热门标签
热门文章
- 1快速获取当天0点0分0秒(00:00:00),23点59分59秒(23:59:59)
- 2SLAM简介
- 3吾剑未尝不利,国内Azure平替,科大讯飞人工智能免费AI语音合成(TTS)服务Python3.10接入_免费语音合成api
- 44.3.2 IP数据报分片_一总八片首四
- 5JAVA Synchronized对象锁和类锁区别(牛逼)_java synchronized 对象和类的区别
- 6SpringBoot+Maven使用profile打包不同环境的配置文件_springboot中使用application.yml,maven如何在打包时将profile指向
- 7如何转换图片格式为jpg?教你两种转换方法_cxr格式用什么打开
- 8AI配音版Sora视频刷屏!绝美逼真音效打破「无声电影」,或颠覆万亿美元产业_ai配音没有纪录片的感觉
- 9ISO27001标准_iso27001条款
- 10查看docker镜像名称_Docker 命令千万个,日常顺手用的就这几个
当前位置: article > 正文
whisper深入-语者分离_autodl whisper
作者:从前慢现在也慢 | 2024-03-22 14:23:11
赞
踩
autodl whisper
学习目标:如何使用whisper
学习内容一:whisper 转文字
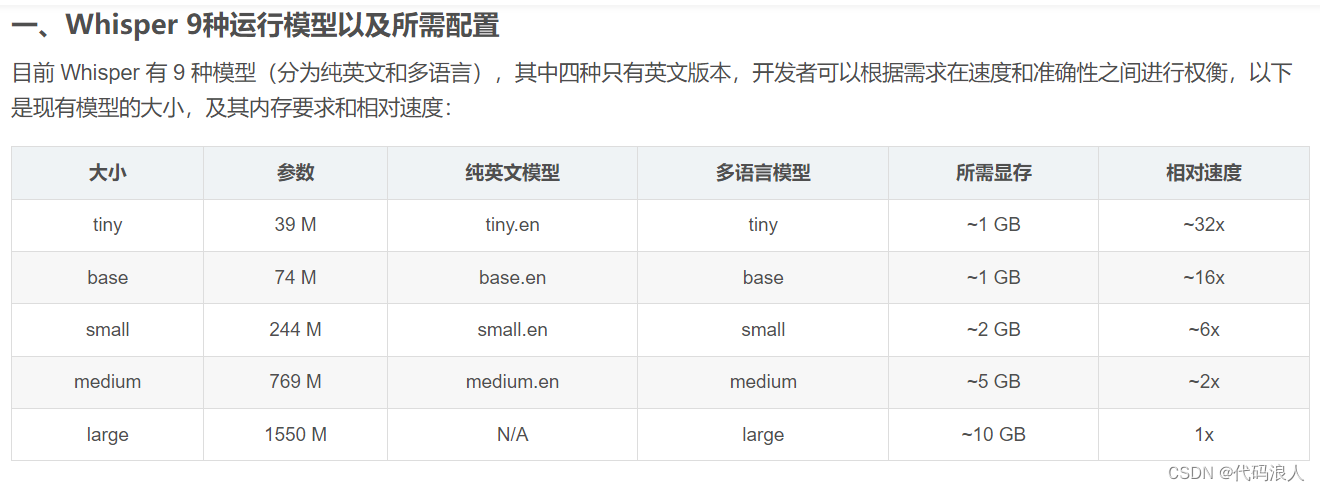
1.1 使用whisper.load_model()方法下载,加载
model=whisper.load_model(参数)
- 1
- name 需要加载的模型,如上图
- device:默认有个方法,有显存使用显存,没有使用cpu
- download_root:下载的根目录,默认使用
~/.cache/whisper - in_memory: 是否将模型权重预加载到主机内存中
返回值
model : Whisper
Whisper语音识别模型实例
def load_model(
name: str,
device: Optional[Union[str, torch.device]] = None,
download_root: str = None,
in_memory: bool = False,
) -> Whisper:
"""
Load a Whisper ASR model
Parameters
----------
name : str
one of the official model names listed by `whisper.available_models()`, or
path to a model checkpoint containing the model dimensions and the model state_dict.
