- 1推荐几个免费的HTTP接口Mock网站和工具_在线mock平台
- 2【复杂网络】图模型在欺诈检测应用一点看法_图模型涉诈终端链路识别
- 3Android 科大讯飞持续语音唤醒识别问题及解决_科大讯飞语音识别 一直开启如何设置
- 4Python中的AIC和BIC_python中的aic是什么意思
- 5Kafka中的ISR、AR又代表什么?ISR的伸缩又指什么?
- 6Java性能优化:35 个小细节,让你提升Java代码的运行效率_怎样让java文件变得更流畅
- 7比 GPT-4 还厉害?Google 发布最强 AI 模型 Gemini
- 8Python与自然语言处理与NLP
- 9Unity3D 引擎学习2022资料整理(一)_rapier voxels
- 10如何辨别AI文章?四招教你识破_ai生成式论文如何甄别?有指导性的文章吗
最细致讲解yolov8模型推理完整代码--(前处理,后处理)_yolov8推理代码
赞
踩
研究yolov8时,一直苦寻不到Yolov8完整的模型推理代码演示,大部分都是基于Yolo已经封装好的函数调用,这个网上教程很多,本文就不赘述这方面的内容了,接下来将细致全面的讲解yolov8模型推理代码,也就是yolov8的predict的前处理(letterbox缩放),后处理(坐标转换,置信度过滤,NMS,绘图)的代码实现(附完整代码)。
前处理
letterbox缩放
yolov8预设的图片输入是640x640大小的,所以我们需要将一般大小的图像resize成标准大小,但是单纯的只是用resize来操作的话有可能会造成图像的失真:
原图: 直接resize后:
直接resize后:
所以yolov5提出letterbox缩放(v8也沿用了),其原理就是等比例缩放,其他的部分用背景色填充:

前处理代码如下:
- def resize_image(image, size, letterbox_image):
- """
- 对输入图像进行resize
- Args:
- size:目标尺寸
- letterbox_image: bool 是否进行letterbox变换
- Returns:指定尺寸的图像
- """
- from PIL import Image
- ih, iw, _ = image.shape
- h, w = size
- if letterbox_image:
- scale = min(w/iw, h/ih) # 缩放比例
- nw = int(iw*scale)
- nh = int(ih*scale)
- image = cv2.resize(image, (nw, nh), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
- # 生成画布
- image_back = np.ones((h, w, 3), dtype=np.uint8) * 128
- # 将image放在画布中心区域-letterbox
- image_back[(h-nh)//2: (h-nh)//2 + nh, (w-nw)//2:(w-nw)//2+nw, :] = image
- else:
- image_back = image
- return image_back

经过前处理后得到的图像尺寸为(640x640x3),为了对应yolov8模型的输入尺寸(N,C,H,W),我们对其进行预处理操作:
数据预处理
- def img2input(img):
- img = np.transpose(img, (2, 0, 1))
- img = img/255
- return np.expand_dims(img, axis=0).astype(np.float32) # (1,3,640,640)
因为只是做预测,所以N取1,C为通道数3。
现在就可以放进模型里计算了,本文采用的yolov8模型是onnx格式的。
- sess = rt.InferenceSession('runs/detect/train49/weights/best.onnx')
- input_name = sess.get_inputs()[0].name
- label_name = sess.get_outputs()[0].name
- pred = sess.run([label_name], {input_name: data})[0] # (bs, 84=80cls+4reg, 8400=3种尺度的特征图叠加), 这里的预测框的回归参数是xywh,而不是中心点到框边界的距离
模型得到的输出格式为(84x8400),84=边界框预测值4+数据集类别80, yolov8不另外对置信度预测, 而是采用类别里面最大的概率作为置信度score,8400是v8模型各尺度输出特征图叠加之后的结果(具体如何叠加可以看源码,一般推理不需要管)。本文对模型的输出进行如下操作,方便后处理:
- def std_output(pred):
- """
- 将(1,84,8400)处理成(8400, 85) 85= box:4 conf:1 cls:80
- """
- pred = np.squeeze(pred) # 因为只是推理,所以没有Batch
- pred = np.transpose(pred, (1, 0))
