- 1数据可视化组件库
- 2ACL—访问控制列表_acl访问控制列表
- 3[开题报告]springboot化妆品商城网站iox21计算机毕业设计_化妆品商城的设计与实现开题报告
- 4ChatGLM-6B 部署与 P-Tuning 微调实战_2e-2是多少啊
- 5WIN11所有的文件重不能重命名_win11文件夹不能重命名
- 6c语言struct的作用和用法,c语言struct用法详解
- 7000001 oracle 报错,MHA中的报错问题!
- 8python语音库_python音频库dejavu原理浅析
- 9【EFK】基于K8S构建EFK+logstash+kafka日志平台
- 10python 海龟 速度_如何在每次运行代码时为海龟设置一个随机速度?
数据分析——R语言中ggplot2用法(1)_ggplot2导入数据
赞
踩
备忘录地址(用来查询一些参数)
https://www.maths.usyd.edu.au/u/UG/SM/STAT3022/r/current/Misc/data-visualization-2.1.pdf
R语言软件参数 R3.6.0
安装包、导入包
install.package('ggplot')
library(ggplot)
- 1
- 2
首先加载数据集
这里用的是示例数据,R自带的一个包提供的数据集。
dslabs包是R中的一个数据科学工具包,它提供了一系列数据集和函数,用于帮助研究人员探索新的数据科学概念,进行数据分析和机器学习模型构建。
library(dslabs)
data(murders)
- 1
- 2
定义ggplot对象
ggplot初始化图形
管道符(|>, %>%, %>%, %$% 和%<>%),|>是R4.1版本开始的自带的管道符,将左侧的输出结果传递给右侧命令,因为这里用的是3.6版本的所以就用%>%管道符,测试发现|>不能被识别。
ggplot(data = murders)##或者murders |> ggplot()
- 1
也可以把ggplot图赋值给一个对象p
p <- ggplot(data = murders)
- 1
然后你就会得到一个初始化的白板,后续的步骤就是在这个白板上添加组件,组件有三个主要要素:数据、图、映射。数据是要分析的数据,图是选用什么图,比如直方图、散点图,映射指的是x轴和y轴是哪个变量。

在ggplot上添加图层
方式一:一般形式DATA %>% ggplot() + LAYER 1 + LAYER 2 + … + LAYER N
murders %>% ggplot()+
