- 1Faster_Rcnn误检解决方案---强制负样本策略
- 2android的内存泄漏有几种,常见Android内存泄漏类型
- 3[Vuex系列] - 细说state的几种用法
- 4总结php的面试题_warning: include(./includes/fun.global.php): faile
- 5Android图表年度最强总结,一篇文章从入门到精通_android 图表
- 6NSLocalizedString和设备支持的语…_#define nslocalizedstring(key, comment) \ [nsbund
- 7Postgresql垃圾回收原理分析_postgresql 进程回收
- 8Faster-RCNN论文及原码解读_fast rcnn论文
- 99、法律法规与标准化知识
- 10springboot整合vosk实现简单的语音识别功能
SSD300网络结构(pytorch)+多尺度训练与测试
赞
踩
一.SSD300
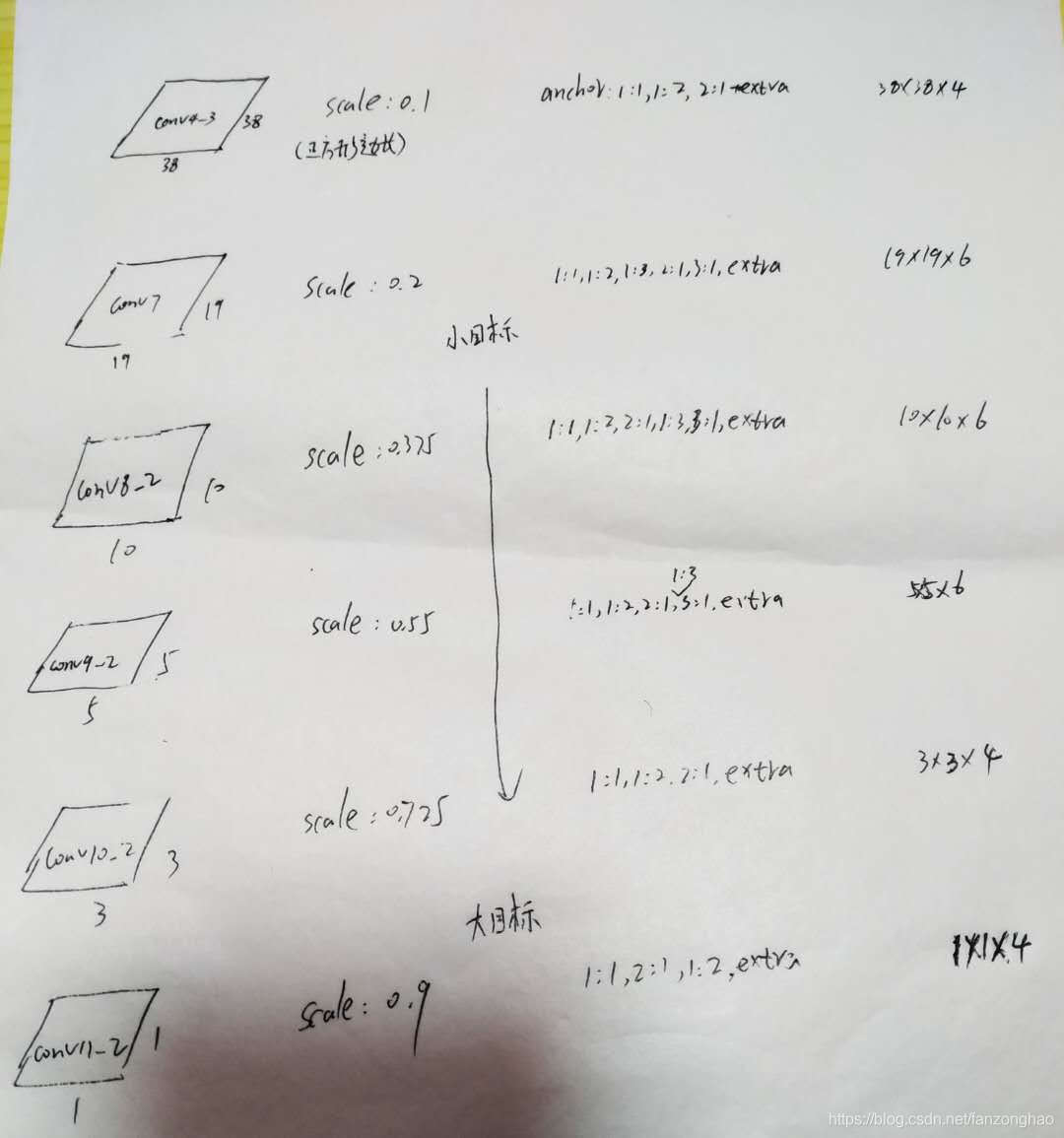
1.如图是预测框的相应feature map
![]()
这里smin是0.2,表示最底层的scale是0.2;smax是0.9,表示最高层的scale是0.9,m代表产生尺度预测的feature map个数。
其中anchor的长宽关系,s就是上图中的scale,a就是上图中的anchor ratio

2.代码
主要由三部分组成
1.vgg作为基础网络

要注意的是作者对38*38*512进行L2正则化,并用一个可学习参数调节通道权重

2.增加大目标检测网络
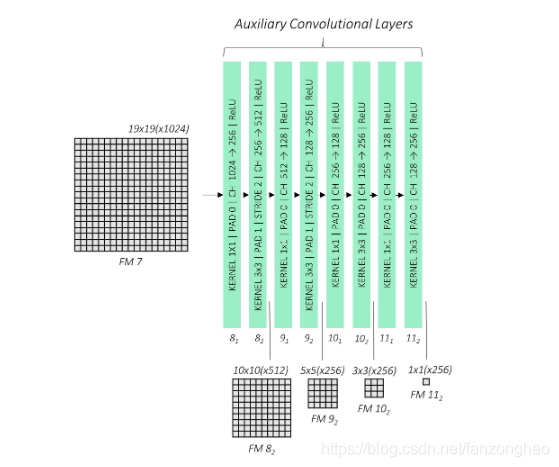
3.输出包括预测框的偏移量输出与分类
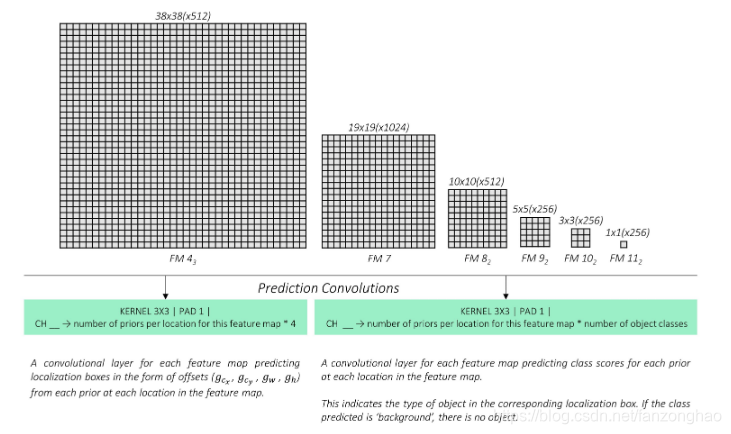
偏移量计算,神经网络学习偏移量即可。


误检的HEM(hard negative mine)loss函数,用于分类

1.回归量与坐标的转换
- def cxcy_to_gcxgcy(cxcy, priors_cxcy):
-
- # See https://github.com/weiliu89/caffe/issues/155
- return torch.cat([(cxcy[:, :2] - priors_cxcy[:, :2]) / (priors_cxcy[:, 2:] / 10), # g_c_x, g_c_y
- torch.log(cxcy[:, 2:] / priors_cxcy[:, 2:]) * 5], 1) # g_w, g_h
-
-
- def gcxgcy_to_cxcy(gcxgcy, priors_cxcy):
-
- return torch.cat([gcxgcy[:, :2] * priors_cxcy[:, 2:] / 10 + priors_cxcy[:, :2], # c_x, c_y
- torch.exp(gcxgcy[:, 2:] / 5) * priors_cxcy[:, 2:]], 1) # w, h
2.anchor与gt框匹配示例,保证每个gt至少有一个anchor
-
- #两个gt框 3个anchor 的框分配示例
- import torch
- objects = 2
- overlap = torch.tensor([[0.4, 0.5, 0.6],
- [0.8, 0.9, 0.7]])
- iou_for_each_prior, index_for_each_prior = torch.max(overlap, dim=0)
- print(iou_for_each_prior, index_for_each_prior)
-
- iou_for_each_box, index_for_each_box = torch.max(overlap, dim=1)
- print(iou_for_each_box, index_for_each_box)
-
- index_for_each_prior[index_for_each_box] = torch.LongTensor(range(objects))
- print(index_for_each_prior)

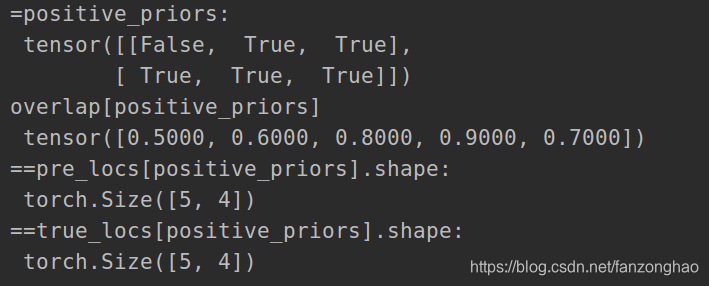
3.gt框与对应anchor框做回归的示例,其中的true_classes是两个样本,每一个样本有3个box框的类别示例,0代表背景
-
- #两个gt框 3个anchor 的框分配示例
- import torch
- objects = 2
- overlap = torch.tensor([[0.4, 0.5, 0.6],
- [0.8, 0.9, 0.7]])
- iou_for_each_prior, index_for_each_prior = torch.max(overlap, dim=0)
- print(iou_for_each_prior, index_for_each_prior)
-
- iou_for_each_box, index_for_each_box = torch.max(overlap, dim=1)
- print(iou_for_each_box, index_for_each_box)
-
- index_for_each_prior[index_for_each_box] = torch.LongTensor(range(objects))
- print(index_for_each_prior)
-
- batch_size = 2
- true_classes = torch.tensor([[0, 1, 3],#每一个样本3个box框的类别示例,0代表背景
- [2, 4, 5]])
- positive_priors = true_classes != 0
- print('=positive_priors:\n', positive_priors)
-
-
- pre_locs = torch.rand((batch_size, 3, 4))
- print('==pre_locs[positive_priors].shape:\n', pre_locs[positive_priors].shape)
-
- true_locs = torch.rand((batch_size, 3, 4))
- print('==true_locs[positive_priors].shape:\n', true_locs[positive_priors].shape)

4.总体代码:
- import torch
- import os
- from torch import nn
- import torch.nn.functional as F
- import torchvision
- from torchvision import models
- from utils import decimate, find_jaccard_overlap, cxcy_to_xy, xy_to_cxcy
