- 1LLM大模型服务器端部署_llm studio 在linux的安装
- 2FLINKSQL自定义UDF函数1之collect_list&collect_set_flink sql collect
- 3[ROS2基础]launch 文件和多节点进程_ros2 launch namespace
- 403_led_horse_run_v1 跑马灯
- 5MYSQL union 联合查询_mysql union使用场景
- 6docker-compose启动项目时报错Version in “./docker-compose.yml“ is unsupported._docker-compose.yml: `version` is obsolete
- 72024第十五届蓝桥杯 C/C++B组真题题解_蓝桥杯2024b组c语言答案
- 8多尺度:传统高斯金字塔,拉普拉斯金字塔及SIFT算法多尺度金字塔_高斯拉普拉斯金字塔 细节增强
- 9格子达AI高风险:如何识别与应对_格子达ai风险判定标准是什么
- 10Android Binder服务的获取与使用
DBSCAN聚类算法原理(含C++代码)
赞
踩
概述
DBSCAN(density-based spatial clustering)是一种基于密度的聚类算法,在机器学习和数据挖掘领域有广泛的应用,其聚类原理通俗点讲是每个簇类的密度高于该簇类周围的密度,噪声点的密度小于任一簇类的密度。如下图簇类ABC的密度大于周围的密度,噪声的密度低于任一簇类的密度,因此DBSCAN算法也能用于异常点检测。本文对DBSCAN算法进行了详细总结 。
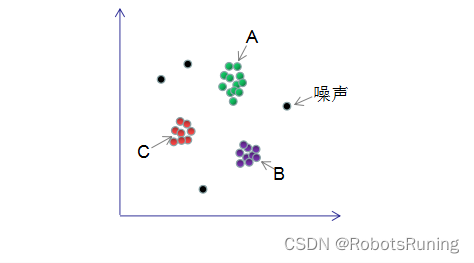
1. DBSCAN算法的样本点组成
DBSCAN算法处理后的聚类样本点分为:核心点(core points),边界点(border points)和噪声点(noise),这三类样本点的定义如下:
核心点:对某一数据集D,若样本p的 ε-领域内至少包含MinPts个样本(包括样本p),那么样本p称核心点。即:
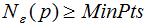
称p为核心点,其中 ε-领域 Nε(p)的表达式为:
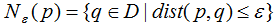
边界点:对于非核心点的样本b,若b在任意核心点p的ε-领域内,那么样本b称为边界点。即:

称b为边界点。
噪声点:对于非核心点的样本n,若n不在任意核心点p的 ε-领域内,那么样本n称为噪声点。即:

称n为噪声点。
假设MinPts=4,如下图的核心点、非核心点与噪声的分布:

2. DBSCAN算法原理
由上节可知,DBSCAN算法划分数据集D为核心点,边界点和噪声点,并按照一定的连接规则组成簇类。介绍连接规则前,先定义下面这几个概念:
密度直达(directly density-reachable):若q处于p的 ε-邻域内,且p为核心点,则称q由p密度直达;
密度可达(density-reachable):若q处于p的 ε-邻域内,且p,q均为核心点,则称q的邻域点由p密度可达;
密度相连(density-connected):若p,q均为非核心点,且p,q处于同一个簇类中,则称q与p密度相连。
下图给出了上述概念的直观显示(MinPts):

其中核心点E由核心点A密度直达,边界点B由核心点A密度可达,边界点B与边界点C密度相连,N为孤单的噪声点。
DBSCAN是基于密度的聚类算法,原理为:只要任意两个样本点是密度直达或密度可达的关系,那么该两个样本点归为同一簇类,上图的样本点ABCE为同一簇类。因此,DBSCAN算法从数据集D中随机选择一个核心点作为“种子”,由该种子出发确定相应的聚类簇,当遍历完所有核心点时,算法结束。
若我们使用的距离是曼哈顿(manhattan)距离,则邻域性状为矩形;若使用的距离是欧拉距离,则邻域形状为圆形。
DBSCAN算法可以抽象为以下几步:
1)找到每个样本的 ε-邻域内的样本个数,若个数大于等于MinPts,则该样本为核心点;
2)找到每个核心样本密度直达和密度可达的样本,且该样本亦为核心样本,忽略所有的非核心样本;
3)若非核心样本在核心样本的 ε-邻域内,则非核心样本为边界样本,反之为噪声。
3. DBSCAN算法的优缺点
优点:
1)DBSCAN不需要指定簇类的数量;
2)DBSCAN可以处理任意形状的簇类;
3)DBSCAN可以检测数据集的噪声,且对数据集中的异常点不敏感;
4)DBSCAN结果对数据集样本的随机抽样顺序不敏感(细心的读者会发现样本的顺序不一样,结果也可能不一样,如非核心点处于两个聚类的边界,若核心点抽样顺序不同,非核心点归于不同的簇类);
缺点:
1)DBSCAN最常用的距离度量为欧式距离,对于高维数据集,会带来维度灾难,导致选择合适的ε-值很难;
2)若不同簇类的样本集密度相差很大,则DBSCAN的聚类效果很差,因为这类数据集导致选择合适的minPts和ε-值非常难,很难适用于所有簇类。
4. C++ 代码实现
main.cpp
- // 包含DBSCAN算法的头文件
- #include"DBSCAN.h"
- // 包含输入输出流的头文件
- #include<iostream>
- // 包含文件流的头文件
- #include<fstream>
- // 包含字符串的头文件
- #include<string>
-
- // 包含PCL库的头文件,用于点云的输入输出、定义点的类型和可视化
- #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
- #include <pcl/point_types.h>