- pred_class = pred[..., 4:]
- pred_conf = np.max(pred_class, axis=-1)
- pred = np.insert(pred, 4, pred_conf, axis=-1)
- return pred #(8400,85)
得到输出(8400,85)。8400个特征图的cell,每个cell里面有4+1+80的输出值,对应4个预测框+1个置信度(最大类别概率)+80类别概率。
后处理
置信度过滤+NMS非极大值抑制
接下来就对刚刚的(8400,85)进行后处理,先进行置信度过滤,再进行NMS非极大值抑制,本文将这两步筛选操作放在了一个函数中:
- def nms(pred, conf_thres, iou_thres):
- """
- 非极大值抑制nms
- Args:
- pred: 模型输出特征图
- conf_thres: 置信度阈值
- iou_thres: iou阈值
- Returns: 输出后的结果
- """
- box = pred[pred[..., 4] > conf_thres] # 置信度筛选
- cls_conf = box[..., 5:]
- cls = []
- for i in range(len(cls_conf)):
- cls.append(int(np.argmax(cls_conf[i])))
-
- total_cls = list(set(cls)) # 记录图像内共出现几种物体
- output_box = []
- # 每个预测类别分开考虑
- for i in range(len(total_cls)):
- clss = total_cls[i]
- cls_box = []
- temp = box[:, :6]
- for j in range(len(cls)):
- # 记录[x,y,w,h,conf(最大类别概率),class]值
- if cls[j] == clss:
- temp[j][5] = clss
- cls_box.append(temp[j][:6])
- # cls_box 里面是[x,y,w,h,conf(最大类别概率),class]
- cls_box = np.array(cls_box)
- sort_cls_box = sorted(cls_box, key=lambda x: -x[4]) # 将cls_box按置信度从大到小排序
- # box_conf_sort = np.argsort(-box_conf)
- # 得到置信度最大的预测框
- max_conf_box = sort_cls_box[0]
- output_box.append(max_conf_box)
- sort_cls_box = np.delete(sort_cls_box, 0, 0)
- # 对除max_conf_box外其他的框进行非极大值抑制
- while len(sort_cls_box) > 0:
- # 得到当前最大的框
- max_conf_box = output_box[-1]
- del_index = []
- for j in range(len(sort_cls_box)):
- current_box = sort_cls_box[j]
- iou = get_iou(max_conf_box, current_box)
- if iou > iou_thres:
- # 筛选出与当前最大框Iou大于阈值的框的索引
- del_index.append(j)
- # 删除这些索引
- sort_cls_box = np.delete(sort_cls_box, del_index, 0)
- if len(sort_cls_box) > 0:
- output_box.append(sort_cls_box[0])
- sort_cls_box = np.delete(sort_cls_box, 0, 0)
- return output_box
-
-
- def xywh2xyxy(*box):
- """
- 将xywh转换为左上角点和左下角点
- Args:
- box:
- Returns: x1y1x2y2
- """
- ret = [box[0] - box[2] // 2, box[1] - box[3] // 2, \
- box[0] + box[2] // 2, box[1] + box[3] // 2]
- return ret
-
- def get_inter(box1, box2):
- """
- 计算相交部分面积
- Args:
- box1: 第一个框
- box2: 第二个框
- Returns: 相交部分的面积
- """
- x1, y1, x2, y2 = xywh2xyxy(*box1)
- x3, y3, x4, y4 = xywh2xyxy(*box2)
- # 验证是否存在交集
- if x1 >= x4 or x2 <= x3:
- return 0
- if y1 >= y4 or y2 <= y3:
- return 0
- # 将x1,x2,x3,x4排序,因为已经验证了两个框相交,所以x3-x2就是交集的宽
- x_list = sorted([x1, x2, x3, x4])
- x_inter = x_list[2] - x_list[1]
