- 12024年华中杯数学建模A题思路与论文助攻_华中杯24a题
- 2计量经济学学习笔记:多重共线性、异方差、自相关_多重共线性与自相关的关系
- 3【转】华为Java笔试题
- 4Gradio 案例——将 dicom 文件转为 nii文件_linux将dicm文件转为nii文件
- 5Cannot find class: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver无法找到驱动文件_cannot find declaration to go to com.mysql.cj.jdbc
- 6编写高质量代码改善C++程序的150个建议_编写高质量c++程序
- 7C#/.NET面试问题总结 第一篇_c#实习生面试
- 8TIA Portal联合Process Simulate搞定SICAR虚拟调试实例步骤_tia+portal++sicar
- 9hfish蜜罐搭建与使用_hfish系统怎么停止ssh蜜罐
- 10【JavaEE 初阶(二)】线程安全问题
Kafka源码解析之内存池原理_kafka 内存池
赞
踩
一、内存池原理简介
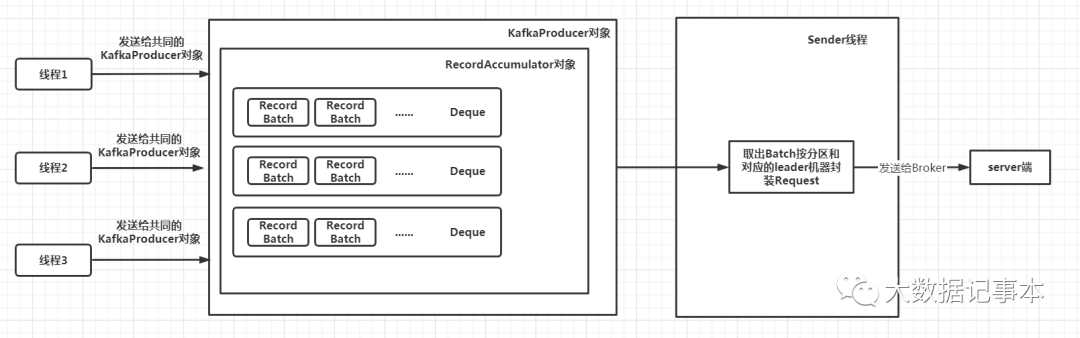
Kafka发送消息的流程如上所示,待发送的消息封装成一个个的批次对象RecordBatch,然后该批次对象被放到对应的Deque队列中,这里每个topic的每个分区对应一个Deque队列。之后Sender线程会从队列中取出RecordBatch对象,然后封装成ProducerRequest对象发送给服务端。所以RecordBatch是存储数据的对象,那么RecordBatch是怎么分配的呢?如果每次都创建一个新的RecordBatch对象,用完之后通过GC回收,那么在Kafka高吞吐的场景下,势必会创建大量的RecordBatch对象,增加GC的频率,而进行GC时对应的STW时间就会增加,从而使吞吐量降低。
Kafka为了解决这个问题,巧妙地运用了内存池。创建RecordBatch对象时,会从内存池中获取对应的内存,用完之后再将这部分内存归还给内存池,因此这部分内存可以循环利用而不必经过GC。
二、关键的几个类
1.RecordAccumulator:暂存消息的类。生产者主线程生产的消息并不会直接发送给服务端,而是先放到RecordAccumulator对象中进行缓存,当满足一定条件时,由Sender线程从该对象中取出消息进行封装并发送给服务端。该类的属性和构造方法如下:
public final class RecordAccumulator {
private volatile boolean closed;
private final AtomicInteger flushesInProgress;
private final AtomicInteger appendsInProgress;
private final int batchSize;//一个批次的大小
private final CompressionType compression;//压缩类型
private final long lingerMs;
private final long retryBackoffMs;
private final BufferPool free;//缓存对象
private final Time time;
private final ConcurrentMap<TopicPartition, Deque<RecordBatch>> batches;
private final IncompleteRecordBatches incomplete;
private final Set<TopicPartition> muted;
private int drainIndex;
public RecordAccumulator(int batchSize, 批次大小默认16k
long totalSize,//缓存大小默认32M
CompressionType compression,
long lingerMs,
long retryBackoffMs,
Metrics metrics,
Time time) {
this.drainIndex = 0;
this.closed = false;
this.flushesInProgress = new AtomicInteger(0);
this.appendsInProgress = new AtomicInteger(0);
this.batchSize = batchSize;
this.compression = compression;
this.lingerMs = lingerMs;
this.retryBackoffMs = retryBackoffMs;
this.batches = new CopyOnWriteMap<>();
String metricGrpName = "producer-metrics";
this.free = new BufferPool(totalSize, batchSize, metrics, time, metricGrpName);
this.incomplete = new IncompleteRecordBatches();