- from utils import cxcy_to_gcxgcy as cx_cy_dxdy
- from math import sqrt
- # vgg16 = models.vgg16(pretrained=True)
- # print(vgg16)
- # vgg16_state_dict = vgg16.state_dict()
- # print(list(vgg16_state_dict.keys()))
- # print(vgg16_state_dict.values())
- # for key, value in vgg16.named_parameters():
- # print('key:', key)
-
- device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
-
- class VGGbase(nn.Module):
- """vgg 主干网络"""
- def __init__(self):
- super(VGGbase, self).__init__()
- self.conv1_1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
- self.conv1_2 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
- self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
-
- self.conv2_1 = nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
- self.conv2_2 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
- self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
-
- self.conv3_1 = nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
- self.conv3_2 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
- self.conv3_3 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
- self.pool3 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
-
- self.conv4_1 = nn.Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
- self.conv4_2 = nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
- self.conv4_3 = nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
- self.pool4 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
-
- self.conv5_1 = nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
- self.conv5_2 = nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
- self.conv5_3 = nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
- self.pool5 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)#为了保证尺寸不在减少
-
- self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(512, 1024, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=6, dilation=6)#空洞卷积扩大感受野
- self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(1024, 1024, kernel_size=1)
-
- self.load_pretrained_layers()#载入预训练权重
- #(BS, 3, 300, 300)
- def forward(self, image):
- out = F.relu(self.conv1_1(image))
- out = F.relu(self.conv1_2(out))
- out = self.pool1(out)#(B,64, 150, 150)
- out = F.relu(self.conv2_1(out))
- out = F.relu(self.conv2_2(out))
- out = self.pool2(out) #(B, 128, 75, 75)
- out = F.relu(self.conv3_1(out))
- out = F.relu(self.conv3_2(out))
- out = F.relu(self.conv3_3(out))
- out = self.pool3(out) # (B, 256, 38, 38)
- out = F.relu(self.conv4_1(out))
- out = F.relu(self.conv4_2(out))
- out = F.relu(self.conv4_3(out))
- conv4_3feats = out # (B, 512, 38, 38)
- out = self.pool4(out) # (B, 512, 19, 19)
- out = F.relu(self.conv5_1(out))
- out = F.relu(self.conv5_2(out))
- out = F.relu(self.conv5_3(out))
- out = self.pool5(out) # (B, 512, 19, 19)
- out = F.relu(self.conv6(out))
- conv7_feats = F.relu(self.conv7(out))# (B, 1024, 19, 19)
- # print(out.shape)
- return conv4_3feats, conv7_feats
- def load_pretrained_layers(self):
- state_dict = self.state_dict()
- param_name = list(state_dict.keys())
- print('param_name', param_name)