- # 将y1,y2,y3,y4排序,因为已经验证了两个框相交,所以y3-y2就是交集的宽
- y_list = sorted([y1, y2, y3, y4])
- y_inter = y_list[2] - y_list[1]
- # 计算交集的面积
- inter = x_inter * y_inter
- return inter
-
- def get_iou(box1, box2):
- """
- 计算交并比: (A n B)/(A + B - A n B)
- Args:
- box1: 第一个框
- box2: 第二个框
- Returns: # 返回交并比的值
- """
- box1_area = box1[2] * box1[3] # 计算第一个框的面积
- box2_area = box2[2] * box2[3] # 计算第二个框的面积
- inter_area = get_inter(box1, box2)
- union = box1_area + box2_area - inter_area #(A n B)/(A + B - A n B)
- iou = inter_area / union
- return iou

坐标转换
筛选完之后得到的输出output_box格式为N * [x,y,w,h,conf(最大类别概率),class] , N是筛选后预测框的个数, 通过[x,y,w,h,conf(最大类别概率),class]这些数据我们就可以将预测框输出绘制在原图像上, 但是要注意,我们此时模型的输入是经过letterbox处理的,所以需要先将预测框的坐标转换回原坐标系的坐标,
- def cod_trf(result, pre, after):
- """
- 因为预测框是在经过letterbox后的图像上做预测所以需要将预测框的坐标映射回原图像上
- Args:
- result: [x,y,w,h,conf(最大类别概率),class]
- pre: 原尺寸图像
- after: 经过letterbox处理后的图像
- Returns: 坐标变换后的结果,并将xywh转换为左上角右下角坐标x1y1x2y2
- """
- res = np.array(result)
- x, y, w, h, conf, cls = res.transpose((1, 0))
- x1, y1, x2, y2 = xywh2xyxy(x, y, w, h) # 左上角点和右下角的点
- h_pre, w_pre, _ = pre.shape
- h_after, w_after, _ = after.shape
- scale = max(w_pre/w_after, h_pre/h_after) # 缩放比例
- h_pre, w_pre = h_pre/scale, w_pre/scale # 计算原图在等比例缩放后的尺寸
- x_move, y_move = abs(w_pre-w_after)//2, abs(h_pre-h_after)//2 # 计算平移的量
- ret_x1, ret_x2 = (x1 - x_move) * scale, (x2 - x_move) * scale
- ret_y1, ret_y2 = (y1 - y_move) * scale, (y2 - y_move) * scale
- ret = np.array([ret_x1, ret_y1, ret_x2, ret_y2, conf, cls]).transpose((1, 0))
- return ret # x1y1x2y2

绘制预测框
输出的ret的格式为N * [x1,y1,x2,y2,conf(最大类别概率),class],接下来就可以进行最后一步操作了,对预测框进行绘制,但是为了美观需要注意将字体大小随着预测框的大小进行动态调整,以及字体显示不能超过边界。
- def draw(res, image, cls):
- """
- 将预测框绘制在image上
- Args:
- res: 预测框数据
- image: 原图
- cls: 类别列表,类似["apple", "banana", "people"] 可以自己设计或者通过数据集的yaml文件获取
- Returns:
- """
- for r in res:
- # 画框
- image = cv2.rectangle(image, (int(r[0]), int(r[1])), (int(r[2]), int(r[3])), (255, 0, 0), 1)
- # 表明类别
- text = "{}:{}".format(cls[int(r[5])], \
- round(float(r[4]), 2))
- h, w = int(r[3]) - int(r[1]), int(r[2]) - int(r[0]) # 计算预测框的长宽
- font_size = min(h/640, w/640) * 3 # 计算字体大小(随框大小调整)
- image = cv2.putText(image, text, (max(10, int(r[0])), max(20, int(r[1]))), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, max(font_size, 0.3), (0, 0, 255), 1) # max()为了确保字体不过界
