_marker"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_above="@+id/fab_poi"
android:layout_marginBottom="16dp"
android:clickable="true"
android:src="@drawable/ic_clear"
android:visibility="invisible"
app:hoveredFocusedTranslationZ="18dp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@+id/fab_poi"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="@+id/fab_poi"
app:pressedTranslationZ="18dp" />
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
添加位置如下图所示:

这是使用的图标ic_clear.xml代码如下所示:
<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:width="32dp"
android:height="32dp"
android:viewportWidth="1024"
android:viewportHeight="1024">
<path
android:fillColor="#323233"
android:pathData="M279.8,206.6a57.6,57.6 0,1 1,57.6 57.3,56.9 56.9,0 0,1 -57.6,-57.3zM572.5,954.6c0,1 -1.9,1.9 -2.9,1.9l-97.6,-58.3a3.6,3.6 0,0 1,-1 -2.9c8.8,-19.4 97.6,-203 87.8,-193.3a1243,1243 0,0 0,-116.1 139.9l-26.3,35.9s-102.4,-69 -134.7,-111.7c0,-1 -1,-1 0,-1.9 20.5,-25.3 129.8,-166.1 129.8,-166.1l-184.4,110.7h-2.9c-8.8,-9.7 -70.3,-77.7 -88.8,-109.8v-1.9c17.6,-14.6 117.1,-98.1 117.1,-98.1l-140.5,49.5a3.6,3.6 0,0 1,-2.9 -1l-51.7,-97.1a1.9,1.9 0,0 1,1 -2.9c24.4,-4.8 230.3,-47.6 330.8,-116.6 2.5,-1.7 5.8,-1.3 7.8,1l287.9,286.5c2.3,2 2.7,5.3 1,7.8a894.9,894.9 0,0 0,-113.2 328.3l0,0.1zM771.6,839a72.2,72.2 0,1 1,-72.2 -71.9,71.9 71.9,0 0,1 72.2,71.9zM827.2,802a38.9,38.9 0,1 1,38.9 -38.7,39.1 39.1,0 0,1 -39,38.9l0.1,-0.1zM947.2,171.6L765.7,353.3c0,2.9 -1,3.9 -1,6.8 41,69.9 40,150.6 -19.5,212.7a4.7,4.7 0,0 1,-6.8 0L450.6,285.3a4.7,4.7 0,0 1,0 -6.8c62.4,-59.2 143.4,-59.2 213.7,-19.4 2.3,0.1 4.6,-0.2 6.8,-1l182.5,-180.6a66.4,66.4 0,1 1,93.7 94.2z" />
</vector>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
下面我们回到MainActivity中,为了方便清除地图上添加的标点,我们在添加的时候就将标点进行存储,放到一个列表中,声明一个变量,如下所示:
//标点列表
private final List<Marker> markerList = new ArrayList<>();
- 1
- 2
添加位置如下图所示:

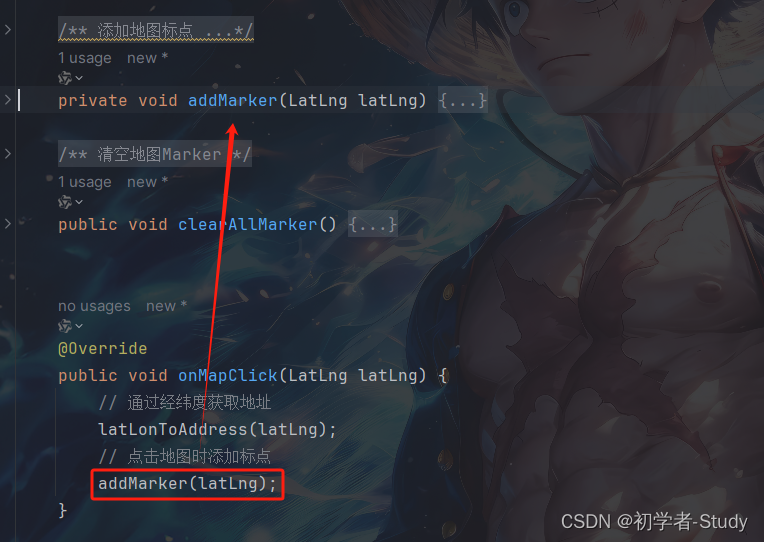
然后写一个添加地图标点和移除地图标点的方法,代码如下所示:
/** * 添加地图标点 * * @param latLng */ private void addMarker(LatLng latLng) { //显示浮动按钮 binding.fabClearMarker.show(); //添加标点 Marker marker = aMap.addMarker(new MarkerOptions().position(latLng).snippet("DefaultMarker")); markerList.add(marker); } /** * 清空地图Marker */ public void clearAllMarker() { if (markerList != null && !markerList.isEmpty()) { for (Marker markerItem : markerList) { markerItem.remove(); } } binding.fabClearMarker.hide(); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
然后在onMapClick()方法中调用,如下图所示:
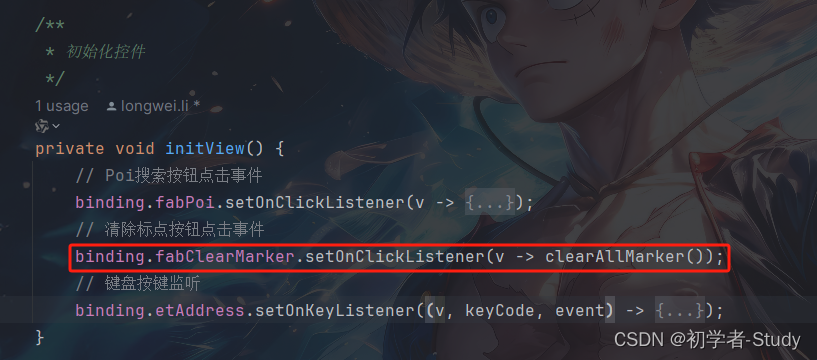
最后我们在initView()方法设置清除标点按钮点击事件,代码如下所示:
// 清除标点按钮点击事件
binding.fabClearMarker.setOnClickListener(v -> clearAllMarker());
- 1
- 2
添加位置如下图所示:
下面运行一下看看

⑤ 绘制动画效果Marker
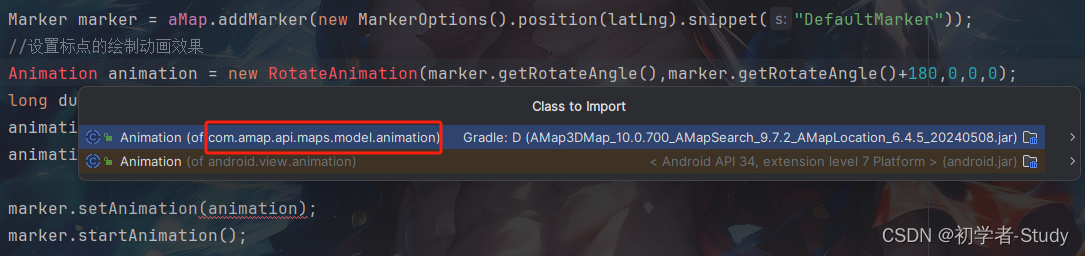
在addMarker()方法中,添加如下代码:
//设置标点的绘制动画效果
Animation animation = new RotateAnimation(marker.getRotateAngle(),marker.getRotateAngle()+180,0,0,0);
long duration = 1000L;
animation.setDuration(duration);
animation.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator());
marker.setAnimation(animation);
marker.startAnimation();
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
这里对于动画类的导包要注意一些,这个包是在高德的SDK中的,如下图所示:
上述代码添加位置如下图所示:
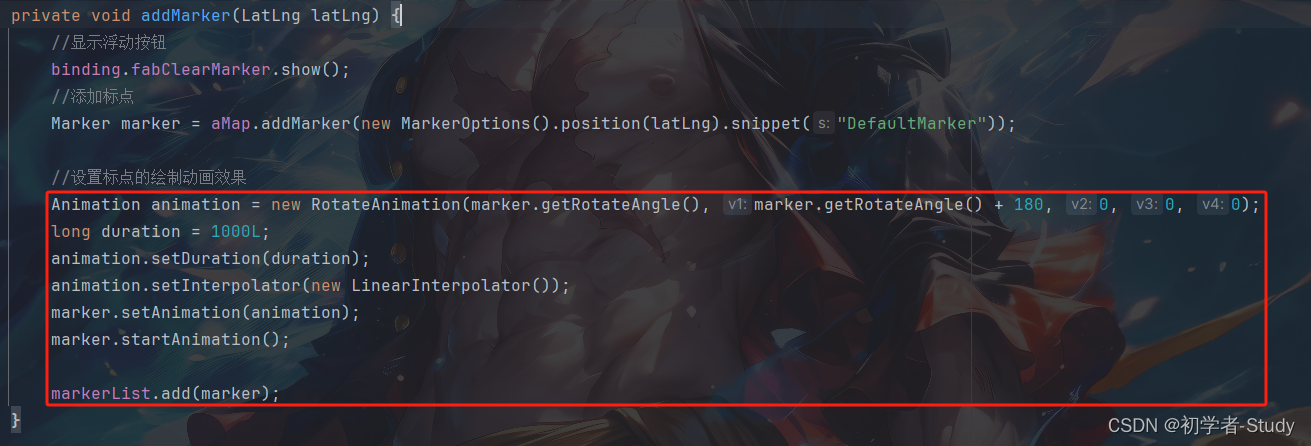
这段代码的意思就是配置一个旋转动画,然后设置旋转的角度和旋转所需要的时间,之后设置给marker。就可以,下面来看看效果吧。

这个动画是逆时针的,可以自己根据需要的效果进行更改。
当然可能这一个动画并不能满足你的需求,SDK中还提供了其他的,比如缩放动画、位移动画、透明度动画、渐变动画。它们都继承自Animation。

可以根据里面的参数进行配置然后达到你要的效果,那么就Marker的绘制动画效果就说到这,如果你有需要我用代码说明其他动画的需求,可以评论一下,我根据你的需求加上去。
⑥ Marker的点击和拖拽事件
Marker的点击和拖拽事件同样是在地图上设置,我们在initMap()方法中,增加如下所示代码:
// 设置地图标点点击事件
aMap.setOnMarkerClickListener(this);
// 设置地图标点拖拽事件
aMap.setOnMarkerDragListener(this);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
添加位置如下图所示:

然后我们实现相应的接口方法,代码如下所示:
@Override public boolean onMarkerClick(Marker marker) { showMsg("点击了标点"); return true; } @Override public void onMarkerDragStart(Marker marker) { Log.d(TAG, "开始拖拽"); } @Override public void onMarkerDrag(Marker marker) { Log.d(TAG, "拖拽中..."); } @Override public void onMarkerDragEnd(Marker marker) { showMsg("拖拽完成"); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
要使标点可以拖拽,需要修改marker的可拖动属性,默认为false,在addMarker()方法中添加一个属性,如下图所示:
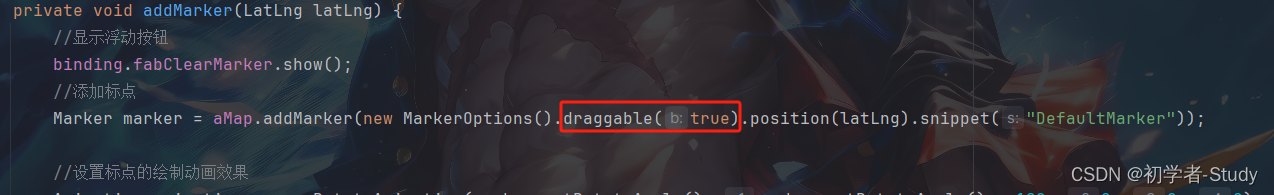
下面我们运行一下看看:

这个标点的点击和拖拽,建议你不要加上动画,就默认的标点,好操作一些。
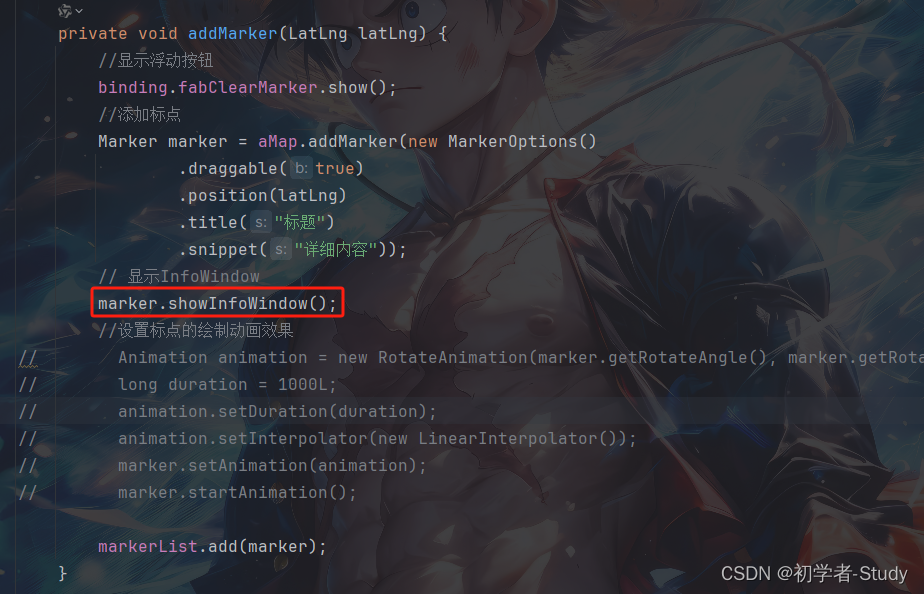
⑦ 绘制 InfoWindow
标点也是可以携带一些信息的,而这个信息可以由InfoWindow(信息窗体)展示处理出来。首先应该显示出来这个infoWindow,上面我们写了这个Marker的点击事件,那么可以在点击的时候显示InfoWindow,再点击就显示。先在addMarker()方法中设置InfoWindow中的信息,如下图所示:

然后在onMarkerClick()方法中,通过marker.isInfoWindowShown()判断当前Marker的InfoWindow是否显示,之后通过showInfoWindow()显示,hideInfoWindow()隐藏,代码如下所示:
@Override
public boolean onMarkerClick(Marker marker) {
if (!marker.isInfoWindowShown()) { // 显示
marker.showInfoWindow();
} else { // 隐藏
marker.hideInfoWindow();
}
return true;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
然后运行一下看看:

刚才是使用了自带的样式,其实InfoWindow是可以自己定义样式的,首先添加两个图片。


建议在我的源码里面复制,直接在博客中保存图片会有问题,下面在layout下创建两个xml。
custom_info_contents.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" > <ImageView android:id="@+id/badge" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginRight="5dp" android:adjustViewBounds="true" > </ImageView> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="vertical" > <TextView android:id="@+id/title" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" android:ellipsize="end" android:singleLine="true" android:textColor="#ff000000" android:textSize="14dp" android:textStyle="bold" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/snippet" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:ellipsize="end" android:singleLine="true" android:textColor="#ff7f7f7f" android:textSize="14dp" /> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
custom_info_window.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="100dp" android:layout_height="100dp" android:background="@mipmap/custom_info_bubble" android:orientation="horizontal" > <ImageView android:id="@+id/badge" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginRight="5dp" > </ImageView> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="vertical" > <TextView android:id="@+id/title" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" android:ellipsize="end" android:singleLine="true" android:textColor="#ff000000" android:textSize="14dp" android:textStyle="bold" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/snippet" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:ellipsize="end" android:singleLine="true" android:textColor="#ff7f7f7f" android:textSize="14dp" /> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
下面回到MainActivity中,在initMap添加InfoWindow适配器监听。代码如下所示:
// 设置InfoWindowAdapter监听
aMap.setInfoWindowAdapter(this);
- 1
- 2
添加位置如下图所示:
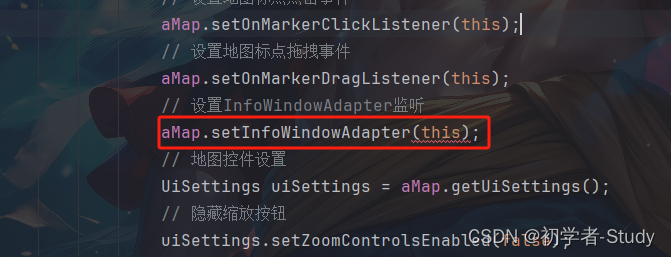
然后实现AMap.InfoWindowAdapter的接口,里面两个方法,代码如下所示:
/** * 修改内容 * * @param marker * @return */ @Override public View getInfoContents(Marker marker) { View infoContent = getLayoutInflater().inflate( R.layout.custom_info_contents, null); render(marker, infoContent); return infoContent; } /** * 修改背景 * * @param marker */ @Override public View getInfoWindow(Marker marker) { View infoWindow = getLayoutInflater().inflate( R.layout.custom_info_window, null); render(marker, infoWindow); return infoWindow; } /** * 渲染 * * @param marker * @param view */ private void render(Marker marker, View view) { ((ImageView) view.findViewById(R.id.badge)) .setImageResource(R.mipmap.ic_yuan); //修改InfoWindow标题内容样式 String title = marker.getTitle(); TextView titleUi = ((TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.title)); if (title != null) { SpannableString titleText = new SpannableString(title); titleText.setSpan(new ForegroundColorSpan(Color.RED), 0, titleText.length(), 0); titleUi.setTextSize(15); titleUi.setText(titleText); } else { titleUi.setText(""); } //修改InfoWindow片段内容样式 String snippet = marker.getSnippet(); TextView snippetUi = ((TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.snippet)); if (snippet != null) { SpannableString snippetText = new SpannableString(snippet); snippetText.setSpan(new ForegroundColorSpan(Color.GREEN), 0, snippetText.length(), 0); snippetUi.setTextSize(20); snippetUi.setText(snippetText); } else { snippetUi.setText(""); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
添加位置如下图所示:
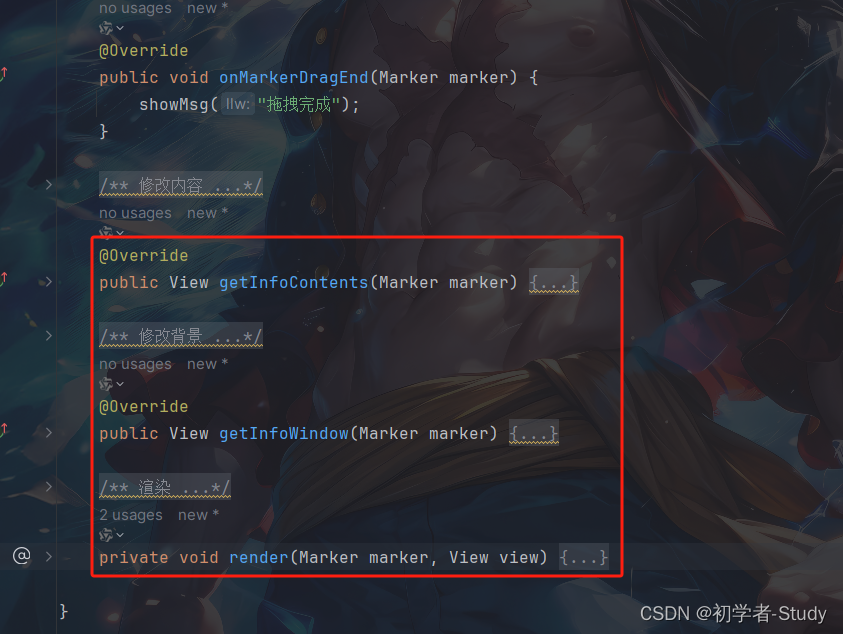
我们可以在添加标点的时候就直接显示InfoWindow,
下面运行一下看看:

⑧ InfoWindow的点击事件
在initMap()方法中添加如下代码:
// 设置InfoWindow点击事件
aMap.setOnInfoWindowClickListener(this);
- 1
- 2
添加位置如下图所示:

实现接口,代码如下所示:
/**
* InfoWindow点击事件
*
* @param marker
*/
@Override
public void onInfoWindowClick(Marker marker) {
showMsg("弹窗内容:标题:" + marker.getTitle() + "\n内容:" + marker.getSnippet());
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
运行一下:

⑨ 改变地图中心点
我们在实际使用中通常会有这样的操作,希望点击一下就可以移动到所在地,这其实是比较容易做到的,回顾我们现在是一进入地图就会定位到当前所在地,而当我点击地图上其他位置时,会增加一个标点,而我们要做的就是把这个标点作为地图中心,然后移动地图位置即可。
现在思路已经有了,很简单下面来写代码,代码也是很简单的,首先新增一个updateMapCenter()方法,里面传递一个LatLng对象作为入参。方法如下:
/**
* 改变地图中心位置
* @param latLng 位置
*/
private void updateMapCenter(LatLng latLng) {
// CameraPosition 第一个参数: 目标位置的屏幕中心点经纬度坐标。
// CameraPosition 第二个参数: 目标可视区域的缩放级别
// CameraPosition 第三个参数: 目标可视区域的倾斜度,以角度为单位。
// CameraPosition 第四个参数: 可视区域指向的方向,以角度为单位,从正北向顺时针方向计算,从0度到360度
CameraPosition cameraPosition = new CameraPosition(latLng, 16, 30, 0);
//位置变更
CameraUpdate cameraUpdate = CameraUpdateFactory.newCameraPosition(cameraPosition);
//改变位置(使用动画)
aMap.animateCamera(cameraUpdate);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
先通过CameraPosition配置一个中心位置对象,对象需要四个参数,在注释中已经说明了,然后通过CameraUpdate配置一个位置改变对象,传入刚才的cameraPosition。最后就是在地图上改变位置了。通过aMap.moveCamera()。这个方法比较简单,但别忘记了去调用,在onMapClick调用即可。

那么下面运行一下看看:

九、出行路线规划
首先要搞清楚什么是路线规划,比如有两个地点,A和B。从A到B有多种方路线和交通工具可以选择,这就是路线规划。那么平时常见的路线规划有哪些呢?步行、驾车、公交地铁等。这也是导航中使用最多的,那么下面先来说说这个步行出行路线规划,以下简称步行。
① 准备工作
这个路线规划我是打算单独放在一个Activity中,这样看起来会更加的清晰,因为我在MainActivity中已经写了很多的其他的功能的业务代码了,再加进去看起来好像就不是很容易去理解。也避免一个Activity打天下的尴尬局面。右键点击这个包名,然后New → Activity → Empty Views Activity
然后命名为RouteActivity,点击Finish完成Activity的创建。
创建好之后先做好准备工作,我先说说需要做好什么样的准备。一进入RouteActivity之后就要定位到当前所在地,这在前面我已经说过了,因此下面这一部分的代码我就不做讲解,如果你不理解是为什么,那么请从头看起。
首先修改activity_route.xml,代码如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/main" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".RouteActivity"> <!--地图--> <com.amap.api.maps.MapView android:id="@+id/map_view" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="0dp" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.0" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" /> </androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
然后修改一下RouteActivity的代码,代码如下所示:
package com.llw.newmapdemo; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; import androidx.activity.EdgeToEdge; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import androidx.core.graphics.Insets; import androidx.core.view.ViewCompat; import androidx.core.view.WindowInsetsCompat; import com.amap.api.location.AMapLocation; import com.amap.api.location.AMapLocationClient; import com.amap.api.location.AMapLocationClientOption; import com.amap.api.location.AMapLocationListener; import com.amap.api.maps.AMap; import com.amap.api.maps.LocationSource; import com.amap.api.maps.UiSettings; import com.amap.api.maps.model.BitmapDescriptorFactory; import com.amap.api.maps.model.MyLocationStyle; import com.llw.newmapdemo.databinding.ActivityRouteBinding; public class RouteActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements AMapLocationListener, LocationSource { private static final String TAG = "RouteActivity"; private ActivityRouteBinding binding; //地图控制器 private AMap aMap = null; //声明AMapLocationClient类对象 public AMapLocationClient mLocationClient = null; //声明AMapLocationClientOption对象 public AMapLocationClientOption mLocationOption = null; //位置更改监听 private LocationSource.OnLocationChangedListener mListener; //定义一个UiSettings对象 private UiSettings mUiSettings; //定位样式 private MyLocationStyle myLocationStyle = new MyLocationStyle(); @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); EdgeToEdge.enable(this); binding = ActivityRouteBinding.inflate(getLayoutInflater()); setContentView(binding.getRoot()); ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(findViewById(R.id.main), (v, insets) -> { Insets systemBars = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars()); v.setPadding(systemBars.left, systemBars.top, systemBars.right, systemBars.bottom); return insets; }); //初始化定位 initLocation(); //初始化地图 initMap(savedInstanceState); //启动定位 mLocationClient.startLocation(); } /** * 初始化定位 */ private void initLocation() { //初始化定位 try { mLocationClient = new AMapLocationClient(getApplicationContext()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } if (mLocationClient != null) { mLocationClient.setLocationListener(this); mLocationOption = new AMapLocationClientOption(); mLocationOption.setLocationMode(AMapLocationClientOption.AMapLocationMode.Hight_Accuracy); mLocationOption.setOnceLocationLatest(true); mLocationOption.setNeedAddress(true); mLocationOption.setHttpTimeOut(20000); mLocationOption.setLocationCacheEnable(false); mLocationClient.setLocationOption(mLocationOption); } } /** * 初始化地图 * * @param savedInstanceState */ private void initMap(Bundle savedInstanceState) { binding.mapView.onCreate(savedInstanceState); //初始化地图控制器对象 aMap = binding.mapView.getMap(); //设置最小缩放等级为12 ,缩放级别范围为[3, 20] aMap.setMinZoomLevel(12); //开启室内地图 aMap.showIndoorMap(true); //实例化UiSettings类对象 mUiSettings = aMap.getUiSettings(); //隐藏缩放按钮 默认显示 mUiSettings.setZoomControlsEnabled(false); //显示比例尺 默认不显示 mUiSettings.setScaleControlsEnabled(true); // 自定义定位蓝点图标 myLocationStyle.myLocationIcon(BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.gps_point)); //设置定位蓝点的Style aMap.setMyLocationStyle(myLocationStyle); // 设置定位监听 aMap.setLocationSource(this); // 设置为true表示显示定位层并可触发定位,false表示隐藏定位层并不可触发定位,默认是false aMap.setMyLocationEnabled(true); } @Override public void onLocationChanged(AMapLocation aMapLocation) { if (aMapLocation != null) { if (aMapLocation.getErrorCode() == 0) { //地址 String address = aMapLocation.getAddress(); //获取纬度 double latitude = aMapLocation.getLatitude(); //获取经度 double longitude = aMapLocation.getLongitude(); Log.d(TAG, aMapLocation.getCity()); Log.d(TAG, address); //停止定位后,本地定位服务并不会被销毁 mLocationClient.stopLocation(); //显示地图定位结果 if (mListener != null) { // 显示系统图标 mListener.onLocationChanged(aMapLocation); } } else { //定位失败时,可通过ErrCode(错误码)信息来确定失败的原因,errInfo是错误信息,详见错误码表。 Log.e("AmapError", "location Error, ErrCode:" + aMapLocation.getErrorCode() + ", errInfo:" + aMapLocation.getErrorInfo()); } } } @Override public void activate(LocationSource.OnLocationChangedListener onLocationChangedListener) { mListener = onLocationChangedListener; if (mLocationClient == null) { mLocationClient.startLocation();//启动定位 } } @Override public void deactivate() { mListener = null; if (mLocationClient != null) { mLocationClient.stopLocation(); mLocationClient.onDestroy(); } mLocationClient = null; } @Override protected void onResume() { super.onResume(); binding.mapView.onResume(); } @Override protected void onPause() { super.onPause(); binding.mapView.onPause(); } @Override protected void onSaveInstanceState(Bundle outState) { super.onSaveInstanceState(outState); binding.mapView.onSaveInstanceState(outState); } @Override protected void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); //销毁定位客户端,同时销毁本地定位服务。 if (mLocationClient != null) { mLocationClient.onDestroy(); } binding.mapView.onDestroy(); } private void showMsg(CharSequence llw) { Toast.makeText(this, llw, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
然后我们需要从MainActivity中进入RouteActivity,因此修改一下activity_main.xml,添加一个浮动按钮,代码如下所示:
<!--浮动按钮 跳转路线Activity--> <com.google.android.material.floatingactionbutton.FloatingActionButton android:id="@+id/fab_route" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" android:layout_marginEnd="16dp" android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/fab_poi" android:clickable="true" android:src="@drawable/ic_route" app:backgroundTint="#FFF" app:backgroundTintMode="screen" app:fabSize="mini" app:hoveredFocusedTranslationZ="18dp" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="@+id/fab_poi" app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/fab_poi" app:pressedTranslationZ="18dp" />
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
添加位置如下图所示:
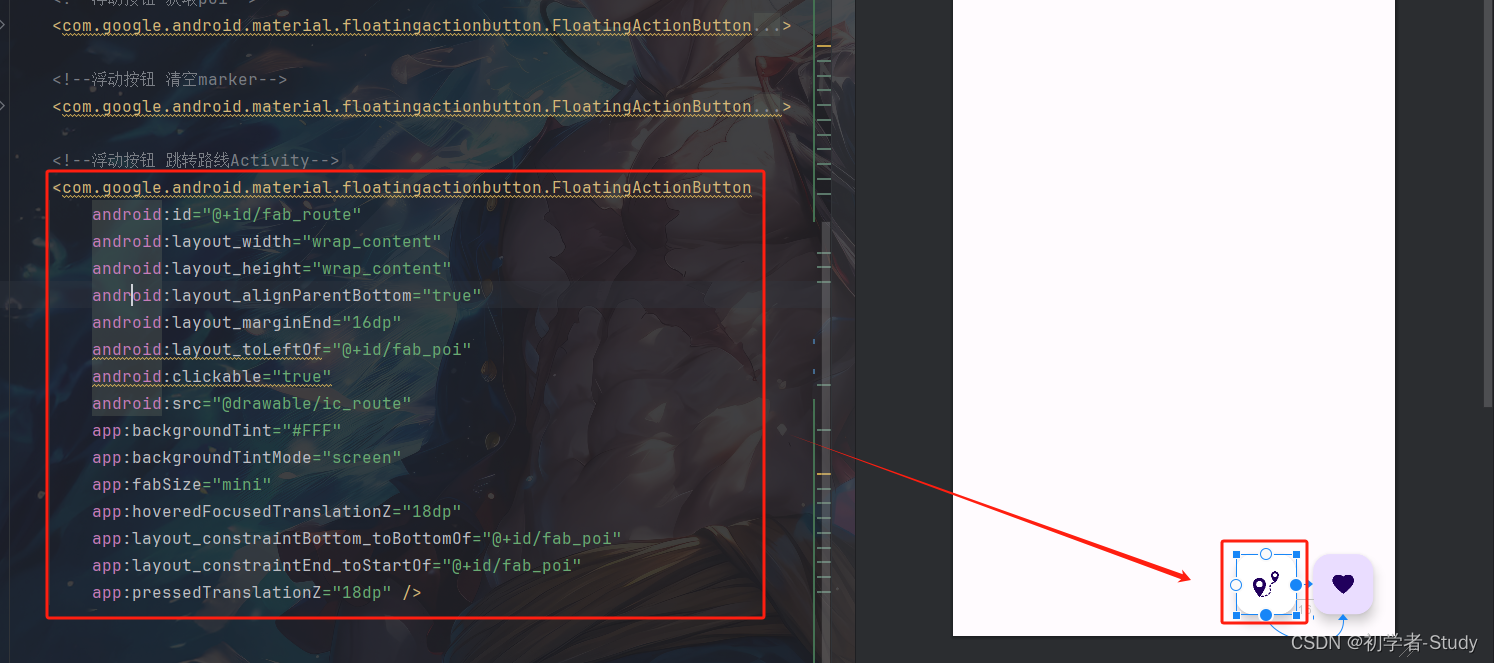
这个图标ic_route.xml的代码如下所示:
<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:width="32dp"
android:height="32dp"
android:viewportWidth="1024"
android:viewportHeight="1024">
<path
android:fillColor="#333333"
android:pathData="M870.4,0a153.6,153.6 0,0 0,-153.6 153.6c0,133.6 153.6,307.2 153.6,307.2s153.6,-173.6 153.6,-307.2a153.6,153.6 0,0 0,-153.6 -153.6zM870.4,230.4A76.8,76.8 0,1 1,947.2 153.6,76.8 76.8,0 0,1 870.4,230.4zM256,256a256,256 0,0 0,-256 256c0,222.7 256,512 256,512s256,-289.3 256,-512a256,256 0,0 0,-256 -256zM256,640A128,128 0,1 1,384 512,128 128,0 0,1 256,640zM669.2,538.6a204.8,204.8 0,0 0,-13.3 81.4v14.8h51.2v-13.3a159.2,159.2 0,0 1,9.2 -61.4,129 129,0 0,1 5.6,-11.8l-45.1,-24.6q-4.1,6.7 -7.7,14.8zM713.7,475.6l34.3,37.9a174.1,174.1 0,0 1,79.4 -38.9l-11.3,-51.2a224.8,224.8 0,0 0,-102.4 52.2zM319.5,972.8l4.6,51.2c36.9,-3.1 71.7,-7.7 102.4,-12.8l-8.7,-51.2c-29.2,5.6 -63,9.7 -98.3,12.8zM606.7,892.9l-6.7,5.1 30.7,41 9.2,-7.2a194.6,194.6 0,0 0,59.9 -86l-48.6,-16.9a141.8,141.8 0,0 1,-44.5 64zM468,950.8l11.3,51.2a530.9,530.9 0,0 0,102.4 -33.3l-21,-47.1a487.4,487.4 0,0 1,-92.7 29.2zM658.9,687.1c0,20.5 3.1,41.5 3.1,62.5v35.3l51.2,5.1a403.5,403.5 0,0 0,0 -40.4c0,-22 0,-44.5 -3.1,-66z" />
</vector>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
在initView()方法中,添加如下代码:
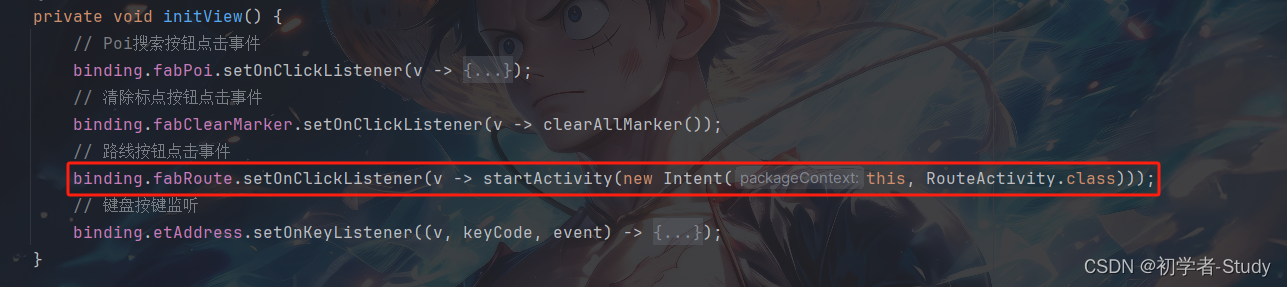
// 路线按钮点击事件
binding.fabRoute.setOnClickListener(v -> startActivity(new Intent(this, RouteActivity.class)));
- 1
- 2
位置如下图所示:
 下面运行一下:
下面运行一下:

那么现在准备工作就做完了。下面正式进入到路线规划的代码编写。
② 步行路线规划
路线规划首先需要两个点,起点和终点。起点其实已经有了,那就是我们当前所在地,至于终点可以由用户来控制,比如我在当前所在位置,然后点击了地图上某一个地方,把这个地方作为终点,这样一想也是可行的。那么按照这个思路来写一下代码。首先我先在RouteActivity创建两个对象。
//起点
private LatLonPoint mStartPoint;
//终点
private LatLonPoint mEndPoint;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
这里面会用到一些帮助方法,因此可以放到一个类里面进行管理,作为一个工具类。而工具类应该放到一个工具包下管理,在com.llw.newmapdemo下新建一个utils包,然后在这个包下新增ChString类,这个类是高德示例Demo里面的,我就直接拿过来了,代码如下:
package com.llw.newmapdemo.utils; public class ChString { public static final String Kilometer = "\u516c\u91cc";// "公里"; public static final String Meter = "\u7c73";// "米"; public static final String ByFoot = "\u6b65\u884c";// "步行"; public static final String To = "\u53bb\u5f80";// "去往"; public static final String Station = "\u8f66\u7ad9";// "车站"; public static final String TargetPlace = "\u76ee\u7684\u5730";// "目的地"; public static final String StartPlace = "\u51fa\u53d1\u5730";// "出发地"; public static final String About = "\u5927\u7ea6";// "大约"; public static final String Direction = "\u65b9\u5411";// "方向"; public static final String GetOn = "\u4e0a\u8f66";// "上车"; public static final String GetOff = "\u4e0b\u8f66";// "下车"; public static final String Zhan = "\u7ad9";// "站"; public static final String cross = "\u4ea4\u53c9\u8def\u53e3"; // 交叉路口 public static final String type = "\u7c7b\u522b"; // 类别 public static final String address = "\u5730\u5740"; // 地址 public static final String PrevStep = "\u4e0a\u4e00\u6b65"; public static final String NextStep = "\u4e0b\u4e00\u6b65"; public static final String Gong = "\u516c\u4ea4"; public static final String ByBus = "\u4e58\u8f66"; public static final String Arrive = "\u5230\u8FBE";// 到达 }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
再在这个包下新增一个MapUtil类,来源于高德示例Demo,我只拿了目前用得到的方法,代码如下:
package com.llw.newmapdemo.utils; import com.amap.api.maps.model.LatLng; import com.amap.api.services.core.LatLonPoint; import java.text.DecimalFormat; /** * 地图帮助类 * @author llw */ public class MapUtil { /** * 把LatLng对象转化为LatLonPoint对象 */ public static LatLonPoint convertToLatLonPoint(LatLng latLng) { return new LatLonPoint(latLng.latitude, latLng.longitude); } /** * 把LatLonPoint对象转化为LatLon对象 */ public static LatLng convertToLatLng(LatLonPoint latLonPoint) { return new LatLng(latLonPoint.getLatitude(), latLonPoint.getLongitude()); } public static String getFriendlyTime(int second) { if (second > 3600) { int hour = second / 3600; int miniate = (second % 3600) / 60; return hour + "小时" + miniate + "分钟"; } if (second >= 60) { int miniate = second / 60; return miniate + "分钟"; } return second + "秒"; } public static String getFriendlyLength(int lenMeter) { if (lenMeter > 10000) // 10 km { int dis = lenMeter / 1000; return dis + ChString.Kilometer; } if (lenMeter > 1000) { float dis = (float) lenMeter / 1000; DecimalFormat fnum = new DecimalFormat("##0.0"); String dstr = fnum.format(dis); return dstr + ChString.Kilometer; } if (lenMeter > 100) { int dis = lenMeter / 50 * 50; return dis + ChString.Meter; } int dis = lenMeter / 10 * 10; if (dis == 0) { dis = 10; } return dis + ChString.Meter; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
下面回到RouteActivity中,首先对起点进行赋值
//设置起点
mStartPoint = convertToLatLonPoint(new LatLng(latitude, longitude));
- 1
- 2

通过经纬度,构建LatLng对象,然后将LatLng转为LatLonPoint。最后赋值给起点mStartPoint。
那么下面就是终点了。刚才说到终点通过点击地图时产生,那么既然要点击地图,自然要使当前RouteActivity实现AMap.OnMapClickListener接口。然后在initMap中,进行监听。
//地图点击监听
aMap.setOnMapClickListener(this);
- 1
- 2

之后重写onMapClick()方法,然后将获取到的LatLng对象转为LatLonPoint,最后赋值给终点mEndPoint。
/**
* 点击地图
*/
@Override
public void onMapClick(LatLng latLng) {
//终点
mEndPoint = convertToLatLonPoint(latLng);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
这样我们就拿到了起点和终点,下面就要去搜索路线了,搜索路线需要一个RouteSearch对象,在RouteActivity中创建。
//路线搜索对象
private RouteSearch routeSearch;
- 1
- 2
然后RouteActivity实现RouteSearch.OnRouteSearchListener接口,新增一个initRoute方法。在这个方法里面初始化,然后设置路线搜索监听,方法代码如下:
/**
* 初始化路线
*/
private void initRoute() {
try {
routeSearch = new RouteSearch(this);
} catch (AMapException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
routeSearch.setRouteSearchListener(this);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
记得在onCreate()方法中调用,如下图所示:

之后需要重写四个方法,如下所示:
@Override public void onBusRouteSearched(BusRouteResult busRouteResult, int code) { } @Override public void onDriveRouteSearched(DriveRouteResult driveRouteResult, int code) { } /** * 步行规划路径结果 * * @param walkRouteResult 结果 * @param code 结果码 */ @Override public void onWalkRouteSearched(WalkRouteResult walkRouteResult, int code) { } @Override public void onRideRouteSearched(RideRouteResult rideRouteResult, int code) { }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
其中onWalkRouteSearched()方法我标注了是步行搜索返回的结果。那么现在先不管这个结果,因为我们需要先去发起路线搜索的请求之后,才会有结果,这里新增一个startRouteSearch()方法,代码如下:
/** * 开始路线搜索 */ private void startRouteSearch() { //在地图上添加起点Marker aMap.addMarker(new MarkerOptions() .position(convertToLatLng(mStartPoint)) .icon(BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.start))); //在地图上添加终点Marker aMap.addMarker(new MarkerOptions() .position(convertToLatLng(mEndPoint)) .icon(BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.end))); //搜索路线 构建路径的起终点 final RouteSearch.FromAndTo fromAndTo = new RouteSearch.FromAndTo( mStartPoint, mEndPoint); //构建步行路线搜索对象 RouteSearch.WalkRouteQuery query = new RouteSearch.WalkRouteQuery(fromAndTo, RouteSearch.WalkDefault); // 异步路径规划步行模式查询 routeSearch.calculateWalkRouteAsyn(query); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
前面两句代码就是给起点和终点各增加一个标注,这里有两个图标,你应该没有,我这里贴一下:


最好去我的源码里面去拿。然后代码继续往下看就是通过起点和终点构建路径的起终点对象fromAndTo,再通过这个对象去构建步行路线搜索对象,最后通过routeSearch对象发起搜索请求。到此为止请求就写完了。我们在onMapClick中去调用它。

下面就该去处理搜索路线的返回了。返回后最重要的是对这个路线进行绘制,从哪里到哪里,绘制在地图上,之前高德的SDK中这一部分是不开放的,不过在地图SDK V4.1.3版本开始,就已经是开源的了,只不过你要到高德示例Demo中去寻找,为了减少你的工作量,我已经提前找好了,并且只拿我需要的。下面在com.llw.newmapdemo下新增一个overlay包,这个包下新增三个类。
AMapServicesUtil.java
package com.llw.newmapdemo.overlay; /** * 地图服务工具类 */ import android.graphics.Bitmap; import com.amap.api.maps.model.LatLng; import com.amap.api.services.core.LatLonPoint; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; class AMapServicesUtil { public static int BUFFER_SIZE = 2048; public static byte[] inputStreamToByte(InputStream in) throws IOException { ByteArrayOutputStream outStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); byte[] data = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE]; int count = -1; while ((count = in.read(data, 0, BUFFER_SIZE)) != -1){ outStream.write(data, 0, count); } data = null; return outStream.toByteArray(); } public static LatLonPoint convertToLatLonPoint(LatLng latlon) { return new LatLonPoint(latlon.latitude, latlon.longitude); } public static LatLng convertToLatLng(LatLonPoint latLonPoint) { return new LatLng(latLonPoint.getLatitude(), latLonPoint.getLongitude()); } public static ArrayList<LatLng> convertArrList(List<LatLonPoint> shapes) { ArrayList<LatLng> lineShapes = new ArrayList<LatLng>(); for (LatLonPoint point : shapes) { LatLng latLngTemp = AMapServicesUtil.convertToLatLng(point); lineShapes.add(latLngTemp); } return lineShapes; } public static Bitmap zoomBitmap(Bitmap bitmap, float res) { if (bitmap == null) { return null; } int width, height; width = (int) (bitmap.getWidth() * res); height = (int) (bitmap.getHeight() * res); Bitmap newbmp = Bitmap.createScaledBitmap(bitmap, width, height, true); return newbmp; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
RouteOverlay.java
package com.llw.newmapdemo.overlay; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import android.content.Context; import android.graphics.Bitmap; import android.graphics.Color; import com.amap.api.maps.AMap; import com.amap.api.maps.CameraUpdateFactory; import com.amap.api.maps.model.BitmapDescriptor; import com.amap.api.maps.model.BitmapDescriptorFactory; import com.amap.api.maps.model.LatLng; import com.amap.api.maps.model.LatLngBounds; import com.amap.api.maps.model.Marker; import com.amap.api.maps.model.MarkerOptions; import com.amap.api.maps.model.Polyline; import com.amap.api.maps.model.PolylineOptions; import com.llw.newmapdemo.R; /** * 路线图层叠加 */ public class RouteOverlay { protected List<Marker> stationMarkers = new ArrayList<Marker>(); protected List<Polyline> allPolyLines = new ArrayList<Polyline>(); protected Marker startMarker; protected Marker endMarker; protected LatLng startPoint; protected LatLng endPoint; protected AMap mAMap; private Context mContext; private Bitmap startBit, endBit, busBit, walkBit, driveBit; protected boolean nodeIconVisible = true; public RouteOverlay(Context context) { mContext = context; } /** * 去掉BusRouteOverlay上所有的Marker。 * @since V2.1.0 */ public void removeFromMap() { if (startMarker != null) { startMarker.remove(); } if (endMarker != null) { endMarker.remove(); } for (Marker marker : stationMarkers) { marker.remove(); } for (Polyline line : allPolyLines) { line.remove(); } destroyBit(); } private void destroyBit() { if (startBit != null) { startBit.recycle(); startBit = null; } if (endBit != null) { endBit.recycle(); endBit = null; } if (busBit != null) { busBit.recycle(); busBit = null; } if (walkBit != null) { walkBit.recycle(); walkBit = null; } if (driveBit != null) { driveBit.recycle(); driveBit = null; } } /** * 给起点Marker设置图标,并返回更换图标的图片。如不用默认图片,需要重写此方法。 * @return 更换的Marker图片。 * @since V2.1.0 */ protected BitmapDescriptor getStartBitmapDescriptor() { return BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.amap_start); } /** * 给终点Marker设置图标,并返回更换图标的图片。如不用默认图片,需要重写此方法。 * @return 更换的Marker图片。 * @since V2.1.0 */ protected BitmapDescriptor getEndBitmapDescriptor() { return BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.amap_end); } /** * 给公交Marker设置图标,并返回更换图标的图片。如不用默认图片,需要重写此方法。 * @return 更换的Marker图片。 * @since V2.1.0 */ protected BitmapDescriptor getBusBitmapDescriptor() { return BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.amap_bus); } /** * 给步行Marker设置图标,并返回更换图标的图片。如不用默认图片,需要重写此方法。 * @return 更换的Marker图片。 * @since V2.1.0 */ protected BitmapDescriptor getWalkBitmapDescriptor() { return BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.amap_man); } protected BitmapDescriptor getDriveBitmapDescriptor() { return BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.amap_car); } protected void addStartAndEndMarker() { startMarker = mAMap.addMarker((new MarkerOptions()) .position(startPoint).icon(getStartBitmapDescriptor()) .title("\u8D77\u70B9")); // startMarker.showInfoWindow(); endMarker = mAMap.addMarker((new MarkerOptions()).position(endPoint) .icon(getEndBitmapDescriptor()).title("\u7EC8\u70B9")); // mAMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(startPoint, // getShowRouteZoom())); } /** * 移动镜头到当前的视角。 * @since V2.1.0 */ public void zoomToSpan() { if (startPoint != null) { if (mAMap == null) { return; } try { LatLngBounds bounds = getLatLngBounds(); mAMap.animateCamera(CameraUpdateFactory .newLatLngBounds(bounds, 100)); } catch (Throwable e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } protected LatLngBounds getLatLngBounds() { LatLngBounds.Builder b = LatLngBounds.builder(); b.include(new LatLng(startPoint.latitude, startPoint.longitude)); b.include(new LatLng(endPoint.latitude, endPoint.longitude)); return b.build(); } /** * 路段节点图标控制显示接口。 * @param visible true为显示节点图标,false为不显示。 * @since V2.3.1 */ public void setNodeIconVisibility(boolean visible) { try { nodeIconVisible = visible; if (this.stationMarkers != null && this.stationMarkers.size() > 0) { for (int i = 0; i < this.stationMarkers.size(); i++) { this.stationMarkers.get(i).setVisible(visible); } } } catch (Throwable e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } protected void addStationMarker(MarkerOptions options) { if(options == null) { return; } Marker marker = mAMap.addMarker(options); if(marker != null) { stationMarkers.add(marker); } } protected void addPolyLine(PolylineOptions options) { if(options == null) { return; } Polyline polyline = mAMap.addPolyline(options); if(polyline != null) { allPolyLines.add(polyline); } } protected float getRouteWidth() { return 18f; } protected int getWalkColor() { return Color.parseColor("#6db74d"); } /** * 自定义路线颜色。 * return 自定义路线颜色。 * @since V2.2.1 */ protected int getBusColor() { return Color.parseColor("#537edc"); } protected int getDriveColor() { return Color.parseColor("#537edc"); } // protected int getShowRouteZoom() { // return 15; // } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
WalkRouteOverlay.java
package com.llw.newmapdemo.overlay; import java.util.List; import com.amap.api.maps.AMap; import com.amap.api.maps.model.BitmapDescriptor; import com.amap.api.maps.model.LatLng; import com.amap.api.maps.model.MarkerOptions; import com.amap.api.maps.model.PolylineOptions; import com.amap.api.services.core.LatLonPoint; import com.amap.api.services.route.WalkPath; import com.amap.api.services.route.WalkStep; import android.content.Context; /** * 步行路线图层类。在高德地图API里,如果要显示步行路线规划,可以用此类来创建步行路线图层。如不满足需求,也可以自己创建自定义的步行路线图层。 * @since V2.1.0 */ public class WalkRouteOverlay extends RouteOverlay { private PolylineOptions mPolylineOptions; private BitmapDescriptor walkStationDescriptor= null; private WalkPath walkPath; /** * 通过此构造函数创建步行路线图层。 * @param context 当前activity。 * @param amap 地图对象。 * @param path 步行路线规划的一个方案。详见搜索服务模块的路径查询包(com.amap.api.services.route)中的类 <strong><a href="../../../../../../Search/com/amap/api/services/route/WalkStep.html" title="com.amap.api.services.route中的类">WalkStep</a></strong>。 * @param start 起点。详见搜索服务模块的核心基础包(com.amap.api.services.core)中的类<strong><a href="../../../../../../Search/com/amap/api/services/core/LatLonPoint.html" title="com.amap.api.services.core中的类">LatLonPoint</a></strong>。 * @param end 终点。详见搜索服务模块的核心基础包(com.amap.api.services.core)中的类<strong><a href="../../../../../../Search/com/amap/api/services/core/LatLonPoint.html" title="com.amap.api.services.core中的类">LatLonPoint</a></strong>。 * @since V2.1.0 */ public WalkRouteOverlay(Context context, AMap amap, WalkPath path, LatLonPoint start, LatLonPoint end) { super(context); this.mAMap = amap; this.walkPath = path; startPoint = AMapServicesUtil.convertToLatLng(start); endPoint = AMapServicesUtil.convertToLatLng(end); } /** * 添加步行路线到地图中。 * @since V2.1.0 */ public void addToMap() { initPolylineOptions(); try { List<WalkStep> walkPaths = walkPath.getSteps(); for (int i = 0; i < walkPaths.size(); i++) { WalkStep walkStep = walkPaths.get(i); LatLng latLng = AMapServicesUtil.convertToLatLng(walkStep .getPolyline().get(0)); addWalkStationMarkers(walkStep, latLng); addWalkPolyLines(walkStep); } addStartAndEndMarker(); showPolyline(); } catch (Throwable e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 检查这一步的最后一点和下一步的起始点之间是否存在空隙 */ private void checkDistanceToNextStep(WalkStep walkStep, WalkStep walkStep1) { LatLonPoint lastPoint = getLastWalkPoint(walkStep); LatLonPoint nextFirstPoint = getFirstWalkPoint(walkStep1); if (!(lastPoint.equals(nextFirstPoint))) { addWalkPolyLine(lastPoint, nextFirstPoint); } } /** * @param walkStep * @return */ private LatLonPoint getLastWalkPoint(WalkStep walkStep) { return walkStep.getPolyline().get(walkStep.getPolyline().size() - 1); } /** * @param walkStep * @return */ private LatLonPoint getFirstWalkPoint(WalkStep walkStep) { return walkStep.getPolyline().get(0); } private void addWalkPolyLine(LatLonPoint pointFrom, LatLonPoint pointTo) { addWalkPolyLine(AMapServicesUtil.convertToLatLng(pointFrom), AMapServicesUtil.convertToLatLng(pointTo)); } private void addWalkPolyLine(LatLng latLngFrom, LatLng latLngTo) { mPolylineOptions.add(latLngFrom, latLngTo); } /** * @param walkStep */ private void addWalkPolyLines(WalkStep walkStep) { mPolylineOptions.addAll(AMapServicesUtil.convertArrList(walkStep.getPolyline())); } /** * @param walkStep * @param position */ private void addWalkStationMarkers(WalkStep walkStep, LatLng position) { addStationMarker(new MarkerOptions() .position(position) .title("\u65B9\u5411:" + walkStep.getAction() + "\n\u9053\u8DEF:" + walkStep.getRoad()) .snippet(walkStep.getInstruction()).visible(nodeIconVisible) .anchor(0.5f, 0.5f).icon(walkStationDescriptor)); } /** * 初始化线段属性 */ private void initPolylineOptions() { if(walkStationDescriptor == null) { walkStationDescriptor = getWalkBitmapDescriptor(); } mPolylineOptions = null; mPolylineOptions = new PolylineOptions(); mPolylineOptions.color(getWalkColor()).width(getRouteWidth()); } private void showPolyline() { addPolyLine(mPolylineOptions); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
这里面有一些图标你应该没有,我贴一下:








最好去我的源码里去拿,因为这样你就不用手动去命名了。
下面你的这三个类应该是不会报错了,OK,回到RouteActivity中,修改onWalkRouteSearched方法,代码如下:
/** * 步行规划路径结果 * * @param walkRouteResult 结果 * @param code 结果码 */ @Override public void onWalkRouteSearched(WalkRouteResult walkRouteResult, int code) { aMap.clear();// 清理地图上的所有覆盖物 if (code != AMapException.CODE_AMAP_SUCCESS) { showMsg("错误码;" + code); return; } if (walkRouteResult == null || walkRouteResult.getPaths() == null) { showMsg("对不起,没有搜索到相关数据!"); return; } if (walkRouteResult.getPaths().isEmpty()) { showMsg("对不起,没有搜索到相关数据!"); return; } final WalkPath walkPath = walkRouteResult.getPaths().get(0); if (walkPath == null) { return; } //绘制路线 WalkRouteOverlay walkRouteOverlay = new WalkRouteOverlay( this, aMap, walkPath, walkRouteResult.getStartPos(), walkRouteResult.getTargetPos()); walkRouteOverlay.removeFromMap(); walkRouteOverlay.addToMap(); walkRouteOverlay.zoomToSpan(); int dis = (int) walkPath.getDistance(); int dur = (int) walkPath.getDuration(); String des = MapUtil.getFriendlyTime(dur) + "(" + MapUtil.getFriendlyLength(dis) + ")"; Log.d(TAG, des); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
返回结果时,先清空地图,然后判断是否搜索成功,否的话调用showMsg方法提示一下,然后判断返回值是否为空,之后判断返回的路径是否大于0,大于的话则就可以开始绘制路线了,绘制完之后清空原来的,然后添加新的图层到地图上,然后进行缩放,之后就是一些其他信息的打印了。写了这么久代码了,也该运行一下了。

