- 1Qt之信号与槽
- 2深入了解Kimi:月之暗面科技有限公司的创新智能助手_kimi 的能力
- 3【数据结构】CH4 串_第1关:求子串
- 4MySQL从安装、配置到日常操作和管理的关键步骤_mysql安装教程8.4
- 5python 中使用opencv_python使用opencv
- 6python3+selenium爬取笔记本电脑详情信息_selenium可以爬取pc端数据吗
- 7【通信中间件】Fdbus HelloWorld实例
- 8搭建单机版伪分布式Hadoop+Spark+Scala
- 9基于MySQL Workbench的表操作_mysql workbench向表中添加数据
- 10苹果app退款_app退款理由写什么好?苹果退款理由怎么写才好?
Fast-Planner(五)详解TopologyPRM_fast planner 理论详细解读
赞
踩
本文上接Fast-Planner第一篇文章的内容,本文主要详解这一系列的第二篇Robust Real-time UAV Replanning Using Guided Gradient-based Optimization and Topological Paths中的TopologyPRM即其代码。如有问题,欢迎各位大佬评论指出,带着我一起进步。
1. 简介
这篇文章主要贡献:
- 为解决GTO(基于梯度的轨迹优化)带来的陷入局部极小值的问题,提出了一种路径引导优化(PGO)来处理局部极小值。
- 一个有效的拓扑路径搜索算法,适用于与PGO结合,生成多条备选拓扑路径再通过剪枝优化生成有效的重规划轨迹。
GTO仅依赖于ESDF提供的梯度信息时,但是在下图这类“谷”和“脊”等位置梯度发生突变,这导致目标函数将轨迹朝着不同方向推离,从而导致优化失败。

2. 拓扑路径搜索
参考博客
最短的路径引导不一定是最优的引导路径,因为路径是低维信息不包含高阶信息(速度、加速度等),不能反映真实运动。仿照笔者整理的可变性路径利用拓扑等价轨迹获得多条轨迹再进一步优化剪枝。
该算法主要体现在topo_prm.cpp代码中,现在解析这部分代码。
2.1 主函数
/* function:拓扑路径搜索主函数 param: - start 起点坐标 - end 终点坐标 - start_pts 不知道干什么 - end_pts 同上 - graph 节点图 - raw_paths 搜索到的路径集合 - filtered_paths 剪枝后的路径合集 - select_paths 最后选择的比较短的几条路径 */ void TopologyPRM::findTopoPaths(Eigen::Vector3d start, Eigen::Vector3d end, vector<Eigen::Vector3d> start_pts, vector<Eigen::Vector3d> end_pts, list<GraphNode::Ptr>& graph, vector<vector<Eigen::Vector3d>>& raw_paths, vector<vector<Eigen::Vector3d>>& filtered_paths, vector<vector<Eigen::Vector3d>>& select_paths) { ros::Time t1, t2; //用于计时每个阶段的时间:生成节点时间、路径搜索时间、路径最短时间、路径剪枝时间、选择路径时间 double graph_time, search_time, short_time, prune_time, select_time; /* ---------- create the topo graph ---------- */ t1 = ros::Time::now(); start_pts_ = start_pts; end_pts_ = end_pts; //生成节点图 graph = createGraph(start, end); graph_time = (ros::Time::now() - t1).toSec(); /* ---------- search paths in the graph ---------- */ t1 = ros::Time::now(); //在节点图中进行拓扑路径搜索 raw_paths = searchPaths(); search_time = (ros::Time::now() - t1).toSec(); /* ---------- path shortening ---------- */ // for parallel, save result in short_paths_ t1 = ros::Time::now(); //路径缩短优化 shortcutPaths(); short_time = (ros::Time::now() - t1).toSec(); /* ---------- prune equivalent paths ---------- */ t1 = ros::Time::now(); //筛选路径 filtered_paths = pruneEquivalent(short_paths_); prune_time = (ros::Time::now() - t1).toSec(); // cout << "prune: " << (t2 - t1).toSec() << endl; /* ---------- select N shortest paths ---------- */ t1 = ros::Time::now(); select_paths = selectShortPaths(filtered_paths, 1); select_time = (ros::Time::now() - t1).toSec(); final_paths_ = select_paths; double total_time = graph_time + search_time + short_time + prune_time + select_time; std::cout << "\n[Topo]: total time: " << total_time << ", graph: " << graph_time << ", search: " << search_time << ", short: " << short_time << ", prune: " << prune_time << ", select: " << select_time << std::endl; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