- cv2.imshow("result", image)
- cv2.waitKey()
- cv2.destroyWindow("result")

输出结果
到此,最后输出结果展示:

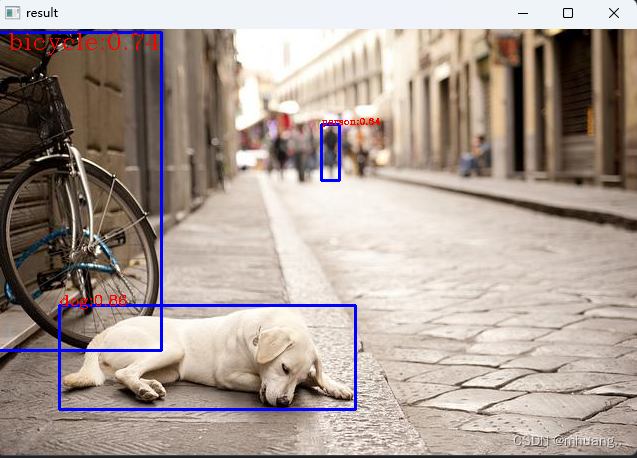
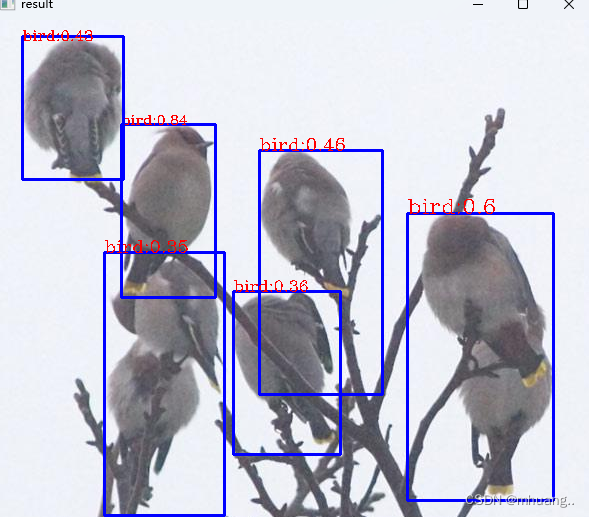
完整代码:(转载请注明本文,谢谢!)
- import copy
- import onnxruntime as rt
- import numpy as np
- import cv2
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- import yaml
-
- # 前处理
- def resize_image(image, size, letterbox_image):
- """
- 对输入图像进行resize
- Args:
- size:目标尺寸
- letterbox_image: bool 是否进行letterbox变换
- Returns:指定尺寸的图像
- """
- ih, iw, _ = image.shape
- print(ih, iw)
- h, w = size
- # letterbox_image = False
- if letterbox_image:
- scale = min(w/iw, h/ih)
- nw = int(iw*scale)
- nh = int(ih*scale)
- image = cv2.resize(image, (nw, nh), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
- # cv2.imshow("img", img)
- # cv2.waitKey()
- # print(image.shape)
- # 生成画布
- image_back = np.ones((h, w, 3), dtype=np.uint8) * 128
- # 将image放在画布中心区域-letterbox
- image_back[(h-nh)//2: (h-nh)//2 + nh, (w-nw)//2:(w-nw)//2+nw , :] = image
- else:
- image_back = image
- # cv2.imshow("img", image_back)
- # cv2.waitKey()
- return image_back
-
-
- def img2input(img):
- img = np.transpose(img, (2, 0, 1))
- img = img/255
- return np.expand_dims(img, axis=0).astype(np.float32)
-
- def std_output(pred):
- """
- 将(1,84,8400)处理成(8400, 85) 85= box:4 conf:1 cls:80
- """
- pred = np.squeeze(pred)
- pred = np.transpose(pred, (1, 0))
- pred_class = pred[..., 4:]
- pred_conf = np.max(pred_class, axis=-1)
- pred = np.insert(pred, 4, pred_conf, axis=-1)
- return pred
-
- def xywh2xyxy(*box):
- """
- 将xywh转换为左上角点和左下角点
- Args:
- box:
- Returns: x1y1x2y2
- """
- ret = [box[0] - box[2] // 2, box[1] - box[3] // 2, \
- box[0] + box[2] // 2, box[1] + box[3] // 2]
- return ret
-
- def get_inter(box1, box2):
- """
- 计算相交部分面积
- Args:
- box1: 第一个框
- box2: 第二个狂
- Returns: 相交部分的面积
- """
- x1, y1, x2, y2 = xywh2xyxy(*box1)
- x3, y3, x4, y4 = xywh2xyxy(*box2)
- # 验证是否存在交集
- if x1 >= x4 or x2 <= x3:
- return 0
- if y1 >= y4 or y2 <= y3:
- return 0
- # 将x1,x2,x3,x4排序,因为已经验证了两个框相交,所以x3-x2就是交集的宽
- x_list = sorted([x1, x2, x3, x4])
- x_inter = x_list[2] - x_list[1]
- # 将y1,y2,y3,y4排序,因为已经验证了两个框相交,所以y3-y2就是交集的宽
- y_list = sorted([y1, y2, y3, y4])
- y_inter = y_list[2] - y_list[1]
- # 计算交集的面积
