热门标签
热门文章
- 1MPU6050/ICM20608寄存器笔记_icm20608和mpu6050
- 2基于YOLOv5算法实现人数统计和人脸识别并部署于开发板rk3588_yolo人脸识别
- 3【Java】如何通过一次请求获取多张图片_get请求获取多个图片流的时候,怎么把图片一个一个弄出来
- 4Android调用浏览器打开指定页面
- 5【基于Pytorch的手写汉字识别】_pytorch 手写汉字识别
- 6Python filter函数完全指南_python list filter
- 7HarmonyOS Codelab 优秀样例——购物应用,体验一次开发多端部署魅力_鸿蒙harmony简单应用-商品列表
- 8Ceph对可用存储空间的校验与控制_mon_osd_full_ratio
- 92021年超详细的Java面试题及答案整理 - 基础入门篇
- 10vscode运行shell脚本的详细配置_vscode怎么运行shell script
当前位置: article > 正文
手动模拟一个很简单的web server服务器实现_websocketserver模拟器
作者:2023面试高手 | 2024-03-10 02:23:27
赞
踩
websocketserver模拟器
新建一个普通的Java Project项目
创建三个普通类

类的作用
- HttpServer :使用 java.net.ServerSocket 监听客户端的请求,与客户端(浏览器)建立连接,获取 java.net.Socket对象以及java.io.InputStream 输入流对象和 java.io.OutputStream 输出流对象。
- Request 将客户端请求的数据封装成一个request对象。
- Response将服务器端响应的数据封装成一个Response对象。
代码
HttpServer的核心代码
- 创建一个SeverSokcet对象监听到指定端口上
int port = 8080;
try {
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port, 1, InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"));
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 使用serverSocket监听客户端(浏览器)的连接请求,监听到连接后生成Socket对象
Socket socket = null;
InputStream input = null;
OutputStream output = null;
try {
socket = serverSocket.accept();
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
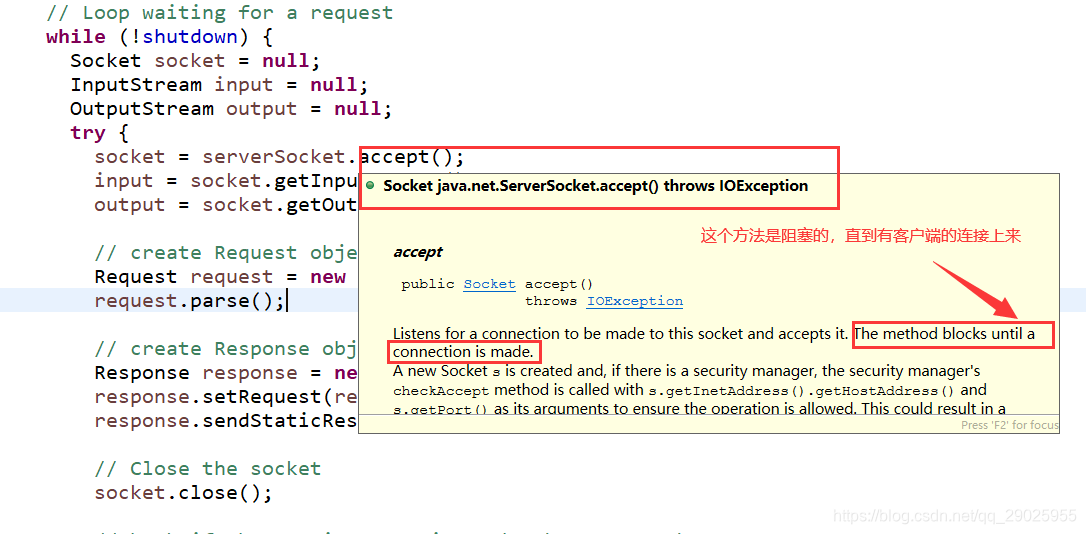
- 根据连接的Socket对象获取输入input/输出output流对象,将输入流InputStream对象传递给Request对象,将输入流OutputStream对象传递给Response对象。
try { socket = serverSocket.accept(); input = socket.getInputStream(); output = socket.getOutputStream(); // create Request object and parse Request request = new Request(input); request.parse(); // create Response object Response response = new Response(output); response.setRequest(request); response.sendStaticResource(); // Close the socket socket.close(); //check if the previous URI is a shutdown command shutdown = request.getUri().equals(SHUTDOWN_COMMAND); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
HttpServer的完整代码
package ex01.pyrmont; import java.net.Socket; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.File; public class HttpServer { /** WEB_ROOT is the directory where our HTML and other files reside. * For this package, WEB_ROOT is the "webroot" directory under the working * directory. * The working directory is the location in the file system * from where the java command was invoked. */ public static final String WEB_ROOT = System.getProperty("user.dir") + File.separator + "webroot"; // shutdown command private static final String SHUTDOWN_COMMAND = "/SHUTDOWN"; // the shutdown command received private boolean shutdown = false; public static void main(String[] args) { HttpServer server = new HttpServer(); server.await(); } public void await() { ServerSocket serverSocket = null; int port = 8080; try { serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port, 1, InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1")); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.exit(1); } // Loop waiting for a request while (!shutdown) { Socket socket = null; InputStream input = null; OutputStream output = null; try { socket = serverSocket.accept(); input = socket.getInputStream(); output = socket.getOutputStream(); // create Request object and parse Request request = new Request(input); request.parse(); // create Response object Response response = new Response(output); response.setRequest(request); response.sendStaticResource(); // Close the socket socket.close(); //check if the previous URI is a shutdown command shutdown = request.getUri().equals(SHUTDOWN_COMMAND); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); continue; } } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
Request的核心代码:将输入流中的数据读取/解析出来
public void parse() { // Read a set of characters from the socket StringBuffer request = new StringBuffer(2048); int i; byte[] buffer = new byte[2048]; try { i = input.read(buffer); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); i = -1; } for (int j=0; j<i; j++) { request.append((char) buffer[j]); } System.out.print(request.toString()); uri = parseUri(request.toString()); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
举例:在浏览器中输入:http://localhost:8080/test.html,上面的代码System.out.print(request.toString());就会打印出来如下请求信息:
GET /test.html HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:8080
Connection: keep-alive
Cache-Control: max-age=0
sec-ch-ua: "Chromium";v="92", " Not A;Brand";v="99", "Google Chrome";v="92"
sec-ch-ua-mobile: ?0
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.107 Safari/537.36
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.9
Sec-Fetch-Site: none
Sec-Fetch-Mode: navigate
Sec-Fetch-User: ?1
Sec-Fetch-Dest: document
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
以上就是request解析出来的请求信息,可以看到包括请求的地址(资源文件)/test.html 、请求头信息等。
Request的完整代码
package ex01.pyrmont; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class Request { private InputStream input; private String uri; public Request(InputStream input) { this.input = input; } public void parse() { // Read a set of characters from the socket StringBuffer request = new StringBuffer(2048); int i; byte[] buffer = new byte[2048]; try { i = input.read(buffer); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); i = -1; } for (int j=0; j<i; j++) { request.append((char) buffer[j]); } System.out.print(request.toString()); uri = parseUri(request.toString()); } private String parseUri(String requestString) { int index1, index2; index1 = requestString.indexOf(' '); if (index1 != -1) { index2 = requestString.indexOf(' ', index1 + 1); if (index2 > index1) return requestString.substring(index1 + 1, index2); } return null; } public String getUri() { return uri; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
