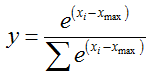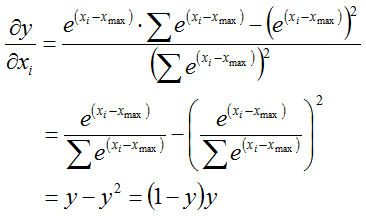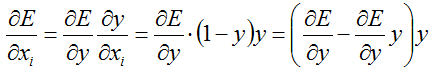- 1操作系统进程实验课程设计_试编制一个程序段, 完成下图所示流程图的功能。
- 2python中npy转txt文件(科学计数法/十进制类型)_npy文件
- 3详解进程虚拟地址空间区域划分_进程地址空间怎么识别地址是什么区的
- 4DNS学习总结_dns服务器配置实验心得
- 5Multi-Video Temporal Synchronization论文笔记_multi-camera spatio-temporal synchronization
- 6MYSQL每日一用:SELECT 语句中比对(between and \ like \ left)
- 7es6标准下ajax类封装及使用_使用es6class封装ajax类
- 8【jellyfin】解决使用自定义域名和免费ssl证书安卓端无法访问服务器的问题_jellyfin绑定域名
- 9Ubuntu 安装pytorch指定版本_ubuntu torch==2.1.2 安装制定版本
- 10CentOS停服遭替代,这些操作差异,你了解了吗?_centos7.9 替代
caffe-损失层-SoftmaxWithLossLayer 和SoftmaxLayer_softmaxloss layer是什么层
赞
踩
类SoftmaxWithLossLayer包含类SoftmaxLayer的实例。其中SoftmaxLayer层在正向传导函数中将64*10的bottom_data,通过计算得到64*10的top_data。这可以理解为输入数据为64个样本,每个样本特征数量为10,计算这64个样本分别在10个类别上的概率。公式如下,其中n=10,
SoftmaxWithLossLayer层利用SoftmaxLayer层的输出计算损失,公式如下,其中N为一个batch的大小(MNIST训练时batch_size为64,测试时batch_size为100)。 根据Cross-Entropy的定义有,
反向传导时,计算偏导
需要注意的一点是,在反向传导时SoftmaxWithLossLayer层并没有向正向传导时借用SoftmaxLayer层实现一部分,而是一手全部包办了。因此SoftmaxLayer::Backward_cpu()函数也就被闲置了。
如果网络在训练期间发散了,则最终计算结果accuracy ≈ 0.1(说明机器完全没有预测精度,纯靠蒙), loss ≈-log(0.1) = 2.3026。如果大家看见loss为2.3左右,就应该了解当前网络没有收敛,需要调节参数配置。至于怎么调节嘛,这往往就依赖经验了……
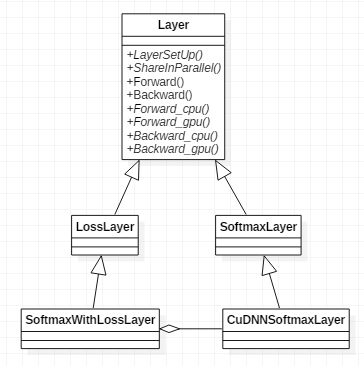
几个类的类关系图如下图所示,
为了搞清楚传导的流程,我们首先看下SoftmaxLayer是如何工作的,头文件为softmax_layer.hpp
- template <typename Dtype>
- class SoftmaxLayer : public Layer<Dtype> {
- public:
- explicit SoftmaxLayer(const LayerParameter& param)
- : Layer<Dtype>(param) {}
- virtual void Reshape(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
- const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
-
- virtual inline const char* type() const { return "Softmax"; }
- virtual inline int ExactNumBottomBlobs() const { return 1; }
- virtual inline int ExactNumTopBlobs() const { return 1; }
-
- protected:
- // 重载CPU和GPU正反向传导虚函数
- virtual void Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
- const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
- virtual void Forward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
- const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
- virtual void Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
- const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom);
- virtual void Backward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
- const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom);
-
- int outer_num_;
- int inner_num_;
- int softmax_axis_;
- /// 乘子
- Blob<Dtype> sum_multiplier_;
- /// scale is an intermediate Blob to hold temporary results.