- inter = x_inter * y_inter
- return inter
-
- def get_iou(box1, box2):
- """
- 计算交并比: (A n B)/(A + B - A n B)
- Args:
- box1: 第一个框
- box2: 第二个框
- Returns: # 返回交并比的值
- """
- box1_area = box1[2] * box1[3] # 计算第一个框的面积
- box2_area = box2[2] * box2[3] # 计算第二个框的面积
- inter_area = get_inter(box1, box2)
- union = box1_area + box2_area - inter_area #(A n B)/(A + B - A n B)
- iou = inter_area / union
- return iou
- def nms(pred, conf_thres, iou_thres):
- """
- 非极大值抑制nms
- Args:
- pred: 模型输出特征图
- conf_thres: 置信度阈值
- iou_thres: iou阈值
- Returns: 输出后的结果
- """
- box = pred[pred[..., 4] > conf_thres] # 置信度筛选
- cls_conf = box[..., 5:]
- cls = []
- for i in range(len(cls_conf)):
- cls.append(int(np.argmax(cls_conf[i])))
- total_cls = list(set(cls)) # 记录图像内共出现几种物体
- output_box = []
- # 每个预测类别分开考虑
- for i in range(len(total_cls)):
- clss = total_cls[i]
- cls_box = []
- temp = box[:, :6]
- for j in range(len(cls)):
- # 记录[x,y,w,h,conf(最大类别概率),class]值
- if cls[j] == clss:
- temp[j][5] = clss
- cls_box.append(temp[j][:6])
- # cls_box 里面是[x,y,w,h,conf(最大类别概率),class]
- cls_box = np.array(cls_box)
- sort_cls_box = sorted(cls_box, key=lambda x: -x[4]) # 将cls_box按置信度从大到小排序
- # box_conf_sort = np.argsort(-box_conf)
- # 得到置信度最大的预测框
- max_conf_box = sort_cls_box[0]
- output_box.append(max_conf_box)
- sort_cls_box = np.delete(sort_cls_box, 0, 0)
- # 对除max_conf_box外其他的框进行非极大值抑制
- while len(sort_cls_box) > 0:
- # 得到当前最大的框
- max_conf_box = output_box[-1]
- del_index = []
- for j in range(len(sort_cls_box)):
- current_box = sort_cls_box[j]
- iou = get_iou(max_conf_box, current_box)
- if iou > iou_thres:
- # 筛选出与当前最大框Iou大于阈值的框的索引
- del_index.append(j)
- # 删除这些索引
- sort_cls_box = np.delete(sort_cls_box, del_index, 0)
- if len(sort_cls_box) > 0:
- # 我认为这里需要将clas_box先按置信度排序, 才能每次取第一个
- output_box.append(sort_cls_box[0])
- sort_cls_box = np.delete(sort_cls_box, 0, 0)
- return output_box
-
- def cod_trf(result, pre, after):
- """
- 因为预测框是在经过letterbox后的图像上做预测所以需要将预测框的坐标映射回原图像上
- Args:
- result: [x,y,w,h,conf(最大类别概率),class]
- pre: 原尺寸图像
- after: 经过letterbox处理后的图像
- Returns: 坐标变换后的结果,
- """
- res = np.array(result)
- x, y, w, h, conf, cls = res.transpose((1, 0))
- x1, y1, x2, y2 = xywh2xyxy(x, y, w, h) # 左上角点和右下角的点
- h_pre, w_pre, _ = pre.shape
- h_after, w_after, _ = after.shape
- scale = max(w_pre/w_after, h_pre/h_after) # 缩放比例