Response核心代码:封装响应信息,如响应头信息(协议名称http,Content-Type:Text/html等)以及读取请求的文件/资源,如test.html文件,然后放到输出流OutputStream里面,最后在返回给请求的客户端。请求的文件/资源会提前放在服务器的指定目录下,这里是webroot目录

public void sendStaticResource() throws IOException { byte[] bytes = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE]; FileInputStream fis = null; try { File file = new File(HttpServer.WEB_ROOT, request.getUri()); if (file.exists()) { // String responseHeader = "HTTP/1.1 200 success\r\n" + "Content-Type: text/html\r\n" + "\r\n"; String responseHeader = "HTTP/1.1 200 success\r\n" + "\r\n"; output.write(responseHeader.getBytes()); fis = new FileInputStream(file); int ch = fis.read(bytes, 0, BUFFER_SIZE); while (ch != -1) { output.write(bytes, 0, ch); ch = fis.read(bytes, 0, BUFFER_SIZE); } } else { // file not found String errorMessage = "HTTP/1.1 404 File Not Found\r\n" + "Content-Type: text/html\r\n" + "Content-Length: 26\r\n" + "\r\n" + "<h1>File Not Found555</h1>"; output.write(errorMessage.getBytes()); } } catch (Exception e) { // thrown if cannot instantiate a File object System.out.println(e.toString()); } finally { if (fis != null) fis.close(); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
Response完整代码
package ex01.pyrmont; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.File; /* HTTP Response = Status-Line *(( general-header | response-header | entity-header ) CRLF) CRLF [ message-body ] Status-Line = HTTP-Version SP Status-Code SP Reason-Phrase CRLF */ public class Response { private static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 1024; Request request; OutputStream output; public Response(OutputStream output) { this.output = output; } public void setRequest(Request request) { this.request = request; } public void sendStaticResource() throws IOException { byte[] bytes = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE]; FileInputStream fis = null; try { File file = new File(HttpServer.WEB_ROOT, request.getUri()); if (file.exists()) { // String responseHeader = "HTTP/1.1 200 success\r\n" + "Content-Type: text/html\r\n" + "\r\n"; String responseHeader = "HTTP/1.1 200 success\r\n" + "\r\n"; output.write(responseHeader.getBytes()); fis = new FileInputStream(file); int ch = fis.read(bytes, 0, BUFFER_SIZE); while (ch != -1) { output.write(bytes, 0, ch); ch = fis.read(bytes, 0, BUFFER_SIZE); } } else { // file not found String errorMessage = "HTTP/1.1 404 File Not Found\r\n" + "Content-Type: text/html\r\n" + "Content-Length: 26\r\n" + "\r\n" + "<h1>File Not Found555</h1>"; output.write(errorMessage.getBytes()); } } catch (Exception e) { // thrown if cannot instantiate a File object System.out.println(e.toString()); } finally { if (fis != null) fis.close(); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
测试
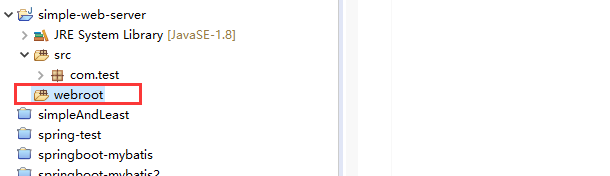
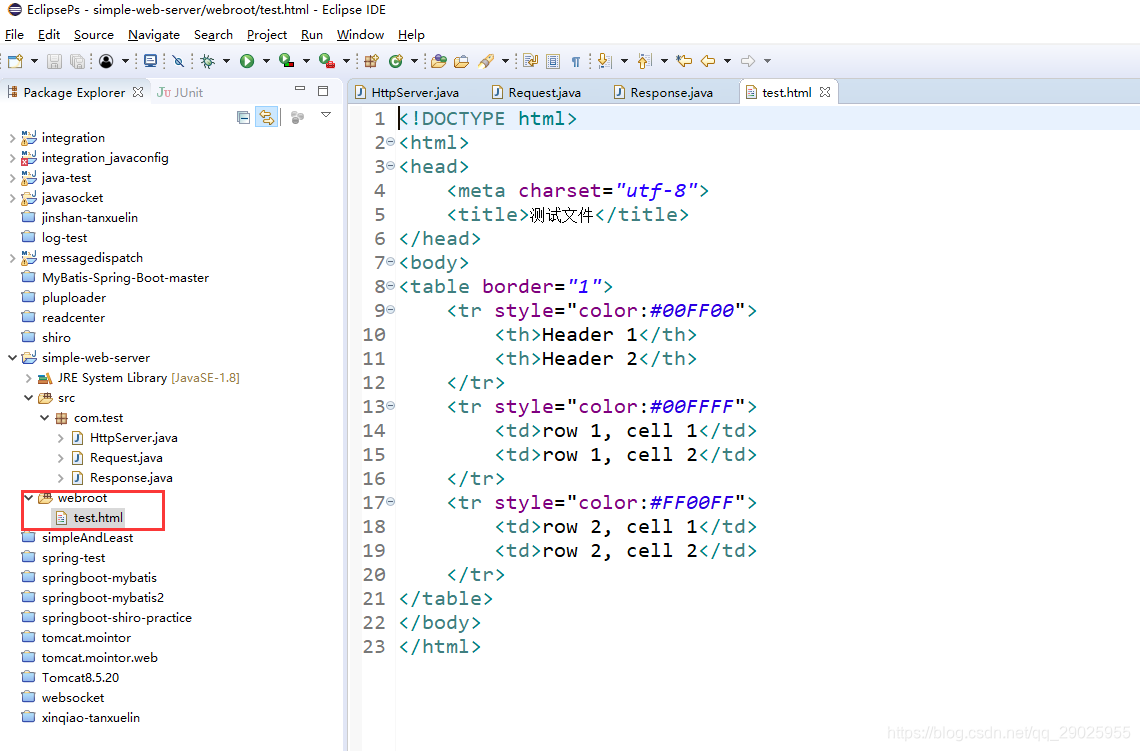
随便找一个test.html文件放到工程(服务器)指定的目录里,根据上面的代码可知,指定的目录为webroot.