this.muted = new HashSet<>();
this.time = time;
registerMetrics(metrics, metricGrpName);
}
}
重点看三个属性:
-
batchSize:批次的大小,默认为16K(由参数batch.size设置)
-
free:缓存对象。
-
batches:一个map,key是消息发往的topic和partition,而value是待发送的消息队列
构造方法中,totalSize为缓存的总大小,默认为32M(由参数buffer.memory设置)。
2.BufferPool:缓存对应的类。该类的属性如下:
public final class BufferPool {
private final long totalMemory;//缓存的总大小
private final int poolableSize;//默认的批次大小
private final ReentrantLock lock;
private final Deque<ByteBuffer> free;//内存池
private final Deque<Condition> waiters;//存放Condition对象的队列
private long availableMemory;//未申请的内存空间
private final Metrics metrics;
private final Time time;
private final Sensor waitTime;
}
重点属性:
-
totalMemory:缓存的总内存大小
-
poolableSize:默认的批次大小
-
free:注意区别这个free和RecordAccumulator中的free,此处的free就是内存池,是一个存放ByteBuffer对象的队列。
-
availableMemory:未申请使用的缓存空间。
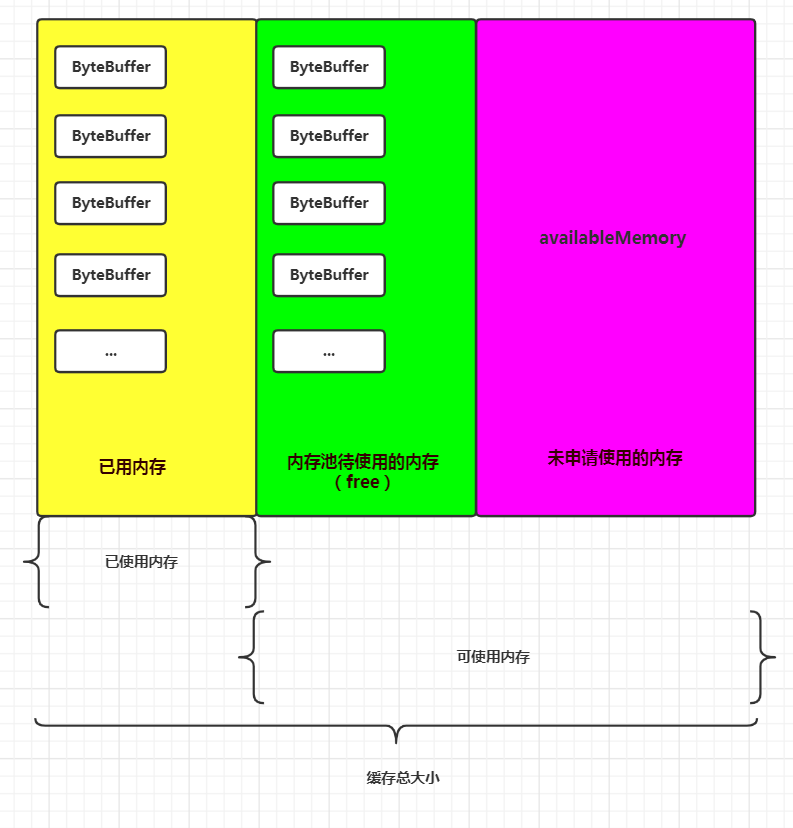
下面我们看一下缓存中的内存分配:
三、向内存池申请内存步骤详解
向内存池申请内存对应的是BufferPool类的allocate方法,该方法有两个参数:①int类型的size,即申请的内存大小;②long类型的maxTimeToBlockMs,即最长等待的时间,单位毫秒。具体方法如下:
public ByteBuffer allocate(int size, long maxTimeToBlockMs) throws InterruptedException {
//判断消息占用的空间是否大于内存池总容量32M
if (size > this.totalMemory)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Attempt to allocate " + size
+ " bytes, but there is a hard limit of "
+ this.totalMemory
+ " on memory allocations.");
this.lock.lock();
try {
// check if we have a free buffer of the right size pooled
//判断申请的内存大小是否为默认批次的内存大小(16k),且是否存在已申请但未使用的批次
//如果申请内存大小等于批次默认值,且存在已申请未使用的批次,那么返回已申请未使用的第一个批次,free是一个队列
if (size == poolableSize && !this.free.isEmpty())
return this.free.pollFirst();
// now check if the request is immediately satisfiable with the
// memory on hand or if we need to block
//poolableSize为默认批次大小,freeListSize为已申请但未使用的内存大小
int freeListSize = this.free.size() * this.poolableSize;
//size是本次我们要申请的内存
//this.availableMemory + freeListSize:目前可用的总内存
if (this.availableMemory + freeListSize >= size) {
// we have enough unallocated or pooled memory to immediately
// satisfy the request
freeUp(size);
//进行内存的扣减,此时的可用内存已满足申请内存
this.availableMemory -= size;
lock.unlock();
//分配内存
return ByteBuffer.allocate(size);
} else {
//如果可用内存无法满足申请的内存值,只能等待释放内存
//定义一个变量来记录释放的内存
int accumulated = 0;
ByteBuffer buffer = null;
//创建一个Condition 对象
Condition moreMemory = this.lock.newCondition();