- h_pre, w_pre = h_pre/scale, w_pre/scale # 计算原图在等比例缩放后的尺寸
- x_move, y_move = abs(w_pre-w_after)//2, abs(h_pre-h_after)//2 # 计算平移的量
- ret_x1, ret_x2 = (x1 - x_move) * scale, (x2 - x_move) * scale
- ret_y1, ret_y2 = (y1 - y_move) * scale, (y2 - y_move) * scale
- ret = np.array([ret_x1, ret_y1, ret_x2, ret_y2, conf, cls]).transpose((1, 0))
- return ret
-
- def draw(res, image, cls):
- """
- 将预测框绘制在image上
- Args:
- res: 预测框数据
- image: 原图
- cls: 类别列表,类似["apple", "banana", "people"] 可以自己设计或者通过数据集的yaml文件获取
- Returns:
- """
- for r in res:
- # 画框
- image = cv2.rectangle(image, (int(r[0]), int(r[1])), (int(r[2]), int(r[3])), (255, 0, 0), 1)
- # 表明类别
- text = "{}:{}".format(cls[int(r[5])], \
- round(float(r[4]), 2))
- h, w = int(r[3]) - int(r[1]), int(r[2]) - int(r[0]) # 计算预测框的长宽
- font_size = min(h/640, w/640) * 3 # 计算字体大小(随框大小调整)
- image = cv2.putText(image, text, (max(10, int(r[0])), max(20, int(r[1]))), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, max(font_size, 0.3), (0, 0, 255), 1) # max()为了确保字体不过界
- cv2.imshow("result", image)
- cv2.waitKey()
- return image
-
- # 加载配置文件
- config_file = "my_datasets/my_datasets.yaml"
- with open(config_file, "r") as config:
- config = yaml.safe_load(config)
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- std_h, std_w = 640, 640 # 标准输入尺寸
- dic = config["names"] # 得到的是模型类别字典
- class_list = list(dic.values())
- input_path = "my_datasets/images/" # 输入图片的根目录路径
- img_path = "000000000074.jpg" # 输入图片的文件名
- img = cv2.imread(input_path+img_path)
- if img.size == 0:
- print("路径有误!")
- # 前处理
- img_after = resize_image(img, (std_w, std_h), True) # (640, 640, 3)
- # 将图像处理成输入的格式
- data = img2input(img_after)
- # 输入模型
- sess = rt.InferenceSession('runs/detect/train49/weights/best.onnx') # yolov8模型onnx格式
- input_name = sess.get_inputs()[0].name
- label_name = sess.get_outputs()[0].name
- pred = sess.run([label_name], {input_name: data})[0] # 输出(8400x84, 84=80cls+4reg, 8400=3种尺度的特征图叠加), 这里的预测框的回归参数是xywh, 而不是中心点到框边界的距离
- pred = std_output(pred)
- # 置信度过滤+nms
- result = nms(pred, 0.5, 0.4) # [x,y,w,h,conf(最大类别概率),class]
- # 坐标变换
- result = cod_trf(result, img, img_after)
- image = draw(result, img, class_list)
- # 保存输出图像
- out_path = "./runs/my_predicts/"
- cv2.imwrite(out_path + img_path, image)
- cv2.destroyWindow("result")



