- 1Java多线程共享变量控制
- 2Chapter7 循环神经网络-1_循环神经中词元的概念
- 3基于java+springmvc+mybatis+vue+mysql的电子资源管理系统
- 4Bito----一款Idea智能化代码辅助插件,让你的开发效率飞起来!_bito idea
- 5html 文字滚动
- 6R语言散点图、坐标轴、图例设置,plot/points/axis/legend_r如何给散点图添加坐标轴标签
- 7?Agilent.GoldenGate.RFIC.Simulation.2015.01.v4.9.0.Win64 1CD(RTL验证标准)
- 8神经网络实用工具(整活)系列---使用OpenAI的翻译模型whisper实现语音(中、日、英等等)转中字,从此生肉变熟肉---基础篇_whisper中英文模型
- 9Flutter输入框、界面被键盘遮挡问题解决_flutter 键盘遮挡输入框问题
- 10window10离线安装net3.5的三种方法_开启net3.5挂载iso
PriorityQueue(优先队列)_new priorityqueue
赞
踩
一. 优先级队列(PriorityQueue)
1.1 概念:
我们都知道队列是一种先进先出的数据结构,没有优先级,众数据平等.
但是在某些情况下,我们操作的数据可能带有优先级,出队列时要优先级高的先出,低的后出.
在这种情况下,我们的数据结构应该提供两个最基本的操作,一个是返回最高优先级对象,一个是添加新的对象.这种数据结构就是我们今天要介绍的优先级队列.
1.1.1 PriorityQueue的特性.
在Java的集成框架中主要有两种类型的优先级队列,分别为:PriorityQueue和PriorityBlockingQueue
PriorityQueue是线程不安全的,PriorityBlockingQueue是线程安全的.我们这篇文章主要介绍PriorityQueue.
注意:
a.在使用PriorityQueue时必须要导入PriorityQueue所在的包:import java.util.PriorityQueue;
虽然我们现在使用的IDE会自动导包,但是一些基础的还是要记一下,毕竟面试的时候是没有自动导包的.
b.PriorityQueue中放置的元素必须要能够比较大小,不能插入无法比较大小的对象,否则会抛出ClassCastException(类型转换异常).
c. 不能插入null对象,否则会抛出NullPointerException(空指针异常)
d. 没有容量限制,可以插入任意多个元素,其内部可以自动扩容
e.插入和删除元素的时间复杂度为
f. PriorityQueue底层使用了堆数据结构(堆我会在第二部分进行讲解的)
g. PriorityQueue默认情况下是小堆—即每次获取到的元素都是最小的元素
大堆—即每次获取到的元素都是最大的元素
小堆,大堆都会在第二部分进行讲解的.
1.2 PriorityQueue常用接口介绍.
1.2.1 优先级队列的构造.
先来看一个表格熟悉一下构造器.
| 构造器 | 功能介绍 |
|---|---|
| 无参:PriorityQueue() | 创建一个空的优先级队列,默认容量为11 |
| 有参:PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity) | 创建一个初始容量为initialCapacity的优先级队列,注意:initialCapacity不能小于1,否则会抛IllegalArgumentException异常 |
| PriorityQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) | 用一个集合来创建优先级队列 |
我们来做一个简单测试:
- public static void TestPriorityQueue{
- //创建一个空的优先级队列,存放的是Integer类型数据,底层默认容量是11.
- PriorityQueue<Integer> pq1=new PriorityQueue<>();
- //创建一个空的优先级队列,存放的是Integer类型数据,底层容量为100.
- PriorityQueue<Integer> pq2=new PriorityQueue<>(100);
-
- List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();
- //向list里面添加元素.我这里给的数据无序.
- list.add(2);
- list.add(3);
- list.add(1);
- list.add(4);
- //用ArrayList对象来构造一个优先级队列的对象
- PriorityQueue<Integer> pq3=new PriorityQueue<>(list);
- //打印pq3中有效元素个数
- System.out.println(pq3.size()); //4
- //拿到优先级最高的元素.因为底层默认是小堆,所以堆顶存放的是最小元素,是1.
