热门标签
热门文章
- 1Vue+Spring Boot使用ElementUI el-upload实现视频带参数上传(前后端代码详解)_el-upload上传视频
- 2超哇塞的 SpringBoot性能优化长文_initializing default property filter 慢
- 3Uniapp App离线打包流程(Android、IOS待续)_uniapp 离线打包教程
- 4GPT模型应用:遥感云大数据在林业应用_遥感大模型 林业
- 5Word Embedding的通俗解释_word embedding 怎么生成的
- 6【Linux】Linux C 编程
- 7自己实现C语言strcpy函数_用自己的代码实现strcpy功能
- 8Springboot短信验证码(无需企业商户认证)_阿里云短信验证码需要企业认证吗
- 9(提供数据集下载)基于大语言模型LangChain与ChatGLM3-6B本地知识库调优:数据集优化、参数调整、Prompt提示词优化实战_知识匹配分数阈值
- 10无人机编队算法(Target-point formation control)_无人机编队控制
当前位置: article > 正文
Yolov5/Yolov7加入Yolov8 c2f模块,涨点
作者:AllinToyou | 2024-04-04 11:24:52
赞
踩
c2f模块
1.Yolov8简介
Ultralytics YOLOv8 是由 Ultralytics 开发的一个前沿的 SOTA 模型。它在以前成功的 YOLO 版本基础上,引入了新的功能和改进,进一步提升了其性能和灵活性。YOLOv8 基于快速、准确和易于使用的设计理念,使其成为广泛的目标检测、图像分割和图像分类任务的绝佳选择。
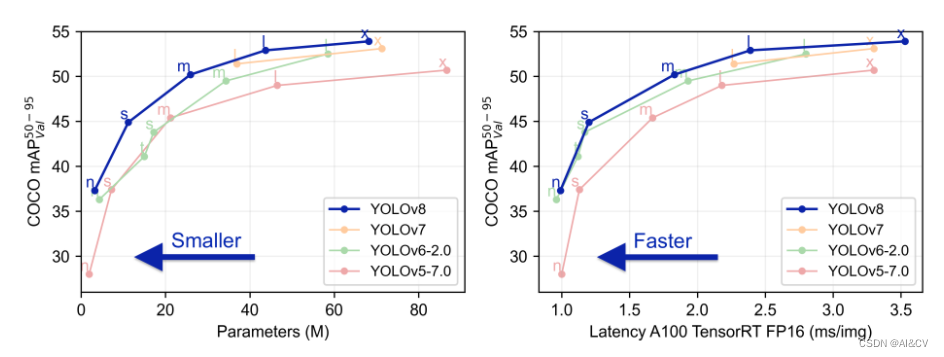
下表为官方在 COCO Val 2017 数据集上测试的 mAP、参数量和 FLOPs 结果。可以看出 YOLOv8 相比 YOLOv5 精度提升非常多,但是 N/S/M 模型相应的参数量和 FLOPs 都增加了不少;
| 模型 | 尺寸 (像素) | mAPval 50-95 | 推理速度 CPU ONNX (ms) | 推理速度 A100 TensorRT (ms) | 参数量 (M) | FLOPs (B) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n | 640 | 37.3 | 80.4 | 0.99 | 3.2 | 8.7 |
| YOLOv8s | 640 | 44.9 | 128.4 | 1.20 | 11.2 | 28.6 |
| YOLOv8m | 640 | 50.2 | 234.7 | 1.83 | 25.9 | 78.9 |
| YOLOv8l | 640 | 52.9 | 375.2 | 2.39 | 43.7 | 165.2 |
| YOLOv8x | 640 | 53.9 | 479.1 | 3.53 | 68.2 | 257.8 |
1.1 Yolov8优化点:
将 YOLOv5 的C3结构换成了梯度流更丰富的 C2f结构,并对不同尺度模型调整了不同的通道数
C3模块的结构图,然后再对比与C2f的具体的区别。针对C3模块,其主要是借助CSPNet提取分流的思想,同时结合残差结构的思想,设计了C3 Block,CSP主分支梯度模块为BottleNeck模块。同时堆叠的个数由参数n来进行控制,也就是说不同规模的模型,n的值是有变化的。
