- 1selenium指定谷歌用户,报错:Message: unknown error: failed to write prefs file
- 2Android APK 省心安装 —— 眼睁睁地看着它完成一切_tap省心装怎么用
- 3面试算法-85-删除有序数组中的重复项 II
- 4CCF CSP 202209_csp 202209-5
- 5midjourney 初级使用说明
- 6cocos creator 音频播放setFinishCallback 有时候不回调_cocos creator cc.audioengine.setfinishcallback
- 7Rockchip Android13 AudioCodecs ES8316调试心得
- 8【机器学习|数学基础】Mathematics for Machine Learning系列之图论(8):割边、割集、割点_图割集
- 9arcgis不同shp文件的拼接_arcgis点和线怎么放在一个shp里
- 10Vue3响应式原理-computed_vue3 computed无效
[论文阅读笔记48]BLURB_domain-specific language model pretraining for bio
赞
踩
一,题目
Domain-Specific Language Model Pretraining for Biomedical Natural Language Processing
作者:YU GU, ROBERT TINN, HAO CHENG, MICHAEL LUCAS, NAOTO USUYAMA, XIAODONG LIU, TRISTAN NAUMANN, JIANFENG GAO, HOIFUNG POON
机构:Microsoft Research
年份:2021
二,研究背景
三,主要内容
Biomedical Language Understanding & Reasoning Benchmark (BLURB)
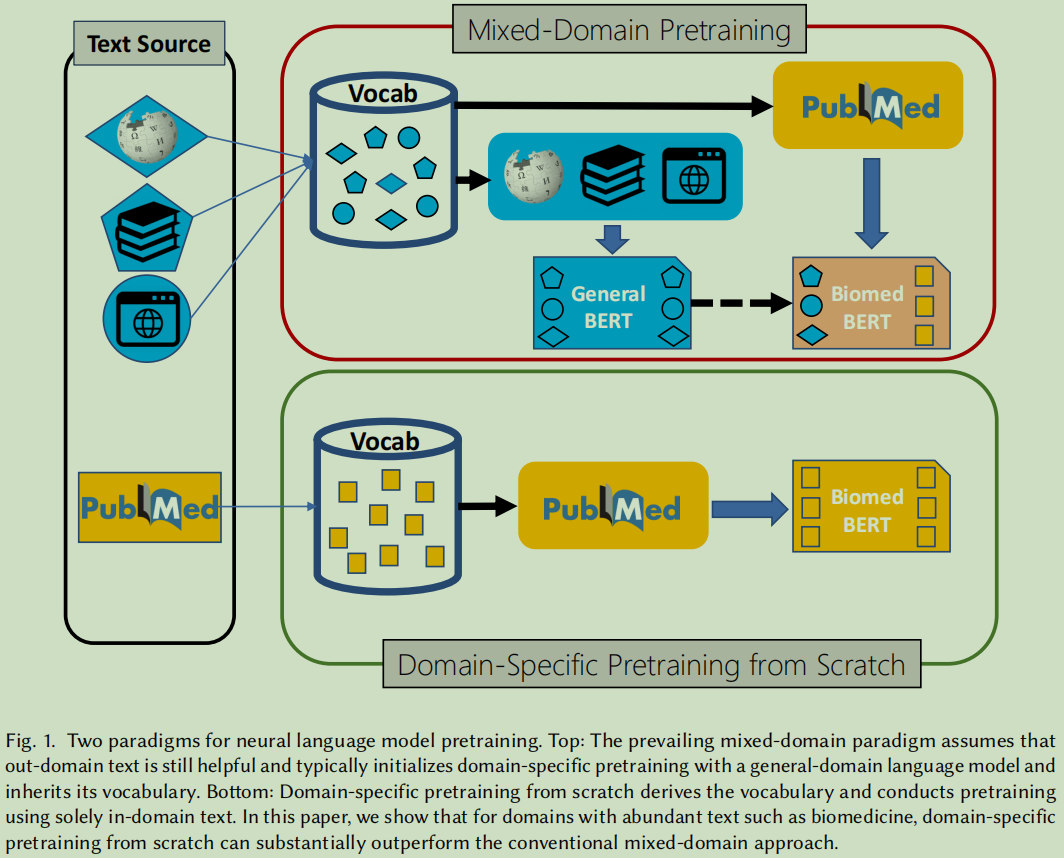
从头开始的特定领域预训练大大优于通用语言模型的持续预训练,从而证明了支持混合领域预训练的普遍假设并不总是适用的。
3.1 Language Model Pretraining
3.1.1 Vocabulary
Byte-Pair Encoding (BPE), WordPiece,
3.1.2 Model Architecture
transformer architectures – BERT
3.1.3 Self-Supervision
Masked Language Model (MLM)
Next Sentence Prediction (NSP)
3.1.4 Advanced Pretraining Techniques
WWM等基于预训练任务的各种变体与任务增加。
3.2 Biomedical Language Model Pretraining
使用PubMed文本的预训练可以在生物医学NLP任务中获得更好的性能
对于下游应用程序,从头开始预训练特定领域比采用混合领域预训练有更好的效果。
3.2.1 Mixed-Domain Pretraining
BioBERT基于标准的bert的初始化:Wikipedia,BookCorpus; 然后基于MLM与NSP任务,采用PubMed的摘要与PubMed论文全文训练;
BlueBERT使用PubMed文本与MIMIC-III 的临床记录来训练。