- System.out.println(pq3.peek()); //1
- }

1.2.2 优先级队列中的常用方法
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| boolean offer(E e) | 插入元素e,插入成功返回true,如果e对象为空,抛出NullPointerException异常,注意:在空间不够时会自动进行扩容 |
| E peek() | 回去优先级最高的元素,如果优先级队列为空,返回null |
| E poll() | 移除优先级最高的元素并返回,如果优先级队列为空,返回null |
| int size() | 获取有效元素的个数 |
| void clear() | 清空 |
| boolean isEmpty() | 检测优先级队列是否为空,为空返回true,否则false |
- public void method2(){
- PriorityQueue<Integer> p=new PriorityQueue<>();
- //插入元素
- p.offer(1);
- p.offer(4);
- p.offer(3);
- p.offer(6);
- p.offer(5);
- //打印有效元素个数.
- System.out.println(p.size()); //5
- //p.offer(null); //优先级队列中不能插入空的元素
- //获取优先级最高的元素
- System.out.println(p.peek()); //1
- p.poll(); //1
- p.poll(); //3
- p.poll(); //4
- System.out.println(p.size()); //2
- p.clear(); //清空,此时优先级队列为空.
- if (p.isEmpty()){ //true
- System.out.println("p is null");
- }else{
- System.out.println("p is not null" );
- }
- System.out.println(p.size());
- }

默认情况下,PriorityQueue是小堆,如果需要大堆的话,就需要自己去实现一个比较器.
- //直接实现Comparator接口,然后重写该接口中的compare方法即可
- class IntCmp implements Comparator<Integer>{
- public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
- return o2-o1;
- //o1-o2是小堆,o2-o1是大堆.
- }
- }
测试一下:
- public class Test{
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- PriorityQueue p=new PriorityQueue(new IntCmp());
- p.offer(2);
- p.offer(4);
- p.offer(6);
- p.offer(1);
- //此时.打印的结果就是6而不是1.
- System.out.println(p.peek());
- }
- }
二:优先级队列(PriorityQueue)的模拟实现
PriorityQueue的底层使用了堆来实现,而堆实际上就是在完全二叉树的基础上进行了一些元素的调整.下来,让我们来认识一下堆吧.
2.1 堆的概念.
先来看一下官方概念:
如果有一个关键码的集合K = {k0,k1, k2,…,kn-1},把它的所有元素按完全二叉树的顺序存储方式存储在一个一维数组中,并满足:Ki <= K2i+1 且 Ki<= K2i+2 (Ki >= K2i+1 且 Ki >= K2i+2) i = 0,1,2…,则称为 小堆(或大堆)。将根节点最大的堆叫做最大堆或大根堆,根节点最小的堆叫做最小堆或小根堆。
非官方概念回答什么是堆:这也是堆的性质
首先,堆结构就是用数组实现的完全二叉树结构
其次,堆中某个节点的值总是不大于或不小于双亲节点的值.
2.2 堆的存储方式
从堆的概念可以知道,堆是一颗完全二叉树,因此可以采取层次遍历的规则来高效存储,
来看图理解一下:
小堆:节点的值都大于等于其双亲节点的值,按照层次遍历存储.
大堆:节点的值都小于等于其双亲节点的值,按照层次遍历存储.
2.3堆的创建
2.3.1 堆的向下调整
现在给你一个序列{ 27, 15, 19, 18, 28, 34, 65, 49, 25, 37 },该怎么将它建成堆呢?
我们先将序列还原成完全二叉树:
如图:根的左右子树都已经符合了堆的性质:节点的值总是大于或者小于双亲节点的值.所以我们只需要将根节点向下调整到该放的位置就行.