-
- pretrained_state_dict = models.vgg16(pretrained=True).state_dict()
- pretrained_param_name = list(pretrained_state_dict.keys())
- print('pretrained_param_name', pretrained_param_name)
- #由于最后两层与原vgg网络相比多出来的,故权重和偏置要点到为止
- for i, param in enumerate(param_name[:-4]):
- # print('pretrained_state_dict[pretrained_param_name[i]].shape', pretrained_state_dict[pretrained_param_name[i]].shape)
- state_dict[param] = pretrained_state_dict[pretrained_param_name[i]]
-
- # #最后两层的权重由分类器权重修改而来
- # print("pretrained_state_dict['classifier.0.weight'].shape",pretrained_state_dict['classifier.0.weight'].shape)
- conv_fc6_weight = pretrained_state_dict['classifier.0.weight'].reshape(4096, 512, 7, 7)
- # print('===conv_fc6_weight.dim()==', conv_fc6_weight.dim())
- state_dict['conv6.weight'] = decimate(conv_fc6_weight, m=[4, None, 3, 3])#(1024, 512, 3, 3)
- conv_fc6_bias = pretrained_state_dict['classifier.0.bias']#(4096)
- state_dict['conv6.bias'] = decimate(conv_fc6_bias, m=[4])#(1024)
- # print(pretrained_state_dict['classifier.3.weight'].shape)
- # print(pretrained_state_dict['classifier.6.weight'].shape)
-
- conv_fc7_weight = pretrained_state_dict['classifier.3.weight'].reshape(4096, 4096, 1, 1)
- state_dict['conv7.weight'] = decimate(conv_fc7_weight, m=[4, 4, None, None]) # (1024, 1024, 1, 1)
- conv_fc7_bias = pretrained_state_dict['classifier.3.bias'] # (4096)
- state_dict['conv7.bias'] = decimate(conv_fc7_bias, m=[4]) # (1024)
-
- self.load_state_dict(state_dict)
-
- class AuxiliaryConvolutions(nn.Module):
- "继续在vgg基础上添加conv网络"
- def __init__(self):
- super(AuxiliaryConvolutions, self).__init__()#调用父类初始化
- self.conv8_1 = nn.Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
- self.conv8_2 = nn.Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
-
- self.conv8_1 = nn.Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
- self.conv8_2 = nn.Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
-
- self.conv9_1 = nn.Conv2d(512, 128, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
- self.conv9_2 = nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
-
- self.conv10_1 = nn.Conv2d(256, 128, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
- self.conv10_2 = nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
-
- self.conv11_1 = nn.Conv2d(256, 128, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
- self.conv11_2 = nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
-
- self.init_conv2d()
-
- def init_conv2d(self):
- for c in self.children():
- if isinstance(c, nn.Conv2d):
- nn.init.xavier_uniform_(c.weight)
- # nn.init.kaiming_normal_(c.weight)
- nn.init.constant_(c.bias, 0)
-
- def forward(self, input):
- out = F.relu(self.conv8_1(input))#(B,1024,19,19)
- out = F.relu(self.conv8_2(out)) #(B,512,19,19)
- conv8_2feats = out
- out = F.relu(self.conv9_1(out)) #(B,512,10,10)
- out = F.relu(self.conv9_2(out)) ##(B,256,5,5)
- conv9_2feats = out
- out = F.relu(self.conv10_1(out)) # (B,128,5,5)
- out = F.relu(self.conv10_2(out)) ##(B,256,3,3)
- conv10_2feats = out
- out = F.relu(self.conv11_1(out)) # (B,128,3,3)