③ 骑行路线规划
骑行其实和步行差不多,只是路线限制时图层不同而已,其他的都类似,写起来也是比较简单的,不过我们的布局要做一下改变,假如我把骑行也就入到RouteActivity中,那么在一个地图上就有两种出行方式了,因此需要方便用户来切换不同的方式才行。因此我们打开activity_route.xml
,修改后的代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/main" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".RouteActivity"> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginStart="16dp" android:text="出行方式:" android:textColor="#000" android:textSize="16sp" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="@+id/spinner" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" /> <Spinner android:id="@+id/spinner" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="50dp" android:layout_marginEnd="8dp" android:layout_weight="1" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" /> <!--地图--> <com.amap.api.maps.MapView android:id="@+id/map_view" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="0dp" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.0" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/spinner" /> </androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
一目了然,很简单的布局代码,首先将外部布局修改为相对布局,然后添加一个TextView,里面添加一个下来选择控件,用于切换不同的出行方式,然后修改一下地图控件,使它置于刚才所添加的顶部布局的下方。
布局修改好了,进入到RouteActivity中,先创建三个成员变量,如下所示:
//出行方式数组
private static final String[] travelModeArray = {"步行出行", "骑行出行"};
//出行方式值
private static int TRAVEL_MODE = 0;
//数组适配器
private ArrayAdapter<String> arrayAdapter;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
这里我们就指定了出现方式的种类,目前三种,后面些其他方式可以再加,然后就是方式值,当我们点击下拉框选择类型之后,通过位置赋值给这个TRAVEL_MODE 变量,然后我们在路线规划的方法中去根据这个值进行不同的路线搜索即可。最后一个是用来配置下拉框数据的。
下面新建一个initTravelMode方法用于初始化出行方式的数据,代码如下:
/** * 初始化出行方式 */ private void initTravelMode() { Spinner spinner = findViewById(R.id.spinner); //将可选内容与ArrayAdapter连接起来 arrayAdapter = new ArrayAdapter<>(this, android.R.layout.simple_spinner_item, travelModeArray); //设置下拉列表的风格 arrayAdapter.setDropDownViewResource(android.R.layout.simple_spinner_dropdown_item); //将adapter 添加到spinner中 spinner.setAdapter(arrayAdapter); //添加事件Spinner事件监听 spinner.setOnItemSelectedListener(new AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener() { @Override public void onItemSelected(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) { TRAVEL_MODE = position; } @Override public void onNothingSelected(AdapterView<?> parent) { } }); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
然后别忘了在onCreate()方法中调用。

然后在startRouteSearch()方法中,进行出行方式的判断,代码如下:
//出行方式判断 switch (TRAVEL_MODE) { case 0://步行 //构建步行路线搜索对象 RouteSearch.WalkRouteQuery query = new RouteSearch.WalkRouteQuery(fromAndTo, RouteSearch.WalkDefault); // 异步路径规划步行模式查询 routeSearch.calculateWalkRouteAsyn(query); break; case 1://骑行 //构建骑行路线搜索对象 RouteSearch.RideRouteQuery rideQuery = new RouteSearch.RideRouteQuery(fromAndTo, RouteSearch.WalkDefault); //骑行规划路径计算 routeSearch.calculateRideRouteAsyn(rideQuery); break; default: break; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
添加位置如下图所示:

然后就是回调了,之前我们写了步行的回调,下面就是骑行的回调,因此有一些东西需要加进来才行,下面先做这一步操作,首先是修改原来的MapUtil工具类,在里面新增一个方法,代码如下:
/**
* 把集合体的LatLonPoint转化为集合体的LatLng
*/
public static ArrayList<LatLng> convertArrList(List<LatLonPoint> shapes) {
ArrayList<LatLng> lineShapes = new ArrayList<LatLng>();
for (LatLonPoint point : shapes) {
LatLng latLngTemp = convertToLatLng(point);
lineShapes.add(latLngTemp);
}
return lineShapes;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
然后在overlay包下,新增一个RideRouteOverlay类,用于在地图上绘制骑行的图层,里面的代码如下:(这个代码是源码里面有的)
package com.llw.newmapdemo.overlay; import android.content.Context; import com.amap.api.maps.AMap; import com.amap.api.maps.model.BitmapDescriptor; import com.amap.api.maps.model.BitmapDescriptorFactory; import com.amap.api.maps.model.LatLng; import com.amap.api.maps.model.MarkerOptions; import com.amap.api.maps.model.PolylineOptions; import com.amap.api.services.core.LatLonPoint; import com.amap.api.services.route.RidePath; import com.amap.api.services.route.RideStep; import com.llw.newmapdemo.R; import com.llw.newmapdemo.utils.MapUtil; import java.util.List; /** * 骑行路线图层类。在高德地图API里,如果要显示步行路线规划,可以用此类来创建骑行路线图层。如不满足需求,也可以自己创建自定义的骑行路线图层。 * @since V3.5.0 */ public class RideRouteOverlay extends RouteOverlay { private PolylineOptions mPolylineOptions; private BitmapDescriptor walkStationDescriptor= null; private RidePath ridePath; /** * 通过此构造函数创建骑行路线图层。 * @param context 当前activity。 * @param amap 地图对象。 * @param path 骑行路线规划的一个方案。详见搜索服务模块的路径查询包(com.amap.api.services.route)中的类 <strong><a href="../../../../../../Search/com/amap/api/services/route/WalkStep.html" title="com.amap.api.services.route中的类">WalkStep</a></strong>。 * @param start 起点。详见搜索服务模块的核心基础包(com.amap.api.services.core)中的类<strong><a href="../../../../../../Search/com/amap/api/services/core/LatLonPoint.html" title="com.amap.api.services.core中的类">LatLonPoint</a></strong>。 * @param end 终点。详见搜索服务模块的核心基础包(com.amap.api.services.core)中的类<strong><a href="../../../../../../Search/com/amap/api/services/core/LatLonPoint.html" title="com.amap.api.services.core中的类">LatLonPoint</a></strong>。 * @since V3.5.0 */ public RideRouteOverlay(Context context, AMap amap, RidePath path, LatLonPoint start, LatLonPoint end) { super(context); this.mAMap = amap; this.ridePath = path; startPoint = MapUtil.convertToLatLng(start); endPoint = MapUtil.convertToLatLng(end); } /** * 添加骑行路线到地图中。 * @since V3.5.0 */ public void addToMap() { initPolylineOptions(); try { List<RideStep> ridePaths = ridePath.getSteps(); for (int i = 0; i < ridePaths.size(); i++) { RideStep rideStep = ridePaths.get(i); LatLng latLng = MapUtil.convertToLatLng(rideStep .getPolyline().get(0)); addRideStationMarkers(rideStep, latLng); addRidePolyLines(rideStep); } addStartAndEndMarker(); showPolyline(); } catch (Throwable e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * @param rideStep */ private void addRidePolyLines(RideStep rideStep) { mPolylineOptions.addAll(MapUtil.convertArrList(rideStep.getPolyline())); } /** * @param rideStep * @param position */ private void addRideStationMarkers(RideStep rideStep, LatLng position) { addStationMarker(new MarkerOptions() .position(position) .title("\u65B9\u5411:" + rideStep.getAction() + "\n\u9053\u8DEF:" + rideStep.getRoad()) .snippet(rideStep.getInstruction()).visible(nodeIconVisible) .anchor(0.5f, 0.5f).icon(walkStationDescriptor)); } /** * 初始化线段属性 */ private void initPolylineOptions() { if(walkStationDescriptor == null) { walkStationDescriptor = BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.amap_ride); } mPolylineOptions = null; mPolylineOptions = new PolylineOptions(); mPolylineOptions.color(getDriveColor()).width(getRouteWidth()); } private void showPolyline() { addPolyLine(mPolylineOptions); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
下面回到RouteActivity中,找到onRideRouteSearched()方法,这是骑行的搜索路线回调方法,修改代码如下:
/** * 骑行规划路径结果 * * @param rideRouteResult 结果 * @param code 结果码 */ @Override public void onRideRouteSearched(final RideRouteResult rideRouteResult, int code) { aMap.clear();// 清理地图上的所有覆盖物 if (code != AMapException.CODE_AMAP_SUCCESS) { showMsg("错误码;" + code); return; } if (rideRouteResult == null || rideRouteResult.getPaths() == null) { showMsg("对不起,没有搜索到相关数据!"); return; } if (rideRouteResult.getPaths().isEmpty()) { showMsg("对不起,没有搜索到相关数据!"); return; } final RidePath ridePath = rideRouteResult.getPaths() .get(0); if (ridePath == null) { return; } RideRouteOverlay rideRouteOverlay = new RideRouteOverlay( this, aMap, ridePath, rideRouteResult.getStartPos(), rideRouteResult.getTargetPos()); rideRouteOverlay.removeFromMap(); rideRouteOverlay.addToMap(); rideRouteOverlay.zoomToSpan(); int dis = (int) ridePath.getDistance(); int dur = (int) ridePath.getDuration(); String des = MapUtil.getFriendlyTime(dur) + "(" + MapUtil.getFriendlyLength(dis) + ")"; Log.d(TAG, des); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
很熟悉的代码吧,和步行的基本没有什么两样,只是里面使用的值不同而已。那么到这里你的代码就写完了,我们来运行一下吧。

这样就完成了骑行的路线规划了。
④ 驾车路线规划
现在来写这个驾车路线规划,步骤还是和前面的差不多,这回你都不用改布局了,在RouteActivity中修改travelModeArray的变量值,
private static final String[] travelModeArray = {"步行出行", "骑行出行", "驾车出行"};
- 1
如下所示。

然后找到startRouteSearch()方法,加一个驾车的条件分支
case 2://驾车
//构建驾车路线搜索对象 剩余三个参数分别是:途经点、避让区域、避让道路
RouteSearch.DriveRouteQuery driveQuery = new RouteSearch.DriveRouteQuery(fromAndTo, RouteSearch.WalkDefault, null, null, "");
//驾车规划路径计算
routeSearch.calculateDriveRouteAsyn(driveQuery);
break;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
添加位置如下图所示:
然后同样要有一个图层。在overlay包下新增DrivingRouteOverlay类,用于在地图上绘制驾车路线图层,代码如下:(SDK中代码)
package com.llw.newmapdemo.overlay; import android.content.Context; import android.graphics.Color; import com.amap.api.maps.AMap; import com.amap.api.maps.model.BitmapDescriptor; import com.amap.api.maps.model.BitmapDescriptorFactory; import com.amap.api.maps.model.LatLng; import com.amap.api.maps.model.LatLngBounds; import com.amap.api.maps.model.Marker; import com.amap.api.maps.model.MarkerOptions; import com.amap.api.maps.model.PolylineOptions; import com.amap.api.services.core.LatLonPoint; import com.amap.api.services.route.DrivePath; import com.amap.api.services.route.DriveStep; import com.amap.api.services.route.TMC; import com.llw.newmapdemo.R; import com.llw.newmapdemo.utils.MapUtil; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * 驾车路线图层类 */ public class DrivingRouteOverlay extends RouteOverlay{ private DrivePath drivePath; private List<LatLonPoint> throughPointList; private List<Marker> throughPointMarkerList = new ArrayList<Marker>(); private boolean throughPointMarkerVisible = true; private List<TMC> tmcs; private PolylineOptions mPolylineOptions; private PolylineOptions mPolylineOptionscolor; private Context mContext; private boolean isColorfulline = true; private float mWidth = 25; private List<LatLng> mLatLngsOfPath; public void setIsColorfulline(boolean iscolorfulline) { this.isColorfulline = iscolorfulline; } /** * 根据给定的参数,构造一个导航路线图层类对象。 * * @param amap 地图对象。 * @param path 导航路线规划方案。 * @param context 当前的activity对象。 */ public DrivingRouteOverlay(Context context, AMap amap, DrivePath path, LatLonPoint start, LatLonPoint end, List<LatLonPoint> throughPointList) { super(context); mContext = context; mAMap = amap; this.drivePath = path; startPoint = MapUtil.convertToLatLng(start); endPoint = MapUtil.convertToLatLng(end); this.throughPointList = throughPointList; } @Override public float getRouteWidth() { return mWidth; } /** * 设置路线宽度 * * @param mWidth 路线宽度,取值范围:大于0 */ public void setRouteWidth(float mWidth) { this.mWidth = mWidth; } /** * 添加驾车路线添加到地图上显示。 */ public void addToMap() { initPolylineOptions(); try { if (mAMap == null) { return; } if (mWidth == 0 || drivePath == null) { return; } mLatLngsOfPath = new ArrayList<LatLng>(); tmcs = new ArrayList<TMC>(); List<DriveStep> drivePaths = drivePath.getSteps(); for (DriveStep step : drivePaths) { List<LatLonPoint> latlonPoints = step.getPolyline(); List<TMC> tmclist = step.getTMCs(); tmcs.addAll(tmclist); addDrivingStationMarkers(step, convertToLatLng(latlonPoints.get(0))); for (LatLonPoint latlonpoint : latlonPoints) { mPolylineOptions.add(convertToLatLng(latlonpoint)); mLatLngsOfPath.add(convertToLatLng(latlonpoint)); } } if (startMarker != null) { startMarker.remove(); startMarker = null; } if (endMarker != null) { endMarker.remove(); endMarker = null; } addStartAndEndMarker(); addThroughPointMarker(); if (isColorfulline && tmcs.size()>0 ) { colorWayUpdate(tmcs); showcolorPolyline(); }else { showPolyline(); } } catch (Throwable e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 初始化线段属性 */ private void initPolylineOptions() { mPolylineOptions = null; mPolylineOptions = new PolylineOptions(); mPolylineOptions.color(getDriveColor()).width(getRouteWidth()); } private void showPolyline() { addPolyLine(mPolylineOptions); } private void showcolorPolyline() { addPolyLine(mPolylineOptionscolor); } /** * 根据不同的路段拥堵情况展示不同的颜色 * * @param tmcSection */ private void colorWayUpdate(List<TMC> tmcSection) { if (mAMap == null) { return; } if (tmcSection == null || tmcSection.size() <= 0) { return; } TMC segmentTrafficStatus; mPolylineOptionscolor = null; mPolylineOptionscolor = new PolylineOptions(); mPolylineOptionscolor.width(getRouteWidth()); List<Integer> colorList = new ArrayList<Integer>(); mPolylineOptionscolor.add(MapUtil.convertToLatLng(tmcSection.get(0).getPolyline().get(0))); colorList.add(getDriveColor()); for (int i = 0; i < tmcSection.size(); i++) { segmentTrafficStatus = tmcSection.get(i); int color = getcolor(segmentTrafficStatus.getStatus()); List<LatLonPoint> mployline = segmentTrafficStatus.getPolyline(); for (int j = 1; j < mployline.size(); j++) { mPolylineOptionscolor.add(MapUtil.convertToLatLng(mployline.get(j))); colorList.add(color); } } colorList.add(getDriveColor()); mPolylineOptionscolor.colorValues(colorList); } private int getcolor(String status) { if (status.equals("畅通")) { return Color.GREEN; } else if (status.equals("缓行")) { return Color.YELLOW; } else if (status.equals("拥堵")) { return Color.RED; } else if (status.equals("严重拥堵")) { return Color.parseColor("#990033"); } else { return Color.parseColor("#537edc"); } } public LatLng convertToLatLng(LatLonPoint point) { return new LatLng(point.getLatitude(),point.getLongitude()); } /** * @param driveStep * @param latLng */ private void addDrivingStationMarkers(DriveStep driveStep, LatLng latLng) { addStationMarker(new MarkerOptions() .position(latLng) .title("\u65B9\u5411:" + driveStep.getAction() + "\n\u9053\u8DEF:" + driveStep.getRoad()) .snippet(driveStep.getInstruction()).visible(nodeIconVisible) .anchor(0.5f, 0.5f).icon(getDriveBitmapDescriptor())); } @Override protected LatLngBounds getLatLngBounds() { LatLngBounds.Builder b = LatLngBounds.builder(); b.include(new LatLng(startPoint.latitude, startPoint.longitude)); b.include(new LatLng(endPoint.latitude, endPoint.longitude)); if (this.throughPointList != null && this.throughPointList.size() > 0) { for (int i = 0; i < this.throughPointList.size(); i++) { b.include(new LatLng( this.throughPointList.get(i).getLatitude(), this.throughPointList.get(i).getLongitude())); } } return b.build(); } public void setThroughPointIconVisibility(boolean visible) { try { throughPointMarkerVisible = visible; if (this.throughPointMarkerList != null && this.throughPointMarkerList.size() > 0) { for (int i = 0; i < this.throughPointMarkerList.size(); i++) { this.throughPointMarkerList.get(i).setVisible(visible); } } } catch (Throwable e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private void addThroughPointMarker() { if (this.throughPointList != null && this.throughPointList.size() > 0) { LatLonPoint latLonPoint = null; for (int i = 0; i < this.throughPointList.size(); i++) { latLonPoint = this.throughPointList.get(i); if (latLonPoint != null) { throughPointMarkerList.add(mAMap .addMarker((new MarkerOptions()) .position( new LatLng(latLonPoint .getLatitude(), latLonPoint .getLongitude())) .visible(throughPointMarkerVisible) .icon(getThroughPointBitDes()) .title("\u9014\u7ECF\u70B9"))); } } } } private BitmapDescriptor getThroughPointBitDes() { return BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.amap_through); } /** * 获取两点间距离 * * @param start * @param end * @return */ public static int calculateDistance(LatLng start, LatLng end) { double x1 = start.longitude; double y1 = start.latitude; double x2 = end.longitude; double y2 = end.latitude; return calculateDistance(x1, y1, x2, y2); } public static int calculateDistance(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) { final double NF_pi = 0.01745329251994329; // 弧度 PI/180 x1 *= NF_pi; y1 *= NF_pi; x2 *= NF_pi; y2 *= NF_pi; double sinx1 = Math.sin(x1); double siny1 = Math.sin(y1); double cosx1 = Math.cos(x1); double cosy1 = Math.cos(y1); double sinx2 = Math.sin(x2); double siny2 = Math.sin(y2); double cosx2 = Math.cos(x2); double cosy2 = Math.cos(y2); double[] v1 = new double[3]; v1[0] = cosy1 * cosx1 - cosy2 * cosx2; v1[1] = cosy1 * sinx1 - cosy2 * sinx2; v1[2] = siny1 - siny2; double dist = Math.sqrt(v1[0] * v1[0] + v1[1] * v1[1] + v1[2] * v1[2]); return (int) (Math.asin(dist / 2) * 12742001.5798544); } //获取指定两点之间固定距离点 public static LatLng getPointForDis(LatLng sPt, LatLng ePt, double dis) { double lSegLength = calculateDistance(sPt, ePt); double preResult = dis / lSegLength; return new LatLng((ePt.latitude - sPt.latitude) * preResult + sPt.latitude, (ePt.longitude - sPt.longitude) * preResult + sPt.longitude); } /** * 去掉DriveLineOverlay上的线段和标记。 */ @Override public void removeFromMap() { try { super.removeFromMap(); if (this.throughPointMarkerList != null && this.throughPointMarkerList.size() > 0) { for (int i = 0; i < this.throughPointMarkerList.size(); i++) { this.throughPointMarkerList.get(i).remove(); } this.throughPointMarkerList.clear(); } } catch (Throwable e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
- 294
- 295
- 296
- 297
- 298
- 299
- 300
- 301
- 302
- 303
- 304
- 305
- 306
- 307
- 308
- 309
- 310
- 311
- 312
- 313
- 314
- 315
- 316
- 317
- 318
- 319
- 320
- 321
- 322
- 323
- 324
- 325
- 326
- 327
然后回到RouteActivity中,找到onDriveRouteSearched方法,里面的代码如下:
/** * 驾车规划路径结果 * * @param driveRouteResult 结果 * @param code 结果码 */ @Override public void onDriveRouteSearched(DriveRouteResult driveRouteResult, int code) { aMap.clear();// 清理地图上的所有覆盖物 if (code != AMapException.CODE_AMAP_SUCCESS) { showMsg("错误码;" + code); return; } if (driveRouteResult == null || driveRouteResult.getPaths() == null) { showMsg("对不起,没有搜索到相关数据!"); return; } if (driveRouteResult.getPaths().isEmpty()) { showMsg("对不起,没有搜索到相关数据!"); return; } final DrivePath drivePath = driveRouteResult.getPaths().get(0); if (drivePath == null) { return; } // 绘制路线 DrivingRouteOverlay drivingRouteOverlay = new DrivingRouteOverlay( this, aMap, drivePath, driveRouteResult.getStartPos(), driveRouteResult.getTargetPos(), null); drivingRouteOverlay.removeFromMap(); drivingRouteOverlay.addToMap(); drivingRouteOverlay.zoomToSpan(); int dis = (int) drivePath.getDistance(); int dur = (int) drivePath.getDuration(); String des = MapUtil.getFriendlyTime(dur) + "(" + MapUtil.getFriendlyLength(dis) + ")"; Log.d(TAG, des); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
下面运行一下:

⑤ 公交路线规划
还有一个公交路线规划,公交的规划其实还包括了步行,不过步行是一点点。打开RouteActivity,修改travelModeArray里面的值,增加一个出行方式。

然后找到startRouteSearch()方法,增加如下case:
case 3://公交
//构建驾车路线搜索对象 第三个参数表示公交查询城市区号,第四个参数表示是否计算夜班车,0表示不计算,1表示计算
RouteSearch.BusRouteQuery busQuery = new RouteSearch.BusRouteQuery(fromAndTo, RouteSearch.BusLeaseWalk, "0755",0);
//公交规划路径计算
routeSearch.calculateBusRouteAsyn(busQuery);
break;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
这里注意一点,那就是城市的区号,这里我填的是0755,表示深圳。你可以通过城市区号查询去查看你所在地的城市区号,当然如果你不想去查询也可以,你可以直接用中文来解决,比如把0755改成深圳,也是可以的。如果你觉得这样也比较麻烦的话,那么你可以定义一个成员变量。
//城市
private String city;
- 1
- 2
然后在onLocationChanged()中赋值。
city = aMapLocation.getCity();
- 1
添加位置如下图所示:

最后在替换,这样的话就会以你当前所在城市为准。
RouteSearch.BusRouteQuery busQuery = new RouteSearch.BusRouteQuery(fromAndTo, RouteSearch.BusLeaseWalk, city, 0);
- 1
如下图所示:
那么下面同样要绘制公交的图层,在overlay包下新建一个BusRouteOverlay类,代码如下:(来源于SDK)
package com.llw.newmapdemo.overlay; import android.content.Context; import com.amap.api.maps.AMap; import com.amap.api.maps.model.LatLng; import com.amap.api.maps.model.MarkerOptions; import com.amap.api.maps.model.PolylineOptions; import com.amap.api.services.busline.BusStationItem; import com.amap.api.services.core.LatLonPoint; import com.amap.api.services.route.BusPath; import com.amap.api.services.route.BusStep; import com.amap.api.services.route.Doorway; import com.amap.api.services.route.RailwayStationItem; import com.amap.api.services.route.RouteBusLineItem; import com.amap.api.services.route.RouteBusWalkItem; import com.amap.api.services.route.RouteRailwayItem; import com.amap.api.services.route.TaxiItem; import com.amap.api.services.route.WalkStep; import com.llw.newmapdemo.utils.MapUtil; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * 公交路线图层类。在高德地图API里,如果需要显示公交路线,可以用此类来创建公交路线图层。如不满足需求,也可以自己创建自定义的公交路线图层。 * @since V2.1.0 */ public class BusRouteOverlay extends RouteOverlay { private BusPath busPath; private LatLng latLng; /** * 通过此构造函数创建公交路线图层。 * @param context 当前activity。 * @param amap 地图对象。 * @param path 公交路径规划的一个路段。详见搜索服务模块的路径查询包(com.amap.api.services.route)中的类<strong> <a href="../../../../../../Search/com/amap/api/services/route/BusPath.html" title="com.amap.api.services.route中的类">BusPath</a></strong>。 * @param start 起点坐标。详见搜索服务模块的核心基础包(com.amap.api.services.core)中的类 <strong><a href="../../../../../../Search/com/amap/api/services/core/LatLonPoint.html" title="com.amap.api.services.core中的类">LatLonPoint</a></strong>。 * @param end 终点坐标。详见搜索服务模块的核心基础包(com.amap.api.services.core)中的类 <strong><a href="../../../../../../Search/com/amap/api/services/core/LatLonPoint.html" title="com.amap.api.services.core中的类">LatLonPoint</a></strong>。 * @since V2.1.0 */ public BusRouteOverlay(Context context, AMap amap, BusPath path, LatLonPoint start, LatLonPoint end) { super(context); this.busPath = path; startPoint = MapUtil.convertToLatLng(start); endPoint = MapUtil.convertToLatLng(end); mAMap = amap; } /** * 添加公交路线到地图上。 * @since V2.1.0 */ public void addToMap() { /** * 绘制节点和线<br> * 细节情况较多<br> * 两个step之间,用step和step1区分<br> * 1.一个step内可能有步行和公交,然后有可能他们之间连接有断开<br> * 2.step的公交和step1的步行,有可能连接有断开<br> * 3.step和step1之间是公交换乘,且没有步行,需要把step的终点和step1的起点连起来<br> * 4.公交最后一站和终点间有步行,加入步行线路,还会有一些步行marker<br> * 5.公交最后一站和终点间无步行,之间连起来<br> */ try { List<BusStep> busSteps = busPath.getSteps(); for (int i = 0; i < busSteps.size(); i++) { BusStep busStep = busSteps.get(i); if (i < busSteps.size() - 1) { BusStep busStep1 = busSteps.get(i + 1);// 取得当前下一个BusStep对象 // 假如步行和公交之间连接有断开,就把步行最后一个经纬度点和公交第一个经纬度点连接起来,避免断线问题 if (busStep.getWalk() != null && busStep.getBusLine() != null) { checkWalkToBusline(busStep); } // 假如公交和步行之间连接有断开,就把上一公交经纬度点和下一步行第一个经纬度点连接起来,避免断线问题 if (busStep.getBusLine() != null && busStep1.getWalk() != null && busStep1.getWalk().getSteps().size() > 0) { checkBusLineToNextWalk(busStep, busStep1); } // 假如两个公交换乘中间没有步行,就把上一公交经纬度点和下一步公交第一个经纬度点连接起来,避免断线问题 if (busStep.getBusLine() != null && busStep1.getWalk() == null && busStep1.getBusLine() != null) { checkBusEndToNextBusStart(busStep, busStep1); } // 和上面的很类似 if (busStep.getBusLine() != null && busStep1.getWalk() == null && busStep1.getBusLine() != null) { checkBusToNextBusNoWalk(busStep, busStep1); } if (busStep.getBusLine() != null && busStep1.getRailway() != null ) { checkBusLineToNextRailway(busStep, busStep1); } if (busStep1.getWalk() != null && busStep1.getWalk().getSteps().size() > 0 && busStep.getRailway() != null) { checkRailwayToNextWalk(busStep, busStep1); } if ( busStep1.getRailway() != null && busStep.getRailway() != null) { checkRailwayToNextRailway(busStep, busStep1); } if (busStep.getRailway() != null && busStep1.getTaxi() != null ){ checkRailwayToNextTaxi(busStep, busStep1); } } if (busStep.getWalk() != null && busStep.getWalk().getSteps().size() > 0) { addWalkSteps(busStep); } else { if (busStep.getBusLine() == null && busStep.getRailway() == null && busStep.getTaxi() == null) { addWalkPolyline(latLng, endPoint); } } if (busStep.getBusLine() != null) { RouteBusLineItem routeBusLineItem = busStep.getBusLine(); addBusLineSteps(routeBusLineItem); addBusStationMarkers(routeBusLineItem); if (i == busSteps.size() - 1) { addWalkPolyline(MapUtil.convertToLatLng(getLastBuslinePoint(busStep)), endPoint); } } if (busStep.getRailway() != null) { addRailwayStep(busStep.getRailway()); addRailwayMarkers(busStep.getRailway()); if (i == busSteps.size() - 1) { addWalkPolyline(MapUtil.convertToLatLng(busStep.getRailway().getArrivalstop().getLocation()), endPoint); } } if (busStep.getTaxi() != null) { addTaxiStep(busStep.getTaxi()); addTaxiMarkers(busStep.getTaxi()); } } addStartAndEndMarker(); } catch (Throwable e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private void checkRailwayToNextTaxi(BusStep busStep, BusStep busStep1) { LatLonPoint railwayLastPoint = busStep.getRailway().getArrivalstop().getLocation(); LatLonPoint taxiFirstPoint = busStep1.getTaxi().getOrigin(); if (!railwayLastPoint.equals(taxiFirstPoint)) { addWalkPolyLineByLatLonPoints(railwayLastPoint, taxiFirstPoint); } } private void checkRailwayToNextRailway(BusStep busStep, BusStep busStep1) { LatLonPoint railwayLastPoint = busStep.getRailway().getArrivalstop().getLocation(); LatLonPoint railwayFirstPoint = busStep1.getRailway().getDeparturestop().getLocation(); if (!railwayLastPoint.equals(railwayFirstPoint)) { addWalkPolyLineByLatLonPoints(railwayLastPoint, railwayFirstPoint); } } private void checkBusLineToNextRailway(BusStep busStep, BusStep busStep1) { LatLonPoint busLastPoint = getLastBuslinePoint(busStep); LatLonPoint railwayFirstPoint = busStep1.getRailway().getDeparturestop().getLocation(); if (!busLastPoint.equals(railwayFirstPoint)) { addWalkPolyLineByLatLonPoints(busLastPoint, railwayFirstPoint); } } private void checkRailwayToNextWalk(BusStep busStep, BusStep busStep1) { LatLonPoint railwayLastPoint = busStep.getRailway().getArrivalstop().getLocation(); LatLonPoint walkFirstPoint = getFirstWalkPoint(busStep1); if (!railwayLastPoint.equals(walkFirstPoint)) { addWalkPolyLineByLatLonPoints(railwayLastPoint, walkFirstPoint); } } private void addRailwayStep(RouteRailwayItem railway) { List<LatLng> railwaylistpoint = new ArrayList<LatLng>(); List<RailwayStationItem> railwayStationItems = new ArrayList<RailwayStationItem>(); railwayStationItems.add(railway.getDeparturestop()); railwayStationItems.addAll(railway.getViastops()); railwayStationItems.add(railway.getArrivalstop()); for (int i = 0; i < railwayStationItems.size(); i++) { railwaylistpoint.add(MapUtil.convertToLatLng(railwayStationItems.get(i).getLocation())); } addRailwayPolyline(railwaylistpoint); } private void addTaxiStep(TaxiItem taxi){ addPolyLine(new PolylineOptions().width(getRouteWidth()) .color(getBusColor()) .add(MapUtil.convertToLatLng(taxi.getOrigin())) .add(MapUtil.convertToLatLng(taxi.getDestination()))); } /** * @param busStep */ private void addWalkSteps(BusStep busStep) { RouteBusWalkItem routeBusWalkItem = busStep.getWalk(); List<WalkStep> walkSteps = routeBusWalkItem.getSteps(); for (int j = 0; j < walkSteps.size(); j++) { WalkStep walkStep = walkSteps.get(j); if (j == 0) { LatLng latLng = MapUtil.convertToLatLng(walkStep .getPolyline().get(0)); String road = walkStep.getRoad();// 道路名字 String instruction = getWalkSnippet(walkSteps);// 步行导航信息 addWalkStationMarkers(latLng, road, instruction); } List<LatLng> listWalkPolyline = MapUtil .convertArrList(walkStep.getPolyline()); this.latLng = listWalkPolyline.get(listWalkPolyline.size() - 1); addWalkPolyline(listWalkPolyline); // 假如步行前一段的终点和下的起点有断开,断画直线连接起来,避免断线问题 if (j < walkSteps.size() - 1) { LatLng lastLatLng = listWalkPolyline.get(listWalkPolyline .size() - 1); LatLng firstlatLatLng = MapUtil .convertToLatLng(walkSteps.get(j + 1).getPolyline() .get(0)); if (!(lastLatLng.equals(firstlatLatLng))) { addWalkPolyline(lastLatLng, firstlatLatLng); } } } } /** * 添加一系列的bus PolyLine * * @param routeBusLineItem */ private void addBusLineSteps(RouteBusLineItem routeBusLineItem) { addBusLineSteps(routeBusLineItem.getPolyline()); } private void addBusLineSteps(List<LatLonPoint> listPoints) { if (listPoints.size() < 1) { return; } addPolyLine(new PolylineOptions().width(getRouteWidth()) .color(getBusColor()) .addAll(MapUtil.convertArrList(listPoints))); } /** * @param latLng * marker * @param title * @param snippet */ private void addWalkStationMarkers(LatLng latLng, String title, String snippet) { addStationMarker(new MarkerOptions().position(latLng).title(title) .snippet(snippet).anchor(0.5f, 0.5f).visible(nodeIconVisible) .icon(getWalkBitmapDescriptor())); } /** * @param routeBusLineItem */ private void addBusStationMarkers(RouteBusLineItem routeBusLineItem) { BusStationItem startBusStation = routeBusLineItem .getDepartureBusStation(); LatLng position = MapUtil.convertToLatLng(startBusStation .getLatLonPoint()); String title = routeBusLineItem.getBusLineName(); String snippet = getBusSnippet(routeBusLineItem); addStationMarker(new MarkerOptions().position(position).title(title) .snippet(snippet).anchor(0.5f, 0.5f).visible(nodeIconVisible) .icon(getBusBitmapDescriptor())); } private void addTaxiMarkers(TaxiItem taxiItem) { LatLng position = MapUtil.convertToLatLng(taxiItem .getOrigin()); String title = taxiItem.getmSname()+"打车"; String snippet = "到终点"; addStationMarker(new MarkerOptions().position(position).title(title) .snippet(snippet).anchor(0.5f, 0.5f).visible(nodeIconVisible) .icon(getDriveBitmapDescriptor())); } private void addRailwayMarkers(RouteRailwayItem railway) { LatLng Departureposition = MapUtil.convertToLatLng(railway .getDeparturestop().getLocation()); String Departuretitle = railway.getDeparturestop().getName()+"上车"; String Departuresnippet = railway.getName(); addStationMarker(new MarkerOptions().position(Departureposition).title(Departuretitle) .snippet(Departuresnippet).anchor(0.5f, 0.5f).visible(nodeIconVisible) .icon(getBusBitmapDescriptor())); LatLng Arrivalposition = MapUtil.convertToLatLng(railway .getArrivalstop().getLocation()); String Arrivaltitle = railway.getArrivalstop().getName()+"下车"; String Arrivalsnippet = railway.getName(); addStationMarker(new MarkerOptions().position(Arrivalposition).title(Arrivaltitle) .snippet(Arrivalsnippet).anchor(0.5f, 0.5f).visible(nodeIconVisible) .icon(getBusBitmapDescriptor())); } /** * 如果换乘没有步行 检查bus最后一点和下一个step的bus起点是否一致 * * @param busStep * @param busStep1 */ private void checkBusToNextBusNoWalk(BusStep busStep, BusStep busStep1) { LatLng endbusLatLng = MapUtil .convertToLatLng(getLastBuslinePoint(busStep)); LatLng startbusLatLng = MapUtil .convertToLatLng(getFirstBuslinePoint(busStep1)); if (startbusLatLng.latitude - endbusLatLng.latitude > 0.0001 || startbusLatLng.longitude - endbusLatLng.longitude > 0.0001) { drawLineArrow(endbusLatLng, startbusLatLng);// 断线用带箭头的直线连? } } /** * * checkBusToNextBusNoWalk 和这个类似 * * @param busStep * @param busStep1 */ private void checkBusEndToNextBusStart(BusStep busStep, BusStep busStep1) { LatLonPoint busLastPoint = getLastBuslinePoint(busStep); LatLng endbusLatLng = MapUtil.convertToLatLng(busLastPoint); LatLonPoint busFirstPoint = getFirstBuslinePoint(busStep1); LatLng startbusLatLng = MapUtil.convertToLatLng(busFirstPoint); if (!endbusLatLng.equals(startbusLatLng)) { drawLineArrow(endbusLatLng, startbusLatLng);// } } /** * 检查bus最后一步和下一各step的步行起点是否一致 * * @param busStep * @param busStep1 */ private void checkBusLineToNextWalk(BusStep busStep, BusStep busStep1) { LatLonPoint busLastPoint = getLastBuslinePoint(busStep); LatLonPoint walkFirstPoint = getFirstWalkPoint(busStep1); if (!busLastPoint.equals(walkFirstPoint)) { addWalkPolyLineByLatLonPoints(busLastPoint, walkFirstPoint); } } /** * 检查 步行最后一点 和 bus的起点 是否一致 * * @param busStep */ private void checkWalkToBusline(BusStep busStep) { LatLonPoint walkLastPoint = getLastWalkPoint(busStep); LatLonPoint buslineFirstPoint = getFirstBuslinePoint(busStep); if (!walkLastPoint.equals(buslineFirstPoint)) { addWalkPolyLineByLatLonPoints(walkLastPoint, buslineFirstPoint); } } /** * @param busStep1 * @return */ private LatLonPoint getFirstWalkPoint(BusStep busStep1) { return busStep1.getWalk().getSteps().get(0).getPolyline().get(0); } /** * */ private void addWalkPolyLineByLatLonPoints(LatLonPoint pointFrom, LatLonPoint pointTo) { LatLng latLngFrom = MapUtil.convertToLatLng(pointFrom); LatLng latLngTo = MapUtil.convertToLatLng(pointTo); addWalkPolyline(latLngFrom, latLngTo); } /** * @param latLngFrom * @param latLngTo * @return */ private void addWalkPolyline(LatLng latLngFrom, LatLng latLngTo) { addPolyLine(new PolylineOptions().add(latLngFrom, latLngTo) .width(getRouteWidth()).color(getWalkColor()).setDottedLine(true)); } /** * @param listWalkPolyline */ private void addWalkPolyline(List<LatLng> listWalkPolyline) { addPolyLine(new PolylineOptions().addAll(listWalkPolyline) .color(getWalkColor()).width(getRouteWidth()).setDottedLine(true)); } private void addRailwayPolyline(List<LatLng> listPolyline) { addPolyLine(new PolylineOptions().addAll(listPolyline) .color(getDriveColor()).width(getRouteWidth())); } private String getWalkSnippet(List<WalkStep> walkSteps) { float disNum = 0; for (WalkStep step : walkSteps) { disNum += step.getDistance(); } return "\u6B65\u884C" + disNum + "\u7C73"; } public void drawLineArrow(LatLng latLngFrom, LatLng latLngTo) { addPolyLine(new PolylineOptions().add(latLngFrom, latLngTo).width(3) .color(getBusColor()).width(getRouteWidth()));// 绘制直线 } private String getBusSnippet(RouteBusLineItem routeBusLineItem) { return "(" + routeBusLineItem.getDepartureBusStation().getBusStationName() + "-->" + routeBusLineItem.getArrivalBusStation().getBusStationName() + ") \u7ECF\u8FC7" + (routeBusLineItem.getPassStationNum() + 1) + "\u7AD9"; } /** * @param busStep * @return */ private LatLonPoint getLastWalkPoint(BusStep busStep) { List<WalkStep> walkSteps = busStep.getWalk().getSteps(); WalkStep walkStep = walkSteps.get(walkSteps.size() - 1); List<LatLonPoint> lonPoints = walkStep.getPolyline(); return lonPoints.get(lonPoints.size() - 1); } private LatLonPoint getExitPoint(BusStep busStep) { Doorway doorway = busStep.getExit(); if (doorway == null) { return null; } return doorway.getLatLonPoint(); } private LatLonPoint getLastBuslinePoint(BusStep busStep) { List<LatLonPoint> lonPoints = busStep.getBusLine().getPolyline(); return lonPoints.get(lonPoints.size() - 1); } private LatLonPoint getEntrancePoint(BusStep busStep) { Doorway doorway = busStep.getEntrance(); if (doorway == null) { return null; } return doorway.getLatLonPoint(); } private LatLonPoint getFirstBuslinePoint(BusStep busStep) { return busStep.getBusLine().getPolyline().get(0); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
- 294
- 295
- 296
- 297
- 298
- 299
- 300
- 301
- 302
- 303
- 304
- 305
- 306
- 307
- 308
- 309
- 310
- 311
- 312
- 313
- 314
- 315
- 316
- 317
- 318
- 319
- 320
- 321
- 322
- 323
- 324
- 325
- 326
- 327
- 328
- 329
- 330
- 331
- 332
- 333
- 334
- 335
- 336
- 337
- 338
- 339
- 340
- 341
- 342
- 343
- 344
- 345
- 346
- 347
- 348
- 349
- 350
- 351
- 352
- 353
- 354
- 355
- 356
- 357
- 358
- 359
- 360
- 361
- 362
- 363
- 364
- 365
- 366
- 367
- 368
- 369
- 370
- 371
- 372
- 373
- 374
- 375
- 376
- 377
- 378
- 379
- 380
- 381
- 382
- 383
- 384
- 385
- 386
- 387
- 388
- 389
- 390
- 391
- 392
- 393
- 394
- 395
- 396
- 397
- 398
- 399
- 400
- 401
- 402
- 403
- 404
- 405
- 406
- 407
- 408
- 409
- 410
- 411
- 412
- 413
- 414
- 415
- 416
- 417
- 418
- 419
- 420
- 421
- 422
- 423
- 424
- 425
- 426
- 427
- 428
- 429
- 430
- 431
- 432
- 433
- 434
- 435
- 436
- 437
- 438
- 439
- 440
- 441
- 442
- 443
- 444
- 445
- 446
- 447
- 448
- 449
- 450
- 451
- 452
- 453
- 454
- 455
- 456
- 457
- 458
- 459
- 460
- 461
- 462
- 463
- 464
- 465
- 466
- 467
- 468
- 469
- 470
- 471
- 472
- 473
- 474
- 475
- 476
- 477
- 478
- 479
- 480
- 481
- 482
- 483
- 484
- 485
- 486
- 487
- 488
- 489
- 490
- 491
- 492
- 493
- 494
- 495
- 496
最后回到RouteActivity,修改onBusRouteSearched()方法中的代码,如下所示:
/** * 公交规划路径结果 * * @param busRouteResult 结果 * @param code 结果码 */ @Override public void onBusRouteSearched(BusRouteResult busRouteResult, int code) { aMap.clear();// 清理地图上的所有覆盖物 if (code != AMapException.CODE_AMAP_SUCCESS) { showMsg("错误码;" + code); return; } if (busRouteResult == null || busRouteResult.getPaths() == null) { showMsg("对不起,没有搜索到相关数据!"); return; } if (busRouteResult.getPaths().isEmpty()) { showMsg("对不起,没有搜索到相关数据!"); return; } final BusPath busPath = busRouteResult.getPaths().get(0); if (busPath == null) { return; } // 绘制路线 BusRouteOverlay busRouteOverlay = new BusRouteOverlay( this, aMap, busPath, busRouteResult.getStartPos(), busRouteResult.getTargetPos()); busRouteOverlay.removeFromMap(); busRouteOverlay.addToMap(); busRouteOverlay.zoomToSpan(); int dis = (int) busPath.getDistance(); int dur = (int) busPath.getDuration(); String des = MapUtil.getFriendlyTime(dur) + "(" + MapUtil.getFriendlyLength(dis) + ")"; Log.d(TAG, des); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
然后来看看运行的效果。