- #include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
-
- // 使用dbscan命名空间
- using namespace dbscan;
-
- // 主函数
- int main() {
-
- // 定义一个新的点云对象
- pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>);
-
- // 从文件中加载点云数据
- if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile<pcl::PointXYZRGB>("/home/fairlee/unknown_motion_state_landmarks.pcd", *cloud) == -1)
- {
- // 如果加载失败,输出错误信息并返回-1
- PCL_ERROR ("Couldn't read file \n");
- return (-1);
- }
-
- // 定义一个存储Point3<float>类型点的vector
- std::vector<Point3<float>> pointCloud;
-
- // 遍历加载的点云数据,将其添加到pointCloud vector中
- for(const auto& point: *cloud)
- {
- pointCloud.emplace_back(point.x, point.y, point.z);
- }
-
- // 使用DBSCAN算法进行聚类
- DBSCAN<float> dbscan(0.8f, 25, pointCloud);
- std::vector<std::vector<size_t>>cluster = dbscan.GetClusterPointSet();
-
- // 定义一个输出文件流对象
- std::ofstream output;
- // 遍历每个聚类
- for (int i = 0; i < cluster.size(); i++)
- {
- // 为每个聚类创建一个新的文本文件
- output.open("cluster" + std::to_string(i + 1) + ".txt");
- // 遍历聚类中的每个点
- for (size_t j = 0; j < cluster[i].size(); j++)
- {
- // 将点的坐标写入文件
- output << pointCloud[cluster[i][j]].x << " "
- << pointCloud[cluster[i][j]].y << " "
- << pointCloud[cluster[i][j]].z << " " << std::endl;
- }
- // 关闭文件
- output.close();
- }
-
- // 输出执行成功的消息
- std::cout << "执行成功!" << std::endl;
-
- // 创建一个新的可视化对象
- pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("Cluster Viewer");
-
- // 遍历每个聚类
- for (int i = 0; i < cluster.size(); i++)
- {
- // 创建一个新的点云对象来存储当前聚类的点
- pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr cluster_cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>);
-
- // 为当前聚类分配一个随机颜色
- uint8_t r = static_cast<uint8_t>(rand() % 256);
- uint8_t g = static_cast<uint8_t>(rand() % 256);
- uint8_t b = static_cast<uint8_t>(rand() % 256);
-
- // 从原始点云中提取当前聚类的点,并将它们添加到新的点云对象中
- for (size_t j = 0; j < cluster[i].size(); j++)
- {
- pcl::PointXYZRGB point;
- point.x = pointCloud[cluster[i][j]].x;
- point.y = pointCloud[cluster[i][j]].y;
- point.z = pointCloud[cluster[i][j]].z;
- point.r = r;
- point.g = g;
- point.b = b;
- cluster_cloud->points.push_back(point);
- }
-
- // 更新新点云的宽度和高度
- cluster_cloud->width = cluster_cloud->points.size();
- cluster_cloud->height = 1;
-
- // 为当前聚类创建一个唯一的字符串标识符
- std::string cluster_id = "cluster" + std::to_string(i);
-
- // 将当前聚类的点云添加到可视化对象中
- viewer.addPointCloud(cluster_cloud, cluster_id);
-
- // 设置点云的渲染属性(例如,点的大小)
- viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 2, cluster_id);