device : Union[str, torch.device]
the PyTorch device to put the model into
download_root: str
path to download the model files; by default, it uses "~/.cache/whisper"
in_memory: bool
whether to preload the model weights into host memory
Returns
-------
model : Whisper
The Whisper ASR model instance
"""
if device is None:
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
if download_root is None:
default = os.path.join(os.path.expanduser("~"), ".cache")
download_root = os.path.join(os.getenv("XDG_CACHE_HOME", default), "whisper")
if name in _MODELS:
checkpoint_file = _download(_MODELS[name], download_root, in_memory)
alignment_heads = _ALIGNMENT_HEADS[name]
elif os.path.isfile(name):
checkpoint_file = open(name, "rb").read() if in_memory else name
alignment_heads = None
else:
raise RuntimeError(
f"Model {name} not found; available models = {available_models()}"
)
with (
io.BytesIO(checkpoint_file) if in_memory else open(checkpoint_file, "rb")
) as fp:
checkpoint = torch.load(fp, map_location=device)
del checkpoint_file
dims = ModelDimensions(**checkpoint["dims"])
model = Whisper(dims)
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint["model_state_dict"])
if alignment_heads is not None:
model.set_alignment_heads(alignment_heads)
return model.to(device)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
1.2 使用实例对文件进行转录
result = model.transcribe(file_path)
def transcribe(
model: "Whisper",
audio: Union[str, np.ndarray, torch.Tensor],
*,
verbose: Optional[bool] = None,
temperature: Union[float, Tuple[float, ...]] = (0.0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0),
compression_ratio_threshold: Optional[float] = 2.4,
logprob_threshold: Optional[float] = -1.0,
no_speech_threshold: Optional[float] = 0.6,
condition_on_previous_text: bool = True,
initial_prompt: Optional[str] = None,
word_timestamps: bool = False,
prepend_punctuations: str = "\"'“¿([{-",
append_punctuations: str = "\"'.。,,!!??::”)]}、",
**decode_options,
):
"""
将音频转换为文本。
参数:
- model: Whisper模型
- audio: 音频文件路径、NumPy数组或PyTorch张量
- verbose: 是否打印详细信息,默认为None
- temperature: 温度参数,默认为(0.0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0)
- compression_ratio_threshold: 压缩比阈值,默认为2.4
- logprob_threshold: 对数概率阈值,默认为-1.0
- no_speech_threshold: 无语音信号阈值,默认为0.6
- condition_on_previous_text: 是否根据先前的文本进行解码,默认为True
- initial_prompt: 初始提示,默认为None
- word_timestamps: 是否返回单词时间戳,默认为False
- prepend_punctuations: 前缀标点符号,默认为"\"'“¿([{-"
- append_punctuations: 后缀标点符号,默认为"\"'.。,,!!??::”)]}、"
- **decode_options: 其他解码选项
返回:
- 转录得到的文本
"""
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
1.3 实战
建议load_model添加参数
- download_root:下载的根目录,默认使用
~/.cache/whisper
transcribe方法添加参数 - word_timestamps=True
import whisper
import arrow
# 定义模型、音频地址、录音开始时间
def excute(model_name,file_path,start_time):
model = whisper.load_model(model_name)
result = model.transcribe(file_path,word_timestamps=True)
for segment in result["segments"]:
now = arrow.get(start_time)
start = now.shift(seconds=segment["start"]).format("YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss")
end = now.shift(seconds=segment["end"]).format("YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss")
print("【"+start+"->" +end+"】:"+segment["text"])
if __name__ == '__main__':
excute("large","/root/autodl-tmp/no/test.mp3","2022-10-24 16:23:00")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17

学习内容二:语者分离(pyannote.audio)pyannote.audio是huggingface开源音色包
第一步:安装依赖
pip install pyannote.audio
- 1
- 2
第二步:创建key
https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens
第三步:测试pyannote.audio
- 创建实例:Pipeline.from_pretrained(参数)
- 使用GPU加速:import torch # 导入torch库
pipeline.to(torch.device(“cuda”)) - 实例转化音频pipeline(“test.wav”)
from_pretrained(参数)
- cache_dir:路径或str,可选模型缓存目录的路径。默认/pyannote"当未设置时。
pipeline(参数)
- file_path:录音文件
- num_speakers:几个说话者,可以不带
from pyannote.audio import Pipeline
pipeline = Pipeline.from_pretrained("pyannote/speaker-diarization@2.1", use_auth_token="申请的key")
# send pipeline to GPU (when available)
import torch
device='cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
pipeline.to(torch.device(device))
# apply pretrained pipeline
diarization = pipeline("test.wav")
print(diarization)
# print the result
for turn, _, speaker in diarization.itertracks(yield_label=True):
print(f"start={turn.start:.1f}s stop={turn.end:.1f}s speaker_{speaker}")
