热门标签
热门文章
- 1arcgis python 脚本开发视频_ArcGIS Python编程案例(13)-自动执行Python脚本
- 2非科班出身如何转行程序员?_非科班转行程序员
- 3使用Portainer搭建Docker可视化界面_portainer日志是空白页
- 4使用Delphi来跟我学COM (第二部 COM编程)
- 5Set A Light 3D Studio中文--- 打造专业级3D照明效果
- 6ArkTS基础学习笔记_arkts文档
- 7记录:GKI 学习_gki内核
- 8解决ElementPlus中的Menu菜单背景设为透明后导航栏文字下方出现一条细白线_el-menu透明
- 9AI自动识别户型图生成数据建模到3DVR场景解决方案_c# 户型图提取数据
- 10三种梯度下降法对比(Batch gradient descent、Mini-batch gradient descent 和 stochastic gradient descent)_梯度下降的三种形式对比
当前位置: article > 正文
机器学习实战-决策树实战
作者:IT小白 | 2024-04-10 12:31:47
赞
踩
机器学习实战-决策树实战
使用ID3算法构建决策树
ID3算法的核心是在决策树各个结点上对应信息增益准则选择特征,递归地构建决策树。
具体方法是:从根结点(root node)开始,对结点计算所有可能的特征的信息增益;
选择信息增益最大的特征作为结点的特征,由该特征的不同取值建立子节点;
再对子结点递归地调用以上方法,构建决策树;
直到所有特征的信息增益均很小或没有特征可以选择为止;
最后得到一个决策树。ID3相当于用极大似然法进行概率模型的选择。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
from math import log import operator """ 函数说明:计算给定数据集的经验熵(香农熵) Parameters: dataSet - 数据集 Returns: shannonEnt - 经验熵(香农熵) Author: Jack Cui """ def calcShannonEnt(dataSet): numEntires = len(dataSet) #返回数据集的行数 labelCounts = {} #保存每个标签(Label)出现次数的字典 for featVec in dataSet: #对每组特征向量进行统计 currentLabel = featVec[-1] #提取标签(Label)信息 if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys(): #如果标签(Label)没有放入统计次数的字典,添加进去 labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0 labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1 #Label计数 shannonEnt = 0.0 #经验熵(香农熵) for key in labelCounts: #计算香农熵 prob = float(labelCounts[key]) / numEntires #选择该标签(Label)的概率 shannonEnt -= prob * log(prob, 2) #利用公式计算 return shannonEnt #返回经验熵(香农熵) """ 函数说明:创建测试数据集 Parameters: 无 Returns: dataSet - 数据集 labels - 特征标签 Author: Jack Cui """ def createDataSet(): dataSet = [[0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'], #数据集 [0, 0, 0, 1, 'no'], [0, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'], [0, 1, 1, 0, 'yes'], [0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'], [1, 0, 0, 0, 'no'], [1, 0, 0, 1, 'no'], [1, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'], [1, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'], [1, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'], [2, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'], [2, 0, 1, 1, 'yes'], [2, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'], [2, 1, 0, 2, 'yes'], [2, 0, 0, 0, 'no']] labels = ['年龄', '有工作', '有自己的房子', '信贷情况'] #特征标签 return dataSet, labels #返回数据集和分类属性 """ 函数说明:按照给定特征划分数据集 Parameters: dataSet - 待划分的数据集 axis - 划分数据集的特征 value - 需要返回的特征的值 Returns: 无 Author: Jack Cui """ def splitDataSet(dataSet, axis, value): retDataSet = [] #创建返回的数据集列表 for featVec in dataSet: #遍历数据集 if featVec[axis] == value: reducedFeatVec = featVec[:axis] #去掉axis特征 reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:]) #将符合条件的添加到返回的数据集 retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec) return retDataSet #返回划分后的数据集 """ 函数说明:选择最优特征 Parameters: dataSet - 数据集 Returns: bestFeature - 信息增益最大的(最优)特征的索引值 Author: Jack Cui """ def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet): numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) - 1 #特征数量 baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet) #计算数据集的香农熵 bestInfoGain = 0.0 #信息增益 bestFeature = -1 #最优特征的索引值 for i in range(numFeatures): #遍历所有特征 #获取dataSet的第i个所有特征 featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet] uniqueVals = set(featList) #创建set集合{},元素不可重复 newEntropy = 0.0 #经验条件熵 for value in uniqueVals: #计算信息增益 subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, i, value) #subDataSet划分后的子集 prob = len(subDataSet) / float(len(dataSet)) #计算子集的概率 newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet) #根据公式计算经验条件熵 infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy #信息增益 # print("第%d个特征的增益为%.3f" % (i, infoGain)) #打印每个特征的信息增益 if (infoGain > bestInfoGain): #计算信息增益 bestInfoGain = infoGain #更新信息增益,找到最大的信息增益 bestFeature = i #记录信息增益最大的特征的索引值 return bestFeature #返回信息增益最大的特征的索引值 """ 函数说明:统计classList中出现此处最多的元素(类标签) Parameters: classList - 类标签列表 Returns: sortedClassCount[0][0] - 出现此处最多的元素(类标签) Author: Jack Cui """ def majorityCnt(classList): classCount = {} for vote in classList: #统计classList中每个元素出现的次数 if vote not in classCount.keys():classCount[vote] = 0 classCount[vote] += 1 sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(), key = operator.itemgetter(1), reverse = True) #根据字典的值降序排序 return sortedClassCount[0][0] #返回classList中出现次数最多的元素 """ 函数说明:创建决策树 Parameters: dataSet - 训练数据集 labels - 分类属性标签 featLabels - 存储选择的最优特征标签 Returns: myTree - 决策树 Author: Jack Cui """ def createTree(dataSet, labels, featLabels): classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet] #取分类标签(是否放贷:yes or no) if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList): #如果类别完全相同则停止继续划分 return classList[0] if len(dataSet[0]) == 1: #遍历完所有特征时返回出现次数最多的类标签 return majorityCnt(classList) bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet) #选择最优特征 bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat] #最优特征的标签 featLabels.append(bestFeatLabel) myTree = {bestFeatLabel:{}} #根据最优特征的标签生成树 del(labels[bestFeat]) #删除已经使用特征标签 featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet] #得到训练集中所有最优特征的属性值 uniqueVals = set(featValues) #去掉重复的属性值 for value in uniqueVals: #遍历特征,创建决策树。 myTree[bestFeatLabel][value] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeat, value), labels, featLabels) return myTree if __name__ == '__main__': dataSet, labels = createDataSet() featLabels = [] myTree = createTree(dataSet, labels, featLabels) print(myTree)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
递归创建决策树时,递归有两个终止条件:第一个停止条件是所有的类标签完全相同,则直接返回该类标签;第二个停止条件是使用完了所有特征,仍然不能将数据划分仅包含唯一类别的分组,即决策树构建失败,特征不够用。此时说明数据纬度不够,由于第二个停止条件无法简单地返回唯一的类标签,这里挑选出现数量最多的类别作为返回值。
运行结果:
{'有自己的房子': {0: {'有工作': {0: 'no', 1: 'yes'}}, 1: 'yes'}}
- 1
决策树可视化
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from math import log import operator """ 函数说明:计算给定数据集的经验熵(香农熵) Parameters: dataSet - 数据集 Returns: shannonEnt - 经验熵(香农熵) """ def calcShannonEnt(dataSet): numEntires = len(dataSet) #返回数据集的行数 labelCounts = {} #保存每个标签(Label)出现次数的字典 for featVec in dataSet: #对每组特征向量进行统计 currentLabel = featVec[-1] #提取标签(Label)信息 if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys(): #如果标签(Label)没有放入统计次数的字典,添加进去 labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0 labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1 #Label计数 shannonEnt = 0.0 #经验熵(香农熵) for key in labelCounts: #计算香农熵 prob = float(labelCounts[key]) / numEntires #选择该标签(Label)的概率 shannonEnt -= prob * log(prob, 2) #利用公式计算 return shannonEnt #返回经验熵(香农熵) """ 函数说明:创建测试数据集 Parameters: 无 Returns: dataSet - 数据集 labels - 特征标签 """ def createDataSet(): dataSet = [[0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'], #数据集 [0, 0, 0, 1, 'no'], [0, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'], [0, 1, 1, 0, 'yes'], [0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'], [1, 0, 0, 