- 1nlp 中文文本纠错_百度中文纠错技术
- 2geth下载安装配置环境及联盟链的搭建
- 3OSPF在广播类型的网络拓扑中DR和BDR的选举_h3c ospf dr和bdr选举
- 4信号处理-小波变换(python实现)1_python连续小波变换
- 5harmonyOS鸿蒙官网教程-给应用添加通知和提醒_鸿蒙 notificationmanager
- 6测试人员如何通过AI提高工作效率!_ai 提效测试
- 7C#毕业设计——基于C#+asp.net的图像检索技术设计与实现(毕业论文+程序源码)——图像检索技术_c#.net图像检索系统
- 82023 年 GESP 12 月认证 C++一级试卷解析_2023年12月gespc++一级真题
- 9朴素贝叶斯算法(Naive Bayes)_采用鸢尾花数据集实现朴素贝叶斯算法
- 10Hadoop 完全分布式部署
机器学习入门实战——波士顿房价预测(简单预测)_波斯顿房价预测怎么导入本地数据集
赞
踩
前言
波士顿房价预测是一个经典的机器学习任务,类似于程序员世界的“Hello World”。利用机器学习方法完成波士顿房价的预测。理解机器学习解决简单实际问题的基本步骤和方法。
一、实验步骤及运行结果
1.数据分析
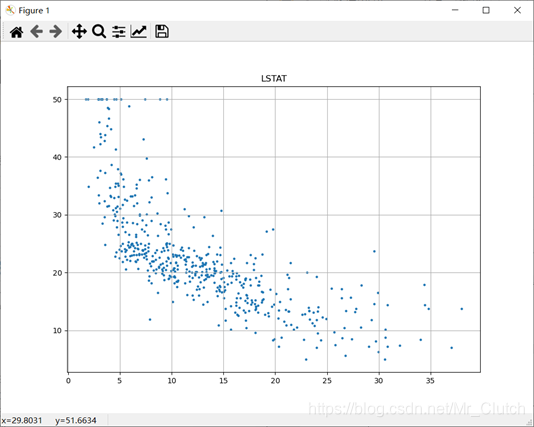
①.分析各个影响房价的特征信息
import numpy as np from sklearn.datasets import load_boston # 导入数据集 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib.pyplot import