long remainingTimeToBlockNs = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toNanos(maxTimeToBlockMs);
//waiters是一个队列,里面存放来Condition对象,只要队列中有对象,说明此时内存是不够分配的,
this.waiters.addLast(moreMemory);
// loop over and over until we have a buffer or have reserved
// enough memory to allocate one
/**
* 如果内存不够,总的分配思路就是一点点地分配,有一点分配一点
*/
//只要累计释放的内存小于申请的内存,就继续循环
while (accumulated < size) {
long startWaitNs = time.nanoseconds();
long timeNs;
boolean waitingTimeElapsed;
try {
//condition对象调用await方法进行等待,结束等待有两种情况:1。时间到了;2。被人唤醒了(内存池回收内存时,会唤醒)
waitingTimeElapsed = !moreMemory.await(remainingTimeToBlockNs, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
this.waiters.remove(moreMemory);
throw e;
} finally {
long endWaitNs = time.nanoseconds();
timeNs = Math.max(0L, endWaitNs - startWaitNs);
this.waitTime.record(timeNs, time.milliseconds());
}
//如果是等待时间到了,那么就把这个condition对象从队列中移除,并抛出异常
if (waitingTimeElapsed) {
this.waiters.remove(moreMemory);
throw new TimeoutException("Failed to allocate memory within the configured max blocking time " + maxTimeToBlockMs + " ms.");
}
remainingTimeToBlockNs -= timeNs;
// check if we can satisfy this request from the free list,
// otherwise allocate memory
//检查是否可以满足申请的内存;如果还没有释放内存,且申请内存大小正好等于批次大小,且已申请未使用队列中有批次
if (accumulated == 0 && size == this.poolableSize && !this.free.isEmpty()) {
// just grab a buffer from the free list
//那么就直接从已申请未使用队列中拿出一个批次的内存
buffer = this.free.pollFirst();
//释放内存就等于批次大小
accumulated = size;
} else {//如果可用内存小于申请内存
// we'll need to allocate memory, but we may only get
// part of what we need on this iteration
//从已申请未使用内存中拿出批次,大小为申请内存-释放内存
freeUp(size - accumulated);
int got = (int) Math.min(size - accumulated, this.availableMemory);
//更新可用内存和释放内存
this.availableMemory -= got;
accumulated += got;
}
}
// remove the condition for this thread to let the next thread
// in line start getting memory
//当释放的内存大于等于申请内存,就把之前的condition从队列中移除
Condition removed = this.waiters.removeFirst();
if (removed != moreMemory)
throw new IllegalStateException("Wrong condition: this shouldn't happen.");
// signal any additional waiters if there is more memory left
// over for them
if (this.availableMemory > 0 || !this.free.isEmpty()) {
if (!this.waiters.isEmpty())
this.waiters.peekFirst().signal();
}
// unlock and return the buffer