过程(我们这里以小堆为例):
a.用parent标记要调整的节点,用cur标记parent的左孩子.
child和parent为数组下标,左孩子节点=双亲节点*2+1;
int child=parent * 2+1;
b.判断左孩子是否存在,存在的话进行下面的操作,直到child不存在.
~判断parent的右孩子是否存在,如果存在的话,找到左右孩子中较小的值,用cur进行标记.
~然后用parent存放的值与cur存放的值进行比较,如果array[parent]<array[child],则表示不需要进行调整.
~如果array[parent]>array[child],两个值进行交换.此时,子树可能不满足堆的性质,因此需要继续调整,让parent标记此时的cur位置,cur标记parent的左孩子,重复b步骤.
图形理解如下:
当child>size的话,说明已经调整好了.
代码实现如下:
- public void shiftDown(int parent){
- //默认为左孩子
- int child=parent*2+1;
- //size是有效元素个数.
- while (child < size) {
- //在这里对右孩子也进行范围判断.如果child+1>size的话会数组小标越界.
- if (child + 1 < size && array[child + 1] < array[child]) {
- //如果右孩子小于左孩子,将child下标放在右孩子位置.
- child += 1;
- }
- //如果parent处的值大于child处的值,则进行交换.让大的值往下走.
- if (array[parent] > array[child]) {
- //swap()是交换函数,我会在后面堆模拟实现优先级队列的时候给出的.
- swap(parent,child);
- //交换完后,将parent放在child位置,再让child放在当前parent的左孩子位置.
- parent = child;
- child = 2 * parent + 1;
- }else {
- return;
- }
- }
- }

注意:在调整以parent为根的二叉树时,必须要满足parent的左子树和右子树已经是堆了才可以向下调整。
时间复杂度分析:最差的情况下,从根开始一直比较到叶子节点,比较的次数为完全二叉树的高度,所以时间复杂度为:
2.3.2 堆的向上调整.
代码实现如下:
- public void shiftUp(int child){
- int parent=(size-2)/2;
- while(child!=0){
- if (array[child]<array[parent]){
- swap(child,parent);
- child=parent;
- parent=(child-1)/2;
- }else{
- return;
- }
- }
-
- }
2.3.3 堆的创建(对于普通序列的调整)
我们不难发现,上面给的是一个特殊的序列,堆的左右子树都满足堆的性质.而在这个部分,我们要给的是一个普通的序列.
假如我们使用{65, 37, 34, 49, 28, 19, 27, 18, 25, 15}这组序列去创建一个小堆,该怎么做呢?
我们先来将它还原成完全二叉树(图不好看,但是可以说明问题):
~~如果我们要用向下调整的方法,我们就要让根的左右子树都满足堆的性质.
假如要调整以37为节点的这颗子树,我们发现37的左右子树也不满足条件,
所以我们还要调整以37为根节点的左右子树.让它满足堆的性质.
就这样以此类推,等将65这个根节点的左右子树全部调整完毕后,65就可以向下调整了.
做法:先找到倒数第一个非叶子节点,从该节点开始往前一直到根节点,遇到一个节点,就调用向下调整的方法.
如下图,绿色节点是倒数第一个非叶子节点,蓝色节点是最后一个节点.
倒数第一个非叶子节点刚好是最后一个节点的双亲,
最后一个节点下标为size-1,
那么倒数第一个非叶子节点就是((size-1)-1)/2,即(size-2)/2;
绿色节点的左右子树都是堆以后,让绿色节点下标-1,到下一个位置,调用向下调整方法.
最后当parent来到根节点的位置时,发现他的左右子树都已经是堆了,所以再调用一次向下调整方法,这个非特殊序列就被建成小堆了:
代码如下:
- public MyPriorityQueue(Integer[] arr){
- //将arr中的元素拷贝到数组array中
- //原因: 因为我们要调用shiftDown方法,而shiftDown中的用的数组是成员变量array,
- //所以先要将arr中的内容拷贝到array中.在后面模拟实现部分大家就会懂了.