- }
-
- // 启动可视化循环
- while (!viewer.wasStopped())
- {
- viewer.spinOnce();
- }
-
- // 输出提示信息并等待用户输入,防止程序立即退出
- std::cout << "Press enter to continue...";
- std::cin.ignore(std::numeric_limits<std::streamsize>::max(), '\n');
-
- // 返回0表示程序正常退出
- return 0;
- }
-
-
-
-
Point3.h
- // 防止头文件被多次包含
- #ifndef POINT3
- #define POINT3
-
- // 定义一个常量表示未分类的点的类别标签
- const int NOT_CLASSIFIED = -1;
-
- // 定义一个命名空间dbscan,以便将Point3类与其他类区分开
- namespace dbscan {
-
- // 定义一个模板类Point3,T是点的坐标数据类型(例如float或double)
- template<typename T>
- class Point3
- {
- public:
- // 点的x, y, z坐标
- T x, y, z;
- // 点所属的聚类的标签
- int cluster = NOT_CLASSIFIED;
-
- // 带参数的构造函数,用于初始化点的坐标
- Point3(T x, T y, T z) :x(x), y(y), z(z) {
- }
-
- // 析构函数
- ~Point3() {
- }
-
- // 重载减法运算符,用于计算两个点的差
- Point3 operator-(const Point3& other) {
- return Point3(x - other.x, y - other.y, z - other.z);
- }
-
- // 重载加法运算符,用于计算两个点的和
- Point3 operator+(const Point3& other) {
- return Point3(x + other.x, y + other.y, z + other.z);
- }
-
- // 计算当前点到另一个点的平方距离的函数
- T getSqaureDistanceTo(const Point3& other) {
- T dx = x - other.x;
- T dy = y - other.y;
- T dz = z - other.z;
- return (dx*dx + dy*dy + dz*dz);
- }
- private:
- // 这个类没有私有成员或方法
- };
- }
-
- // 结束防止头文件被多次包含的预处理块
- #endif // !POINT3
PointDataSource.h
- // 防止头文件被多次包含
- #ifndef POINTDATASOURCE
- #define POINTDATASOURCE
-
- // 包含Point3类的定义
- #include"Point3.h"
- // 包含vector类模板的定义
- #include<vector>
-
- // 定义一个命名空间dbscan,以便将PointDataSource类与其他类区分开
- namespace dbscan {
-
- // 定义一个模板类PointDataSource,T是点的坐标数据类型(例如float或double)
- template<typename T>
- class PointDataSource
- {
- public:
- // 构造函数,用于通过Point3类型的指针和点的数量来初始化点云数据
- PointDataSource(Point3<T>* ptr, size_t count) :m_ptr(ptr), m_count(count) {
- }
-
- // 构造函数,用于通过一个Point3类型的vector来初始化点云数据
- PointDataSource(std::vector<Point3<T>>& pointCloud) :m_ptr(&pointCloud[0]), m_count(pointCloud.size()) {
- }
-
- // 默认构造函数,将点云数据的指针和数量初始化为nullptr和0
- PointDataSource() :m_ptr(nullptr), m_count(0) {
- }
-
- // 析构函数
- ~PointDataSource(){
- }
-
- // 默认的赋值运算符
- PointDataSource& operator=(const PointDataSource& other) = default;
-
- // 返回点云中的点的数量
- size_t size() {
- return m_count;
- }
-
- // 重载下标运算符,用于访问点云中的点
- Point3<T>& operator[](size_t index){
- return m_ptr[index];
- }
-
- // 返回指向点云数据开始的指针
- const Point3<T>* begin() {
- return m_ptr;
- }
-
- // 返回指向点云数据结束的指针
- const Point3<T>* end() {
- return m_ptr + m_count;
- }
-
- private:
- // 指向点云数据的指针
- Point3<T>* m_ptr;