- out = F.relu(self.conv11_2(out)) ##(B,256,1,1)
- conv11_2feats = out
- # print(out.size())
- return conv8_2feats, conv9_2feats, conv10_2feats, conv11_2feats
-
- class PredictionConvolutions(nn.Module):
- """卷积层输出框偏移量与分类"""
- def __init__(self, n_classes):
- super(PredictionConvolutions, self).__init__()
- self.n_classes = n_classes
- bboxs={
- 'conv4_3': 4,
- 'conv7': 6,
- 'conv8_2': 6,
- 'conv9_2': 6,
- 'conv10_2': 4,
- 'conv11_2': 4
- }
- self.loc_conv4_3 = nn.Conv2d(512, bboxs['conv4_3']*4, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
- self.loc_conv7 = nn.Conv2d(1024, bboxs['conv7'] * 4, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
- self.loc_conv8_2 = nn.Conv2d(512, bboxs['conv8_2'] * 4, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
- self.loc_conv9_2 = nn.Conv2d(256, bboxs['conv9_2'] * 4, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
- self.loc_conv10_2 = nn.Conv2d(256, bboxs['conv10_2'] * 4, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
- self.loc_conv11_2 = nn.Conv2d(256, bboxs['conv11_2'] * 4, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
-
- self.cl_conv4_3 = nn.Conv2d(512, bboxs['conv4_3'] * n_classes, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
- self.cl_conv7 = nn.Conv2d(1024, bboxs['conv7'] * n_classes, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
- self.cl_conv8_2 = nn.Conv2d(512, bboxs['conv8_2'] * n_classes, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
- self.cl_conv9_2 = nn.Conv2d(256, bboxs['conv9_2'] * n_classes, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
- self.cl_conv10_2 = nn.Conv2d(256, bboxs['conv10_2'] * n_classes, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
- self.cl_conv11_2 = nn.Conv2d(256, bboxs['conv11_2'] * n_classes, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
- self.init_conv2d()
-
- def init_conv2d(self):
- for c in self.children():
- if isinstance(c, nn.Conv2d):
- nn.init.xavier_uniform_(c.weight)
- # nn.init.kaiming_normal_(c.weight)
- nn.init.constant_(c.bias, 0)
- def forward(self, conv4_3feats,conv7_feats,conv8_2feats, conv9_2feats, conv10_2feats, conv11_2feats):
- batch_size = conv4_3feats.size(0)
- loc_conv4_3 = self.loc_conv4_3(conv4_3feats)#(N, 4*4, 38, 38)
- loc_conv4_3 = loc_conv4_3.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)#(N, 38, 38, 4*4)
- loc_conv4_3 = loc_conv4_3.reshape(batch_size, -1, 4)
- # print(loc_conv4_3.shape)
-
- loc_conv7 = self.loc_conv7(conv7_feats) # (N, 6*4, 19, 19)
- loc_conv7 = loc_conv7.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
- loc_conv7 = loc_conv7.reshape(batch_size, -1, 4)
-
- loc_conv8_2 = self.loc_conv8_2(conv8_2feats) # (N, 6*4, 10, 10)
- loc_conv8_2 = loc_conv8_2.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
- loc_conv8_2 = loc_conv8_2.reshape(batch_size, -1, 4)
-
- loc_conv9_2 = self.loc_conv9_2(conv9_2feats) # (N, 6*4, 5, 5)
- loc_conv9_2 = loc_conv9_2.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
- loc_conv9_2 = loc_conv9_2.reshape(batch_size, -1, 4)
-
- loc_conv10_2 = self.loc_conv10_2(conv10_2feats) # (N, 4*4, 3, 3)