- array=new Integer[arr.length];
- for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
- array[i]=arr[i];
- }
- size=arr.length;
- //找当前完全二叉树中倒数第一个非叶子节点
- // 倒数第一个非叶子节点刚好是最后一个节点的双亲
- int lastLeafParent=(size-2)/2;
- for (int root = lastLeafParent; root>=0 ; root--) {
- //向下调整
- shiftDown(root);
- }
- }

这个代码我是在构造方法中实现的,所以只要你创建对象,并且传入一个数组时,方法会被调用:
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Integer[] array={65,37,34,49,28,19,27,18,25,15};
- MyPriorityQueue mpq=new MyPriorityQueue(array);
- }
2.4 堆的插入和删除
2.4.1 插入(包括向上调整)
假如我们现在的堆为下图:
现在我们要插入一个新的元素10.
先将10放到size的位置,
然后size++,
最后将10向上调整就行.
向上调整:
a.用child标记要调整的元素.parent标记此元素的双亲.
b.如果 array[child]<array[parent], 则将两个元素互换位置.否则证明已经调整好了,直接return.
c.然后让child走到parent的位置,parent再次标记child的双亲.
循环执行 b c 步骤.直到child=0时,说明child已经到达根节点了,退出循环.
图行演示:
向上调整代码:
- public void shiftUp(int child){
- int parent=(size-2)/2;
- while(child!=0){
- if (array[child]<array[parent]){
- swap(child,parent);
- child=parent;
- parent=(child-1)/2;
- }else{
- return;
- }
- }
- }
插入元素时的代码:
- public boolean offer(Integer e){
- if (e==null){
- throw new NullPointerException("插入的时候元素为空");
- }
- array[size]=e;
- size++;
- //当新元素插入以后,可能会破坏堆的结构.
- shiftUp(size-1);
- return true;
- }
2.4.2 删除
堆的删除肯定删除的是堆顶元素.我们继续以小堆来进行举例.
这个小堆的序列为{15, 18, 19, 25, 28, 34, 27, 49, 65, 28, 37}.我们要删除堆顶的元素,也就是15.
那么底层应该如何实现呢.
如果我们直接删除15这个节点,那么我们要调整的就太多了,问题就不好处理了.
所以我们用另外一种方式:将堆顶和最后位置的元素进行交换,然后size- -就可以删除最后位置元素.
因为删除最后位置元素后,根节点的左右子树结构没有被破坏,还是符合堆的性质,最后再让堆顶元素向下调整即可.向下调整:
代码:
- public Integer poll(){
- if(isEmpty()){
- return null;
- }
- //因为最后还要返回被删除的元素,所以提前用ret来保存一下.
- Integer ret=array[0];
- //将堆顶的元素与堆中最后一个元素进行交换
- swap(0,size-1);
- size--;
- //将堆顶的元素往下调整到合适位置.
- //0是下标.
- shiftDown(0);
- return ret;
- }
2.5 用堆进行模拟实现优先级队列
这里我只给出代码,具体的解释方法的解释我在其他都解释了
我没有写测试的方法,代码大家可以直接复制到idea中进行测试.
代码:
- package demo07PriorityQueue;
- //用堆模拟实现优先级队列
- public class MyPriorityQueue {
- //用来保存数据.
- Integer[] array;
- //记录当前堆中有效元素个数.