公交路线规划就写完了,下面我们就可以去写详情了。
十、出行路线详情
考虑页面展示的问题,我们需要创建一个RouteDetailActivity来展示页路线详情,试想一下,在路线页面得到路线规划之后,点击详情进入详情页面,就可以看到具体的详细出行规划了。
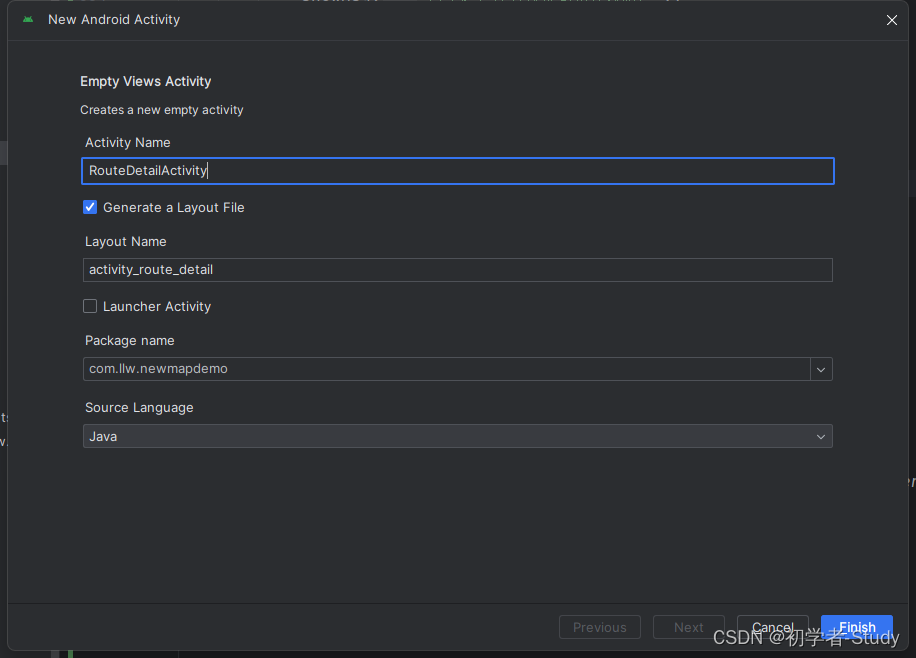
① 准备工作
下面我们首先修改activity_route_detail.xml中的代码,如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/main" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="#efefef" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context=".RouteDetailActivity"> <com.google.android.material.appbar.MaterialToolbar android:id="@+id/toolbar" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize" android:background="@color/white" app:navigationIcon="@drawable/ic_black_back" app:titleCentered="true" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_time" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="70dp" android:layout_marginTop="2dp" android:background="#FFF" android:gravity="center_vertical" android:orientation="vertical" android:padding="5dp" android:paddingStart="12dp" android:textColor="#333333" android:textSize="16sp" /> <View android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="1dp" android:background="#e0e0e0" /> <androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView android:id="@+id/rv_route_detail" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:cacheColorHint="#00000000" android:divider="#00000000" android:fadingEdge="none" android:fadingEdgeLength="0dp" android:footerDividersEnabled="false" android:headerDividersEnabled="false" android:listSelector="#00000000" /> </LinearLayout>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
这里面有一个返回图标ic_black_back.xml,代码如下所示:
<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:width="24dp"
android:height="24dp"
android:autoMirrored="true"
android:tint="#000000"
android:viewportWidth="24"
android:viewportHeight="24">
<path
android:fillColor="@android:color/white"
android:pathData="M16.62,2.99c-0.49,-0.49 -1.28,-0.49 -1.77,0L6.54,11.3c-0.39,0.39 -0.39,1.02 0,1.41l8.31,8.31c0.49,0.49 1.28,0.49 1.77,0s0.49,-1.28 0,-1.77L9.38,12l7.25,-7.25c0.48,-0.48 0.48,-1.28 -0.01,-1.76z" />
</vector>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
下面我们就该去写跳转的动作了,首先要做的是在路线规划页面显示出简单路线详情内容,比如距离和时间,让我们首先修改activity_route.xml中的代码,如下所示:
<!--地图路线规划详情布局--> <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout android:id="@+id/lay_bottom" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="60dp" android:background="@color/white" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_time" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:layout_marginStart="16dp" android:layout_weight="1" android:singleLine="true" android:text="距离和时间" android:textColor="#333333" android:textSize="16sp" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_detail" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_marginEnd="16dp" android:drawableEnd="@drawable/ic_blue_open" android:drawablePadding="4dp" android:gravity="center_vertical" android:text="详情" android:textColor="#4c90f9" android:textSize="14sp" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="@+id/tv_time" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="@+id/tv_time" /> </androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
添加位置如下图所示

这里有一个ic_blue_open.xml图标,代码如下所示:
<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:width="18dp"
android:height="18dp"
android:autoMirrored="true"
android:tint="#4C90F9"
android:viewportWidth="24"
android:viewportHeight="24">
<path
android:fillColor="@android:color/white"
android:pathData="M7.38,21.01c0.49,0.49 1.28,0.49 1.77,0l8.31,-8.31c0.39,-0.39 0.39,-1.02 0,-1.41L9.15,2.98c-0.49,-0.49 -1.28,-0.49 -1.77,0s-0.49,1.28 0,1.77L14.62,12l-7.25,7.25c-0.48,0.48 -0.48,1.28 0.01,1.76z" />
</vector>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
② 步行路线详情
下面要显示步行花费的时间,回到RouteActivity,找到onWalkRouteSearched()方法,在里面增加如下代码:
//显示步行花费时间
binding.tvTime.setText(des);
binding.layBottom.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
//跳转到路线详情页面
binding.tvDetail.setOnClickListener(v -> {
Intent intent = new Intent(RouteActivity.this,
RouteDetailActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("type",0);
intent.putExtra("path", walkPath);
startActivity(intent);
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
添加位置如下图所示
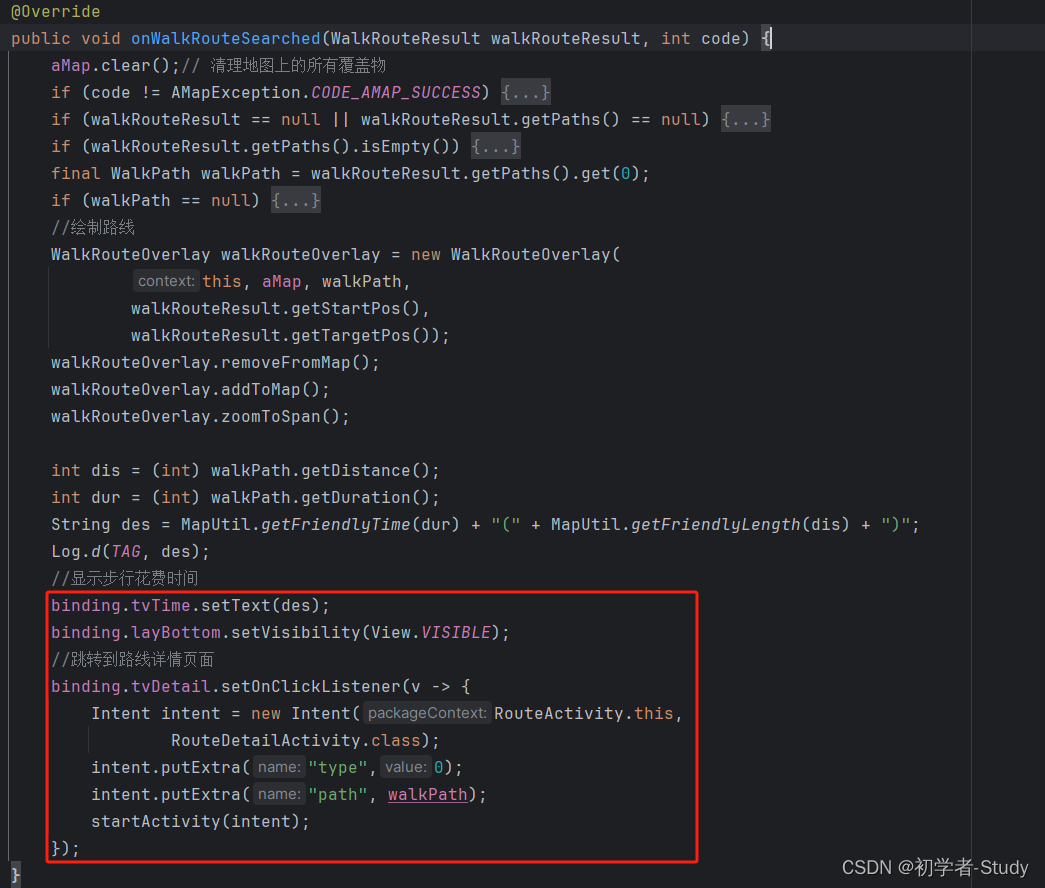
这里在点击的时候通过跳转页面传递数据到路线详情页面里,下面我们就进入RouteDetailActivity,首先进行初始化,代码如下所示:
public class RouteDetailActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private ActivityRouteDetailBinding binding; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); EdgeToEdge.enable(this); binding = ActivityRouteDetailBinding.inflate(getLayoutInflater()); setContentView(binding.getRoot()); ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(findViewById(R.id.main), (v, insets) -> { Insets systemBars = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars()); v.setPadding(systemBars.left, systemBars.top, systemBars.right, systemBars.bottom); return insets; }); initView(); } /** * 初始化视图 */ private void initView() { binding.toolbar.setNavigationOnClickListener(v -> finish()); Intent intent = getIntent(); if (intent == null) { return; } switch (intent.getIntExtra("type", 0)) { case 0://步行 break; case 1://骑行 break; case 2://驾车 break; case 3://公交 break; default: break; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
从代码上来看比较的简单,下面我们要做的就是显示传递过来的数据了,因为数据比较多,所以我们采用列表显示出来。页面布局已经写好了,下面要写就是列表Item布局和适配器了。首先我们写Item布局,在layout下创建item_segment.xml,代码如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#FFF" > <ImageView android:id="@+id/bus_seg_split_line" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="1dp" android:layout_marginLeft="50dp" android:layout_marginStart="50dp" android:background="#e0e0e0"/> <RelativeLayout android:id="@+id/bus_route_direction" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="44dp" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_alignParentStart="true" android:layout_marginLeft="11dp" android:layout_marginStart="11dp" > <ImageView android:id="@+id/bus_dir_icon" android:layout_width="22dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:src="@drawable/dir_start" /> <ImageView android:id="@+id/bus_dir_icon_up" android:layout_width="2dp" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_above="@id/bus_dir_icon" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:background="#b6b6b6" android:visibility="gone"/> <ImageView android:id="@+id/bus_dir_icon_down" android:layout_width="2dp" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_below="@id/bus_dir_icon" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:background="#b6b6b6" android:visibility="gone"/> </RelativeLayout> <RelativeLayout android:id="@+id/bus_item" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="44dp" > <RelativeLayout android:id="@+id/stationinfo" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:layout_alignParentEnd="true" android:layout_alignParentRight="true"> <ImageView android:id="@+id/bus_expand_image" android:layout_width="25dp" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_alignParentEnd="true" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:layout_marginEnd="6dp" android:layout_marginRight="6dp" android:clickable="true" android:scaleType="centerInside" android:src="@drawable/down" android:visibility="gone" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/bus_station_num" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/bus_expand_image" android:layout_toStartOf="@id/bus_expand_image" android:gravity="center_vertical" android:textColor="#4c90f9" android:textSize="12sp" android:visibility="gone" > </TextView> </RelativeLayout> <TextView android:id="@+id/bus_line_name" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:layout_marginLeft="50dp" android:layout_marginStart="50dp" android:layout_marginRight="70dp" android:layout_marginEnd="70dp" android:textColor="#333333" android:text="出发" android:textSize="14sp" /> </RelativeLayout> <LinearLayout android:id="@+id/expand_content" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/bus_item" android:orientation="vertical"> </LinearLayout> </RelativeLayout>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
图标可以去我的源码中获取,下面我们在MapUtil中添加getWalkActionID()方法,代码如下所示:
public static int getWalkActionID(String actionName) { if (actionName == null || actionName.equals("")) { return R.drawable.dir13; } if ("左转".equals(actionName)) { return R.drawable.dir2; } if ("右转".equals(actionName)) { return R.drawable.dir1; } if ("向左前方".equals(actionName) || "靠左".equals(actionName) || actionName.contains("向左前方")) { return R.drawable.dir6; } if ("向右前方".equals(actionName) || "靠右".equals(actionName) || actionName.contains("向右前方")) { return R.drawable.dir5; } if ("向左后方".equals(actionName)|| actionName.contains("向左后方")) { return R.drawable.dir7; } if ("向右后方".equals(actionName)|| actionName.contains("向右后方")) { return R.drawable.dir8; } if ("直行".equals(actionName)) { return R.drawable.dir3; } if ("通过人行横道".equals(actionName)) { return R.drawable.dir9; } if ("通过过街天桥".equals(actionName)) { return R.drawable.dir11; } if ("通过地下通道".equals(actionName)) { return R.drawable.dir10; } return R.drawable.dir13; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
然后在com.llw.newmapdemo下新建一个adapter包,用于放置所有的适配器,在这个包下新建一个WalkSegmentListAdapter类,里面的代码如下:
package com.llw.newmapdemo.adapter; import android.view.LayoutInflater; import android.view.View; import android.view.ViewGroup; import androidx.annotation.NonNull; import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView; import com.amap.api.services.route.WalkStep; import com.llw.newmapdemo.R; import com.llw.newmapdemo.databinding.ItemSegmentBinding; import com.llw.newmapdemo.utils.MapUtil; import java.util.List; /** * 步行段列表适配器 */ public class WalkSegmentListAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<WalkSegmentListAdapter.ViewHolder> { private List<WalkStep> mItemList; public WalkSegmentListAdapter(List<WalkStep> data) { this.mItemList = data; } @NonNull @Override public ViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) { return new ViewHolder(ItemSegmentBinding.inflate(LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext()), parent, false)); } @Override public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull ViewHolder holder, int position) { WalkStep item = mItemList.get(position); if (position == 0) { holder.binding.busDirIcon.setImageResource(R.drawable.dir_start); holder.binding.busLineName.setText("出发"); holder.binding.busDirIconUp.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE); holder.binding.busDirIconDown.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busSegSplitLine.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE); } else if (position == mItemList.size() - 1) { holder.binding.busDirIcon.setImageResource(R.drawable.dir_end); holder.binding.busLineName.setText("到达终点"); holder.binding.busDirIconUp.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busDirIconDown.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE); } else { holder.binding.busSegSplitLine.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busDirIconUp.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busDirIconDown.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); String actionName = item.getAction(); int resID = MapUtil.getWalkActionID(actionName); holder.binding.busDirIcon.setImageResource(resID); holder.binding.busLineName.setText(item.getInstruction()); } } @Override public int getItemCount() { return mItemList == null || mItemList.isEmpty() ? 0 : mItemList.size(); } static class ViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder { ItemSegmentBinding binding; public ViewHolder(ItemSegmentBinding itemView) { super(itemView.getRoot()); this.binding = itemView; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
最后在RouteDetailActivity中增加如下方法,再调用。
/**
* 步行详情
* @param intent
*/
private void walkDetail(Intent intent) {
binding.toolbar.setTitle("步行路线规划");
WalkPath walkPath = intent.getParcelableExtra("path");
String dur = MapUtil.getFriendlyTime((int) walkPath.getDuration());
String dis = MapUtil.getFriendlyLength((int) walkPath.getDistance());
binding.tvTime.setText(dur + "(" + dis + ")");
binding.rvRouteDetail.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(this));
binding.rvRouteDetail.setAdapter(new WalkSegmentListAdapter(walkPath.getSteps()));
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
如下图所示
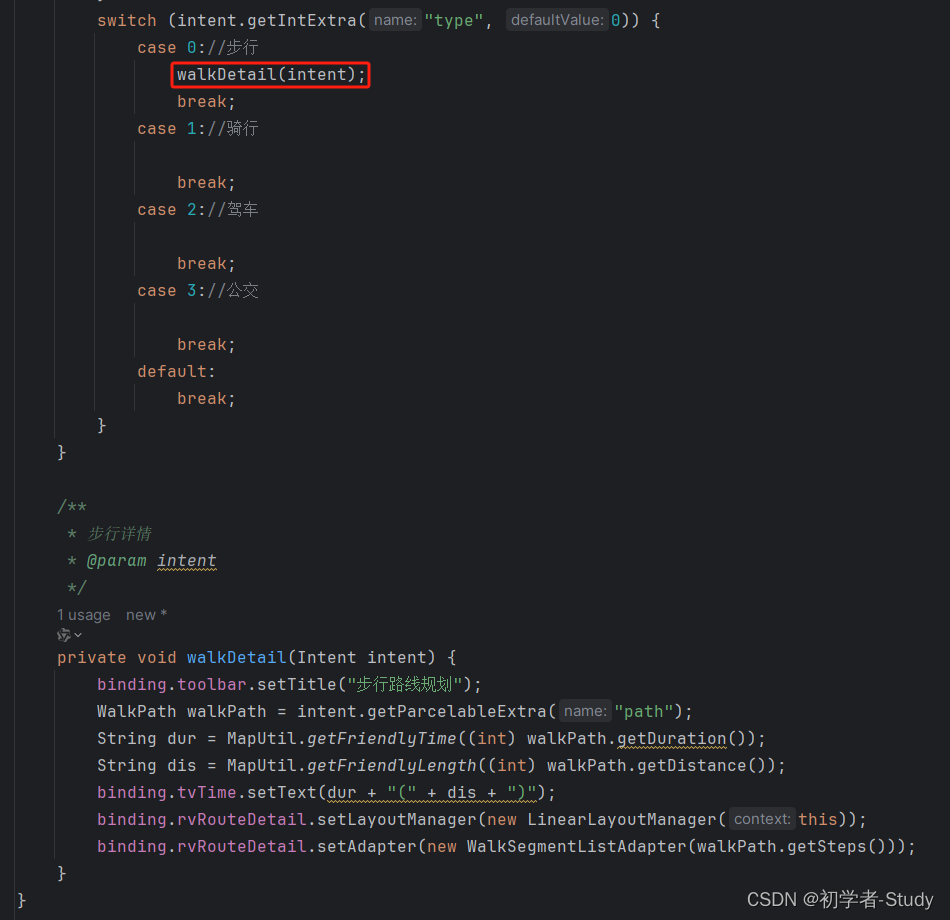
下面运行一下