- loc_conv10_2 = loc_conv10_2.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
- loc_conv10_2 = loc_conv10_2.reshape(batch_size, -1, 4)
-
- loc_conv11_2 = self.loc_conv11_2(conv11_2feats) # (N, 4*4, 1, 1)
- loc_conv11_2 = loc_conv11_2.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
- loc_conv11_2 = loc_conv11_2.reshape(batch_size, -1, 4)
-
- cl_conv4_3 = self.cl_conv4_3(conv4_3feats) # (N, 4*n_classes, 38, 38)
- cl_conv4_3 = cl_conv4_3.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
- cl_conv4_3 = cl_conv4_3.reshape(batch_size, -1, self.n_classes)
-
- cl_conv7 = self.cl_conv7(conv7_feats) # (N, 6*n_classes, 19, 19)
- cl_conv7 = cl_conv7.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
- cl_conv7 = cl_conv7.reshape(batch_size, -1, self.n_classes)
-
- cl_conv8_2 = self.cl_conv8_2(conv8_2feats) # (N, 6*n_classes, 10, 10)
- cl_conv8_2 = cl_conv8_2.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
- cl_conv8_2 = cl_conv8_2.reshape(batch_size, -1, self.n_classes)
-
- cl_conv9_2 = self.cl_conv9_2(conv9_2feats) # (N, 6*n_classes, 5, 5)
- cl_conv9_2 = cl_conv9_2.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
- cl_conv9_2 = cl_conv9_2.reshape(batch_size, -1, self.n_classes)
-
- cl_conv10_2 = self.cl_conv10_2(conv10_2feats) # (N, 4*n_classes, 3, 3)
- cl_conv10_2 = cl_conv10_2.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
- cl_conv10_2 = cl_conv10_2.reshape(batch_size, -1, self.n_classes)
-
- cl_conv11_2 = self.cl_conv11_2(conv11_2feats) # (N, 4*n_classes, 1, 1)
- cl_conv11_2 = cl_conv11_2.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
- cl_conv11_2 = cl_conv11_2.reshape(batch_size, -1, self.n_classes)
- # return loc_conv4_3, loc_conv7, loc_conv8_2, loc_conv9_2, loc_conv10_2, loc_conv11_2,\
- # cl_conv4_3, cl_conv7, cl_conv8_2, cl_conv9_2, cl_conv10_2, cl_conv11_2
- locs = torch.cat((loc_conv4_3, loc_conv7, loc_conv8_2, loc_conv9_2, loc_conv10_2, loc_conv11_2),dim=1)
- class_scores = torch.cat((cl_conv4_3, cl_conv7, cl_conv8_2, cl_conv9_2, cl_conv10_2, cl_conv11_2),dim=1)
- return locs,class_scores#(10, 8732, 4) (10, 8732, 21)
-
- class SSD300(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, n_classes):
- super(SSD300, self).__init__()
- self.n_classes = n_classes
- self.base_vgg = VGGbase()
- self.aux_convs = AuxiliaryConvolutions()
- self.pre_convs = PredictionConvolutions(self.n_classes)
-
- #对conv4_3添加每个通道添加可学习参数,并进行L2正则化
- self.rescale_factors = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(1, 512, 1, 1))
- nn.init.constant_(self.rescale_factors, 20)
-
- self.create_prior_boxes()
-
- def forward(self, input):
- conv4_3feats, conv7_feats = self.base_vgg(input)#(N,512,38,38) (N,1024,19,19)
- norm = torch.pow(conv4_3feats, 2).sum(dim=1, keepdim=True).sqrt()#(B, 1, 38, 38)对所有通道的每一行求平方和L2正则 开更号
- conv4_3feats = conv4_3feats/norm*self.rescale_factors
-
- conv8_2feats, conv9_2feats, conv10_2feats, conv11_2feats = self.aux_convs(conv7_feats)
-
- locs, class_scores = self.pre_convs(conv4_3feats, conv7_feats, conv8_2feats, conv9_2feats, conv10_2feats, conv11_2feats)