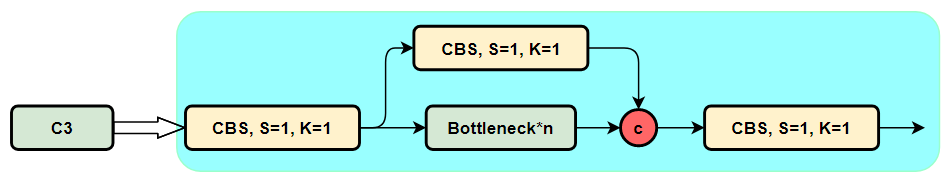
C3模块的Pytorch的实现如下:
- class C3(nn.Module):
- # CSP Bottleneck with 3 convolutions
- def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
- super().__init__()
- c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
- self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
- self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
- self.cv3 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1) # optional act=FReLU(c2)
- self.m = nn.Sequential(*(Bottleneck(c_, c_, shortcut, g, e=1.0) for _ in range(n)))
-
- def forward(self, x):
- return self.cv3(torch.cat((self.m(self.cv1(x)), self.cv2(x)), 1))
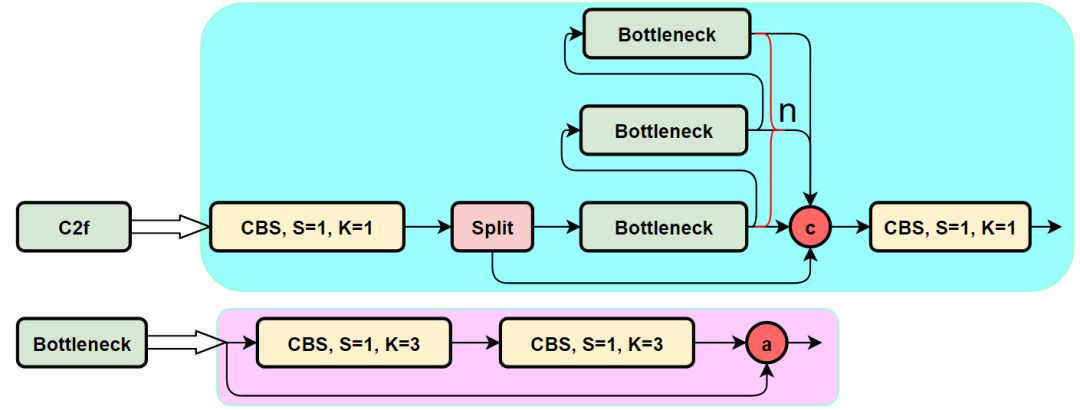
C2f模块的结构图如下:
C2f模块就是参考了C3模块以及ELAN的思想进行的设计,让YOLOv8可以在保证轻量化的同时获得更加丰富的梯度流信息。
- class C2f(nn.Module):
- # CSP Bottleneck with 2 convolutions
- def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
- super().__init__()
- self.c = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
- self.cv1 = Conv(c1, 2 * self.c, 1, 1)
- self.cv2 = Conv((2 + n) * self.c, c2, 1) # optional act=FReLU(c2)
- self.m = nn.ModuleList(Bottleneck(self.c, self.c, shortcut, g, k=((3, 3), (3, 3)), e=1.0) for _ in range(n))
-
- def forward(self, x):
- y = list(self.cv1(x).split((self.c, self.c), 1))
- y.extend(m(y[-1]) for m in self.m)
- return self.cv2(torch.cat(y, 1))
2.涨点技巧:Yolov5加入C2F提升小目标检测精度
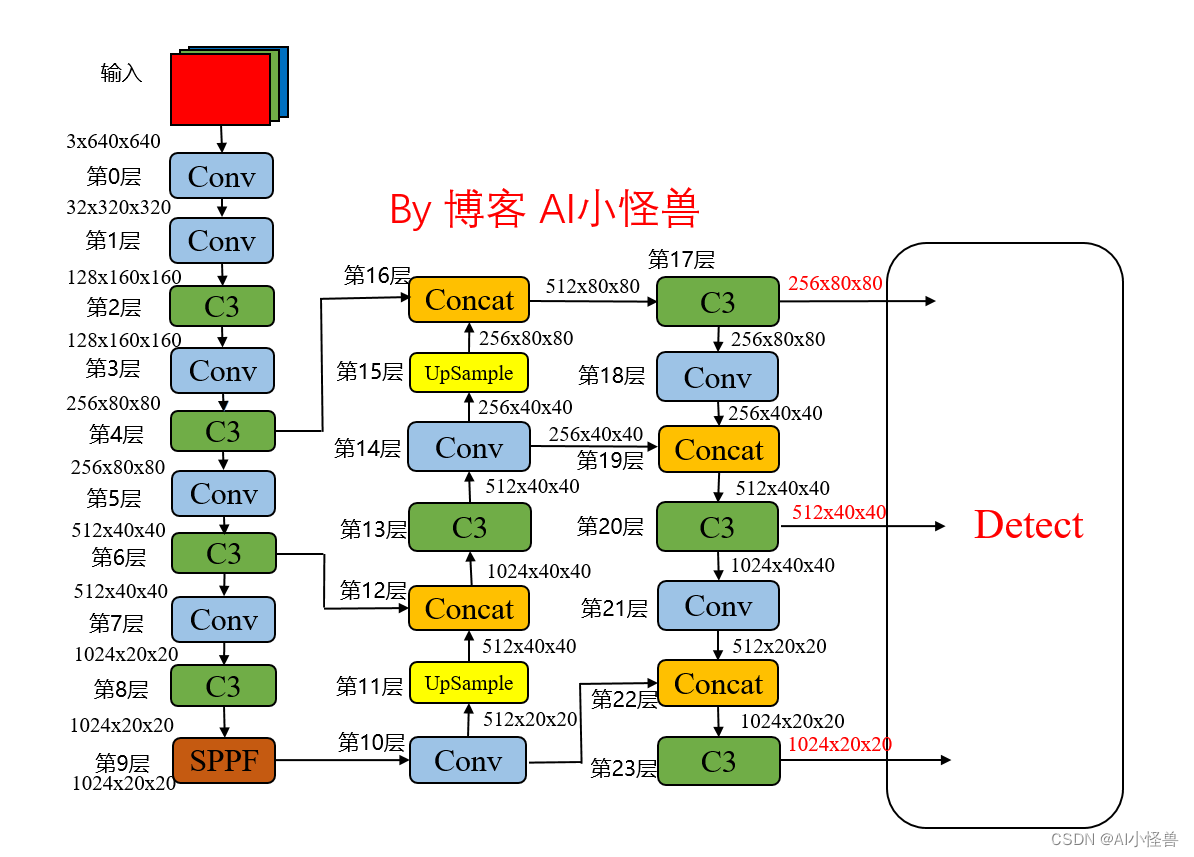