③ 骑行路线详情
在RouteActivity中找到onRideRouteSearched()方法,方法里面添加如下代码:
binding.tvTime.setText(des);
binding.layBottom.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
binding.tvDetail.setOnClickListener(v -> {
Intent intent = new Intent(RouteActivity.this,
RouteDetailActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("type",1);
intent.putExtra("path", ridePath);
startActivity(intent);
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
添加位置如下图所示

然后在adapter包下新增一个RideSegmentListAdapter类,里面的代码如下;
package com.llw.newmapdemo.adapter; import android.view.LayoutInflater; import android.view.View; import android.view.ViewGroup; import androidx.annotation.NonNull; import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView; import com.amap.api.services.route.RideStep; import com.amap.api.services.route.WalkStep; import com.llw.newmapdemo.R; import com.llw.newmapdemo.databinding.ItemSegmentBinding; import com.llw.newmapdemo.utils.MapUtil; import java.util.List; /** * 骑行段列表适配器 */ public class RideSegmentListAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<RideSegmentListAdapter.ViewHolder> { private List<RideStep> mItemList; public RideSegmentListAdapter(List<RideStep> data) { this.mItemList = data; } @NonNull @Override public ViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) { return new ViewHolder(ItemSegmentBinding.inflate(LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext()), parent, false)); } @Override public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull ViewHolder holder, int position) { RideStep item = mItemList.get(position); if (position == 0) { holder.binding.busDirIcon.setImageResource(R.drawable.dir_start); holder.binding.busLineName.setText("出发"); holder.binding.busDirIconUp.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE); holder.binding.busDirIconDown.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busSegSplitLine.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE); } else if (position == mItemList.size() - 1) { holder.binding.busDirIcon.setImageResource(R.drawable.dir_end); holder.binding.busLineName.setText("到达终点"); holder.binding.busDirIconUp.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busDirIconDown.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE); } else { holder.binding.busSegSplitLine.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busDirIconUp.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busDirIconDown.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); String actionName = item.getAction(); int resID = MapUtil.getWalkActionID(actionName); holder.binding.busDirIcon.setImageResource(resID); holder.binding.busLineName.setText(item.getInstruction()); } } @Override public int getItemCount() { return mItemList == null || mItemList.isEmpty() ? 0 : mItemList.size(); } static class ViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder { ItemSegmentBinding binding; public ViewHolder(ItemSegmentBinding itemView) { super(itemView.getRoot()); this.binding = itemView; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
下面再进入到RouteDetailActivity,新增如下方法:
/**
* 骑行详情
* @param intent
*/
private void rideDetail(Intent intent) {
binding.toolbar.setTitle("骑行路线规划");
RidePath ridePath = intent.getParcelableExtra("path");
String dur = MapUtil.getFriendlyTime((int) ridePath.getDuration());
String dis = MapUtil.getFriendlyLength((int) ridePath.getDistance());
binding.tvTime.setText(dur + "(" + dis + ")");
binding.rvRouteDetail.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(this));
binding.rvRouteDetail.setAdapter(new RideSegmentListAdapter(ridePath.getSteps()));
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
然后在initView()中调用。

然后你就可以运行了。

④ 驾车路线详情
在RouteActivity中找到onDriveRouteSearched()方法,方法里面添加如下代码:
//显示驾车花费时间
binding.tvTime.setText(des);
binding.layBottom.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
//跳转到路线详情页面
binding.tvDetail.setOnClickListener(v -> {
Intent intent = new Intent(RouteActivity.this,
RouteDetailActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("type",2);
intent.putExtra("path", drivePath);
startActivity(intent);
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11

下面我们在MapUtil中添加getDriveActionID()方法,代码如下所示:
public static int getDriveActionID(String actionName) { if (actionName == null || actionName.isEmpty()) { return R.drawable.dir3; } if ("左转".equals(actionName)) { return R.drawable.dir2; } if ("右转".equals(actionName)) { return R.drawable.dir1; } if ("向左前方行驶".equals(actionName) || "靠左".equals(actionName)) { return R.drawable.dir6; } if ("向右前方行驶".equals(actionName) || "靠右".equals(actionName)) { return R.drawable.dir5; } if ("向左后方行驶".equals(actionName) || "左转调头".equals(actionName)) { return R.drawable.dir7; } if ("向右后方行驶".equals(actionName)) { return R.drawable.dir8; } if ("直行".equals(actionName)) { return R.drawable.dir3; } if ("减速行驶".equals(actionName)) { return R.drawable.dir4; } return R.drawable.dir3; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
然后在adapter包下新增一个DriveSegmentListAdapter类,里面的代码如下;
package com.llw.newmapdemo.adapter; import android.view.LayoutInflater; import android.view.View; import android.view.ViewGroup; import androidx.annotation.NonNull; import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView; import com.amap.api.services.route.DriveStep; import com.llw.newmapdemo.R; import com.llw.newmapdemo.databinding.ItemSegmentBinding; import com.llw.newmapdemo.utils.MapUtil; import java.util.List; /** * 驾车段列表适配器 */ public class DriveSegmentListAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<DriveSegmentListAdapter.ViewHolder> { private List<DriveStep> mItemList; public DriveSegmentListAdapter(List<DriveStep> data) { this.mItemList = data; } @NonNull @Override public ViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) { return new ViewHolder(ItemSegmentBinding.inflate(LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext()), parent, false)); } @Override public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull ViewHolder holder, int position) { DriveStep item = mItemList.get(position); if (position == 0) { holder.binding.busDirIcon.setImageResource(R.drawable.dir_start); holder.binding.busLineName.setText("出发"); holder.binding.busDirIconUp.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE); holder.binding.busDirIconDown.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busSegSplitLine.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE); } else if (position == mItemList.size() - 1) { holder.binding.busDirIcon.setImageResource(R.drawable.dir_end); holder.binding.busLineName.setText("到达终点"); holder.binding.busDirIconUp.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busDirIconDown.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE); } else { holder.binding.busSegSplitLine.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busDirIconUp.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busDirIconDown.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); String actionName = item.getAction(); int resID = MapUtil.getDriveActionID(actionName); holder.binding.busDirIcon.setImageResource(resID); holder.binding.busLineName.setText(item.getInstruction()); } } @Override public int getItemCount() { return mItemList == null || mItemList.isEmpty() ? 0 : mItemList.size(); } static class ViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder { ItemSegmentBinding binding; public ViewHolder(ItemSegmentBinding itemView) { super(itemView.getRoot()); this.binding = itemView; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
适配器没有问题了,下面进入到RouteDetailActivity,新增如下方法:
/**
* 驾车详情
* @param intent
*/
private void driveDetail(Intent intent) {
tvTitle.setText("驾车路线规划");
DrivePath drivePath = intent.getParcelableExtra("path");
String dur = MapUtil.getFriendlyTime((int) drivePath.getDuration());
String dis = MapUtil.getFriendlyLength((int) drivePath.getDistance());
tvTime.setText(dur + "(" + dis + ")");
rv.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(this));
rv.setAdapter(new DriveSegmentListAdapter(R.layout.item_segment, drivePath.getSteps()));
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
然后在initView中调用。

然后运行一下:

⑤ 公交路线详情
最后这个公交路线详情是最麻烦的,前面三个其实都还蛮简单的,同样在RouteActivity中找到onBusRouteSearched()方法,然后在里面添加如下代码:
//显示公交花费时间
binding.tvTime.setText(des);
binding.layBottom.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
//跳转到路线详情页面
binding.tvDetail.setOnClickListener(v -> {
Intent intent = new Intent(RouteActivity.this,
RouteDetailActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("type",3);
intent.putExtra("path", busPath);
startActivity(intent);
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11