- return locs, class_scores#(10, 8732, 4) (10, 8732, 21)
-
- def create_prior_boxes(self):
- """创建SSD300的先验框(cx, cy, w, h)
- (8372,4)个box"""
- fmap_size = {'conv4_3': 38, 'conv7': 19, 'conv8_2': 10,
- 'conv9_2': 5, 'conv10_2': 3, 'conv11_2': 1}
- anchor_scale = {'conv4_3': 0.1, 'conv7': 0.2, 'conv8_2': 0.375,
- 'conv9_2': 0.55, 'conv10_2': 0.725, 'conv11_2': 0.9}
- anchor_ratio = {'conv4_3': [1, 2, 0.5], 'conv7': [1, 2, 3, 0.5, 0.33], 'conv8_2': [1, 2, 3, 0.5, 0.33],
- 'conv9_2': [1, 2, 3, 0.5, 0.33], 'conv10_2': [1, 2, 0.5], 'conv11_2': [1, 2, 0.5]}
- prior_boxes = []
- for index, fmap in enumerate(fmap_size):
- for i in range(fmap_size[fmap]):
- for j in range(fmap_size[fmap]):
- cy, cx = (i + 0.5) / fmap_size[fmap], (j + 0.5) / fmap_size[fmap]
- for ratio in anchor_ratio[fmap]:
- prior_boxes.append([cx, cy, anchor_scale[fmap] * sqrt(ratio), anchor_scale[fmap] / sqrt(ratio)])
-
- if ratio == 1: # 添加额外框
- try:
- extra_scale = sqrt(anchor_scale[fmap] * anchor_scale[fmap_size[index + 1]])
- except:
- extra_scale = 1.
- prior_boxes.append([cx, cy, extra_scale, extra_scale])
- # print('len(prior_boxes)',len(prior_boxes))
- # prior_boxes = [[1,2,3,4],
- # [3,4,5,6]]
- prior_boxes = torch.FloatTensor(prior_boxes).to(device)
- prior_boxes.clamp_(0, 1) # 防止越界
- print('prior_boxes.shape', prior_boxes.shape)
- # print(prior_boxes)
- return prior_boxes#(8732, 4)
-
- class MultiBoxLoss(nn.Module):
- """定位loss和分类loss,其中定位loss采用Hard Negative Mining."""
- def __init__(self, prior_cxcy, threshold=0.5, neg_pos_ratio=3, alph=1.):
- super(MultiBoxLoss, self).__init__()
- self.prior_cxcy = prior_cxcy#(8732,4)
- self.priors_xy = cxcy_to_xy(prior_cxcy)
- self.threshold = threshold
- self.neg_pos_ratio = neg_pos_ratio
- self.alph = alph
-
- self.smooth_l1 = nn.L1Loss()
- self.cross_entropy = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduce=False)#不计算batch的平均loss因为要用到hard mine模式
-
- def forward(self, prediction_locs, prediction_scores, boxes, labels):
- """
- prediction_locs,(N, 8732, 4)
- prediction_scores,(N, 8732, n_classes)
- boxes,[[],[[],[]]]
- labels[[],[]]
- """
- batch_size = prediction_locs.shape[0]#(N,)
- n_priors = self.prior_cxcy.shape[0]#(8732,)
- n_classes = prediction_scores.shape[-1]#(n_classes)
- # print('==batch_size', batch_size)
- assert batch_size == len(boxes)
- assert n_priors == prediction_locs.shape[1] == prediction_scores.shape[1]
-
- true_locs = torch.zeros((batch_size, n_priors, 4),dtype=torch.float)#(N, 8732, 4)
- true_classes = torch.zeros((batch_size, n_priors),dtype=torch.long)#(N, 8732)
- for i in range(batch_size):
- # print('===boxes[i]', boxes[i])
- objects = boxes[i].shape[0] #(objects, 4) (8732, 4)
- overlap = find_jaccard_overlap(boxes[i], self.priors_xy)#(objects, 8732)
- # 每个先验框与gt框的最大IOU 以及索引
- iou_for_each_prior, index_for_each_prior = overlap.max(dim=0)
- # 每个gt框与先验框的最大IOU 以及索引
- iou_for_each_box, index_for_each_box = overlap.max(dim=1)
-
- #为了防止没有相应的先验框与gt相交
- index_for_each_prior[index_for_each_box] = torch.LongTensor(range(objects)).to(device)
- iou_for_each_prior[index_for_each_box] = 1.
