- 1无公网IP,使用ZeroTier免费内网穿透_allow assignment of global ips
- 2华为OD机试 - 小明找位置(Python、Java、C++、Javascript)_小朋友出操,按学号从小到大排成一列;小明来迟了,请你给小明出个主意,让他尽快找到
- 3hive表中使用testfile格式保存时,常用的字段分隔符_hive textfile 分隔符
- 4基于微信小程序的鲜花预定系统的设计与实现_鲜花商城系统需求分析
- 5【数据结构】如何设计循环队列?图文解析(LeetCode)_数据结构循环图怎么画
- 6数据结构初识_初识数据结构
- 7RAG - LlamaIndex + modelscope + Qwen1.5 构建本地知识库
- 8DES加密
- 9CTF_ CRYPTO(Cryptography)_密码学/密码编码学_ctf——crypto密码学
- 10git push -f 找回文件:需要在90天内有效_git push -f 如何找回原有文件
算法学习——LeetCode力扣补充篇8(146. LRU 缓存、 215. 数组中的第K个最大元素、25. K 个一组翻转链表)
赞
踩
算法学习——LeetCode力扣补充篇8

146. LRU 缓存
描述
请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。
实现 LRUCache 类:
LRUCache(int capacity) 以 正整数 作为容量 capacity 初始化 LRU 缓存
int get(int key) 如果关键字 key 存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回 -1 。
void put(int key, int value) 如果关键字 key 已经存在,则变更其数据值 value ;如果不存在,则向缓存中插入该组 key-value 。如果插入操作导致关键字数量超过 capacity ,则应该 逐出 最久未使用的关键字。
函数 get 和 put 必须以 O(1) 的平均时间复杂度运行。
示例
示例:
输入
[“LRUCache”, “put”, “put”, “get”, “put”, “get”, “put”, “get”, “get”, “get”]
[[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]]
输出
[null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4]
解释
LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2);
lRUCache.put(1, 1); // 缓存是 {1=1}
lRUCache.put(2, 2); // 缓存是 {1=1, 2=2}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 1
lRUCache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废,缓存是 {1=1, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废,缓存是 {4=4, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.get(3); // 返回 3
lRUCache.get(4); // 返回 4
提示
1 <= capacity <= 3000
0 <= key <= 10000
0 <= value <= 105
最多调用 2 * 105 次 get 和 put
代码解析
链表法(超时)
class LRUCache {
public:
list<pair<int,int>> my_list;
int max_size = 0;
LRUCache(int capacity) {
max_size = capacity;
}
int get(int key) {
auto it = my_list.begin();
for(int i=0 ; i<my_list.size() ;i++,it++)
{
if(it->first == key)
{
pair<int,int> tmp = *it;
my_list.erase(it);
my_list.push_front(tmp);
return tmp.second;
}
}
return -1;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
auto it = my_list.begin();
for(int i=0 ; i<my_list.size() ;i++,it++)
{
if(it->first == key)
{
my_list.erase(it);
break;
}
}
my_list.push_front({key,value});
if(my_list.size() > max_size) my_list.pop_back();
return ;
}
};
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache* obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj->get(key);
* obj->put(key,value);
*/
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
自制双向链表
class LRUCache {
public:
struct Node
{
int key;
int value;
Node* pre;
Node* next;
Node():key(0),value(0),pre(nullptr),next(nullptr) {}
Node(int x,int y):key(x),value(y),pre(nullptr),next(nullptr) {}
};
LRUCache(int capacity) {
_capacity = capacity;
head = new Node();
tail = new Node();
head->next = tail;
tail->pre = head;
}
int get(int key) {
if(my_map.find(key) == my_map.end() ) return -1;
Node* tmp = my_map[key];
remove_node(tmp);
add_head(tmp);
return tmp->value;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
if(my_map.find(key) == my_map.end() ) //不存在
{
Node* new_node = new Node(key,value);
my_map[key] = new_node;
add_head(new_node);
size++;
if(size > _capacity)
{
my_map.erase(tail->pre->key);
remove_node(tail->pre);
}
}else
{
Node* tmp = my_map[key];
tmp->value = value;
remove_node(tmp);
add_head(tmp);
}
}
void add_head(Node* new_node)
{
new_node->pre = head;
new_node->next = head->next;
head->next->pre = new_node;
head->next = new_node;