- Blob<Dtype> scale_;
- };
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31

这里的sum_multiplier_一样全部被初始化为1了的。而scale_的大小尺寸有点奇怪,在批处理的时候通常都会有num这个东西来表示数量,而scale又是单通道的。
大概是要将所有通道的数据的计算结果全部放在一起吧。
实现在softmax_layer.cpp文件中,
- template <typename Dtype>
- void SoftmaxLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
- const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
- softmax_axis_ =
- bottom[0]->CanonicalAxisIndex(this->layer_param_.softmax_param().axis());
- top[0]->ReshapeLike(*bottom[0]);
- vector<int> mult_dims(1, bottom[0]->shape(softmax_axis_));
- sum_multiplier_.Reshape(mult_dims);
- Dtype* multiplier_data = sum_multiplier_.mutable_cpu_data();
- // 乘子初始化为1
- caffe_set(sum_multiplier_.count(), Dtype(1), multiplier_data);
- outer_num_ = bottom[0]->count(0, softmax_axis_);
- inner_num_ = bottom[0]->count(softmax_axis_ + 1);
- vector<int> scale_dims = bottom[0]->shape();
- scale_dims[softmax_axis_] = 1;
- scale_.Reshape(scale_dims);
- }
-
- // CPU正向传导
- template <typename Dtype>
- void SoftmaxLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
- const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
- const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data();
- Dtype* top_data = top[0]->mutable_cpu_data();
- Dtype* scale_data = scale_.mutable_cpu_data();
- int channels = bottom[0]->shape(softmax_axis_);
- int dim = bottom[0]->count() / outer_num_;
- caffe_copy(bottom[0]->count(), bottom_data, top_data);
- // 遍历bottom_data查找最大值,存入scale_data
- for (int i = 0; i < outer_num_; ++i) {
- // 初始化scale_data为bottom_data首元素
- caffe_copy(inner_num_, bottom_data + i * dim, scale_data);
- for (int j = 0; j < channels; j++) {
- for (int k = 0; k < inner_num_; k++) {
- scale_data[k] = std::max(scale_data[k],
- bottom_data[i * dim + j * inner_num_ + k]);
- }
- }
- // 减去最大值(top_data = bottom_data - max(bottom_data))
- caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, channels, inner_num_,
- 1, -1., sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), scale_data, 1., top_data);
- // exp求幂
- caffe_exp<Dtype>(dim, top_data, top_data);
- // 累加求和,存放在scale_data中
- caffe_cpu_gemv<Dtype>(CblasTrans, channels, inner_num_, 1.,
- top_data, sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), 0., scale_data);
- // division
- for (int j = 0; j < channels; j++) {
- // top_data = top_data / scale_data
- caffe_div(inner_num_, top_data, scale_data, top_data);
- // 加偏移跳转指针
- top_data += inner_num_;
- }
- }
- }
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85

从代码中可以看到,反向的时候,批处理中每个图像是分别处理的:
先将某个图像按照通道维度计算最大值,存入scale_data中,所以感觉上scale_data只需要height*width大小的存储空间就够了,但是实际上却开辟了num*height*width。
这里的反向计算过程中可能与斯坦福的介绍稍微有点差别,不过原理上都是一样的,这里的反向计算如下:
假设某一个图像在某一个(channel, height, width)的坐标上的数据为x,在通道(channel, :, :)上的最大值为x_max;
在for后面的两个小for里面就是计算这个x_max;
之后的计算可以理解成遍历该通道的所有数据:(实际上是所有通道一起计算的)
之后再计算: x - x_max;
再之后计算指数:exp(x-x_max);
在求和这些指数:sum(x: exp(x-x_max));
最后再用除法,即:
在源码中解释道了为什么要减去最大值,这是因为避免所谓的“数值问题”,那么到底是什么问题呢?我们知道指数函数是一个严格递增的函数,如果直接使用x的话,可能会造成大数吃小数的问题,因为sum的分母会因为某一个x很大而整体很大,其余的很多小x都会因此变得非常小。估计源码中说到的就是这个问题吧。
整个反向过程看完了,还是不明白为啥scale_data开辟的空间会比实际使用的大很多呢?