- int size;
- public MyPriorityQueue(){
- //默认容量
- array=new Integer[11];
- size=0;
- }
- public MyPriorityQueue(int initCapacity){
- //自定义容量
- if (initCapacity<1){
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("初始容量小于1");
- }
- array=new Integer[initCapacity];
- size=0;
- }
- //建堆
- public MyPriorityQueue(Integer[] arr){
- //将arr中的元素拷贝到数组array中
- array=new Integer[arr.length];
- for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
- array[i]=arr[i];
- }
- size=arr.length;
- //找当前完全二叉树中倒数第一个非叶子节点
- // 倒数第一个非叶子节点刚好是最后一个节点的双亲
- int lastLeafParent=(size-2)/2;
- for (int root = lastLeafParent; root>=0 ; root--) {
- //向下调整
- shiftDown(root);
- }
- }
- //向上调整
- private void shiftUp(int child){
- int parent=(size-2)/2;
- while(child!=0){
- if (array[child]<array[parent]){
- swap(child,parent);
- child=parent;
- parent=(child-1)/2;
- }else{
- return;
- }
- }
- }
- //向下调整,调整以parent为根的二叉树.
- //前提是,必须要保证parent的左右子树已经满足堆的特性.
- private void shiftDown(int parent){
- //默认为左孩子
- int child=parent*2+1;
- //当child的值小于size时,只是满足了左孩子在范围内,没有满足右孩子.
- while (child<size) {
- //在这里对右孩子也进行范围判断.
- if (child + 1 < size && array[child + 1] < array[child]) {
- //如果右孩子小于左孩子,将child下标放在右孩子位置.
- child += 1;
- }
- //如果parent处的值大于child处的值,则进行交换.让大的值往下走.
- if (array[parent] > array[child]) {
- swap(parent,child);
- //交换完后,将parent放在child位置,在让child放在当前parent的左孩子位置.
- parent = child;
- child = 2 * parent + 1;
- } else {
- return;
- }
- }
- }
- //让内容交换的方法.
- //left和right是数组的下标.
- private void swap(int left,int right){
- int temp=array[left];
- array[left]=array[right];
- array[right]=temp;
- }
- //往堆中插入元素.
- public boolean offer(Integer e){
- if (e==null){
- throw new NullPointerException("插入的时候元素为空");
- }
- array[size]=e;
- size++;
- //当新元素插入以后,可能会破坏堆的结构.
- shiftUp(size-1);
- return true;
- }
- //删除堆顶元素,并返回堆顶元素的值.
- public Integer poll(){
- if(isEmpty()){
- return null;
- }
- Integer ret=array[0];
- //将堆顶的元素与堆中最后一个元素进行交换
- swap(0,size-1);
- size--;
- //将堆顶的元素往下调整到合适位置.
- shiftDown(0);
- return ret;
- }
- //返回堆中元素的个数
- public int size(){
- return size;
- }
- public boolean isEmpty(){
- return size==0;
- }
- }
-

2.6 堆的应用
2.6.1 PriorityQueue的实现
PriorityQueue(优先队列),一个基于优先级堆的无界优先级队列,该优先级使得队列始终按照自然顺序进行排序,队列的头部为最小值。
实际上是一个堆(不指定Comparator时默认是小顶堆),通过传入自定义的compara函数可以实现大根堆。
java内置优先队列的API
- PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue(new Comparator<Integer>() {
- @Override
- public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
- return o1 - o2;
- }
- });
Lambda表达式写法(推荐使用)
- PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1 , o2) -> o1 - o2); // 小根堆
- PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1 , o2) -> o2 - o1); // 大根堆
2.6.2 堆排序(见堆排序(Heap Sort)实现_EvilChou的博客-CSDN博客)
升序排列建大根堆;降序排列建小根堆
2.6.3 Top-K问题
例1.前k个高频元素(小根堆)
概念:求数据结合中前K个最大或者最小的的元素,一般情况下数据量都比较大.
比如:专业前10,世界500强,游戏中全服前100等等.
解决Top-K问题最简单直接的方法就是排序,但是如果数据量非常大,排序就不可取了,最佳的方式就是用堆来解决.
a.用数据集合的前K个元素进行建堆
~前K个最大的元素,建小堆(大堆堆顶元素始终最大)
~前K个最小的元素,建大堆(小堆堆顶元素始终最小)
b.用剩余的N-K个元素依次与堆顶元素进行比较,不满足条件就替换堆顶元素.比较完成之后,堆中剩余的K个元素就是所求的最大或者最小的前K个元素.