}
void remove_node(Node* node)
{
node->pre->next = node->next;
node->next->pre = node->pre;
}
private:
int _capacity;
Node* head;
Node* tail;
int size=0;
unordered_map<int,Node*> my_map;
};
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache* obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj->get(key);
* obj->put(key,value);
*/
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
215. 数组中的第K个最大元素
215. 数组中的第K个最大元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)
描述
给定整数数组 nums 和整数 k,请返回数组中第 k 个最大的元素。
请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。
你必须设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 的算法解决此问题。
示例
示例 1:
输入: [3,2,1,5,6,4], k = 2
输出: 5
示例 2:
输入: [3,2,3,1,2,4,5,5,6], k = 4
输出: 4
提示
1 <= k <= nums.length <= 105
-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
代码解析
库函数
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
return nums[nums.size()-k];
}
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
快速排序
class Solution {
public:
void swap(int &a , int &b)
{
int tmp = b;
b = a;
a = tmp;
}
int part(vector<int>& nums , int left , int right)
{
int key = nums[left];
while(left<right)
{
while(left < right && nums[right] <= key) right--;
swap(nums[left] , nums[right]);
while(left < right && nums[left] >= key) left++;
swap(nums[left] , nums[right]);
}
return left;
}
void quick_sort(vector<int>& nums , int left , int right)
{
if(left > right) return;
int mid = part(nums,left,right);
quick_sort(nums,left,mid-1);
quick_sort(nums,mid+1,right);
}
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
quick_sort(nums,0,nums.size()-1);
return nums[k-1];
}
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
快速排序
class Solution {
public:
void quickSort(vector<int>& arr, int left, int right)
{
// 定义枢轴
int pivot = arr[(left + right) / 2];
//int pivot = arr[left]; 也可以
// 定义两个指针
int i = left;
int j = right;
// 当左指针比右指针小时继续循环
while (i <= j)
{
// 左指针从左往右扫描,直到找到一个元素比枢轴大
while (arr[i] > pivot) i++;
// 右指针从右往左扫描,直到找到一个元素比枢轴小
while (arr[j] < pivot) j--;
// 如果两个指针没有相遇,交换它们所指向的元素
if (i <= j)
{
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
i++;
j--;
}
}
// 如果左边还有元素,递归左边的排序
if (left < j) quickSort(arr, left, j);
// 如果右边还有元素,递归右边的排序
if (i < right) quickSort(arr, i, right);
}
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
quickSort(nums,0,nums.size()-1);
return nums[k-1];
}
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
25. K 个一组翻转链表
描述
给你链表的头节点 head ,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回修改后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例
示例 1:
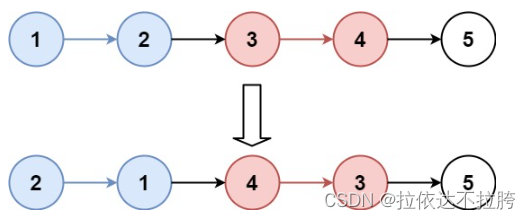
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
示例 2:
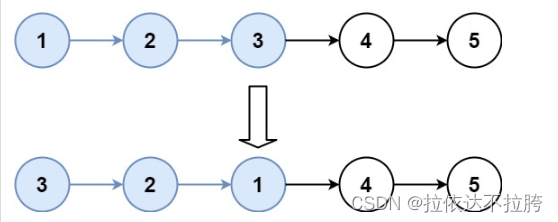
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3
输出:[3,2,1,4,5]
提示
链表中的节点数目为 n
1 <= k <= n <= 5000
0 <= Node.val <= 1000
进阶:你可以设计一个只用 O(1) 额外内存空间的算法解决此问题吗?
代码解析
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
stack<int> my_stack;
vector<int> v_nums;
ListNode* tmp = head;
int num = 0;
while(tmp != nullptr && num < k)
{
num++;
v_nums.push_back(tmp->val);
my_stack.push(tmp->val);
if(num == k)
{
while(num--) v_nums.pop_back();
num = k;
while(num--)
{
v_nums.push_back(my_stack.top());
my_stack.pop();
}
cout<<num<<' ';
num = 0;
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
tmp = head;
int i=0;
while(tmp != nullptr)
{
tmp->val = v_nums[i];
tmp = tmp->next;
i++;
}
return head;
}
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48