- // CPU反向传导(此函数未被调用)
- template <typename Dtype>
- void SoftmaxLayer<Dtype>::Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
- const vector<bool>& propagate_down,
- const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {
- const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->cpu_diff();
- const Dtype* top_data = top[0]->cpu_data();
- Dtype* bottom_diff = bottom[0]->mutable_cpu_diff();
- Dtype* scale_data = scale_.mutable_cpu_data();
- int channels = top[0]->shape(softmax_axis_);
- int dim = top[0]->count() / outer_num_;
- caffe_copy(top[0]->count(), top_diff, bottom_diff);
- for (int i = 0; i < outer_num_; ++i) {
- // 计算top_diff和top_data的点积
- for (int k = 0; k < inner_num_; ++k) {
- scale_data[k] = caffe_cpu_strided_dot<Dtype>(channels,
- bottom_diff + i * dim + k, inner_num_,
- top_data + i * dim + k, inner_num_);
- }
- // 从bottom_diff减去该值
- caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, channels, inner_num_, 1,
- -1., sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), scale_data, 1., bottom_diff + i * dim);
- }
- // 逐点相乘
- caffe_mul(top[0]->count(), bottom_diff, top_data, bottom_diff);
-
- // 以上步骤等价于bottom_diff = top_diff * (top_data - top_data * top_data)
- // 此公式更容易推导和理解
- }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85

反向的过程其实很优雅,说优雅是因为softmax本身就非常优雅,看似很复杂的函数表达式,导数的计算确实非常的简便:
所以,误差传递过程是:
这个误差传递的过程,也是源码的计算思路过程:
先直接将top_diff存入bottom_diff中;
再计算这个误差与top_data的乘积存放在scale_data中;
在计算误差减掉scale_data,还是存放在bottom_diff中;
最后再计算bottom_diif与top_data的乘积,存入bottom_diff中。
再回过来看SoftmaxWithLossLayer的源代码,先看一下它的基类LossLayer是如何实现的。
- template <typename Dtype>
- class LossLayer : public Layer<Dtype> {
- public:
- explicit LossLayer(const LayerParameter& param)
- : Layer<Dtype>(param) {}
- virtual void LayerSetUp(
- const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
- virtual void Reshape(
- const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
-
- virtual inline int ExactNumBottomBlobs() const { return 2; }
-
- // 自动添加top blob
- virtual inline bool AutoTopBlobs() const { return true; }
- virtual inline int ExactNumTopBlobs() const { return 1; }
-
- virtual inline bool AllowForceBackward(const int bottom_index) const {
- return bottom_index != 1;
- }
- };
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20

cpp实现如下,
- template <typename Dtype>
- void LossLayer<Dtype>::LayerSetUp(
- const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
- // LossLayers have a non-zero (1) loss by default.
- if (this->layer_param_.loss_weight_size() == 0) {
- this->layer_param_.add_loss_weight(Dtype(1));
- }
- }
-
- template <typename Dtype>
- void LossLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(
- const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
- CHECK_EQ(bottom[0]->num(), bottom[1]->num())
- << "The data and label should have the same number.";
- vector<int> loss_shape(0); // Loss layers output a scalar; 0 axes.