geom_point(aes(x = population/10^6, y = total))#添加散点图,添加x轴population,y轴total
- 1
- 2
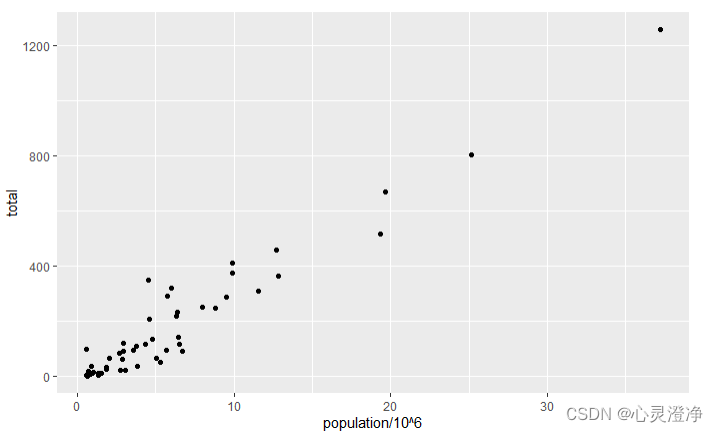
几何函数名称遵循以下模式:geom_X其中 X 是几何的名称,这里散点图是point,要用其他图的话可以去备忘录上的geoms上看。
方式二,在定义的对象p上叠加图层
p + geom_point(aes(x = population/10^6, y = total))#p是前面定义过的含有数据的初始图
- 1
继续添加图层
在散点图基础上添加一个文本组件
p + geom_point(aes(population/10^6, total)) +
geom_text(aes(population/10^6, total, label = abb))#Label = abb 指的是标签 (label) 的缩写
- 1
- 2
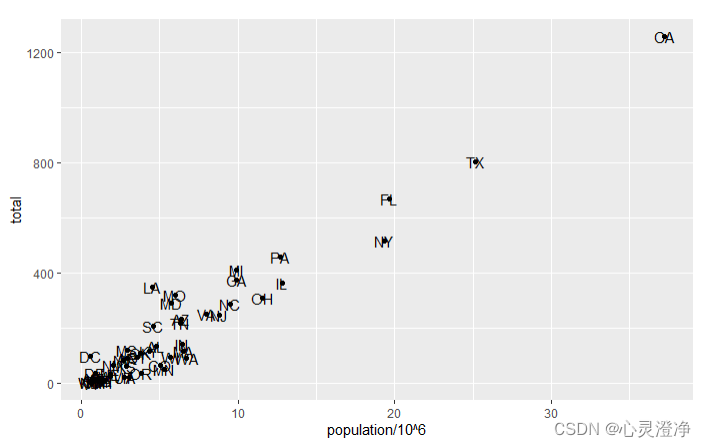
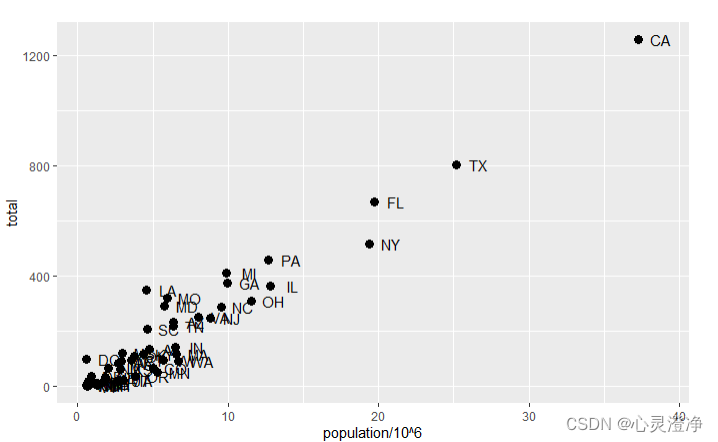
对文本组件进行参数调整
#size 控制点的大小, nudge_x 文本稍微向右或向左移动
p + geom_point(aes(population/10^6, total), size = 3) +
geom_text(aes(population/10^6, total, label = abb), nudge_x = 1.5)
- 1
- 2
- 3
可以看到文本向右移动了 ,点也变大了
全局与局部映射aes()
先查看下ggplot参数
args(ggplot)
- 1
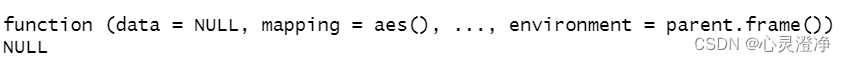
全局映射:在定义对象时将坐标映射定义
p <- murders %>% ggplot(aes(population/10^6, total, label = abb))
- 1
然后就可以直接使用了,不用在每个组件中定义x轴,y轴
p + geom_point(size = 3) +
geom_text(nudge_x = 1.5)
- 1
- 2
得到

在全局映射中进行局部映射
想要单独让某个组件有自己的坐标
p + geom_point(size = 3) +
geom_text(aes(x = 10, y = 800, label = "Hello there!"))