- // 点云中的点的数量
- size_t m_count;
- };
- }
-
- // 结束防止头文件被多次包含的预处理块
- #endif // ! POINTDATASOURCE
DBSCAN.h
- // 防止头文件被多次包含
- #ifndef Dbscan
- #define Dbscan
-
- #include"Point3.h" // 包含Point3类的定义
- #include"PointDataSource.h" // 包含PointDataSource类的定义
-
- #include <pcl/point_types.h> // PCL库中定义的点类型
- #include <pcl/kdtree/kdtree_flann.h> // PCL库中的Kd树搜索方法
-
- // 定义一个命名空间dbscan,以便将DBSCAN类与其他类区分开
- namespace dbscan {
- const int NOISE = -2; // 定义一个常量表示噪声点的类别标签
- const int NOT_CLASSIFIED = -1; // 定义一个常量表示未分类点的类别标签
-
- // 定义一个模板类DBSCAN,T是点的数据类型(例如float或double)
- template<typename T>
- class DBSCAN
- {
- public:
-
- // 默认构造函数
- DBSCAN() = default;
-
- // 带参数的构造函数
- // Neighbourhood: 用于确定邻域的半径
- // MinPts: 形成一个聚类所需的最小点数
- // pointCloud: 输入的点云数据
- DBSCAN(float Neighbourhood, int MinPts, std::vector<Point3<T>>& pointCloud)
- :Neighbourhood(Neighbourhood), MinPts(MinPts), pointCloud(pointCloud) {
- }
-
- // 析构函数
- ~DBSCAN() {
- }
-
- // 获取聚类结果的函数
- std::vector<std::vector<size_t>> GetClusterPointSet() {
- std::vector<std::vector<size_t>> cluster; // 存储最终的聚类结果
- std::vector<size_t> kernelObj; // 存储核心对象的索引
- neighbourPoints.resize(pointCloud.size()); // 调整邻近点的大小与点云大小相同
- neighbourDistance.resize(pointCloud.size()); // 调整邻近点距离的大小与点云大小相同
-
- // 选择核心对象并找出它们的邻居
- SelectKernelAndNeighbour(kernelObj);
-
- // 迭代标记同一聚类的点
- int k = -1; // 初始化聚类数
- for (int i = 0; i < kernelObj.size(); i++)
- {
- if (pointCloud[kernelObj[i]].cluster != NOT_CLASSIFIED)
- {
- continue;
- }
- std::vector<T> queue;
- queue.push_back(kernelObj[i]);
- pointCloud[kernelObj[i]].cluster = ++k;
- while (!queue.empty())
- {
- size_t index = queue.back(); // 弹出最后一个核心对象
- queue.pop_back();
-
- if (neighbourPoints[index].size() > MinPts)
- {
- for (int j = 0; j < neighbourPoints[index].size(); j++)
- {
- if (k == pointCloud[neighbourPoints[index][j]].cluster)
- {
- continue;
- }
- queue.push_back(neighbourPoints[index][j]);
- pointCloud[neighbourPoints[index][j]].cluster = k;
- }
- }
- }
- }
-
- // 将聚类结果存储在cluster变量中
- cluster.resize(k + 1);
- for (size_t i = 0; i < pointCloud.size(); i++)
- {
- if (pointCloud[i].cluster != NOISE)
- {
- cluster[pointCloud[i].cluster].push_back(i);
- }
- }
-
- return cluster;
- }
-
- private:
- float Neighbourhood; // 邻域半径
- int MinPts; // 形成聚类的最小点数
- PointDataSource<T> pointCloud; // 点云数据
- std::vector<std::vector<int>> neighbourPoints; // 存储每个点的邻近点的索引
- std::vector<std::vector<T>> neighbourDistance; // 存储每个点到其邻近点的距离
-