lock.unlock();
if (buffer == null)
return ByteBuffer.allocate(size);
else
return buffer;
}
} finally {
if (lock.isHeldByCurrentThread())
lock.unlock();
}
}
1.判断申请的内存是否超过了缓存的总大小,如果超出,则抛异常。
if (size > this.totalMemory)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Attempt to allocate " + size
+ " bytes, but there is a hard limit of "
+ this.totalMemory
+ " on memory allocations.");
2.加锁
this.lock.lock();
3.判断申请内存大小是否为默认批次大小,且内存池中还有内存对象。如果均满足,直接返回内存池队列中的第一个ByteBuffer对象。
if (size == poolableSize && !this.free.isEmpty())
return this.free.pollFirst();
4.如果不满足,则计算内存池占用的内存大小。
//poolableSize为默认批次大小,freeListSize为内存池占用内存大小
int freeListSize = this.free.size() * this.poolableSize
5.判断可用内存是否大于申请内存,如果大于,释放内存池中的内存,直到availableMemory大于申请内存。然后availableMemory进行内存扣减,解锁,最后返回一个容量为申请内存大小的ByteBuffer对象。
if (this.availableMemory + freeListSize >= size) {
freeUp(size);
//进行内存的扣减,此时的可用内存已满足申请内存
this.availableMemory -= size;
lock.unlock();
//分配内存
return ByteBuffer.allocate(size);
}
freeUp方法:
//如果未申请使用内存不满足申请内存,那么就从内存池末尾,
//不断取出ByteBuffer对象释放内存,直到未申请内存满足申请内存
private void freeUp(int size) {
while (!this.free.isEmpty() && this.availableMemory < size)
this.availableMemory += this.free.pollLast().capacity();
}
6.如果可用内存小于申请内存,只能等待释放内存。这里定义一个变量accumulated 用来累计释放的内存,且创建一个Condition对象,然后放到等待队列末尾。
int accumulated = 0;
Condition moreMemory = this.lock.newCondition();
this.waiters.addLast(moreMemory);
7.如果累计释放的内存小于申请内存,就一直循环等待内存释放。这里调用Condition对象moreMemory 的await方法进行等待,结束等待有两种情况:①等待时间到了;②被唤醒。如果是时间到了,就将moreMemory从等待队列移除,然后抛出异常。
while (accumulated < size) {
long startWaitNs = time.nanoseconds();
long timeNs;
boolean waitingTimeElapsed;
try {
//condition对象调用await方法进行等待,结束等待有两种情况:1。时间到了;2。被人唤醒了(内存池回收内存时,会唤醒)
waitingTimeElapsed = !moreMemory.await(remainingTimeToBlockNs, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
this.waiters.remove(moreMemory);
throw e;
} finally {
long endWaitNs = time.nanoseconds();
timeNs = Math.max(0L, endWaitNs - startWaitNs);
this.waitTime.record(timeNs, time.milliseconds());
}
//如果是等待时间到了,那么就把这个condition对象从队列中移除,并抛出异常
if (waitingTimeElapsed) {
this.waiters.remove(moreMemory);
throw new TimeoutException("Failed to allocate memory within the configured max blocking time " + maxTimeToBlockMs + " ms.");
}
8.如果是被唤醒的,说明有内存被归还了。判断申请的内存是否正好等于内存池中一个批次的大小,且内存池中有ByteBuffer对象。如果是,则直接从内存池头部取出一个ByteBuffer对象,更新累计释放内存变量accumulated 。