- 1
- 2
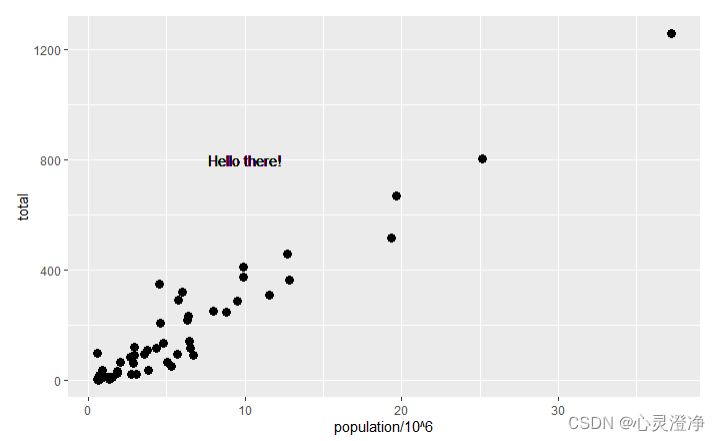
可以看到在(x=10,y=800)的坐标位置有个文本
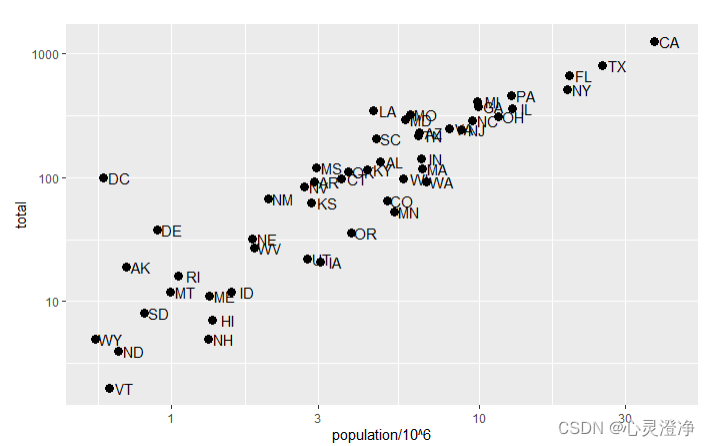
控制坐标轴刻度
scale_x_continuous函数可以用来在指定的坐标轴上对数据进行缩放。
p + geom_point(size = 3) +
geom_text(nudge_x = 0.05) +
scale_x_continuous(trans = "log10") +
scale_y_continuous(trans = "log10") #用于将坐标轴的连续数据变换为以10为底的对数尺度
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
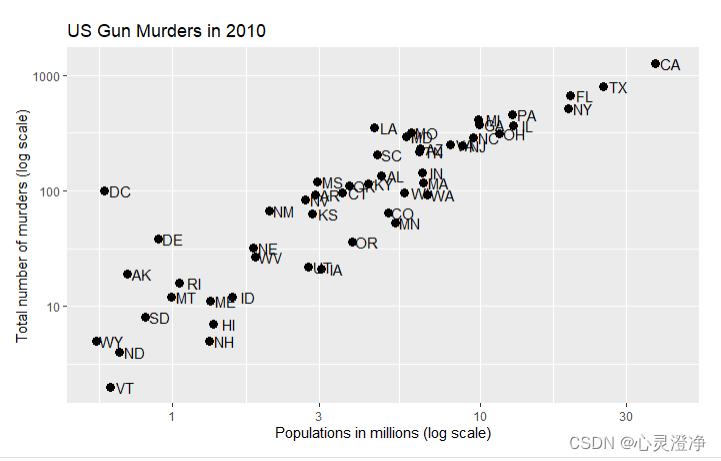
标签和标题
使用xlab,ylab和ggtitle
p + geom_point(size = 3) +
geom_text(nudge_x = 0.05) +
scale_x_log10() +
scale_y_log10() +
xlab("Populations in millions (log scale)") +
ylab("Total number of murders (log scale)") +
ggtitle("US Gun Murders in 2010")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
给类别添加颜色
p <- murders %>% ggplot(aes(population/10^6, total, label = abb)) +
geom_text(nudge_x = 0.05) +
scale_x_log10() +
scale_y_log10() +
xlab("Populations in millions (log scale)") +
ylab("Total number of murders (log scale)") +
ggtitle("US Gun Murders in 2010")