-
- label_for_each_prior = labels[i][index_for_each_prior]#得到对应的每个先验框的标签
- label_for_each_prior[iou_for_each_prior<self.threshold] = 0#将小于阈值的置为背景
-
- #依次存储batchsize
- true_classes[i] = label_for_each_prior
- true_locs[i] = cx_cy_dxdy(xy_to_cxcy(boxes[i][index_for_each_prior]), self.prior_cxcy)#得到偏移量
- print('true_classes.dtype',true_classes.dtype)
- positive_priors = true_classes != 0#batch_size 正样本(N,8732)
- print('positive_priors.dtype',positive_priors.dtype)
- print('==positive_priors.shape', positive_priors.shape)
- print('==positive_priors', positive_priors)
- loc_loss = self.smooth_l1(prediction_locs[positive_priors], true_locs[positive_priors])
- n_postives = positive_priors.sum(dim=1)#(N,)
- n_hard_negatives = self.neg_pos_ratio*n_postives#(N,)
-
- confidence_loss_all = self.cross_entropy(prediction_scores.reshape(-1, n_classes), true_classes.reshape(-1))
- confidence_loss_all = confidence_loss_all.reshape(batch_size, n_priors)
- print('==confidence_loss_all.shape', confidence_loss_all.shape)
- confidence_loss_pos = confidence_loss_all[positive_priors]
- #
- print('==confidence_loss_pos.shape', confidence_loss_pos.shape)
-
- confidence_loss_neg = confidence_loss_all.clone()#(N, 8732)
- confidence_loss_neg[positive_priors] = 0.#(N, 8732)#把正样本loss清零再去做HEM
- confidence_loss_neg, _ = confidence_loss_neg.sort(dim=1, descending=True)#(N,8732)按行从大到小
- hardness_ranks = torch.LongTensor(range(n_priors)).unsqueeze(0).expand_as(confidence_loss_neg) # (N, 8732)
- hard_negatives = hardness_ranks < n_hard_negatives.unsqueeze(1) # (N, 8732)
- confidence_loss_hard = confidence_loss_all[hard_negatives]
- # print('==confidence_loss_hard.shape', confidence_loss_hard.shape)
- confidence_loss = (confidence_loss_pos.sum()+confidence_loss_hard.sum())/n_postives.sum().float()
-
- return loc_loss+self.alph*confidence_loss
-
- def test_vgg_base():
- model = VGGbase()
- x = torch.rand((10, 3, 300, 300))
- conv4_3feats, conv7_feats = model(x)
- print('conv4_3feats.shape:', conv4_3feats.shape)
- print('conv7_feats.shape:', conv7_feats.shape)
- def test_AUx_conv():
- model = AuxiliaryConvolutions()
- # (B, 1024, 19, 19)
- x = torch.rand((10, 1024, 19, 19))
- conv8_2feats, conv9_2feats, conv10_2feats, conv11_2feats = model(x)
- print('conv8_2feats.shape:', conv8_2feats.shape)
- print('conv9_2feats.shape:', conv9_2feats.shape)
- print('conv10_2feats.shape:', conv10_2feats.shape)
- print('conv11_2feats.shape:', conv11_2feats.shape)
-
- def test_pre_conv():
- n_classes = 21
- model = PredictionConvolutions(n_classes)
- conv4_3feats = torch.rand((10, 512, 38, 38))
- conv7_feats = torch.rand((10, 1024, 19, 19))
- conv8_2feats = torch.rand((10, 512, 10, 10))
- conv9_2feats = torch.rand((10, 256, 5, 5))
- conv10_2feats = torch.rand((10, 256, 3, 3))
- conv11_2feats = torch.rand((10, 256, 1, 1))
- locs, class_scores = model(conv4_3feats, conv7_feats, conv8_2feats, conv9_2feats, conv10_2feats, conv11_2feats)
- # print(loc_conv4_3.shape, loc_conv7.shape, loc_conv8_2.shape, loc_conv9_2.shape,
- # loc_conv10_2.shape, loc_conv11_2.shape,\
- # cl_conv4_3.shape, cl_conv7.shape, cl_conv8_2.shape, cl_conv9_2.shape,
- # cl_conv10_2.shape, cl_conv11_2.shape)
- print(locs.shape)
- print(class_scores.shape)
- def test_SSD300():
- os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = '0'
-
- n_classes = 21
- model = SSD300(n_classes)
- print('==model', model)
- x = torch.rand((10, 3, 300, 300))
- locs, class_scores = model(x)
- print('locs.shape', locs.shape)
- print('class_scores.shape', class_scores.shape)
-
- def test_mutiboxloss():
- prior_boxes = create_prior_boxes()
- loss_model = MultiBoxLoss(prior_boxes)
- prediction_locs = torch.rand(2, 8732, 4)
- prediction_scores = torch.rand(2, 8732, 21)
- boxes = [torch.tensor([[0.1040, 0.1946, 0.9400, 0.9480],
- [0.3140, 0.0973, 0.5760, 0.3756]]).to(device),
- torch.tensor([[0.0000, 0.6107, 0.8540, 0.7787]]).to(device)]