0, 'no'], [1, 0, 0, 1, 'no'], [1, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'], [1, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'], [1, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'], [2, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'], [2, 0, 1, 1, 'yes'], [2, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'], [2, 1, 0, 2, 'yes'], [2, 0, 0, 0, 'no']] labels = ['年龄', '有工作', '有自己的房子', '信贷情况'] #特征标签 return dataSet, labels #返回数据集和分类属性 """ 函数说明:按照给定特征划分数据集 Parameters: dataSet - 待划分的数据集 axis - 划分数据集的特征 value - 需要返回的特征的值 Returns: 无 """ def splitDataSet(dataSet, axis, value): retDataSet = [] #创建返回的数据集列表 for featVec in dataSet: #遍历数据集 if featVec[axis] == value: reducedFeatVec = featVec[:axis] #去掉axis特征 reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:]) #将符合条件的添加到返回的数据集 retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec) return retDataSet #返回划分后的数据集 """ 函数说明:选择最优特征 Parameters: dataSet - 数据集 Returns: bestFeature - 信息增益最大的(最优)特征的索引值 """ def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet): numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) - 1 #特征数量 baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet) #计算数据集的香农熵 bestInfoGain = 0.0 #信息增益 bestFeature = -1 #最优特征的索引值 for i in range(numFeatures): #遍历所有特征 #获取dataSet的第i个所有特征 featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet] uniqueVals = set(featList) #创建set集合{},元素不可重复 newEntropy = 0.0 #经验条件熵 for value in uniqueVals: #计算信息增益 subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, i, value) #subDataSet划分后的子集 prob = len(subDataSet) / float(len(dataSet)) #计算子集的概率 newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet) #根据公式计算经验条件熵 infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy #信息增益 # print("第%d个特征的增益为%.3f" % (i, infoGain)) #打印每个特征的信息增益 if (infoGain > bestInfoGain): #计算信息增益 bestInfoGain = infoGain #更新信息增益,找到最大的信息增益 bestFeature = i #记录信息增益最大的特征的索引值 return bestFeature #返回信息增益最大的特征的索引值 """ 函数说明:统计classList中出现此处最多的元素(类标签) Parameters: classList - 类标签列表 Returns: sortedClassCount[0][0] - 出现此处最多的元素(类标签) """ def majorityCnt(classList): classCount = {} for vote in classList: #统计classList中每个元素出现的次数 if vote not in classCount.keys():classCount[vote] = 0 classCount[vote] += 1 sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(), key = operator.itemgetter(1), reverse = True) #根据字典的值降序排序 return sortedClassCount[0][0] #返回classList中出现次数最多的元素 """ 函数说明:创建决策树 Parameters: dataSet - 训练数据集 labels - 分类属性标签 featLabels - 存储选择的最优特征标签 Returns: myTree - 决策树 """ def createTree(dataSet, labels, featLabels): classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet] #取分类标签(是否放贷:yes or no) if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList): #如果类别完全相同则停止继续划分 return classList[0] if len(dataSet[0]) == 1: #遍历完所有特征时返回出现次数最多的类标签 return majorityCnt(classList) bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet) #选择最优特征 bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat] #最优特征的标签 featLabels.append(bestFeatLabel) myTree = {bestFeatLabel:{}} #根据最优特征的标签生成树 del(labels[bestFeat]) #删除已经使用特征标签 featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet] #得到训练集中所有最优特征的属性值 uniqueVals = set(featValues) #去掉重复的属性值 for value in uniqueVals: #遍历特征,创建决策树。 