p + geom_point(size = 3, color ="green")#在散点图里添加color
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
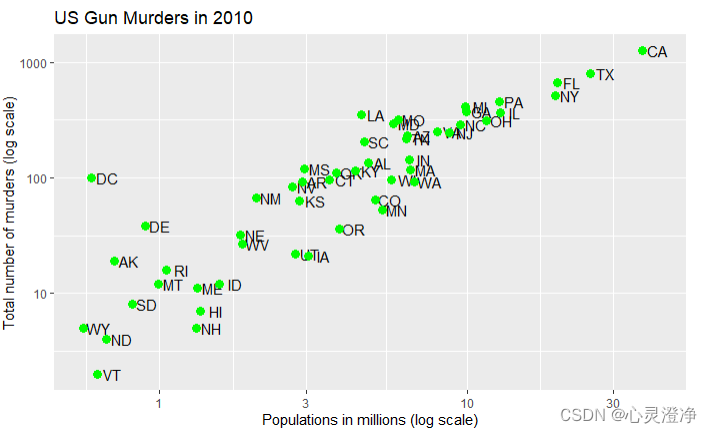
可以选择按什么分类颜色,比如这个数据里有的region,使用aes
p + geom_point(aes(col=region))
- 1

上面的图例可以通过show.legend = FALSE删除
添加一条直线
这里代表全国的平均谋杀率 y=rx
geom_abline是画线的,log10是因为之前坐标轴是转换到log10标准的
geom_abline(intercept, slope, linetype, color, size)
参数说明:intercept:y轴的截距 slope:斜率linetype:线条样式color:线条颜色size:线条宽度
pull()函数是R语言中用于提取对象的函数。它的作用是从已有的数据框、向量或列表中提取特定行或列的数据。
#计算斜率
r <- murders %>%
summarize(rate = sum(total) / sum(population) * 10^6) %>%
pull(rate)
p <- p + geom_abline(intercept = log10(r), lty = 2, color = "darkgrey") +
geom_point(aes(col=region), size = 3)
p
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
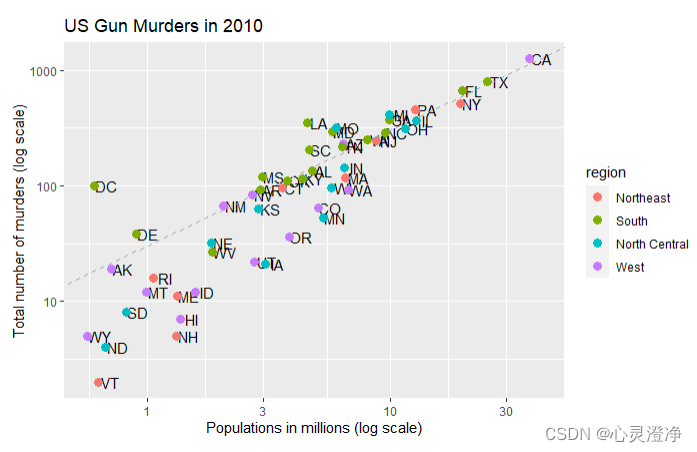
附加软件包: ggthemes,ggrepel
ggthemes是R语言中的一个用于设置ggplot2图表主题的包。
Ggrepel旨在帮助解决图中文本标签重叠的问题。
ds_theme_set()是dslabs包中的一个函数,它可以自动设置默认主题。
install.packages('ggthemes')
library(ggthemes)
p + theme_economist()
- 1
- 2
- 3