MultipleLocator boston = load_boston() x = boston['data'] # 影响房价的特征信息 y = boston['target'] # 房价 name = boston['feature_names'] for i in range(13): plt.figure(figsize=(10, 7)) plt.grid() plt.scatter(x[:, i], y, s=5) # 横纵坐标和点的大小 plt.title(name[i]) print(name[i], np.corrcoef(x[:i]), y) plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
运行结果:
犯罪率:高房价的房屋大都集中在低犯罪率地区。
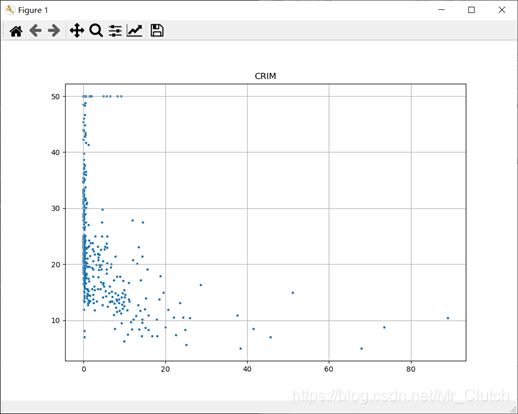
住宅用地比例:与房价无明显的线性关系。
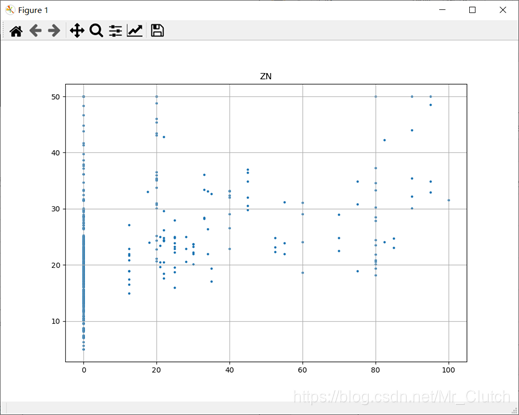
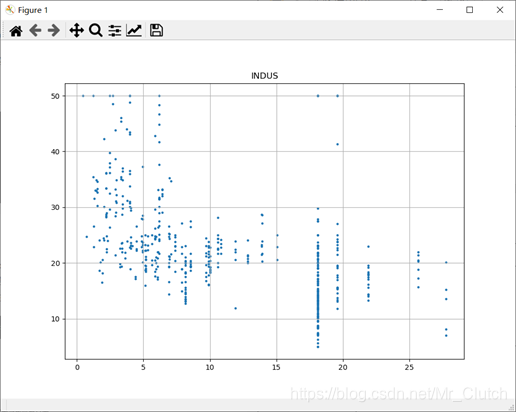
城镇中非商业用地的所占比例:与房价无明显的线性关系,只能说在某一区间内房价呈现一定特征。
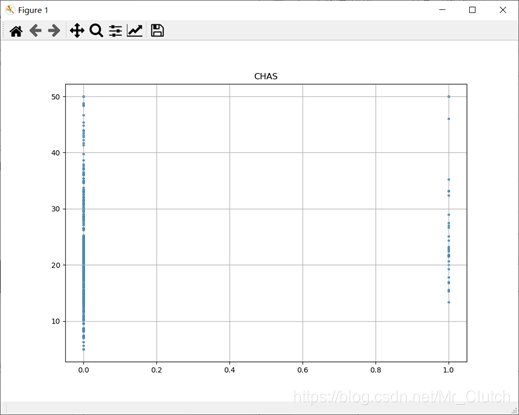
是否处于查尔斯河边(1表示在河边,0表示不在河边):是否在查尔斯河边影响房价也不明显。
一氧化氮浓度: 一氧化氮浓度与房价的关系呈现极其微弱的线性关系,一氧化氮低于0.5的情况下,房价绝大部分高于15。
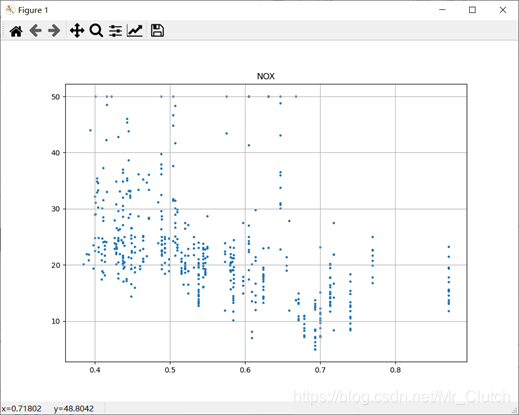