- labels = [torch.tensor([13, 15]).to(device),
- torch.tensor([4]).to(device)]
- # boxes = torch.tensor([[[1, 2, 3, 4]],
- # [[7, 8, 9, 10],
- # [4, 5, 6, 7]]])
- # labels = torch.tensor([[1],
- # [1, 3]])
- loss_sclar = loss_model(prediction_locs, prediction_scores, boxes, labels)
- print('==loss_sclar',loss_sclar)
-
- def create_prior_boxes():
- """创建SSD300的先验框(cx, cy, w, h)
- (8prediction_locs, prediction_scores, boxes, labels372,4)个box"""
- os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = '0'
- device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
- from math import sqrt
- fmap_size = {'conv4_3':38, 'conv7':19, 'conv8_2':10,
- 'conv9_2':5, 'conv10_2':3, 'conv11_2':1}
- anchor_scale = {'conv4_3':0.1,'conv7':0.2,'conv8_2':0.375,
- 'conv9_2':0.55,'conv10_2':0.725,'conv11_2':0.9}
- anchor_ratio = {'conv4_3':[1,2,0.5], 'conv7':[1,2,3,0.5,0.33], 'conv8_2':[1,2,3,0.5,0.33],
- 'conv9_2':[1,2,3,0.5,0.33], 'conv10_2':[1,2,0.5], 'conv11_2':[1,2,0.5]}
- prior_boxes = []
- for index,fmap in enumerate(fmap_size):
- for i in range(fmap_size[fmap]):
- for j in range(fmap_size[fmap]):
- cy,cx = (i+0.5)/fmap_size[fmap], (j+0.5)/fmap_size[fmap]
- for ratio in anchor_ratio[fmap]:
- prior_boxes.append([cx, cy, anchor_scale[fmap]*sqrt(ratio), anchor_scale[fmap]/sqrt(ratio)])
-
- if ratio==1:#添加额外框
- try:
- extra_scale = sqrt(anchor_scale[fmap]*anchor_scale[fmap_size[index+1]])
- except:
- extra_scale = 1.
- prior_boxes.append([cx, cy, extra_scale, extra_scale])
- # print('len(prior_boxes)',len(prior_boxes))
- # prior_boxes = [[1,2,3,4],
- # [3,4,5,6]]
- prior_boxes = torch.FloatTensor(prior_boxes).to(device)
- prior_boxes.clamp_(0,1)#防止越界
- print('prior_boxes.shape', prior_boxes.shape)
- # print(prior_boxes)
- return prior_boxes
-
- def decimate(tensor, m):
- """
- Decimate a tensor by a factor 'm', i.e. downsample by keeping every 'm'th value.
- This is used when we convert FC layers to equivalent Convolutional layers, BUT of a smaller size.
- :param tensor: tensor to be decimated
- :param m: list of decimation factors for each dimension of the tensor; None if not to be decimated along a dimension
- :return: decimated tensor
- """
- assert tensor.dim() == len(m)
- for d in range(tensor.dim()):
- if m[d] is not None:
- tensor = tensor.index_select(dim=d,
- index=torch.arange(start=0, end=tensor.size(d), step=m[d]).long())
- # print('==tensor.shape:', tensor.shape)
- return tensor
- def test_fc_conv():
- """fc (4096,25088)-->conv (1024,512,3,3)"""
- fc_weight_init = torch.rand(4096, 25088)
- fc_weight = fc_weight_init.reshape(4096, 512, 7, 7)
- m = [4, None, 3, 3]
- conv_weight = decimate(fc_weight, m)
- print('==conv_weight.shape', conv_weight.shape)
-
- def index_select():
- x = torch.linspace(1, 12, steps=12, requires_grad=True).reshape(3, 4)
- print('==x', x)
- print(x.dtype)
- print(x.data)
- print(x.data.dtype)
- # indices = torch.LongTensor([0, 2])
- # y = torch.index_select(x, 0, indices) # 对行操作
- # print('==y', y)
- #
- # z = torch.index_select(x, 1, indices) # 对列操作
- # print('==z', z)
- #
- # z = torch.index_select(y, 1, indices) # 对列操作
- # print('==z', z)
-
-
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = '0'
- # test_vgg_base()
- # test_AUx_conv()
- # test_pre_conv()
- # test_fc_conv()
- # index_select()
- # create_prior_boxes()
- # test_SSD300()
- test_mutiboxloss()
-
-
-
-

二.多尺度训练与测试
1.多尺度训练
目的:用不同的尺度去帮助模型适应各种大小的目标,获得对尺寸的鲁棒性。一般是每个batch随机选择一个合适的尺度进行训练即可.
2.多尺度测试
2.1 one-stage 多尺度测试

对单个尺度的结果先进行NMS,在resize成同一个尺度大小在进行一次NMS.先对单个尺度结果进行NMS可以减少推理时间.
2.2 two-stage 多尺度测试

(1) 不同尺度图,通过Backbone+RPN和各自的NMS之后,会得到各自的proposals。再把尺度统一到同一张图的大小上去,然后合并到一起做阈值为0.7的NMS,得到Proposals。
(2) R-CNN阶段依然希望用多尺度,所以需要把proposals分别resize到橙色和绿色的图的尺寸上去,然后各自过R-CNN。后面的步骤与RPN和one stage是一样的,先各自做NMS,然后Resize到统一尺寸后再合并做阈值为0.5的NMS。
参考:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/lBhPjOiT_05WXwxFCXj2mQ