myTree[bestFeatLabel][value] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeat, value), labels, featLabels) return myTree """ 函数说明:获取决策树叶子结点的数目 Parameters: myTree - 决策树 Returns: numLeafs - 决策树的叶子结点的数目 """ def getNumLeafs(myTree): numLeafs = 0 #初始化叶子 firstStr = next(iter(myTree)) #python3中myTree.keys()返回的是dict_keys,不在是list,所以不能使用myTree.keys()[0]的方法获取结点属性,可以使用list(myTree.keys())[0] secondDict = myTree[firstStr] #获取下一组字典 for key in secondDict.keys(): if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict': #测试该结点是否为字典,如果不是字典,代表此结点为叶子结点 numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key]) else: numLeafs +=1 return numLeafs """ 函数说明:获取决策树的层数 Parameters: myTree - 决策树 Returns: maxDepth - 决策树的层数 """ def getTreeDepth(myTree): maxDepth = 0 #初始化决策树深度 firstStr = next(iter(myTree)) #python3中myTree.keys()返回的是dict_keys,不在是list,所以不能使用myTree.keys()[0]的方法获取结点属性,可以使用list(myTree.keys())[0] secondDict = myTree[firstStr] #获取下一个字典 for key in secondDict.keys(): if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict': #测试该结点是否为字典,如果不是字典,代表此结点为叶子结点 thisDepth = 1 + getTreeDepth(secondDict[key]) else: thisDepth = 1 if thisDepth > maxDepth: maxDepth = thisDepth #更新层数 return maxDepth """ 函数说明:绘制结点 Parameters: nodeTxt - 结点名 centerPt - 文本位置 parentPt - 标注的箭头位置 nodeType - 结点格式 Returns: 无 """ def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType): arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-") #定义箭头格式 font = FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc", size=14) #设置中文字体 createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction', #绘制结点 xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction', va="center", ha="center", bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args, FontProperties=font) """ 函数说明:标注有向边属性值 Parameters: cntrPt、parentPt - 用于计算标注位置 txtString - 标注的内容 Returns: 无 """ def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString): xMid = (parentPt[0]-cntrPt[0])/2.0 + cntrPt[0] #计算标注位置 yMid = (parentPt[1]-cntrPt[1])/2.0 + cntrPt[1] createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30) """ 函数说明:绘制决策树 Parameters: myTree - 决策树(字典) parentPt - 标注的内容 nodeTxt - 结点名 Returns: 无 """ def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt): decisionNode = dict(boxstyle="sawtooth", fc="0.8") #设置结点格式 leafNode = dict(boxstyle="round4", fc="0.8") #设置叶结点格式 numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree) #获取决策树叶结点数目,决定了树的宽度 depth = getTreeDepth(myTree) #获取决策树层数 firstStr = next(iter(myTree)) #下个字典 cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs))/2.0/plotTree.totalW, plotTree.yOff) #中心位置 plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt) #标注有向边属性值 plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode) #绘制结点 secondDict = myTree[firstStr] #下一个字典,也就是继续绘制子结点 plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0/plotTree.totalD #y偏移 for key in secondDict.keys(): if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict': #测试该结点是否为字典,如果不是字典,代表此结点为叶子结点 plotTree(secondDict[key],cntrPt,str(key)) #不是叶结点,递归调用继续绘制 else: #如果是叶结点,绘制叶结点,并标注有向边属性值 plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalW plotNode(secondDict[key], (plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, leafNode) plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, str(key)) plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalD """ 函数说明:创建绘制面板 Parameters: inTree - 决策树(字典) Returns: 无 """ def createPlot(inTree): fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white') #创建fig fig.clf() #清空fig axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[]) createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops) #去掉x、y轴 plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree)) #获取决策树叶结点数目 plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree)) #获取决策树层数 plotTree.xOff = -0.5/plotTree.totalW; plotTree.yOff = 1.0; #x偏移 plotTree(inTree, (0.5,1.0), '') #绘制决策树 plt.show() #显示绘制结果 if __name__ == '__main__': dataSet, labels = createDataSet() featLabels = [] myTree = createTree(dataSet, labels, featLabels) print(myTree) createPlot(myTree)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