- // 选择核心对象并找出它们的邻居的函数
- void SelectKernelAndNeighbour(std::vector<size_t>& kernelObj) {
- pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
- cloud->points.resize(pointCloud.size());
- for (size_t i = 0; i < pointCloud.size(); i++)
- {
- cloud->points[i].x = pointCloud[i].x;
- cloud->points[i].y = pointCloud[i].y;
- cloud->points[i].z = pointCloud[i].z;
- }
-
- pcl::KdTreeFLANN<pcl::PointXYZ> kdtree;
- kdtree.setInputCloud(cloud);
-
- for (size_t i = 0; i < pointCloud.size(); i++)
- {
- kdtree.radiusSearch(cloud->points[i], Neighbourhood, neighbourPoints[i], neighbourDistance[i]);
- if (neighbourPoints[i].size() >= MinPts)
- {
- kernelObj.push_back(i);
- }
- else
- {
- pointCloud[i].cluster = NOISE;
- }
- }
- }
- };
- }
-
- #endif // !Dbscan
算法运行结果:

5. MATLAB 代码实现
DBSCAN.m
- %DBSCAN聚类函数
- %data:点云数据
- %radius:搜索半径
- %MinPts:最小点数
- function clusters=DBSCAN(data,radius,MinPts)
- n = size(data,1);
- kdtree = KDTreeSearcher(data);
- clusters = zeros(n,1);
- nearPointIndexs = rangesearch(kdtree,data,radius);
-
- %找出所有符合条件的核心对象
- kenelObj = [];
- for i=1:size(nearPointIndexs,1)
- nearPoints = nearPointIndexs{i};
- if length(nearPoints) >= MinPts
- kenelObj(end+1) = i;
- else
- clusters(i) = -1;
- end
- end
-
- %根据密度进行聚类,-1为噪声点,0代表未定义
- classes = 0;
- for i=1:length(kenelObj)
- if clusters(kenelObj(i)) ~= 0
- continue;
- end
-
- result = kenelObj(i);
- classes = classes+1;
- clusters(kenelObj(i)) = classes;
- pointer = 1;
- fprintf("第%d类开始进行聚类...\n",classes);
- %通过广度遍历的方式来进行聚类
- while(pointer <= length(result))
- index = result(pointer);
-
- nearPoints = nearPointIndexs{index};
- if(length(nearPoints) > MinPts)
- tmp = clusters(nearPoints) ~= classes;
- tmpRes = nearPoints(tmp);
- clusters(tmpRes) = classes;
- result=[result,tmpRes];
- end
- pointer = pointer + 1;
- end
- end
- end
main.m
- %DBSCAN聚类方法
- clc
- clear
- close all;
-
- %获取点云数据
- [fileName,pathName]=uigetfile({'*.pcd';'*.txt'},'Input Data-File'); %选择要进行计算的三维点云数据文件路径
-
- if isempty(fileName) || length(fileName) == 1
- fprintf("未选择点云文件!\n");
- return;
- end
- pc = pcread([pathName,fileName]);
- Data = pc.Location; %获取点云的位置信息
-
- tic
- clusters = DBSCAN(Data,0.4,10);
- classes = unique(clusters);
- toc
- fprintf("共有%d个类别(包含噪声点)\n",length(classes));
-
- figure
- hold on
- grid on
- rotate3d on
- for i=1:length(classes)
- clusterRes = Data(clusters==classes(i),:);
- plot3(clusterRes(:,1),clusterRes(:,2),clusterRes(:,3),'.');
- end
-
- title('dbscan聚类');