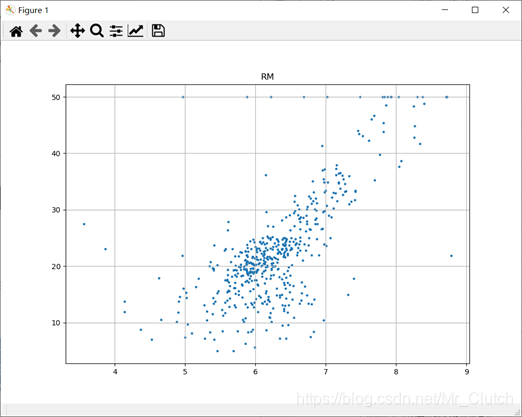
每栋住宅的房间数:与房价之间具有较强的线性关系。
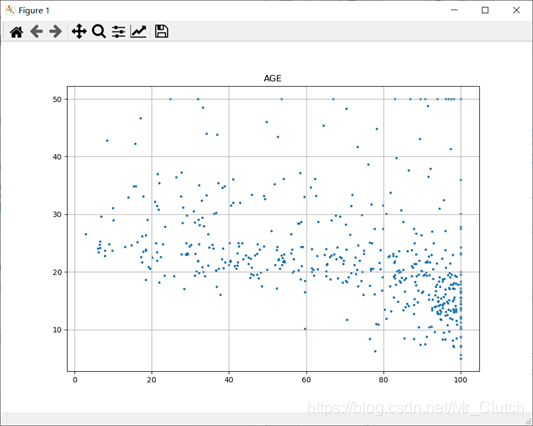
1940年以前建成的业主自住单位的占比:对房价的影响较小。
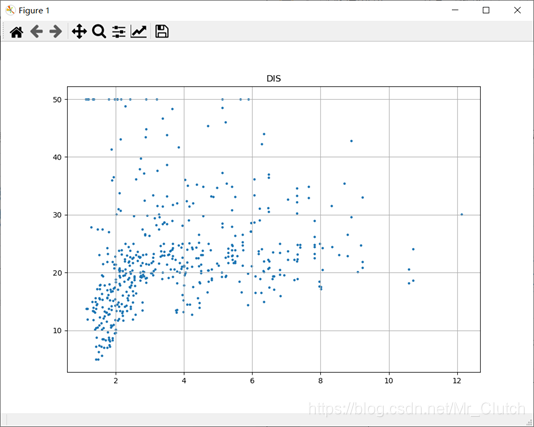
距离5个波士顿就业中心的平均距离:平均距离较小的情况下,房价对应也较低。
距离高速公路的便利指数:房价高于30的房产,近乎都集中在距离高速公路的便利指数低的地区。
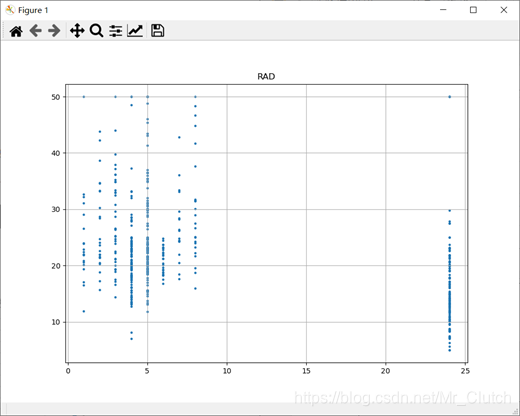
每一万美元的不动产税率:与房价的线性相关度较小。
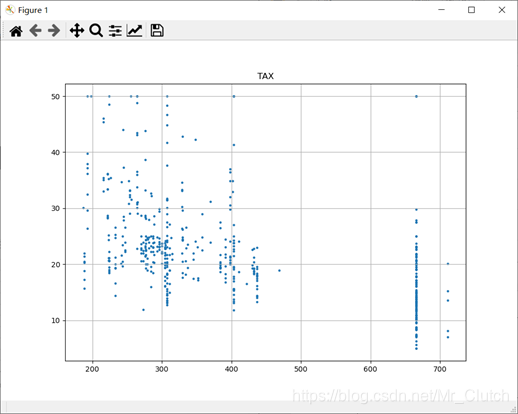
城镇中学生教师比例:对房价的影响较小,呈微弱的线性关系。
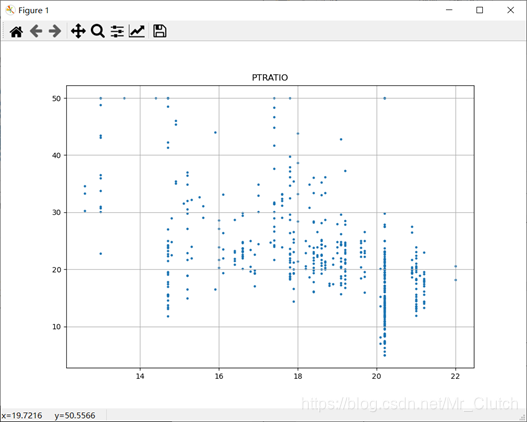
黑人比例:黑人比例对波士顿房价的影响尤其是往后的影响越趋于更小。
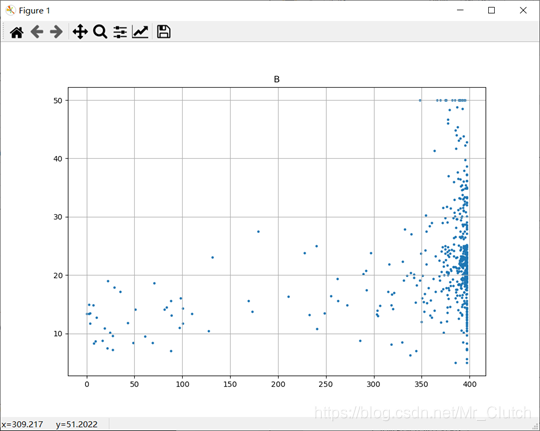
低收入阶层占比:与房价具有较强的线性关系,是影响房价的重要因素。
②.对房价的分析
import numpy as np from sklearn.datasets import load_boston # 导入数据集 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib.pyplot import MultipleLocator boston = load_boston() x = boston['data'] # 影响房价的特征信息 