- top[0]->Reshape(loss_shape);
- }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17

再看一下子类SoftmaxWithLossLayer的实现,
- template <typename Dtype>
- class SoftmaxWithLossLayer : public LossLayer<Dtype> {
- public:
- // 构造函数
- explicit SoftmaxWithLossLayer(const LayerParameter& param)
- : LossLayer<Dtype>(param) {}
- virtual void LayerSetUp(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
- const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
- virtual void Reshape(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
- const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
-
- virtual inline const char* type() const { return "SoftmaxWithLoss"; }
- virtual inline int ExactNumTopBlobs() const { return -1; }
- virtual inline int MinTopBlobs() const { return 1; }
- virtual inline int MaxTopBlobs() const { return 2; }
-
- protected:
- // 重载CPU和GPU正反向传导虚函数
- virtual void Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
- const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
- virtual void Forward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
- const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
-
- virtual void Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
- const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom);
- virtual void Backward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
- const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom);
-
- // 返回归一化计数
- virtual Dtype get_normalizer(
- LossParameter_NormalizationMode normalization_mode, int valid_count);
-
- /// SoftmaxLayer类实例
- shared_ptr<Layer<Dtype> > softmax_layer_;
- /// prob_作为SoftmaxLayer的输出blob
- Blob<Dtype> prob_;
- /// 指针指向bottom[0],作为SoftmaxLayer的输入blob
- vector<Blob<Dtype>*> softmax_bottom_vec_;
- /// 指针指向prob_
- vector<Blob<Dtype>*> softmax_top_vec_;
- /// 标识位,是否忽略标签
- bool has_ignore_label_;
- /// 被忽略的标签值
- int ignore_label_;
- /// 标识如何归一化loss
- LossParameter_NormalizationMode normalization_;
-
- // 维数、输出样本数
- int softmax_axis_, outer_num_, inner_num_;
- };
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50

softmax_loss_layer.cpp定义如下,
- template <typename Dtype>
- void SoftmaxWithLossLayer<Dtype>::LayerSetUp(
- const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
- LossLayer<Dtype>::LayerSetUp(bottom, top);
- LayerParameter softmax_param(this->layer_param_);
- softmax_param.set_type("Softmax");
- // 创建SoftmaxLayer层
- softmax_layer_ = LayerRegistry<Dtype>::CreateLayer(softmax_param);
- softmax_bottom_vec_.clear();
- // bottom[0]作为SoftmaxLayer层输入
- softmax_bottom_vec_.push_back(bottom[0]);
- softmax_top_vec_.clear();
- // prob_作为SoftmaxLayer层输出
- softmax_top_vec_.push_back(&prob_);
- // 建立SoftmaxLayer层
- softmax_layer_->SetUp(softmax_bottom_vec_, softmax_top_vec_);
-
- has_ignore_label_ =
- this->layer_param_.loss_param().has_ignore_label();
- if (has_ignore_label_) {
- // 如果支持忽略标签,则读取被忽略标签的值
- ignore_label_ = this->layer_param_.loss_param().ignore_label();
- }
- // 确定归一化计数方式
- if (!this->layer_param_.loss_param().has_normalization() &&
- this->layer_param_.loss_param().has_normalize()) {
- normalization_ = this->layer_param_.loss_param().normalize() ?
- LossParameter_NormalizationMode_VALID :
- LossParameter_NormalizationMode_BATCH_SIZE;
- } else {
- normalization_ = this->layer_param_.loss_param().normalization();
- }
- }
-
- template <typename Dtype>
- void SoftmaxWithLossLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(
- const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
- LossLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(bottom, top);
- softmax_layer_->Reshape(softmax_bottom_vec_, softmax_top_vec_);
- softmax_axis_ =
- bottom[0]->CanonicalAxisIndex(this->layer_param_.softmax_param().axis());
- outer_num_ = bottom[0]->count(0, softmax_axis_);
- inner_num_ = bottom[0]->count(softmax_axis_ + 1);
- CHECK_EQ(outer_num_ * inner_num_, bottom[1]->count())