2.2 Algorithm 1: Topological Roadmap
 对应的函数是createGraph
对应的函数是createGraph
/* function:根据起始点和终点的位置信息,采样地图节点(对应文章算法1 Topological Roadmap) param: - start 起点坐标 - end 终点坐标 */ list<GraphNode::Ptr> TopologyPRM::createGraph(Eigen::Vector3d start, Eigen::Vector3d end) { // std::cout << "[Topo]: searching----------------------" << std::endl; /* init the start, end and sample region */ graph_.clear(); // collis_.clear(); //将起点和值哦观点设为守卫节点,并标定id号分别为0和1 GraphNode::Ptr start_node = GraphNode::Ptr(new GraphNode(start, GraphNode::Guard, 0)); GraphNode::Ptr end_node = GraphNode::Ptr(new GraphNode(end, GraphNode::Guard, 1)); graph_.push_back(start_node); graph_.push_back(end_node); // sample region // 采样区域 sample_r_(0) = 0.5 * (end - start).norm() + sample_inflate_(0); //x方向采样的半径 sample_r_(1) = sample_inflate_(1); //y方向采样的半径 sample_r_(2) = sample_inflate_(2); //z方向采样的半径 // transformation // 姿态改变参数 translation_ = 0.5 * (start + end); //创建局部坐标系切线-法线-副法线坐标系 Eigen::Vector3d xtf, ytf, ztf, downward(0, 0, -1); xtf = (end - translation_).normalized(); ytf = xtf.cross(downward).normalized(); ztf = xtf.cross(ytf); //局部坐标系和全局坐标系的旋转关系 rotation_.col(0) = xtf; rotation_.col(1) = ytf; rotation_.col(2) = ztf; int node_id = 1; /* ---------- main loop ---------- */ int sample_num = 0; //采样数目 double sample_time = 0.0; //采样时间 Eigen::Vector3d pt; ros::Time t1, t2; //采样数目和采样时间阈值内循环 while (sample_time < max_sample_time_ && sample_num < max_sample_num_) { t1 = ros::Time::now(); pt = getSample(); ++sample_num; double dist; Eigen::Vector3d grad; //梯度 // edt_environment_->evaluateEDTWithGrad(pt, -1.0, dist, grad); dist = edt_environment_->evaluateCoarseEDT(pt, -1.0); //距离esdf地图最近的障碍物的距离 if (dist <= clearance_) { //最小距离小于安全距离,舍弃该采样点 sample_time += (ros::Time::now() - t1).toSec(); continue; } /* find visible guard */ /* 找到前采样点的可视守卫点合集 */ vector<GraphNode::Ptr> visib_guards = findVisibGuard(pt); if (visib_guards.size() == 0) { //没有可视守卫点,将其设为守卫点 GraphNode::Ptr guard = GraphNode::Ptr(new GraphNode(pt, GraphNode::Guard, ++node_id)); graph_.push_back(guard); } else if (visib_guards.size() == 2) { //如果有且只有两个可见guard,则要利用needConnection函数判断是否要添加新的connector。 /* try adding new connection between two guard */ // vector<pair<GraphNode::Ptr, GraphNode::Ptr>> sort_guards = // sortVisibGuard(visib_guards); bool need_connect = needConnection(visib_guards[0], visib_guards[1], pt); if (!need_connect) { sample_time += (ros::Time::now() - t1).toSec(); continue; } // new useful connection needed, add new connector // 如果需要新的节点,添加新的节点 GraphNode::Ptr connector = GraphNode::Ptr(new GraphNode(pt, GraphNode::Connector, ++node_id)); graph_.push_back(connector); // connect guards visib_guards[0]->neighbors_.push_back(connector); visib_guards[1]->neighbors_.push_back(connector); connector->neighbors_.push_back(visib_guards[0]); connector->neighbors_.push_back(visib_guards[1]); } sample_time += (ros::Time::now() - t1).toSec(); } /* print record */ std::cout << "[Topo]: sample num: " << sample_num; // 修剪节点图 pruneGraph(); // std::cout << "[Topo]: node num: " << graph_.size() << std::endl; return graph_; // return searchPaths(start_node, end_node); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
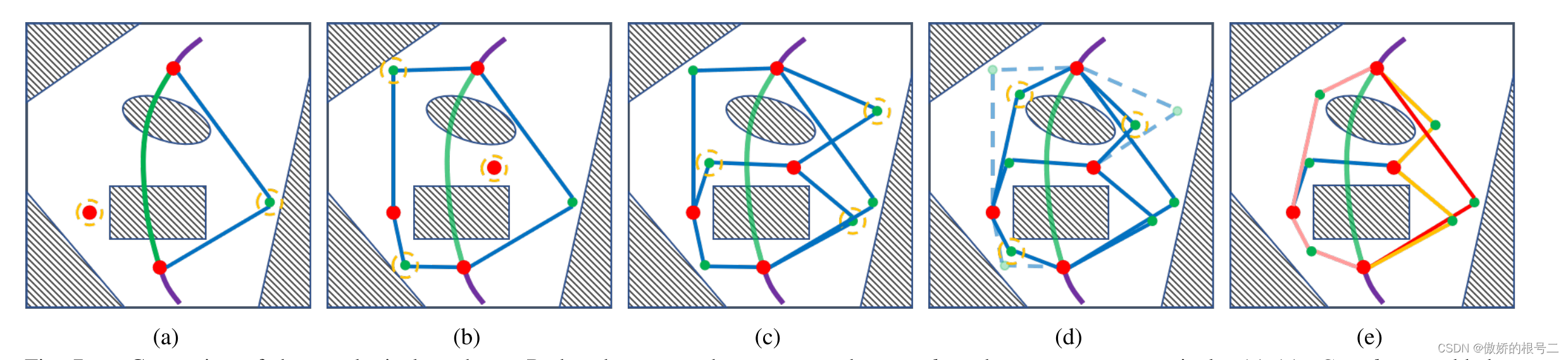
这个函数里提到一个概念叫做UVD(uniform visibility deformation)均匀可视变形,同样来自上文提到的整理的论文笔记中,其中不一样的点在于相比于右图的分均匀可视变形,可视变形的检测可以通过均匀采样一一可视检测完成,然后从两条可视变形的路径中挑选出最短的一条添加进节点图,这个算法的代码函数为sameTopoPath。论文中提到在概念上,UVD不太普遍,它是VD类型的子集的特征。实际上,它捕获的不同路径的类别比VD略多,但等价性检查的成本要低得多。
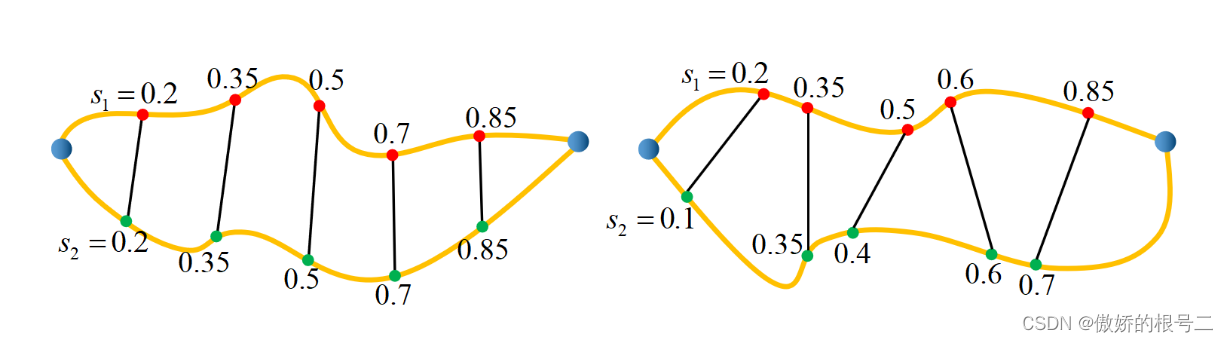
bool TopologyPRM::sameTopoPath(const vector<Eigen::Vector3d>& path1, const vector<Eigen::Vector3d>& path2, double thresh) { // 计算两条路径的长度 double len1 = pathLength(path1); double len2 = pathLength(path2); double max_len = max(len1, len2); int pt_num = ceil(max_len / resolution_); // std::cout << "pt num: " << pt_num << std::endl; // 离散path的路径点 vector<Eigen::Vector3d> pts1 = discretizePath(path1, pt_num); vector<Eigen::Vector3d> pts2 = discretizePath(path2, pt_num); Eigen::Vector3d pc; for (int i = 0; i < pt_num; ++i) { // 判断轨迹上是否有障碍物(两条轨迹均匀可视变形) if (!lineVisib(pts1[i], pts2[i], thresh, pc)) { return false; } } return true; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
2.2 深度搜索
在获得节点图后,从起点到终点有好多个点,本文采用深度搜索找到所用节点最少的路径集合。
// search for useful path in the topo graph by DFS // 通过DFS在节点图中搜索有用的路径,按节点数目对路径进行排序,选择节点数目较少的路径进行保留 vector<vector<Eigen::Vector3d>> TopologyPRM::searchPaths() { raw_paths_.clear(); vector<GraphNode::Ptr> visited; //标记节点是否被访问 visited.push_back(graph_.front()); //存入起点 depthFirstSearch(visited); //进行DFS更新raw_paths向量 // 路径排序 int min_node_num = 100000, max_node_num = 1; vector<vector<int>> path_list(100); for (int i = 0; i < raw_paths_.size(); ++i) { if (int(raw_paths_[i].size()) > max_node_num) max_node_num = raw_paths_[i].size(); if (int(raw_paths_[i].size()) < min_node_num) min_node_num = raw_paths_[i].size(); path_list[int(raw_paths_[i].size())].push_back(i); } // 选择节点数较少的路径 vector<vector<Eigen::Vector3d>> filter_raw_paths; for (int i = min_node_num; i <= max_node_num; ++i) { bool reach_max = false; for (int j = 0; j < path_list[i].size(); ++j) { filter_raw_paths.push_back(raw_paths_[path_list[i][j]]); if (filter_raw_paths.size() >= max_raw_path2_) { reach_max = true; break; } } if (reach_max) break; } std::cout << ", raw path num: " << raw_paths_.size() << ", " << filter_raw_paths.size(); raw_paths_ = filter_raw_paths; return raw_paths_; } void TopologyPRM::depthFirstSearch(vector<GraphNode::Ptr>& vis) { GraphNode::Ptr cur = vis.back(); //从已访问节点列表中获取最后一个节点作为当前节点 for (int i = 0; i < cur->neighbors_.size(); ++i) { // 检查邻居点中是否有目标节点 if (cur->neighbors_[i]->id_ == 1) { // 将当前路径添加到raw_paths vector<Eigen::Vector3d> path; for (int j = 0; j < vis.size(); ++j) { path.push_back(vis[j]->pos_); } path.push_back(cur->neighbors_[i]->pos_); raw_paths_.push_back(path); if (raw_paths_.size() >= max_raw_path_) return; break; } } for (int i = 0; i < cur->neighbors_.size(); ++i) { // 跳过目标节点 if (cur->neighbors_[i]->id_ == 1) continue; // 检查是否已访问过当前邻居节点 bool revisit = false; for (int j = 0; j < vis.size(); ++j) { if (cur->neighbors_[i]->id_ == vis[j]->id_) { revisit = true; break; } } if (revisit) continue; //如果已访问过,则跳过该邻居节点 // 将当前邻居节点添加到访问列表中,并递归搜索 vis.push_back(cur->neighbors_[i]); depthFirstSearch(vis); if (raw_paths_.size() >= max_raw_path_) return; vis.pop_back(); //回溯,从访问列表中移除当前邻居节点 } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
2.3 路径缩短
将原路径离散化成多个点,然后从起点出发,遍历原路径上的离散点连成线,如果与障碍物碰撞,从碰撞处的障碍的ESDF梯度结合连线向外推出一定距离形成新路径的一个点,然后以这个新点做遍历直到达到目标点。这部分代码为函数shortcutPaths,可选择并行缩短多条路径。


/* function:通过对路径进行优化,找到一条更短或更高效的路径,同时避免与障碍物或其他不可行区域发生碰撞(对应论文中的算法2) param: - path: 待优化的原始路径 - path_id: 编号 - iter_num:迭代次数 */ void TopologyPRM::shortcutPath(vector<Eigen::Vector3d> path, int path_id, int iter_num) { vector<Eigen::Vector3d> short_path = path; vector<Eigen::Vector3d> last_path; for (int k = 0; k < iter_num; ++k) { last_path = short_path; //将路径稠密化 vector<Eigen::Vector3d> dis_path = discretizePath(short_path); if (dis_path.size() < 2) { short_paths_[path_id] = dis_path; return; } /* visibility path shortening */ // 障碍物id 梯度 方向 推力方向 Eigen::Vector3d colli_pt, grad, dir, push_dir; double dist; short_path.clear(); short_path.push_back(dis_path.front()); for (int i = 1; i < dis_path.size(); ++i) { //利用lineVisib来衡量可见性,找到线上不可见的第一个点 if (lineVisib(short_path.back(), dis_path[i], resolution_, colli_pt, path_id)) continue; //计算障碍点上的梯度 