y = boston['target'] # 房价 plt.figure(figsize=(20, 15)) y_major_locator = MultipleLocator(5) # 把y轴的刻度间隔设置为10,并存在变量里 ax = plt.gca() # ax为两条坐标轴的实例 ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(y_major_locator) # 把y轴的主刻度设置为5的倍数 plt.ylim(0, 51) plt.grid() for i in range(len(y)): plt.scatter(i, y[i], s=20) plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
运行结果:
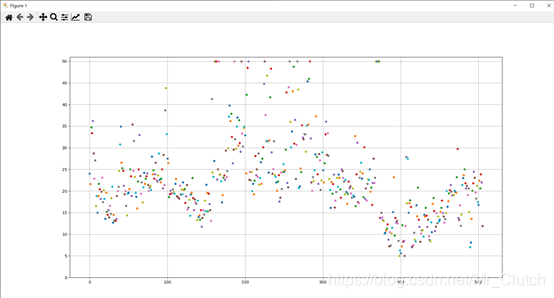
经分析,将房价大于等于46的数据视为异常数据,在划分训练集和测试集之前先把这些数据从数据集中除去。
2.数据处理
经上述分析,去除房价中大于等于46的数据,对于房价的影响信息,只保留NOX,RM,AGE,DIS,LSTAT, INDUS, PTRATIO几个特征信息,将剩下的特征信息均除去。
3.建模测试并运行
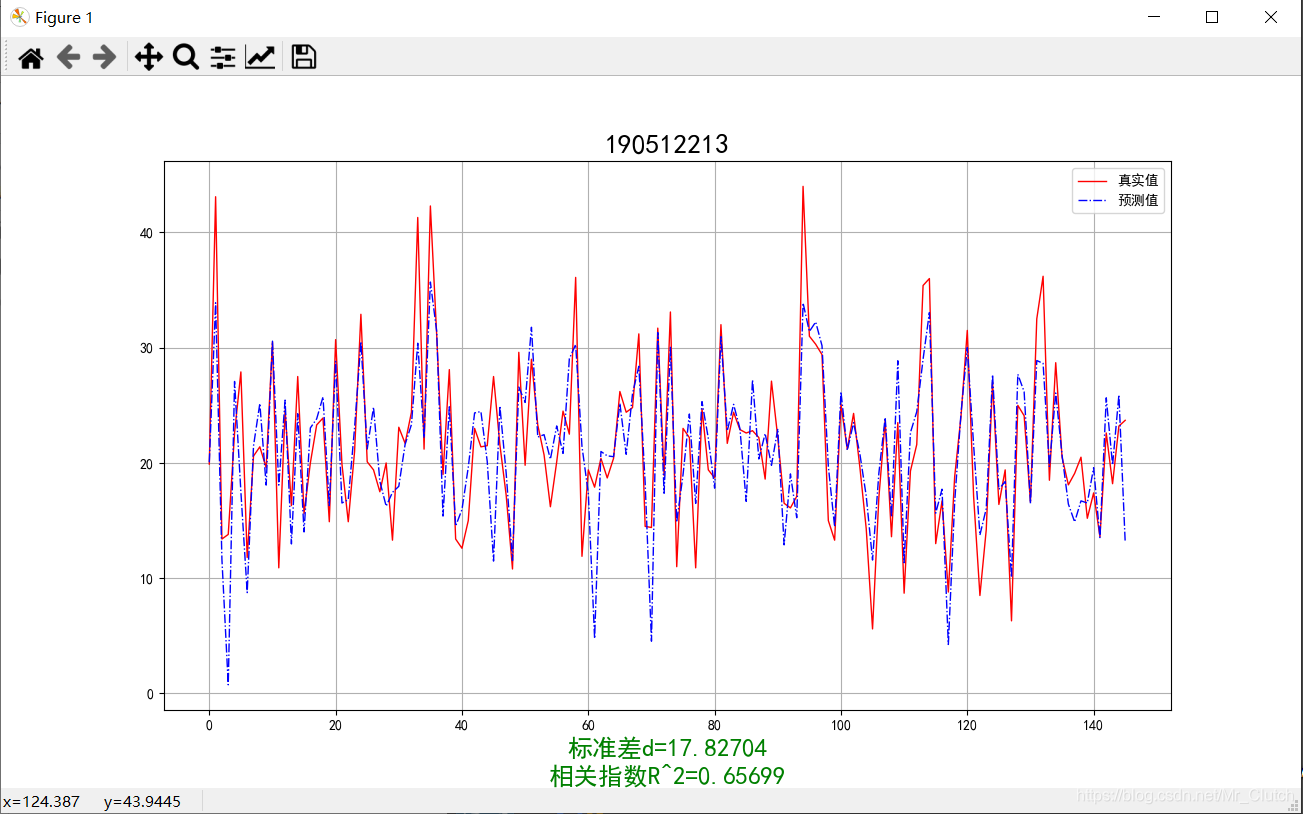
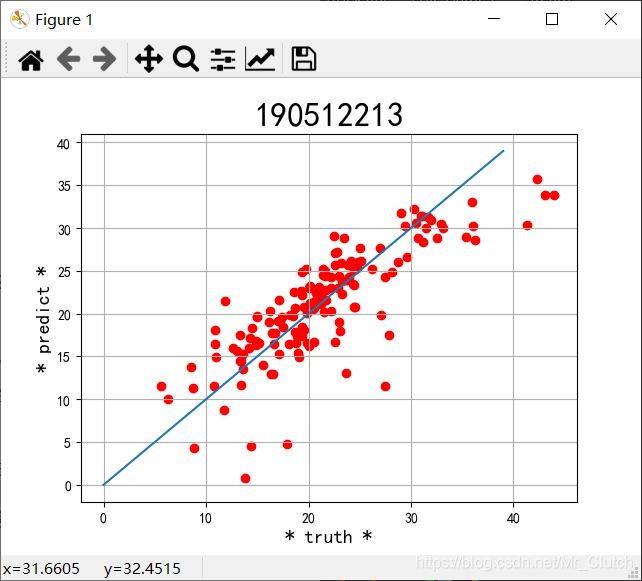