- << "Number of labels must match number of predictions; "
- << "e.g., if softmax axis == 1 and prediction shape is (N, C, H, W), "
- << "label count (number of labels) must be N*H*W, "
- << "with integer values in {0, 1, ..., C-1}.";
- if (top.size() >= 2) {
- // softmax output
- top[1]->ReshapeLike(*bottom[0]);
- }
- }
-
- // 返回归一化计数
- template <typename Dtype>
- Dtype SoftmaxWithLossLayer<Dtype>::get_normalizer(
- LossParameter_NormalizationMode normalization_mode, int valid_count) {
- Dtype normalizer;
- switch (normalization_mode) {
- case LossParameter_NormalizationMode_FULL:
- // 返回全部输出样本数
- normalizer = Dtype(outer_num_ * inner_num_);
- break;
- case LossParameter_NormalizationMode_VALID:
- if (valid_count == -1) {
- normalizer = Dtype(outer_num_ * inner_num_);
- } else {
- // 只返回有效统计的样本数
- normalizer = Dtype(valid_count);
- }
- break;
- case LossParameter_NormalizationMode_BATCH_SIZE:
- normalizer = Dtype(outer_num_);
- break;
- case LossParameter_NormalizationMode_NONE:
- normalizer = Dtype(1);
- break;
- default:
- LOG(FATAL) << "Unknown normalization mode: "
- << LossParameter_NormalizationMode_Name(normalization_mode);
- }
- // 防止使用不带标签的数据出现归一化计数为0,从而导致分母为零
- return std::max(Dtype(1.0), normalizer);
- }
-
- // CPU正向传导
- template <typename Dtype>
- void SoftmaxWithLossLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(
- const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
- // 先对SoftmaxLayer层正向传导
- softmax_layer_->Forward(softmax_bottom_vec_, softmax_top_vec_);
- const Dtype* prob_data = prob_.cpu_data();
- const Dtype* label = bottom[1]->cpu_data();
- int dim = prob_.count() / outer_num_;
- int count = 0;
- Dtype loss = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < outer_num_; ++i) {
- for (int j = 0; j < inner_num_; j++) {
- // 取出真实标签值
- const int label_value = static_cast<int>(label[i * inner_num_ + j]);
- if (has_ignore_label_ && label_value == ignore_label_) {
- continue;
- }
- DCHECK_GE(label_value, 0);
- DCHECK_LT(label_value, prob_.shape(softmax_axis_));
- // 从SoftmaxLayer层输出(prob_data)中,找到与标签值对应位的预测概率,对其取-log,并对batch_size个值累加
- loss -= log(std::max(prob_data[i * dim + label_value * inner_num_ + j],
- Dtype(FLT_MIN)));
- ++count;
- }
- }
- // loss除以样本总数batch,得到平均单个样本的loss
- top[0]->mutable_cpu_data()[0] = loss / get_normalizer(normalization_, count);
- if (top.size() == 2) {
- top[1]->ShareData(prob_);
- }
- }
-
- // CPU反向传导
- template <typename Dtype>
- void SoftmaxWithLossLayer<Dtype>::Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
- const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {
- if (propagate_down[1]) {
- LOG(FATAL) << this->type()
- << " Layer cannot backpropagate to label inputs.";
- }
- if (propagate_down[0]) {
- Dtype* bottom_diff = bottom[0]->mutable_cpu_diff();
- const Dtype* prob_data = prob_.cpu_data();
- // 先将正向传导时计算的prob_数据(f(y_k))拷贝至偏导
- caffe_copy(prob_.count(), prob_data, bottom_diff);
- const Dtype* label = bottom[1]->cpu_data();
- int dim = prob_.count() / outer_num_;
- int count = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < outer_num_; ++i) {
- for (int j = 0; j < inner_num_; ++j) {
- const int label_value = static_cast<int>(label[i * inner_num_ + j]);
- // 如果为忽略标签,则偏导为0
- if (has_ignore_label_ && label_value == ignore_label_) {
- for (int c = 0; c < bottom[0]->shape(softmax_axis_); ++c) {
- bottom_diff[i * dim + c * inner_num_ + j] = 0;
- }
- } else {
- // 计算偏导,预测正确的bottom_diff = f(y_k) - 1,其它不变
- bottom_diff[i * dim + label_value * inner_num_ + j] -= 1;
- ++count;
- }
- }
- }
- // top[0]->cpu_diff()[0] = 1.0,已在SetLossWeights()函数中初始化
- Dtype loss_weight = top[0]->cpu_diff()[0] /
- get_normalizer(normalization_, count);
- // 将bottom_diff归一化
- caffe_scal(prob_.count(), loss_weight, bottom_diff);
- }
- }

反向传导时,计算偏导
需要注意的一点是,在反向传导时SoftmaxWithLossLayer层并没有向正向传导时借用SoftmaxLayer层实现一部分,而是一手全部包办了。因此SoftmaxLayer::Backward_cpu()函数也就被闲置了。