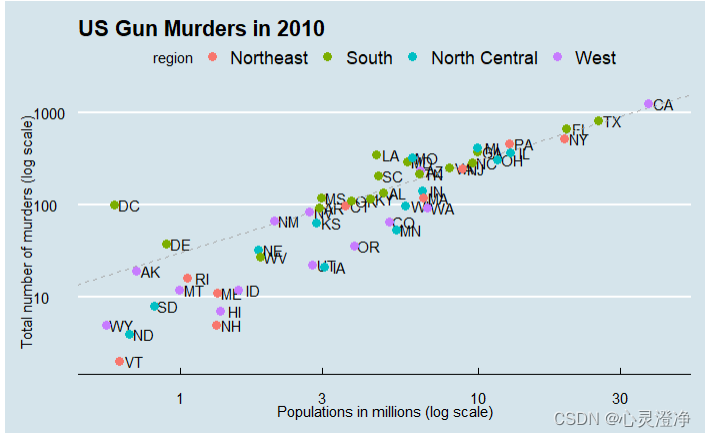
完整的一个ggplot图代码
library(ggthemes) library(ggrepel) r <- murders %>% summarize(rate = sum(total) / sum(population) * 10^6) %>% pull(rate) murders %>% ggplot(aes(population/10^6, total, label = abb)) + geom_abline(intercept = log10(r), lty = 2, color = "darkgrey") + geom_point(aes(col=region), size = 3) + geom_text_repel() + scale_x_log10() + scale_y_log10() + xlab("Populations in millions (log scale)") + ylab("Total number of murders (log scale)") + ggtitle("US Gun Murders in 2010") + scale_color_discrete(name = "Region") + theme_economist()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
描述分布
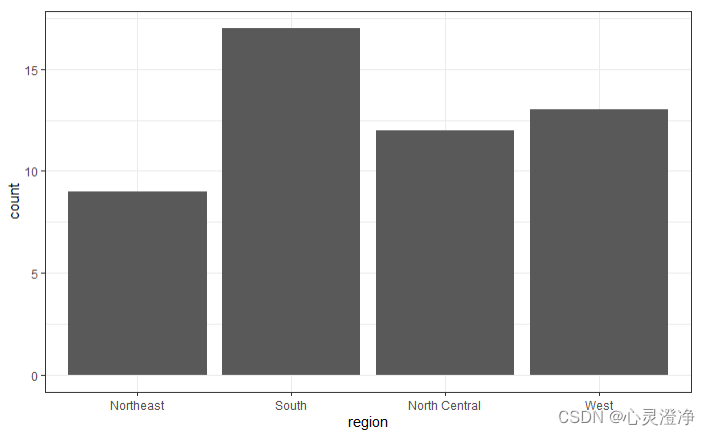
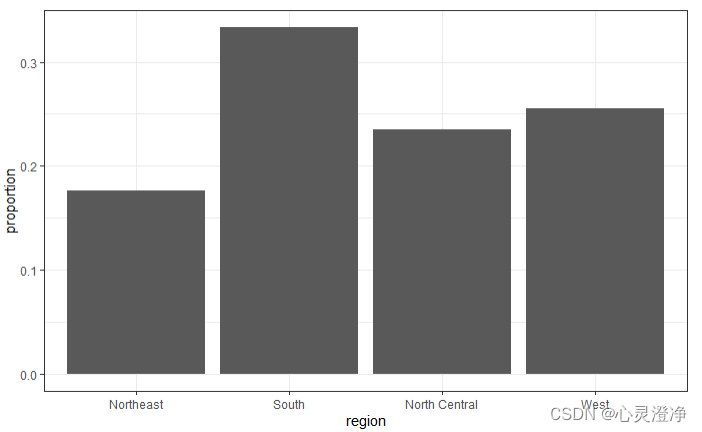
条形图
murders %>% ggplot(aes(region)) + geom_bar()
- 1
不希望geom_bar计数,而是只绘制一个由比例变量提供高度的条形图。为此,提供x(类别)和y(值),并使用stat=“identity”选项。
先计算region每一类的数量然后传入下一行代码中
tab <- murders %>%
count(region) %>%
mutate(proportion = n/sum(n))