import numpy as np import numpy as np from skimage.metrics import mean_squared_error from sklearn import linear_model from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression # 导入线性模型 from sklearn.datasets import load_boston # 导入数据集 from sklearn.metrics import r2_score from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split # 导入数据集划分模块 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.pyplot as plt2 boston = load_boston() x = boston['data'] # 影响房价的特征信息数据 y = boston['target'] # 房价 name = boston['feature_names'] # 数据处理 unsF = [] # 次要特征下标 for i in range(len(name)): if name[i] == 'RM' or name[i] == 'PTRATIO' or name[i] == 'LSTAT' or name[i] == 'AGE' or name[i] == 'NOX' or name[i] == 'DIS' or name[i] == 'INDUS': continue unsF.append(i) x = np.delete(x, unsF, axis=1) # 删除次要特征 unsT = [] # 房价异常值下标 for i in range(len(y)): if y[i] > 46: unsT.append(i) x = np.delete(x, unsT, axis=0) # 删除样本异常值数据 y = np.delete(y, unsT, axis=0) # 删除异常房价 # 将数据进行拆分,一份用于训练,一份用于测试和验证 # 测试集大小为30%,防止过拟合 # 这里的random_state就是为了保证程序每次运行都分割一样的训练集和测试集。 # 否则,同样的算法模型在不同的训练集和测试集上的效果不一样。 x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=0) # 线性回归模型 lf = LinearRegression() lf.fit(x_train, y_train) # 训练数据,学习模型参数 y_predict = lf.predict(x_test) # 预测 # 岭回归模型 # rr = linear_model.Ridge() # 模型岭回归 # rr.fit(x_train, y_train) # 训练模型 # y_predict = rr.predict(x_test) # 预测 # lasso模型 # lassr = linear_model.Lasso(alpha=.0001) # lassr.fit(x_train, y_train) # y_predict = lassr.predict(x_test) # 与验证值作比较 error = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_predict).round(5) # 平方差 score = r2_score(y_test, y_predict).round(5) # 相关系数 # 绘制真实值和预测值的对比图 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(13, 7)) plt.rcParams['font.family'] = "sans-serif" plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = "SimHei" plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 绘图 plt.plot(range(y_test.shape[0]), y_test, color='red', linewidth=1, linestyle='-') plt.plot(range(y_test.shape[0]), y_predict, color='blue', linewidth=1, linestyle='dashdot') plt.legend(['真实值', '预测值']) plt.title("190512213", fontsize=20) error = "标准差d=" + str(error)+"\n"+"相关指数R^2="+str(score) plt.xlabel(error, size=18, color="green") plt.grid() plt.show() plt2.rcParams['font.family'] = "sans-serif" plt2.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = "SimHei" plt2.title('190512213', fontsize=24) xx = np.arange(0, 40) yy = xx plt2.xlabel('* truth *', fontsize=14) plt2.ylabel('* predict *', fontsize=14) plt2.plot(xx, yy) plt2.scatter(y_test, y_predict, color='red') plt2.grid() plt2.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
运行结果:
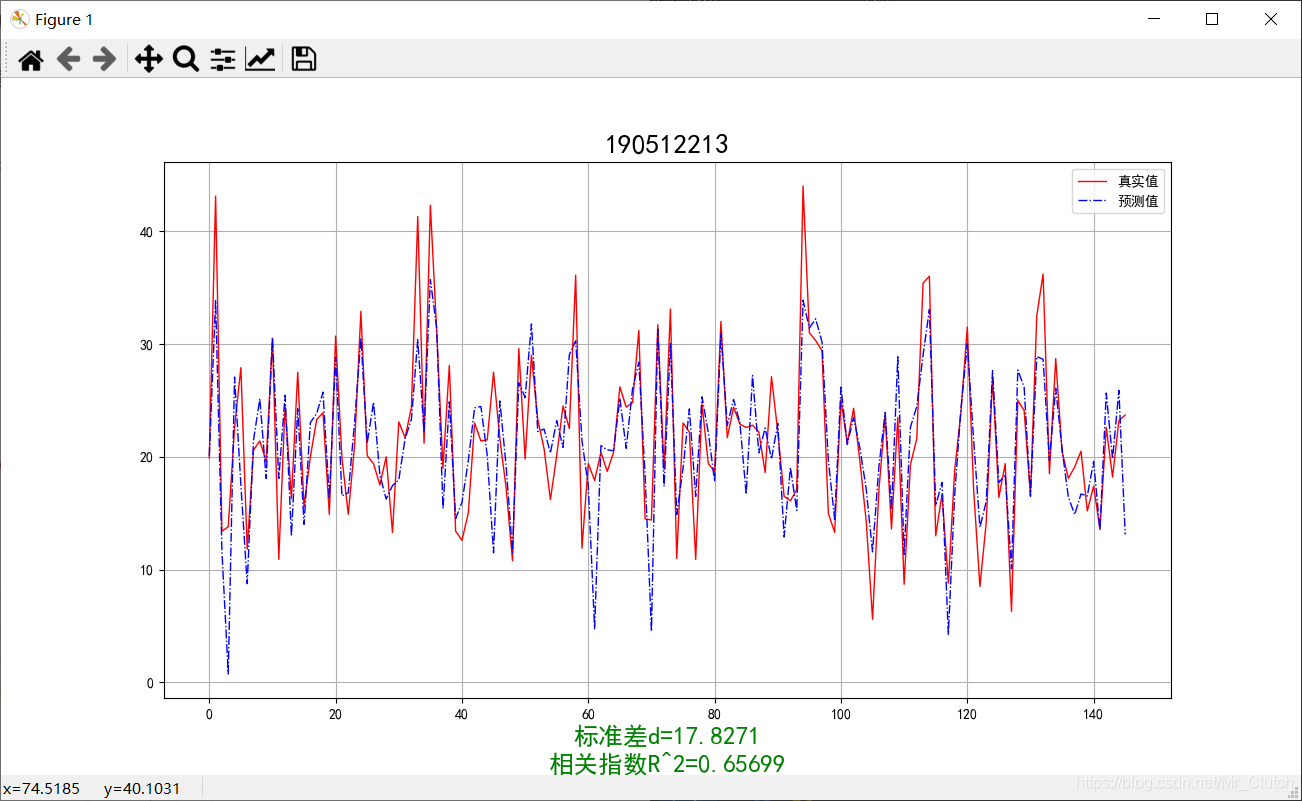
线性回归:
岭回归:
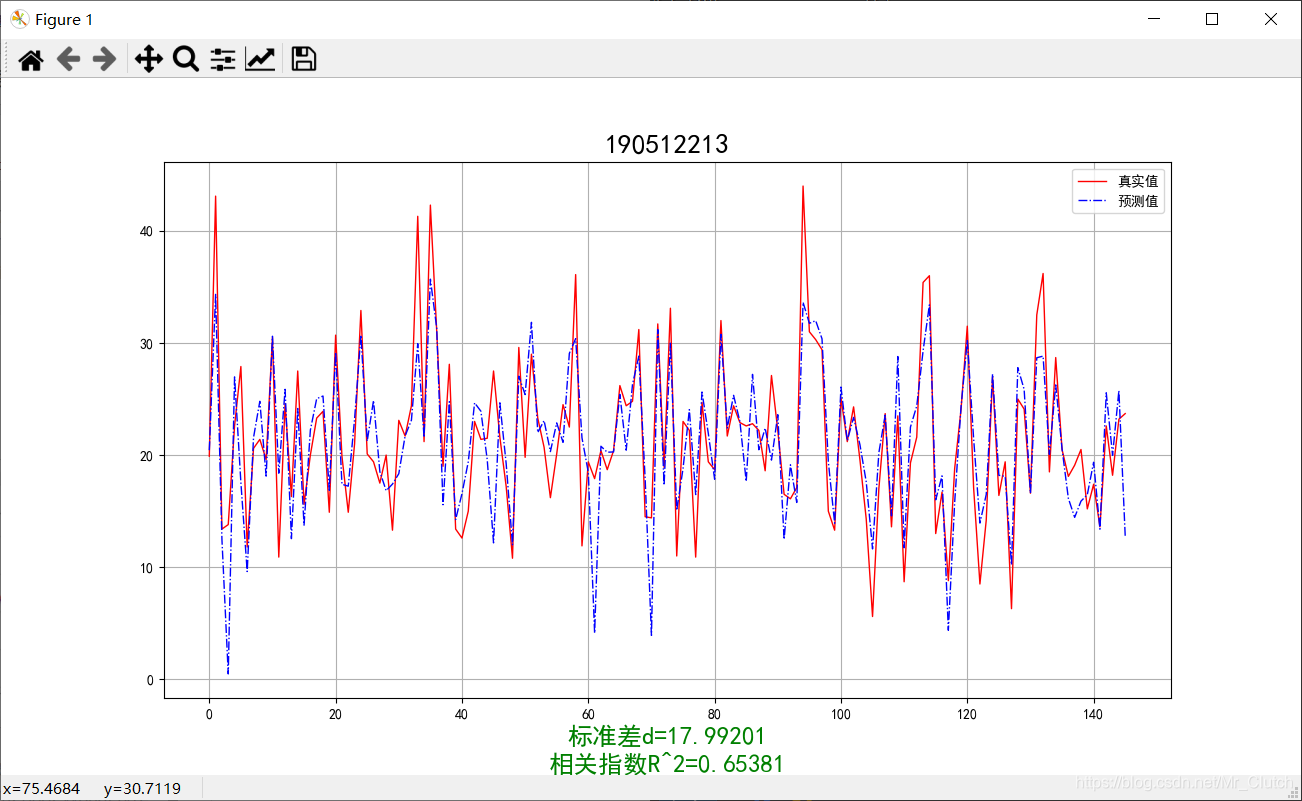

Lasso模型:
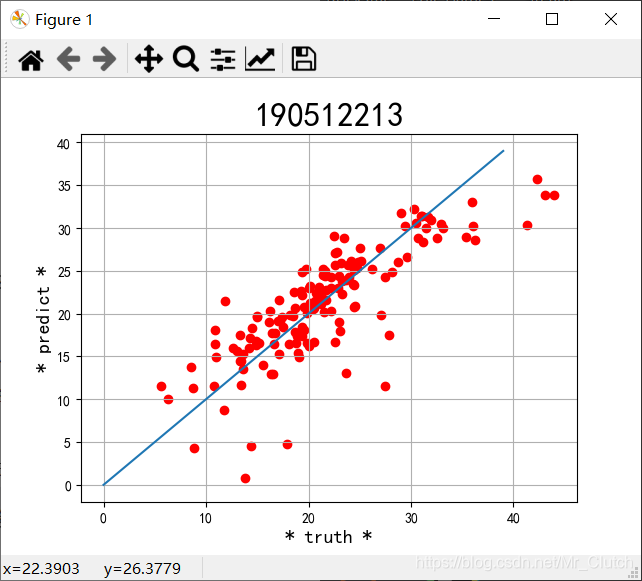
二、实验结果分析
1.由本次实验结果与真实值的对比图可知,无论使用哪种模型预测,预测效果都不是很理想,主要原因仍是数据分析及处理过程中出现了问题。在预测时,应该对数据进行进一步的分析和处理,如对应区间内数据的变化,对极端数据的处理等等。
2.实验采用了相关系数和平方差两种手段去评判预测结果的好坏。相关系数越接近1说明选用的模型回归的效果越好,预测的结果也就越优,在实际解决问题时,应该测试多个模型选用最优的模型进行预测。
3.除了实验中选择的三种模型,还可以进一步利用支持向量机的核函数,SVR中的三种模型进行预测,支持向量机是目前最常用效果最好的分类器之一,但是其消耗的空间和时间代价太大,所以需要结合实际情况使用。