edt_environment_->evaluateEDTWithGrad(colli_pt, -1, dist, grad); if (grad.norm() > 1e-3) { grad.normalize(); //计算到第一个新点的方向 dir = (dis_path[i] - short_path.back()).normalized(); push_dir = grad - grad.dot(dir) * dir; //推离方向 push_dir.normalize(); colli_pt = colli_pt + resolution_ * push_dir; //推离到新点 } short_path.push_back(colli_pt); //添加点 } short_path.push_back(dis_path.back()); /* break if no shortcut */ // 比较两个路径的长度,保留短的 double len1 = pathLength(last_path); double len2 = pathLength(short_path); if (len2 > len1) { // ROS_WARN("pause shortcut, l1: %lf, l2: %lf, iter: %d", len1, len2, k + // 1); short_path = last_path; break; } } short_paths_[path_id] = short_path; } //对通过DFS找到的原始路径进行shortcut处理,用于减少路径中的冗余节点,以得到更短或更高效的路径。 void TopologyPRM::shortcutPaths() { short_paths_.resize(raw_paths_.size()); if (parallel_shortcut_) { //是否开启多线程并行处理每条路径 vector<thread> short_threads; for (int i = 0; i < raw_paths_.size(); ++i) { short_threads.push_back(thread(&TopologyPRM::shortcutPath, this, raw_paths_[i], i, 1)); } for (int i = 0; i < raw_paths_.size(); ++i) { short_threads[i].join(); } } else { for (int i = 0; i < raw_paths_.size(); ++i) shortcutPath(raw_paths_[i], i); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
2.4 剪枝
/* function:将路径集中的其他路径与最短路径进行比较,产生一个长度比值,该比值小于阈值,将该路径放入新的路径集中保留,直到达到新的路径集中保留。 */ vector<vector<Eigen::Vector3d>> TopologyPRM::selectShortPaths(vector<vector<Eigen::Vector3d>>& paths, int step) { /* ---------- only reserve top short path ---------- */ vector<vector<Eigen::Vector3d>> short_paths; vector<Eigen::Vector3d> short_path; double min_len; for (int i = 0; i < reserve_num_ && paths.size() > 0; ++i) { int path_id = shortestPath(paths); if (i == 0) { short_paths.push_back(paths[path_id]); min_len = pathLength(paths[path_id]); paths.erase(paths.begin() + path_id); } else { //路径长度比较 double rat = pathLength(paths[path_id]) / min_len; if (rat < ratio_to_short_) { short_paths.push_back(paths[path_id]); paths.erase(paths.begin() + path_id); } else { break; } } } std::cout << ", select path num: " << short_paths.size(); /* ---------- merge with start and end segment ---------- */ for (int i = 0; i < short_paths.size(); ++i) { short_paths[i].insert(short_paths[i].begin(), start_pts_.begin(), start_pts_.end()); short_paths[i].insert(short_paths[i].end(), end_pts_.begin(), end_pts_.end()); } for (int i = 0; i < short_paths.size(); ++i) { shortcutPath(short_paths[i], i, 5); short_paths[i] = short_paths_[i]; } short_paths = pruneEquivalent(short_paths); return short_paths; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43