2.1 Yolov5网络结构图
2.2 加入C2f代码修改位置
1)将如下代码添加到common.py中:
- class v8_C2fBottleneck(nn.Module):
- # Standard bottleneck
- def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, k=(3, 3), e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, shortcut, groups, kernels, expand
- super().__init__()
- c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
- self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, k[0], 1)
- self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c2, k[1], 1, g=g)
- self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2
-
- def forward(self, x):
- return x + self.cv2(self.cv1(x)) if self.add else self.cv2(self.cv1(x))
-
-
- class C2f(nn.Module):
- # CSP Bottleneck with 2 convolutions
- def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
- super().__init__()
- self.c = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
- self.cv1 = Conv(c1, 2 * self.c, 1, 1)
- self.cv2 = Conv((2 + n) * self.c, c2, 1) # optional act=FReLU(c2)
- self.m = nn.ModuleList(v8_C2fBottleneck(self.c, self.c, shortcut, g, k=((3, 3), (3, 3)), e=1.0) for _ in range(n))
-
- def forward(self, x):
- y = list(self.cv1(x).split((self.c, self.c), 1))
- y.extend(m(y[-1]) for m in self.m)
- return self.cv2(torch.cat(y, 1))

2)在yolo.py中添加C2f(PS:快速搜索C3对应位置)

2.3 修改配置文件yolov8s.yaml
1)加入backbone
- # YOLOv5 声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/AllinToyou/article/detail/358301推荐阅读
相关标签
Copyright © 2003-2013 www.wpsshop.cn 版权所有,并保留所有权利。