注:这里的test.html文件就相当于是服务器的一个资源,远程的客户端可以请求该资源。
启动HttpServer类,运行main方法
浏览器中输入请求地址http://localhost:8080/test.html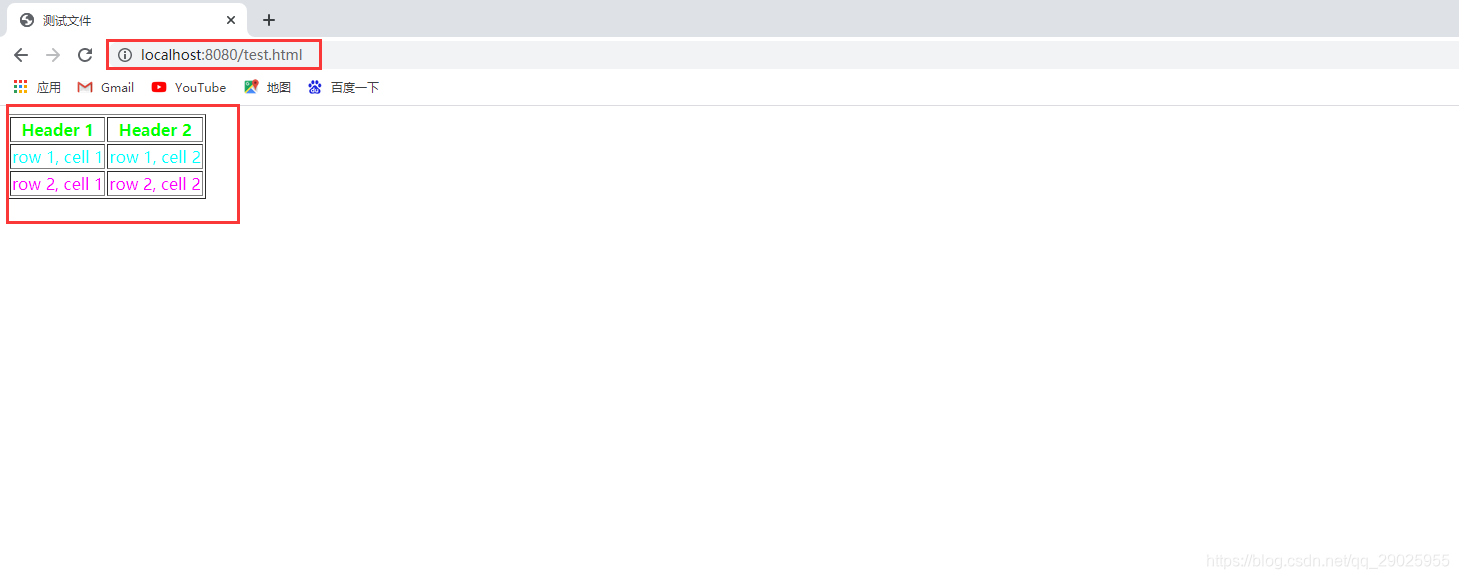
结果
截图显示浏览器获取的了服务器端的资源文件test.html,完成了模拟一个简单的web server。
参考 : 《how tomcat works》
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/2023面试高手/article/detail/216991
推荐阅读
相关标签