运行结果:
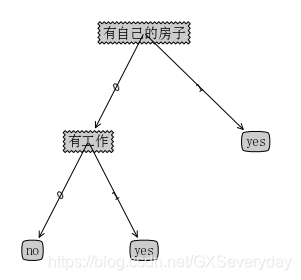
用决策树执行分类
用训练数据构造了决策树之后,我们可以将它用于数据的分类。比如我用上述已经训练好的决策树做分类,那么我只需要提供这个人是否有房子,是否有工作这两个信息即可,无需提供冗余的信息。
from math import log import operator """ 函数说明:计算给定数据集的经验熵(香农熵) Parameters: dataSet - 数据集 Returns: shannonEnt - 经验熵(香农熵) """ def calcShannonEnt(dataSet): numEntires = len(dataSet) #返回数据集的行数 labelCounts = {} #保存每个标签(Label)出现次数的字典 for featVec in dataSet: #对每组特征向量进行统计 currentLabel = featVec[-1] #提取标签(Label)信息 if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys(): #如果标签(Label)没有放入统计次数的字典,添加进去 labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0 labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1 #Label计数 shannonEnt = 0.0 #经验熵(香农熵) for key in labelCounts: #计算香农熵 prob = float(labelCounts[key]) / numEntires #选择该标签(Label)的概率 shannonEnt -= prob * log(prob, 2) #利用公式计算 return shannonEnt #返回经验熵(香农熵) """ 函数说明:创建测试数据集 Parameters: 无 Returns: dataSet - 数据集 labels - 特征标签 """ def createDataSet(): dataSet = [[0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'], #数据集 [0, 0, 0, 1, 'no'], [0, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'], [0, 1, 1, 0, 'yes'], [0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'], [1, 0, 0, 0, 'no'], [1, 0, 0, 1, 'no'], [1, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'], [1, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'], [1, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'], [2, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'], [2, 0, 1, 1, 'yes'], [2, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'], [2, 1, 0, 2, 'yes'], [2, 0, 0, 0, 'no']] labels = ['年龄', '有工作', '有自己的房子', '信贷情况'] #特征标签 return dataSet, labels #返回数据集和分类属性 """ 函数说明:按照给定特征划分数据集 Parameters: dataSet - 待划分的数据集 axis - 划分数据集的特征 value - 需要返回的特征的值 Returns: 无 """ def splitDataSet(dataSet, axis, value): retDataSet = [] #创建返回的数据集列表 for featVec in dataSet: #遍历数据集 if featVec[axis] == value: reducedFeatVec = featVec[:axis] #去掉axis特征 reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:]) #将符合条件的添加到返回的数据集 retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec) return retDataSet #返回划分后的数据集 """ 函数说明:选择最优特征 Parameters: dataSet - 数据集 Returns: bestFeature - 信息增益最大的(最优)特征的索引值 """ def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet): numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) - 1 #特征数量 baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet) #计算数据集的香农熵 bestInfoGain = 0.0 #信息增益 bestFeature = -1 #最优特征的索引值 for i in range(numFeatures): #遍历所有特征 #获取dataSet的第i个所有特征 featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet] uniqueVals = set(featList) #创建set集合{},元素不可重复 newEntropy = 0.0 #经验条件熵 for value in uniqueVals: #计算信息增益 subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, i, value) #subDataSet划分后的子集 prob = len(subDataSet) / float(len(dataSet)) #计算子集的概率 newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet) #根据公式计算经验条件熵 infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy #信息增益 # print("第%d个特征的增益为%.3f" % (i, infoGain)) #打印每个特征的信息增益 if (infoGain > bestInfoGain): #计算信息增益 bestInfoGain = infoGain #更新信息增益,找到最大的信息增益 bestFeature = i #记录信息增益最大的特征的索引值 return bestFeature #返回信息增益最大的特征的索引值 """ 函数说明:统计classList中出现此处最多的元素(类标签) Parameters: classList - 类标签列表 Returns: sortedClassCount[0][0] - 出现此处最多的元素(类标签) """ def majorityCnt(classList): classCount = {} for vote in classList: #统计classList中每个元素出现的次数 if vote not in classCount.keys():classCount[vote] = 0 classCount[vote] += 1 sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(), key = operator.itemgetter(1), reverse = True) #根据字典的值降序排序 return sortedClassCount[0][0] #返回classList中出现次数最多的元素 """ 函数说明:创建决策树 Parameters: dataSet - 训练数据集 labels - 分类属性标签 featLabels - 存储选择的最优特征标签 Returns: myTree - 决策树 """ def createTree(dataSet, labels, featLabels): classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet] #取分类标签(是否放贷:yes or no) if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList): #如果类别完全相同则停止继续划分 return classList[0] if len(dataSet[0]) == 1: #遍历完所有特征时返回出现次数最多的类标签 return majorityCnt(classList) bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet) #选择最优特征 bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat] #最优特征的标签 featLabels.append(bestFeatLabel) myTree = {bestFeatLabel:{}} #根据最优特征的标签生成树 del(labels[bestFeat]) #删除已经使用特征标签 featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet] #得到训练集中所有最优特征的属性值 uniqueVals = set(featValues) #去掉重复的属性值 for value in uniqueVals: #遍历特征,创建决策树。 myTree[bestFeatLabel][value] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeat, value), labels, featLabels) return myTree """ 函数说明:使用决策树分类 Parameters: inputTree - 已经生成的决策树 featLabels - 存储选择的最优特征标签 testVec - 测试数据列表,顺序对应最优特征标签 Returns: classLabel - 分类结果 """ def classify(inputTree, featLabels, testVec): firstStr = next(iter(inputTree)) #获取决策树结点 secondDict = inputTree[firstStr] #下一个字典 featIndex = featLabels.index(firstStr) for key in secondDict.keys(): if testVec[featIndex] == key: if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict': classLabel = classify(secondDict[key], featLabels, testVec) else: classLabel = secondDict[key] return classLabel if __name__ == '__main__': dataSet, labels = createDataSet() featLabels = [] myTree = createTree(dataSet, labels, featLabels) testVec = [0,1] #测试数据 result = classify(myTree, featLabels, testVec) if result == 'yes': print('可以借贷') if result == 'no': print('不可借贷')
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
运行结果:
可以借贷
- 1
决策树的存储
假设我们已经得到决策树{‘有房’: {0: {‘有车’: {0: ‘no’, 1: ‘yes’}}, 1: ‘yes’}},使用pickle.dump存储决策树。
import pickle """ 函数说明:存储决策树 Parameters: inputTree - 已经生成的决策树 filename - 决策树的存储文件名 Returns: 无 """ def storeTree(inputTree, filename): with open(filename, 'wb') as fw: pickle.dump(inputTree, fw) if __name__ == '__main__': myTree = {'有房': {0: {'有车': {0: 'no', 1: 'yes'}}, 1: 'yes'}} storeTree(myTree, 'classify.txt')
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
读取
import pickle """ 函数说明:读取决策树 Parameters: filename - 决策树的存储文件名 Returns: pickle.load(fr) - 决策树字典 """ def grabTree(filename): fr = open(filename, 'rb') return pickle.load(fr) if __name__ == '__main__': myTree = grabTree('classify.txt') print(myTree)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
运行结果:
{'有房': {0: {'有车': {0: 'no', 1: 'yes'}}, 1: 'yes'}}
- 1

声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,转载请注明出处:【wpsshop博客】
推荐阅读
相关标签