下面这个适配器的代码就比较多了,为什么呢?因为公交的话它还有这个公交车的信息,比如你是要做几路车,然后经过几个站,之后再转几路车,最后到达终点。因此先增加一个站点的布局,在layout下创建一个item_segment_ex.xml文件,里面的代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" > <RelativeLayout android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="27dp" android:layout_marginLeft="15.5dp" android:layout_marginStart="15.5dp" > <ImageView android:id="@+id/bus_dir_icon" android:layout_width="13dp" android:layout_height="13dp" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:src="@drawable/dir_station" /> <ImageView android:id="@+id/bus_dir_icon_up" android:layout_width="2dp" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_above="@id/bus_dir_icon" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:background="#b6b6b6" /> <ImageView android:id="@+id/bus_dir_icon_down" android:layout_width="2dp" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_below="@id/bus_dir_icon" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:background="#b6b6b6" /> </RelativeLayout> <TextView android:id="@+id/bus_line_station_name" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center_vertical" android:gravity="center_vertical" android:layout_marginLeft="20dp" android:layout_marginStart="20dp" android:textColor="#999999" android:textSize="13sp" /> </LinearLayout>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
这里还需要对原来的BusStep进行一次封装,而不是直接使用这个BusStep,在utils包下新增一个SchemeBusStep类,代码如下:
package com.llw.newmapdemo.util; import com.amap.api.services.route.BusStep; public class SchemeBusStep extends BusStep { private boolean isWalk = false; private boolean isBus = false; private boolean israilway = false; private boolean istaxi = false; private boolean isStart = false; private boolean isEnd = false; private boolean arrowExpend = false; public SchemeBusStep(BusStep step) { if (step != null) { this.setBusLine(step.getBusLine()); this.setWalk(step.getWalk()); this.setRailway(step.getRailway()); this.setTaxi(step.getTaxi()); } } public boolean isArrowExpend() { return arrowExpend; } public void setArrowExpend(boolean arrowExpend) { this.arrowExpend = arrowExpend; } public boolean isWalk() { return isWalk; } public void setWalk(boolean isWalk) { this.isWalk = isWalk; } public boolean isBus() { return isBus; } public void setBus(boolean isBus) { this.isBus = isBus; } public boolean isStart() { return isStart; } public void setStart(boolean isStart) { this.isStart = isStart; } public boolean isEnd() { return isEnd; } public void setEnd(boolean isEnd) { this.isEnd = isEnd; } public boolean isRailway() { return israilway; } public boolean isTaxi() { return istaxi; } public void setRailway(boolean israilway) { this.israilway = israilway; } public void setTaxi(boolean istaxi) { this.istaxi = istaxi; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
这个里面主要就是对数据的控制,使你在适配器中可以更好处理显示的效果。下面来写这个适配器,在adapter包下新建一个BusSegmentListAdapter类,代码如下:
package com.llw.newmapdemo.adapter; import static com.amap.api.maps.model.BitmapDescriptorFactory.getContext; import android.view.LayoutInflater; import android.view.View; import android.view.ViewGroup; import android.widget.LinearLayout; import android.widget.TextView; import androidx.annotation.NonNull; import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView; import com.amap.api.services.busline.BusStationItem; import com.amap.api.services.route.RailwayStationItem; import com.llw.newmapdemo.R; import com.llw.newmapdemo.databinding.ItemSegmentBinding; import com.llw.newmapdemo.utils.SchemeBusStep; import java.util.List; /** * 公交段列表适配器 */ public class BusSegmentListAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<BusSegmentListAdapter.ViewHolder> { private List<SchemeBusStep> mItemList; public BusSegmentListAdapter(List<SchemeBusStep> data) { this.mItemList = data; } @NonNull @Override public ViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) { return new ViewHolder(ItemSegmentBinding.inflate(LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext()), parent, false)); } @Override public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull ViewHolder holder, int position) { SchemeBusStep item = mItemList.get(position); if (position == 0) { holder.binding.busDirIcon.setImageResource(R.drawable.dir_start); holder.binding.busLineName.setText("出发"); holder.binding.busDirIconUp.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE); holder.binding.busDirIconDown.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busSegSplitLine.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE); } else if (position == mItemList.size() - 1) { holder.binding.busDirIcon.setImageResource(R.drawable.dir_end); holder.binding.busLineName.setText("到达终点"); holder.binding.busDirIconUp.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busDirIconDown.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE); } else { if (item.isWalk() && item.getWalk() != null && item.getWalk().getDistance() > 0) { holder.binding.busDirIcon.setImageResource(R.drawable.dir13); holder.binding.busDirIconUp.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busDirIconDown.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busLineName.setText("步行" + (int) item.getWalk().getDistance() + "米"); holder.binding.busStationNum.setVisibility(View.GONE); holder.binding.busExpandImage.setVisibility(View.GONE); } else if (item.isBus() && item.getBusLines().size() > 0) { holder.binding.busDirIcon.setImageResource(R.drawable.dir14); holder.binding.busDirIconUp.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busDirIconDown.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busLineName.setText(item.getBusLines().get(0).getBusLineName()); holder.binding.busStationNum.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busStationNum .setText((item.getBusLines().get(0).getPassStationNum() + 1) + "站"); holder.binding.busExpandImage.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); } else if (item.isRailway() && item.getRailway() != null) { holder.binding.busDirIcon.setImageResource(R.drawable.dir16); holder.binding.busDirIconUp.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busDirIconDown.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busLineName.setText(item.getRailway().getName()); holder.binding.busStationNum.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busStationNum .setText((item.getRailway().getViastops().size() + 1) + "站"); holder.binding.busExpandImage.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); } else if (item.isTaxi() && item.getTaxi() != null) { holder.binding.busDirIcon.setImageResource(R.drawable.dir14); holder.binding.busDirIconUp.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busDirIconDown.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); holder.binding.busLineName.setText("打车到终点"); holder.binding.busStationNum.setVisibility(View.GONE); holder.binding.busExpandImage.setVisibility(View.GONE); } } holder.binding.busItem.setOnClickListener(v -> { if (item.isBus()) {//公交 if (!item.isArrowExpend()) { item.setArrowExpend(true); holder.binding.busExpandImage.setImageResource(R.drawable.up); addBusStation(item.getBusLine().getDepartureBusStation(), holder.binding.expandContent); for (BusStationItem station : item.getBusLine() .getPassStations()) { addBusStation(station, holder.binding.expandContent); } addBusStation(item.getBusLine().getArrivalBusStation(), holder.binding.expandContent); } else { item.setArrowExpend(false); holder.binding.busExpandImage.setImageResource(R.drawable.down); holder.binding.expandContent.removeAllViews(); } } else if (item.isRailway()) {//火车 if (!item.isArrowExpend()) { item.setArrowExpend(true); holder.binding.busExpandImage.setImageResource(R.drawable.up); addRailwayStation(item.getRailway().getDeparturestop(), holder.binding.expandContent); for (RailwayStationItem station : item.getRailway().getViastops()) { addRailwayStation(station, holder.binding.expandContent); } addRailwayStation(item.getRailway().getArrivalstop(), holder.binding.expandContent); } else { item.setArrowExpend(false); holder.binding.busExpandImage.setImageResource(R.drawable.down); holder.binding.expandContent.removeAllViews(); } } }); } /** * 添加公交车站 * @param station * @param expandContent */ private void addBusStation(BusStationItem station, LinearLayout expandContent) { LinearLayout ll = (LinearLayout) View.inflate(getContext(), R.layout.item_segment_ex, null); TextView tv = ll.findViewById(R.id.bus_line_station_name); tv.setText(station.getBusStationName()); expandContent.addView(ll); } /** * 添加火车站 * @param station * @param expandContent */ private void addRailwayStation(RailwayStationItem station, LinearLayout expandContent) { LinearLayout ll = (LinearLayout) View.inflate(getContext(), R.layout.item_segment_ex, null); TextView tv = ll .findViewById(R.id.bus_line_station_name); tv.setText(station.getName() + " " + getRailwayTime(station.getTime())); expandContent.addView(ll); } /** * 获取铁路时间 * @param time * @return */ public static String getRailwayTime(String time) { return time.substring(0, 2) + ":" + time.substring(2, time.length()); } @Override public int getItemCount() { return mItemList == null || mItemList.isEmpty() ? 0 : mItemList.size(); } static class ViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder { ItemSegmentBinding binding; public ViewHolder(ItemSegmentBinding itemView) { super(itemView.getRoot()); this.binding = itemView; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
里面也是比较简单的代码,不清楚的话和我说一声,我再给你解释一下,那么下面进入RouteDetailActivity,先增加一个getBusSteps方法,对BusStep数据进行组装。
/** * 公交方案数据组装 * @param list * @return */ private List<SchemeBusStep> getBusSteps(List<BusStep> list) { List<SchemeBusStep> busStepList = new ArrayList<>(); SchemeBusStep start = new SchemeBusStep(null); start.setStart(true); busStepList.add(start); for (BusStep busStep : list) { if (busStep.getWalk() != null && busStep.getWalk().getDistance() > 0) { SchemeBusStep walk = new SchemeBusStep(busStep); walk.setWalk(true); busStepList.add(walk); } if (busStep.getBusLine() != null) { SchemeBusStep bus = new SchemeBusStep(busStep); bus.setBus(true); busStepList.add(bus); } if (busStep.getRailway() != null) { SchemeBusStep railway = new SchemeBusStep(busStep); railway.setRailway(true); busStepList.add(railway); } if (busStep.getTaxi() != null) { SchemeBusStep taxi = new SchemeBusStep(busStep); taxi.setTaxi(true); busStepList.add(taxi); } } SchemeBusStep end = new SchemeBusStep(null); end.setEnd(true); busStepList.add(end); return busStepList; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
然后添加一个busDetail方法,里面的代码如下:
/**
* 公交详情
* @param intent
*/
private void busDetail(Intent intent) {
tvTitle.setText("公交路线规划");
BusPath busPath = intent.getParcelableExtra("path");
String dur = MapUtil.getFriendlyTime((int) busPath.getDuration());
String dis = MapUtil.getFriendlyLength((int) busPath.getDistance());
tvTime.setText(dur + "(" + dis + ")");
rv.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(this));
rv.setAdapter(new BusSegmentListAdapter(R.layout.item_segment, getBusSteps(busPath.getSteps())));
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
最后在initView()中调用。

然后运行一下:

⑥ 手动输入目的地和出发地
在实际使用中,通常都是定位到当前所在地,然后用户再输入一个目的地,以此来计算这个两点之间的路线规划,手动点地图这种方式并不常用,因为你很难点到足够精确的位置,其次就是你要在地图上寻找这个地方所在,这样用户花费的时间就会更多,因此日常使用都是手动输入,输入方式有多种,常规的键盘输入、声音输入、扫码输入等。下面我们使用键盘输入。
这里就需要修改activity_route.xml布局了,添加如下代码:
<TextView android:id="@+id/tv_start" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="50dp" android:gravity="center_vertical" android:paddingStart="16dp" android:text="当前所在地" android:textColor="#000" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/spinner" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/et_start_address" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="50dp" android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/tv_start" android:background="@null" android:padding="8dp" android:textColor="#000" android:textSize="12sp" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/tv_start" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="@+id/tv_start" /> <View android:id="@+id/view" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="0.5dp" android:layout_below="@+id/et_start_address" android:background="#000" app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/et_start_address" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_end" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="50dp" android:layout_below="@+id/et_start_address" android:gravity="center_vertical" android:paddingStart="16dp" android:text="前往目的地" android:textColor="#000" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/view" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/et_end_address" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="50dp" android:layout_below="@+id/et_start_address" android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/tv_end" android:background="@null" android:hint="请输入目的地" android:imeOptions="actionSearch" android:padding="8dp" android:singleLine="true" android:textColor="#000" android:textSize="14sp" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/tv_end" app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/tv_start" /> <View android:id="@+id/view2" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="0.5dp" android:layout_below="@+id/et_end_address" android:background="#000" app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/et_end_address" />
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
添加位置如下图所示:
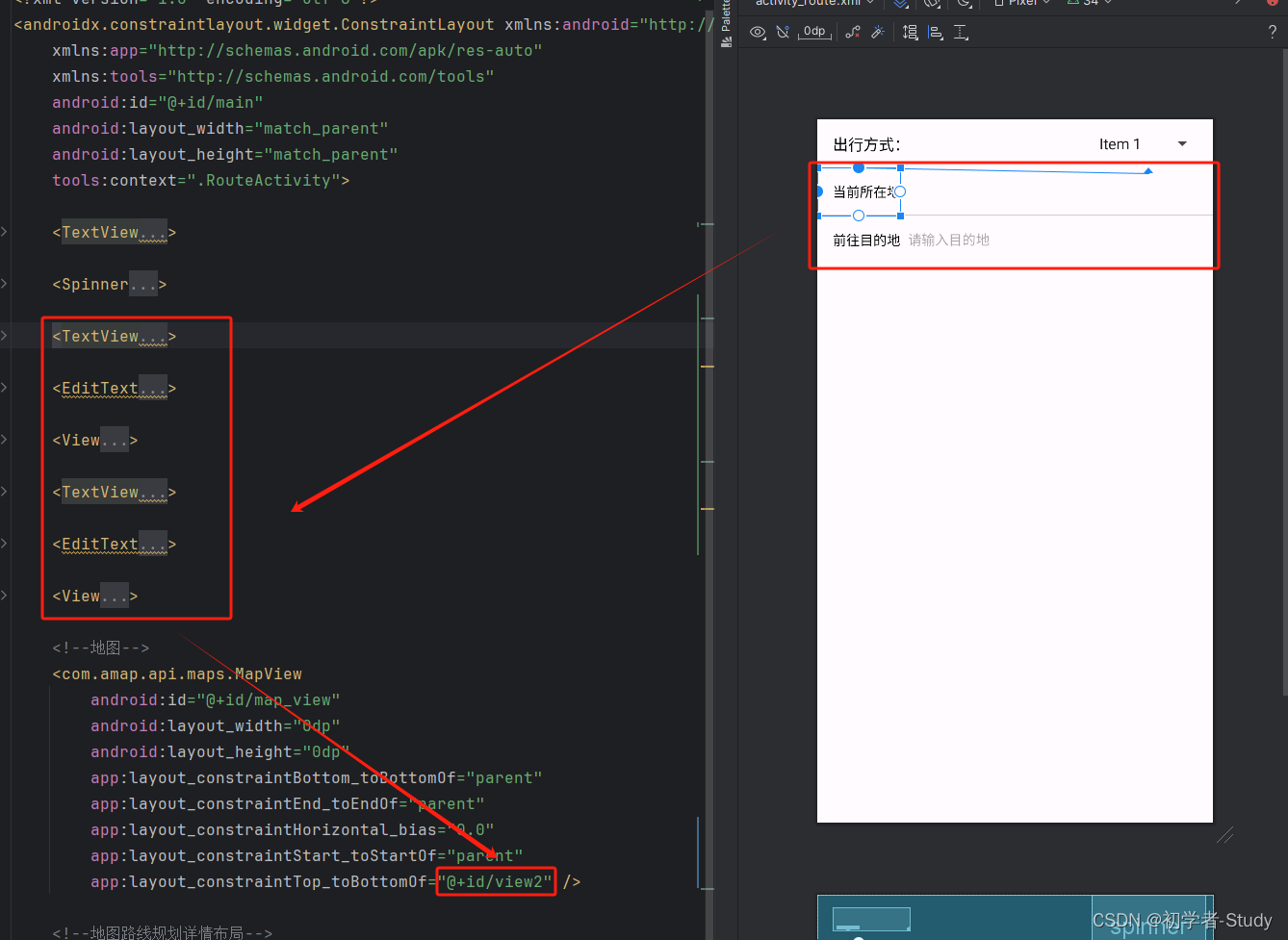
然后进入到RouteActivity,创建变量。
然后在initTravelMode()方法中目的地输入框添加一个软键盘按键监听。
//键盘按键监听 binding.etEndAddress.setOnKeyListener((v, keyCode, event) -> { if (keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_ENTER && event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_UP) { //获取输入框的值 String endAddress = binding.etEndAddress.getText().toString().trim(); if (endAddress.isEmpty()) { showMsg("请输入要前往的目的地"); return false; } InputMethodManager imm = (InputMethodManager) getSystemService(Context.INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE); //隐藏软键盘 imm.hideSoftInputFromWindow(getWindow().getDecorView().getWindowToken(), 0); //通过输入的目的地转为经纬度,然后进行地图上添加标点,最后计算出行路线规划 return true; } return false; });
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
添加位置如下图所示

这里的当前地我还是使用定位所在地,在onLocationChanged()方法中增加如下代码。
//设置当前所在地
etStartAddress.setText(address);
etStartAddress.setEnabled(false);//禁用输入
- 1
- 2
- 3
添加位置如下图所示

现在还差一个地址转换的处理,通过地理编码就可以把地址转化成坐标。在RouteActivity中声明变量,代码如下所示:
//地理编码搜索
private GeocodeSearch geocodeSearch;
//解析成功标识码
private static final int PARSE_SUCCESS_CODE = 1000;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
然后在initMap()方法中
//构造 GeocodeSearch 对象
try {
geocodeSearch = new GeocodeSearch(this);
} catch (AMapException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
//设置监听
geocodeSearch.setOnGeocodeSearchListener(this);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
添加位置如下图所示:

同样Activity依然需要实现GeocodeSearch.OnGeocodeSearchListener。

然后重写如下方法:
@Override public void onRegeocodeSearched(RegeocodeResult regeocodeResult, int i) { } /** * 地址转坐标 * * @param geocodeResult * @param rCode */ @Override public void onGeocodeSearched(GeocodeResult geocodeResult, int rCode) { if (rCode != PARSE_SUCCESS_CODE) { showMsg("获取坐标失败,错误码:" + rCode); return; } List<GeocodeAddress> geocodeAddressList = geocodeResult.getGeocodeAddressList(); if (geocodeAddressList != null && !geocodeAddressList.isEmpty()) { //终点 mEndPoint = geocodeAddressList.get(0).getLatLonPoint(); //开始路线搜索 startRouteSearch(); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
在onGeocodeSearched()方法中通过坐标确定终点,然后进行路线规划,最后一步就是在输入框的键盘按键监听触发这个地理编码搜索。
// name表示地址,第二个参数表示查询城市,中文或者中文全拼,citycode、adcode
GeocodeQuery query = new GeocodeQuery(endAddress, city);
geocodeSearch.getFromLocationNameAsyn(query);
- 1
- 2
- 3
添加位置如下图所示

这样就OK了,运行一下。

现在这个当前所在地是通过定位获取的,那么怎么样改成可以手动输入的呢?其实很简单,一开始我写这个页面时,因为是通过定位获取到这个所在地的地址信息然后设置到控件上,所以控件的字体我做了一些调整,如果说要想设置为可输入的话,那么两个输入框的字体应该一致才行,下面先更改这一个,打开activity_route.xml。

在RouteActivity中定义变量locationAddress,表明这是一个通过定位获得的地址。
//定位地址
private String locationAddress;
- 1
- 2
然后我们修改onLocationChanged(),代码如下所示:
//地址
locationAddress = aMapLocation.getAddress();
//设置当前所在地
binding.etStartAddress.setText(locationAddress);
//binding.etStartAddress.setEnabled(false);//禁用输入
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
添加位置如下图所示

对于路线的规划是在输入完目的地之后,点击软键盘上的搜索按钮之后执行的。还记得之前的目的地输入后,有一个地址转坐标的操作,在这里进行了目的地的构建,然后才是路线的规划。

那么你现在的出发地也是手动输入的话,那就同样要转换成坐标,然后去构建这个出发地,也就是起点左标,而解析只有一个返回,那么你就需要区分这个解析是起点还是终点了。然后来看这一块的代码,这里就是对这个目的地输入框进行了检查,这是之前的代码,现在这一块的代码就要做更改了。

首先定义变量。
//起点地址转坐标标识 1
private int tag = -1;
- 1
- 2
然后设置起点这个输入框的软键盘搜索按键监听,而因为有两个输入框都需要进行监听,因此通过类来实现。修改initTravelMode()方法中的代码。
//起点 键盘按键监听
binding.etStartAddress.setOnKeyListener(this);
//终点 键盘按键监听
binding.etEndAddress.setOnKeyListener(this);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
如下图所示

会实现一个onKey()方法。代码如下所示:
@Override public boolean onKey(View v, int keyCode, KeyEvent event) { if (keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_ENTER && event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_UP) { //获取输入框的值 出发地(起点) String startAddress = etStartAddress.getText().toString().trim(); //获取输入框的值 目的地(终点) String endAddress = etEndAddress.getText().toString().trim(); //判断出发地是否有值 不管这个值是定位还是手动输入 if (startAddress.isEmpty()) { showMsg("请输入当前的出发地"); return false; } //判断目的地是否有值 if (endAddress.isEmpty()) { showMsg("请输入要前往的目的地"); return false; } //当出发地输入框有值的时候,判断这个值是否是定位的地址,是则说明你没有更改过,则不需要进行地址转坐标,不是则需要转换。 if (!locationAddress.equals(startAddress)) { tag = 1; GeocodeQuery startQuery = new GeocodeQuery(startAddress, city); geocodeSearch.getFromLocationNameAsyn(startQuery); } else { tag = -1; } InputMethodManager imm = (InputMethodManager) getSystemService(Context.INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE); //隐藏软键盘 imm.hideSoftInputFromWindow(getWindow().getDecorView().getWindowToken(), 0); //通过输入的目的地转为经纬度,然后进行地图上添加标点,最后计算出行路线规划 // name表示地址,第二个参数表示查询城市,中文或者中文全拼,citycode、adcode GeocodeQuery endQuery = new GeocodeQuery(endAddress, city); geocodeSearch.getFromLocationNameAsyn(endQuery); return true; } return false; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
然后再去修改onGeocodeSearched()方法的代码:
@Override public void onGeocodeSearched(GeocodeResult geocodeResult, int rCode) { if (rCode != PARSE_SUCCESS_CODE) { showMsg("获取坐标失败,错误码:" + rCode); return; } List<GeocodeAddress> geocodeAddressList = geocodeResult.getGeocodeAddressList(); if (geocodeAddressList != null && !geocodeAddressList.isEmpty()) { //判断是不是起点的搜索 if (tag == 1) { //起点 mStartPoint = geocodeAddressList.get(0).getLatLonPoint(); } else { //终点 mEndPoint = geocodeAddressList.get(0).getLatLonPoint(); } if (mStartPoint != null && mEndPoint != null) { //开始路线搜索 startRouteSearch(); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
下面就可以运行了。

十一、源码
如果对你有所帮助的话,不妨欢迎Star和Fork。
源码地址:NewGaodeMapDemo