# start=0.2s stop=1.5s speaker_0
# start=1.8s stop=3.9s speaker_1
# start=4.2s stop=5.7s speaker_0
# ...
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
学习内容三:整合
这里要借助一个开源代码,用于整合以上两种产生的结果
报错No module named 'pyannote_whisper'
如果你使用使用AutoDL平台,你可以使用学术代理加速
source /etc/network_turbo
- 1
git clone https://github.com/yinruiqing/pyannote-whisper.git
cd pyannote-whisper
pip install -r requirements.txt
- 1
- 2
- 3
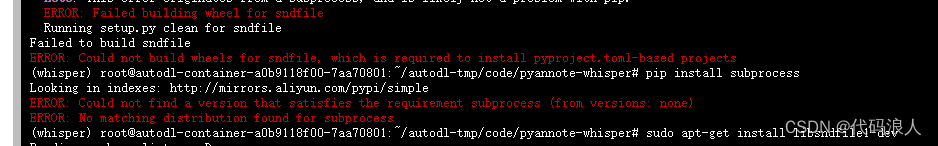
这个错误可能是由于缺少或不正确安装了所需的 sndfile 库。sndfile 是一个用于处理音频文件的库,它提供了多种格式的读写支持。
你可以尝试安装 sndfile 库,方法如下:
在 Ubuntu 上,使用以下命令安装:sudo apt-get install libsndfile1-dev
在 CentOS 上,使用以下命令安装:sudo yum install libsndfile-devel
在 macOS 上,使用 Homebrew 安装:brew install libsndfile
然后重新执行如上指令
在项目里面写代码就可以了,或者复制代码里面的pyannote_whisper.utils模块代码
import os
import whisper
from pyannote.audio import Pipeline
from pyannote_whisper.utils import diarize_text
import concurrent.futures
import subprocess
import torch
print("正在加载声纹模型")
pipeline = Pipeline.from_pretrained("pyannote/speaker-diarization@2.1",use_auth_token="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")
output_dir = '/root/autodl-tmp/no/out'
print("正在whisper模型")
model = whisper.load_model("large", device="cuda")
# MP3转化为wav
def convert_to_wav(path):
new_path = ''
if path[-3:] != 'wav':
new_path = '.'.join(path.split('.')[:-1]) + '.wav'
try:
subprocess.call(['ffmpeg', '-i', path, new_path, '-y', '-an'])
except:
return path, 'Error: Could not convert file to .wav'
else:
new_path = ''
return new_path, None
def process_audio(file_path):
file_path, retmsg = convert_to_wav(file_path)
print(f"===={file_path}=======")
asr_result = model.transcribe(file_path, initial_prompt="语音转换")
pipeline.to(torch.device('cuda'))
diarization_result = pipeline(file_path, num_speakers=2)
final_result = diarize_text(asr_result, diarization_result)
output_file = os.path.join(output_dir, os.path.basename(file_path)[:-4] + '.txt')
with open(output_file, 'w') as f:
for seg, spk, sent in final_result:
line = f'{seg.start:.2f} {seg.end:.2f} {spk} {sent}\n'
f.write(line)
if not os.path.exists(output_dir):
os.makedirs(output_dir)
wave_dir = '/root/autodl-tmp/no'
# 获取当前目录下所有wav文件名
wav_files = [os.path.join(wave_dir, file) for file in os.listdir(wave_dir) if file.endswith('.mp3')]
# 处理每个wav文件
# with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=1) as executor:
# executor.map(process_audio, wav_files)
for wav_file in wav_files:
process_audio(wav_file)
print('处理完成!')
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56

声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/从前慢现在也慢/article/detail/288732
推荐阅读
相关标签