缺点: 词典还是通用语料的词典;词典代表不了目标生物医学领域;
SciBERT:它所以的训练都是从头开始的,包括词典,预训练所用的语料等等。
3.2.2 Domain-Specific Pretraining from Scratch
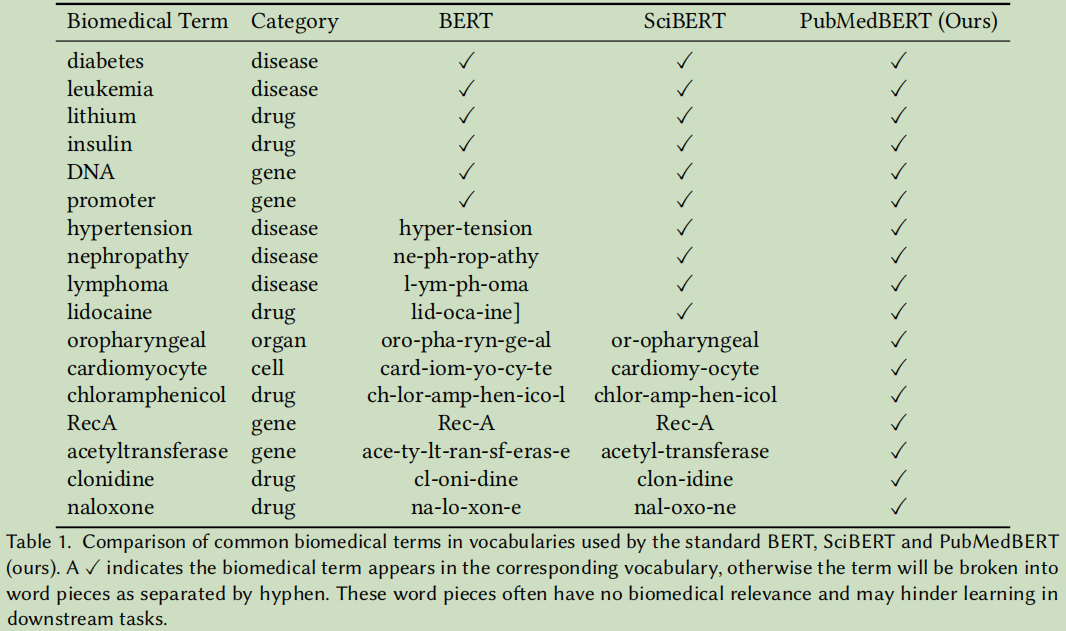
优点:拥有一个领域内的词汇表;
语言模型是纯粹是使用领域内的数据来训练的;
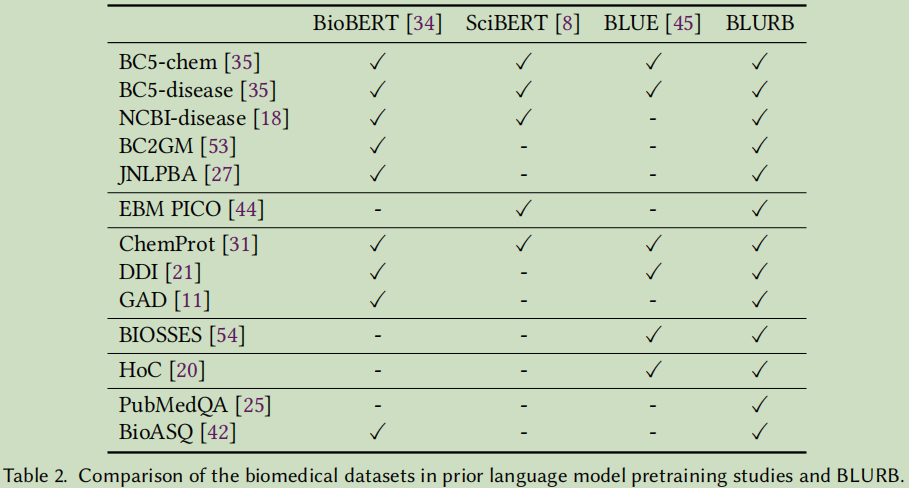
2.3 BLURB: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Biomedical NLP
相关研究对比
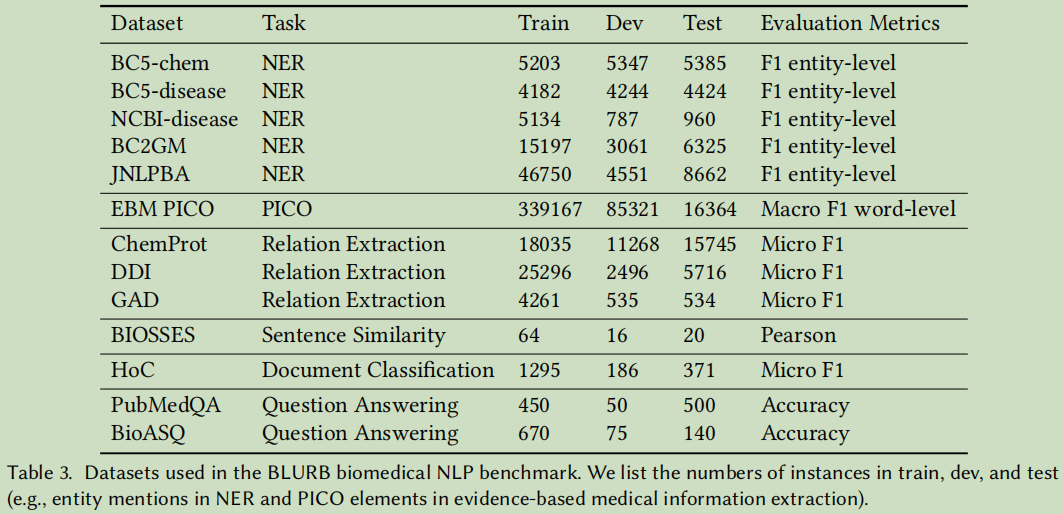
任务说明
2.4 Task-Specific Fine-Tuning
2.4.1 A General Architecture for Fine-Tuning Neural Language Models
Fine Tuning自然语言模型框架
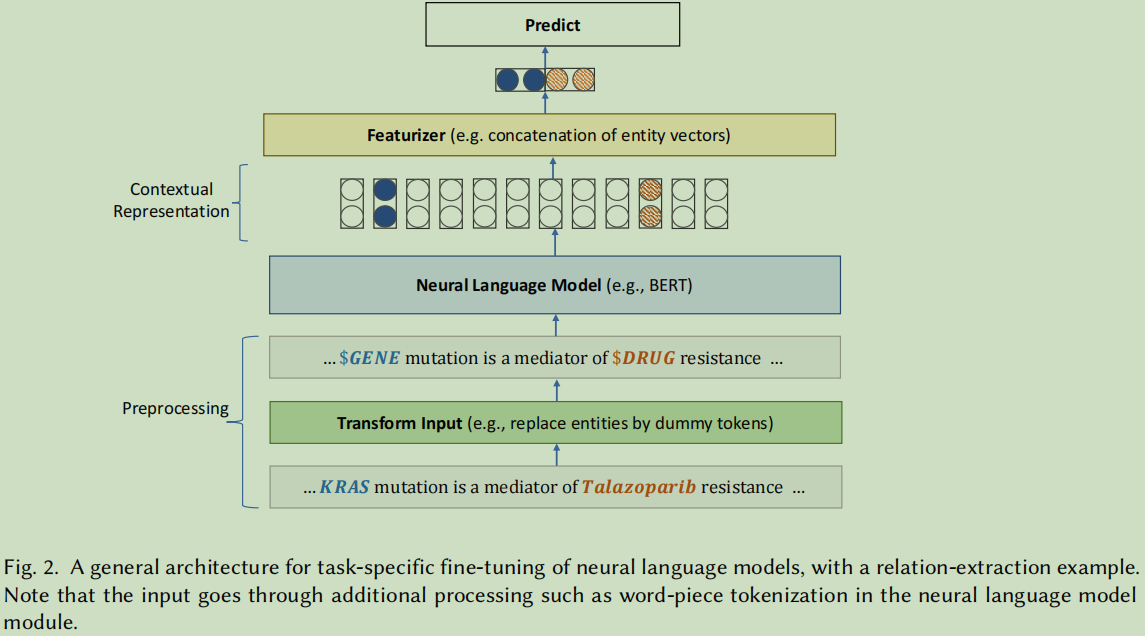
2.4.2 Task-Specific Problem Formulation and Modeling Choices
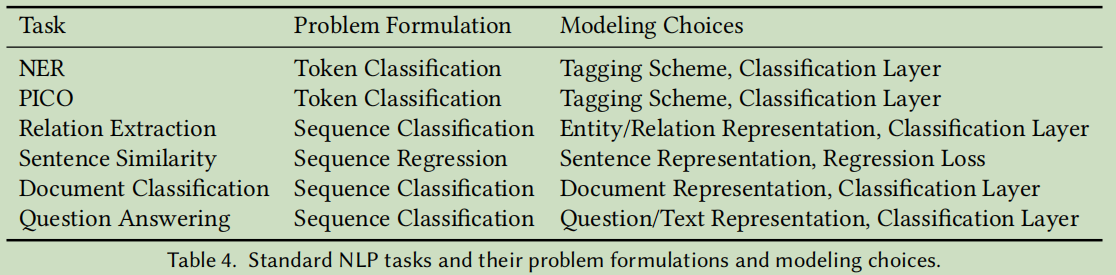
NER:
TransformInput: returns the input sequence as is.
Featurizer: returns the BERT encoding of a given token.
Tagging scheme: BIO*; BIOUL; IO.
Classification layer: linear layer*; LSTM; CRF
PICO:
TransformInput: returns the input sequence as is.
Featurizer: returns the BERT encoding of a given token.
Tagging scheme: BIO*; BIOUL; IO.
Classification layer: linear layer*; LSTM; CRF.
Relation Extraction:
TransformInput: entity (dummification*; start/end marker; original); relation ([CLS]*; original).
Featurizer: entity (dummy token; pooling); relation ([CLS] BERT encoding; concatenation of the mention BERT encoding).
Classification layer: linear layer; more sophisticated classifiers (e.g., MLP).
Sentence Similarity:
TransformInput: [CLS]
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/AllinToyou/article/detail/348169
Copyright © 2003-2013 www.wpsshop.cn 版权所有,并保留所有权利。


