- 13.5动态规划--凸多边形的最优三角剖分_凸多边形最优三角剖分动态规划
- 2达梦8命令行创建数据库实例_达梦8建库语句
- 3Python与OpenCV:图像处理与计算机视觉实战指南_python opencv图片处理
- 4MySQL查询生成行号_mysql 生成行号 100
- 5Python学习笔记_一个Tkinter示例,使用FileDialog
- 6Module not found: Error: Can‘t resolve ‘sass-loader‘_module not found: error: can't resolve 'sass-loade
- 7超硬核Java工程师学习指南,真正的从入门到精通,众多粉丝亲测已拿offer!
- 8哈哈,苹果系统在虚拟机上运行的效果_虚拟机装苹果系统体验怎么样
- 9Java设计模式 _行为型模式_空对象模式
- 10FTP文件传输服务器有替代品吗?_server2022 ftp替代
论文阅读 (97):Differentiable Zooming for Multiple Instance Learning on Whole-slide Images_扰动最大化方法(perturbed maximum method)
赞
踩
1 要点
1.1 概述
题目:用于全幻灯片图像的多示例学习可微缩放 (Differentiable zooming for multiple instance learning on whole-slide images)
背景:多示例学习 (MIL) 在数字病理学中对十亿像素级的全幻灯片图像 (WSI) 分类变得愈发流行
问题:
- 已有的方法在单一放大的WSI上处理所有的组织区块,这将WSI级的上下文限制在单一尺度,且需要极大的计算资源;
- 扩展到多尺度的方法,需要更大的计算资源要求;
方法:受病理学诊断过程的启发,提出了ZoomMIL,其以端到端的方式学习且执行多级缩放,即汇聚多级尺度上的组织-上下文信息为多个WSI表示
1.2 代码
https://github.com/histocartography/zoommil
1.3 引用
@inproceedings{Thandiackal:2022:699715,
authorq = {Kevin Thandiackal and Bo Qi Chen and Pushpak Pati and Guillaume Jaume and Drew FK Williamson and Maria Gabrani and Orcun Goksel},
title = {Differentiable zooming for multiple instance learning on whole-slide images},
booktitle = {{ECCV}},
pages = {699--715},
year = {2022}
url = {https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19803-8_41}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
2 可微缩放MIL
2.1 注意力MIL
详情参见GAMIL中的门控注意力。
2.2 多级缩放
假设WSI在不同缩放下是可评估的,以 m ∈ { 1 , 2 , … , M } m\in\{ 1,2,\dots, M \} m∈{1,2,…,M}为索引,其中 M M M表示最大的缩放尺度。与特征金字塔类似,假设 m + 1 m+1 m+1处的放大倍数是 m m m处的两倍。为了高效地将MIL扩展到多级缩放,本文将从低到高倍率放大以分级鉴别高信息区块,并汇聚为最终的WSI表示:
- 计算每个区块的注意力得分 a m ∈ R N \mathbf{a}_m\in\mathbb{R}^N am∈RN;
- 具有最大注意力得分的
K
K
K个区块用于更高放大倍率下的操作,被选择的区块特征矩阵表示为:
H ~ m = T m ⊤ H m , (3) \tag{3} \tilde{\mathbf{H}}_m=\mathbf{T}_m^\top\mathbf{H}_m, H~m=Tm⊤Hm,(3)其中 T m ∈ { 0 , 1 } N × K \mathbf{T}_{m}\in\{ 0,1 \}^{N\times K} Tm∈{0,1}N×K是索引矩阵, H m ∈ R N × D \mathbf{H}_m\in\mathbb{R}^{N\times D} Hm∈RN×D是在 m m m处的区块特征矩阵。