tab %>% ggplot(aes(region, proportion)) + geom_bar(stat = "identity")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
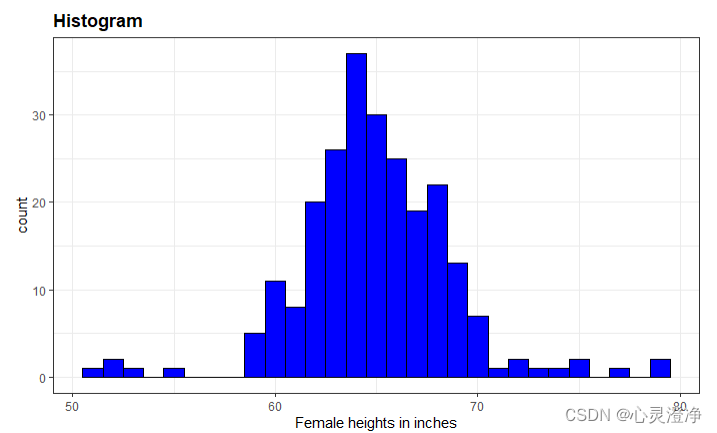
直方图
用的是范例数据里的heights的数据,geom_histogram()函数,添加了标题,x轴标签
library(dslabs)
data(heights)
x <- heights$height[heights$sex=="Male"]
heights %>%
filter(sex == "Female") %>%
ggplot(aes(height)) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = 1, fill = "blue", col = "black") +
xlab("Female heights in inches") +
ggtitle("Histogram")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
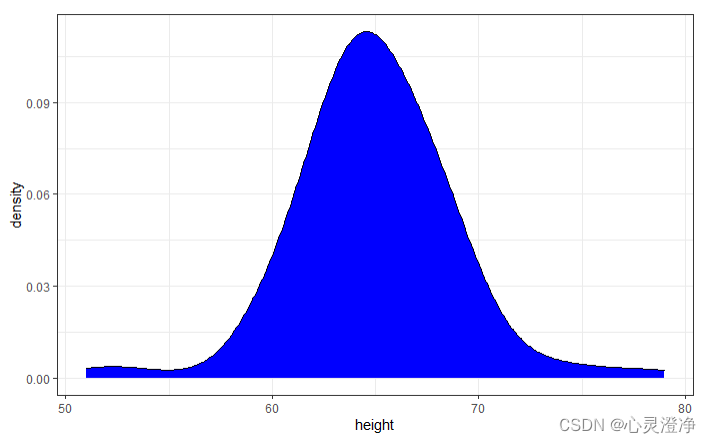
密度图
adjust参数控制密度图的平滑度,取值范围为0~1,默认值为1,值越大,则平滑度越高。
heights %>%
filter(sex == "Female") %>%
ggplot(aes(height)) +
geom_density(fill="blue",adjust = 2)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
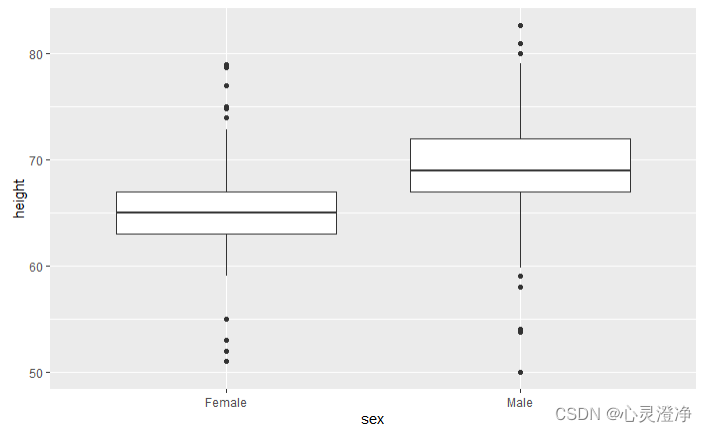
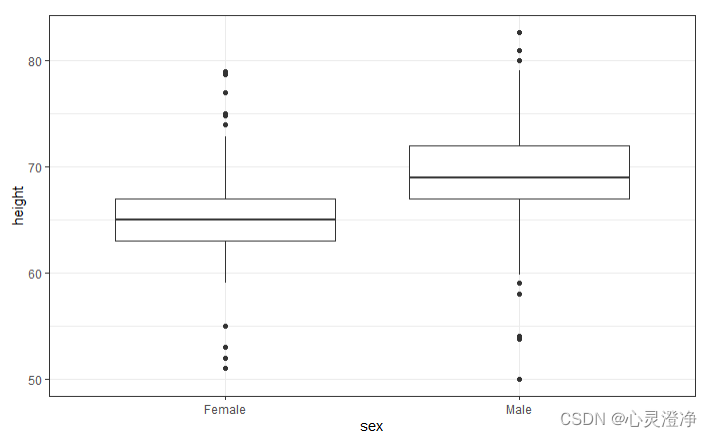
箱线图
heights %>%
ggplot(aes(sex,height)) +
geom_boxplot()
- 1
- 2
- 3
使用qplot快速绘图
快速绘制一个向量值的直方图、两个向量值的散点图或使用分类向量和数值向量的箱线图
qplot(x, y, data, geom, color, fill, size, shape, alpha, etc.)
