热门标签
热门文章
- 1Python实现的一个简单的GAN(生成对抗网络)例子
- 2异地远程访问本地SQL Server数据库【无公网IP内网穿透】_异地装了一台服务器,如何看是否可以访问数据库
- 3minio对象存储
- 4机器学习毕设题目有哪些_毕业后,我才知道计算机毕设该这样做
- 5微信小程序引入echarts折线图在ios真机上无法上下滑动的问题_echarts图表ios上滑动不了怎么解决
- 6charles对iOS手机的https进行抓包(图文教程)_ios charles
- 7入门javascript_现代javascript代理入门
- 8使用maven创建Flink项目_mvn创建flink项目
- 9vs 2022 如何拉取gitlab项目_vs2022 gitlab
- 10基于Python的云南旅游景点分析_python旅游景点预测
当前位置: article > 正文
鸢尾花数据集分类-随机森林_使用随机森林对鸢尾花数据集进行分类python代码
作者:笔触狂放9 | 2024-05-03 08:59:03
赞
踩
使用随机森林对鸢尾花数据集进行分类python代码
随机森林
鸢尾花数据集分类-决策树
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42567027/article/details/107487428
Bagging + 决策树 = 随机森林
Bagging
Bagging(套袋法):
- 从原始样本集中使用Bootstraping方法随机抽取n个训练样本,共进行k轮抽取,得到k个训练集。(k个训练集之间相互独立,元素可以有重复)
- 针对k个训练集,训练k个模型
- 分类问题:由投票表决产生分类结果;回归问题:由k个模型预测结果的均值作为最后预测结果。
数据集
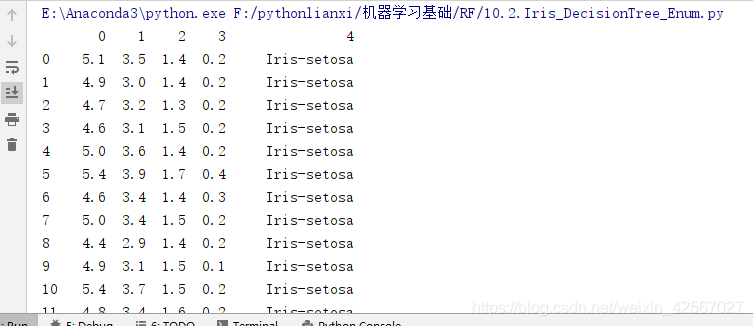
代码
// An highlighted block
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
# 'sepal length', 'sepal width', 'petal length', 'petal width'
iris_feature = u'花萼长度', u'花萼宽度', u'花瓣长度', u'花瓣宽度'
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 字体颜色:黑体 FangSong/KaiTi
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = [u'SimHei']
mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
'''加载数据'''
data = pd.read_csv('F:\pythonlianxi\shuju\iris.data', header=None)
#样本集,标签集
x_prime = data[range(4)]
y = pd.Categorical(data[4]).codes
x = x_prime.iloc[:, 2:4]
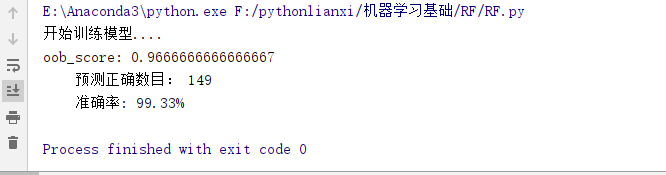
print('开始训练模型....')
'''训练随机森林'''
# 200棵树,深度为3
clf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=200, criterion='entropy', max_depth=10)
clf.fit(x, y.ravel())
#print(clf.oob_score_,)
#测试数据
#y_test_hat = clf.predict(x_test) # 测试数据
#print(y_test_hat)
# 横纵坐标的采样值
N, M = 50, 50
x1_min, x2_min = x.min()
x1_max, x2_max = x.max()
t1 = np.linspace(x1_min, x1_max, N)
t2 = np.linspace(x2_min, x2_max, M)
# 生成网格采样点
x1, x2 = np.meshgrid(t1, t2)
# 测试点
x_show = np.stack((x1.flat, x2.flat), axis=1)
#图形添加颜色
cm_light = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['#A0FFA0', '#FFA0A0', '#A0A0FF'])
cm_dark = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['g', 'r', 'b'])
# 预测值
y_show_hat = clf.predict(x_show)
# 使之与输入的形状相同
y_show_hat = y_show_hat.reshape(x1.shape)
'''绘图'''
plt.figure(facecolor='w')
plt.pcolormesh(x1, x2, y_show_hat, cmap=cm_light) # 预测值的显示
#第两列,第三列的特征
plt.scatter(x[2], x[3], c=y.ravel(), edgecolors='k', s=40, cmap=cm_dark)
plt.xlabel(iris_feature[2], fontsize=15)
plt.ylabel(iris_feature[3], fontsize=15)
plt.xlim(x1_min, x1_max)
plt.ylim(x2_min, x2_max)
plt.grid(True)
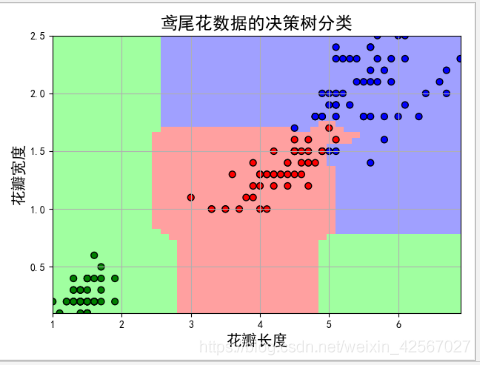
plt.title(u'鸢尾花数据的决策树分类', fontsize=17)
plt.show()
'''测试样本'''
# 训练集上的预测结果
y_hat = clf.predict(x)
y = y.reshape(-1)
c = np.count_nonzero(y_hat == y) # 统计预测正确的个数
print('\t预测正确数目:', c)
print('\t准确率: %.2f%%' % (100 * float(c) / float(len(y))))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
实验分析
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/笔触狂放9/article/detail/528795
推荐阅读
相关标签