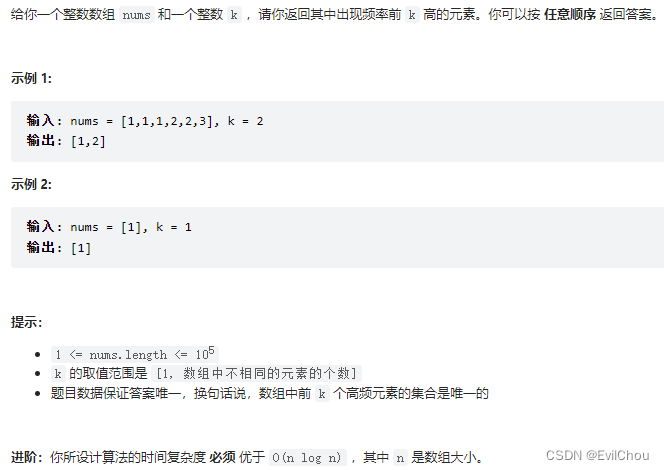
解题思路:
有的同学一想,题目要求前 K 个高频元素,那么果断用大顶堆啊。
那么问题来了,定义一个大小为k的大顶堆,在每次移动更新大顶堆的时候,每次弹出都把最大的元素弹出去了,那么怎么保留下来前K个高频元素呢。
而且使用大顶堆就要把所有元素都进行排序,那能不能只排序k个元素呢?
所以我们要用小顶堆,因为要统计最大前k个元素,只有小顶堆每次将最小的元素弹出,最后小顶堆里积累的才是前k个最大元素。
- class Solution{
- public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
- Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
- for(int num : nums){
- map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
- }
- //一:遍历map时,使用entrySet方法
- PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, 02) -> o1.getValue() - o2.getValue());
- for(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> entry : map.entrySet()){
- //int num = map.getKey(), count = map.getValue();
- if(queue.size() == k){
- if(queue.peek().getValue() < map.getValue()){
- queue.poll();
- queue.offer(entry);
- }
- }else{
- queue.offer(entry);
- }
- }
- //建立结果数组的时间复杂度:O(k logk),是一个常数时间复杂度
- int[] res = new int[k];
- for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
- res[i] = queue.poll().getKey();
- }
- return res;
- //总的时间复杂度O(n logk),空间复杂度O(n)
- //建立哈希表的时间复杂度为O(n),而遍历哈希表入堆时间复杂度为O(k)
- //哈希表的空间复杂度为O(n),而堆的空间复杂度为O(k)
-
-
- //二:遍历map时,使用keySet方法
- Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
- for(int num : nums){
- map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
- }
-
- PriOrityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> map.get(o1) - map.get(o2));
-
- /**
- PriorityQueue类实现了优先队列,默认是一个小根堆的形式,如果要定义大根堆,需要在初始化的时候
- 加入一个自定义的比较器
- PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
- @Override
- public int compare(Integer a, Integer b) {
- return map.get(a) - map.get(b);
- }
- });
- */
-
- for(Integer key : map.keySet()){
- if(queue.size() == k){
- if(map.get(queue.peek()) < map.get(key)){
- queue.poll();
- queue.offer(key);
- }
- }else{
- queue.offer(key);
- }
- }
- int[] res = new int[k];
- for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
- res[i] = queue.poll();
- }
- return res;
-
-
- /**
- //更简洁的写法
- int[] res = new int[k];
- Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
- for(int num : nums){
- map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
- }
- PriOrityQueue<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, 02) -> o1.getValue() - o2.getValue());
- for(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> entry : map.entrySet()){
- queue.offer(entry);
- if(queue.size() > k){
- queue.poll();
- }
- }
- for(int i = k - 1; i >= 0; i--){
- res[i] = queue.poll().getKey();
- }
- return res;
- */
- }
- }

例2.数组中的第k个最大元素 (小根堆)

- class Solution {
- public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
- // 小根堆(默认情况下,PriorityQueue是小堆,如果需要大堆的话,就需要自己去实现一个比较器.)
- PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();//小根堆
- //PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o2 - o1); 大根堆
- for (int num : nums) {
- queue.offer(num);
- // 堆中元素多于k个时,删除堆顶元素
- if(queue.size() > k){
- queue.poll();
- }
- }
- return queue.peek(); // 堆顶元素即为第k个最大元素
-
-
- /**
- PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
- for (int num : nums) {
- if(queue.size() == k){
- if(queue.peek() < num){
- queue.poll();
- queue.offer(num);
- }
- }else{
- queue.offer(num);
- }
- }
- return queue.peek(); // 堆顶元素即为第k个最大元素
- */
- }
- }

例3.最后一块石头的重量(大根堆)
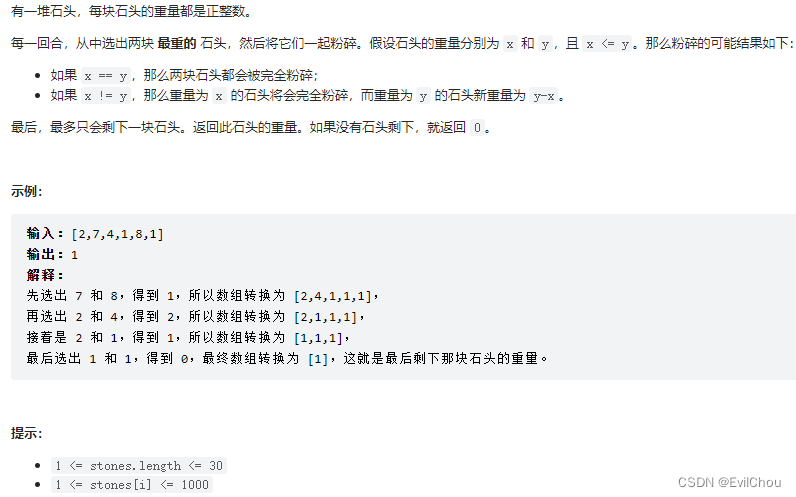
本题采用PriorityQueue实现大根堆来解题
- class Solution {
- public int lastStoneWeight(int[] stones) {
- //采用大根堆来实现
- PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> b - a);
- for(int stone : stones){
- queue.offer(stone);
- }
- while(queue.size() > 1){
- int a = queue.poll();
- int b = queue.poll();
- if(a > b){
- queue.offer(a - b);
- }
- }
- return queue.isEmpty() ? 0 : queue.poll();
- }
- }

例4.合并k个升序链表

- /**
- * Definition for singly-linked list.
- * public class ListNode {
- * int val;
- * ListNode next;
- * ListNode() {}
- * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
- * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
- * }
- */
- class Solution {
- public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
- if(lists == null || lists.length == 0){
- return null;
- }
- //小根堆
- PriorityQueue<ListNode> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o1.val - o2.val);
- for(ListNode list : lists){
- if(list != null){
- queue.offer(list);
- }
- }
- ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
- ListNode cur = dummy;
- while(!queue.isEmpty()){
- ListNode head = queue.poll();
- cur.next = head;
- if(head.next != null){
- queue.offer(head.next);
- }
- }
- return dummy.next;
-
- /**
- if(lists != null || lists.length == 0){
- return null;
- }
- PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o1 - o2);
- for(int i = 0; i < lists.length; i++){
- while(lists[i] != null){
- queue.offer(lists[i].val);
- lists[i] = lists[i].next;
- }
- }
- ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
- ListNode cur = dummy;
- while(!queue.isEmpty){
- cur.next = new ListNode(queue.poll());
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return dummy.next;
- */
- }
- }