其中,x和y参数用于指定绘图变量,data参数指定数据集,geom参数用于指定绘图类型,color、fill、size、shape、alpha等参数则可用于控制图表的外观。
两个向量的值绘制散点图
data(murders)
x <- log10(murders$population)
y <- murders$total
qplot(x, y)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
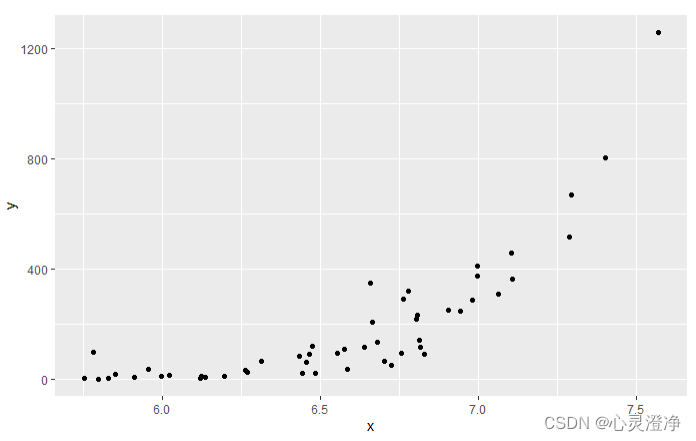
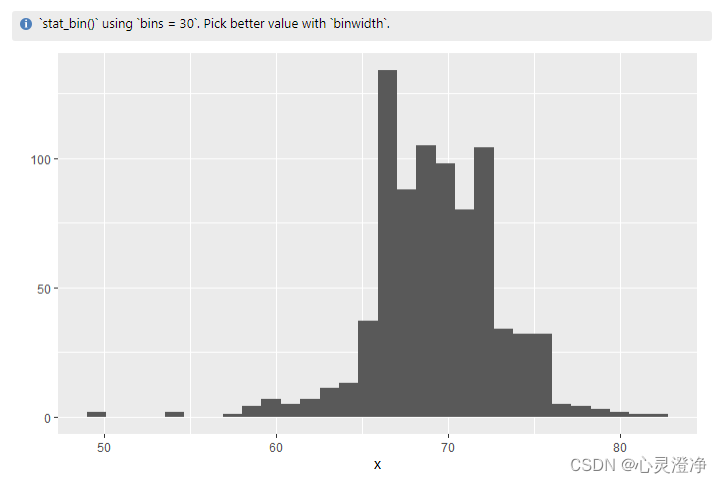
直方图:1个对象
x <- heights %>%
filter(sex=="Male") %>%
pull(height)
qplot(x)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
提供一个因子和一个数值向量画的图
heights %>% qplot(sex, height,data=.)
- 1
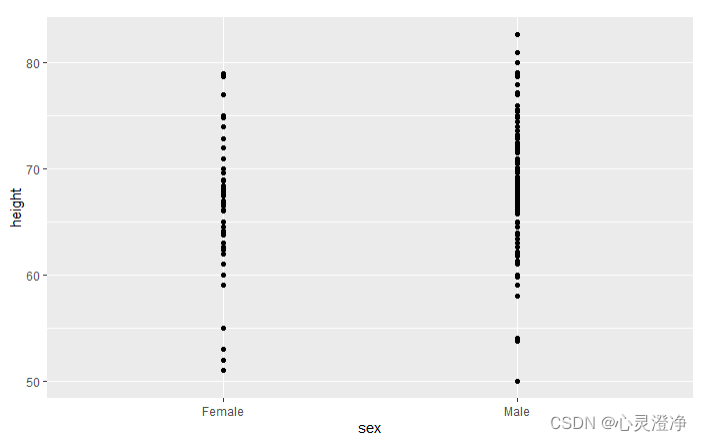
##箱线图
heights %>% qplot(sex, height, data = ., geom = "boxplot")
- 1