if (accumulated == 0 && size == this.poolableSize && !this.free.isEmpty()) {
//那么就直接从内存池头部拿出一个ByteBuffer对象
buffer = this.free.pollFirst();
//累计释放内存就等于申请内存
accumulated = size;
}
9.如果可用内存还不够申请内存,则一点点地分配。即释放一点,就分配一点,直到累计释放的内存达到申请内存。
else {
//只有内存池有ByteBuffer对象,就释放其内存
freeUp(size - accumulated);
int got = (int) Math.min(size - accumulated, this.availableMemory);
//更新未申请内存,即只要有未申请的内存,就把它分配出去
this.availableMemory -= got;
//更新累计释放内存,只要有未申请的内存,就拿过来进行累计
accumulated += got;
}
10.当累计释放内存大于申请内存时,将之前放到等待队列中的Condition对象移除。
Condition removed = this.waiters.removeFirst();
11.如果分配了申请内存之后,还有未分配内存,或者内存池不为空;同时等待队列不为空,则从等待队列中取出一个Condition对象,并唤醒。
if (this.availableMemory > 0 || !this.free.isEmpty()) {
if (!this.waiters.isEmpty())
this.waiters.peekFirst().signal();
}
12.解锁,并返回申请的内存。如果buffer为null,说明申请内存大于默认批次16K,返回实际申请的内存;buffer不为null,说明申请内存为默认的批次大小,直接返回。
lock.unlock();
if (buffer == null)
return ByteBuffer.allocate(size);
else
return buffer;
四、向内存池归还内存步骤详解
向内存池归还内存对应的是BufferPool类的deallocate方法,该方法有两个参数:①ByteBuffer类型的buffer;②int类型的size,即归还的内存大小。具体方法如下:
public void deallocate(ByteBuffer buffer, int size) {
lock.lock();
try {
//如果申请的批次大小和默认大小一致,且大小正好等于buffer的容量,则直接清空buffer,然后把这个buffer放回内存池
//TODO 内存池只能回收和默认批次大小一致的内存,不一致的只能等待GC进行回收
if (size == this.poolableSize && size == buffer.capacity()) {
buffer.clear();
this.free.add(buffer);
} else {
//否则,可用内存增加归还内存大小
this.availableMemory += size;
}
//归还内存后,取出等待队列中的第一个Condition对象,然后唤醒等待内存释放的线程
Condition moreMem = this.waiters.peekFirst();
if (moreMem != null)
moreMem.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
1.加锁
lock.lock();
2.如果归还的内存大小正好等于默认的批次大小16k,且buffer的容量正好也为16K,则直接将buffer清空,然后将其放回内存池队列中。
if (size == this.poolableSize && size == buffer.capacity()) {
buffer.clear();
this.free.add(buffer);
}
3.否则,直接在未申请内存上增加size大小的内存,此时不会将内存归还到内存池中。
else {
//否则,可用内存增加size大小
this.availableMemory += size;
}
注意:从上面的代码可以看出,只有释放的内存大小正好等于批次大小时,才会归还给内存池。否则,是直接增加了availableMemory未申请内存值,之前申请的内存无法复用,只能等待GC进行回收。
4.如果等待队列waiters不为空,则取出头部的Condition对象,然后唤醒。
Condition moreMem = this.waiters.peekFirst();
if (moreMem != null)
moreMem.signal();
总结:
-
内存池的设计是为了复用内存,减少GC,从而提高吞吐量。
-
批次的默认大小为16K,缓存的默认大小为32M。
-
缓存包含已用内存、内存池内存和未申请使用内存三部分。
-
只有归还的内存大小等于批次大小时,内存池才可以进行回收并复用;否则要等待GC进行回收。所以生产中要根据单条消息的大小调整批次大小(由参数batch.size设置)。