与已有通过预处理获得多级缩放的方法不同,本文通过分类器 f ( ⋅ ) f(\cdot) f(⋅)的预测结果在第 m m m步直接选择区块。该过程不需要任何的损失或者额外的超参数。然后,由于top- K K K操作,该方法是不可导的。对此,扰动最大方法 (Perturbed maximum method) 被使用:
- 注意力系数 a m \mathbf{a}_m am添加均匀高斯噪声 Z ∈ R N \mathbf{Z}\in\mathbb{R}^N Z∈RN;
- 针对每个受扰动的注意力权重求解一个线性规划,其结果将被平均。因此,可微top-
K
K
K被重写为:
T = E Z ∼ N ( 0 , 1 ) [ arg max T ^ ⟨ T ^ , ( a m + σ Z ) 1 ⊤ ⟩ ] , (4) \tag{4} \mathbf{T}={\mathbb{E}}_{\mathbf{Z}\sim\mathcal{N}(0,\mathbb{1})}\left[ \argmax_{\hat{\mathbf{T}}}\langle \hat{\mathbf{T}}, (\mathbf{a}_m + \sigma \mathbf{Z}) \mathbf{1}^\top \rangle \right], T=EZ∼N(0,1)[T^argmax⟨T^,(am+σZ)1⊤⟩],(4)其中 1 ⊤ = [ 1 ⋯ 1 ] ∈ R 1 × K \mathbf{1}^\top=[1\cdots1]\in\mathbb{R}^{1\times K} 1⊤=[1⋯1]∈R1×K、 ( a m + σ Z ) ∈ R T × K (\mathbf{a}_m + \sigma \mathbf{Z})\in\mathbb{R}^{T\times K} (am+σZ)∈RT×K表示重复 K K K次后的扰动注意力权重,以及 ⟨ ⋅ ⟩ \langle\cdot\rangle ⟨⋅⟩表示点积。相应的Jacobian定义为:
J a m T = E Z ∼ N ( 0 , 1 ) [ arg max T ^ ⟨ T ^ , ( a m + σ Z ) 1 ⊤ ⟩ Z ⊤ / σ ] , (5) \tag{5} J_{\mathbf{a}_m}\mathbf{T}={\mathbb{E}}_{\mathbf{Z}\sim\mathcal{N}(0,\mathbb{1})}\left[ \argmax_{\hat{\mathbf{T}}}\langle \hat{\mathbf{T}}, (\mathbf{a}_m + \sigma \mathbf{Z}) \mathbf{1}^\top \rangle\mathbf{Z}^\top/\sigma \right], JamT=EZ∼N(0,1)[T^argmax⟨T^,(am+σZ)1⊤⟩Z⊤/σ],(5)
为了实验缩放目标,我们将索引矩阵
T
m
\mathbf{T}_m
Tm进行扩充,以选择区块特征
H
m
′
∈
R
N
⋅
4
(
m
′
−
1
)
×
D
\mathbf{H}_{m'}\in\mathbf{R}^{N\cdot4^{(m'-1)\times D}}
Hm′∈RN⋅4(m′−1)×D,其中
m
′
>
m
m'>m
m′>m。特别地,计算
T
m
\mathbf{T}_m
Tm和单位矩阵
1
m
′
=
diag
(
1
,
…
,
1
)
∈
R
4
(
m
′
−
1
)
×
4
(
m
′
−
1
)
1_{m'}=\text{diag}(1,\dots,1)\in\mathbb{R}^{4^{(m'-1)}\times4^{(m'-1)}}
1m′=diag(1,…,1)∈R4(m′−1)×4(m′−1)的Kronecker内积来获得索引矩阵
T
m
′
∈
{
0
,
1
}
N
⋅
4
(
m
′
−
1
)
×
K
⋅
4
(
m
′
−
1
)
\mathbf{T}_{m'}\in\{0,1\}^{N\cdot4^{(m'-1)}\times K\cdot4^{(m'-1)}}
Tm′∈{0,1}N⋅4(m′−1)×K⋅4(m′−1)。与公式3类似,在更高放大倍率
m
′
m'
m′使用注意力权重的区块选择可以计算为:
H
~
m
′
=
(
T
m
⊗
1
m
′
)
⊤
H
m
′
.
(6)
\tag{6} \tilde{\mathbf{H}}_{m'}=(\mathbf{T}_m\otimes1_{m'})^\top\mathbf{H}_{m'}.
H~m′=(Tm⊗1m′)⊤Hm′.(6)
2.3 双门注意力和多尺度聚合
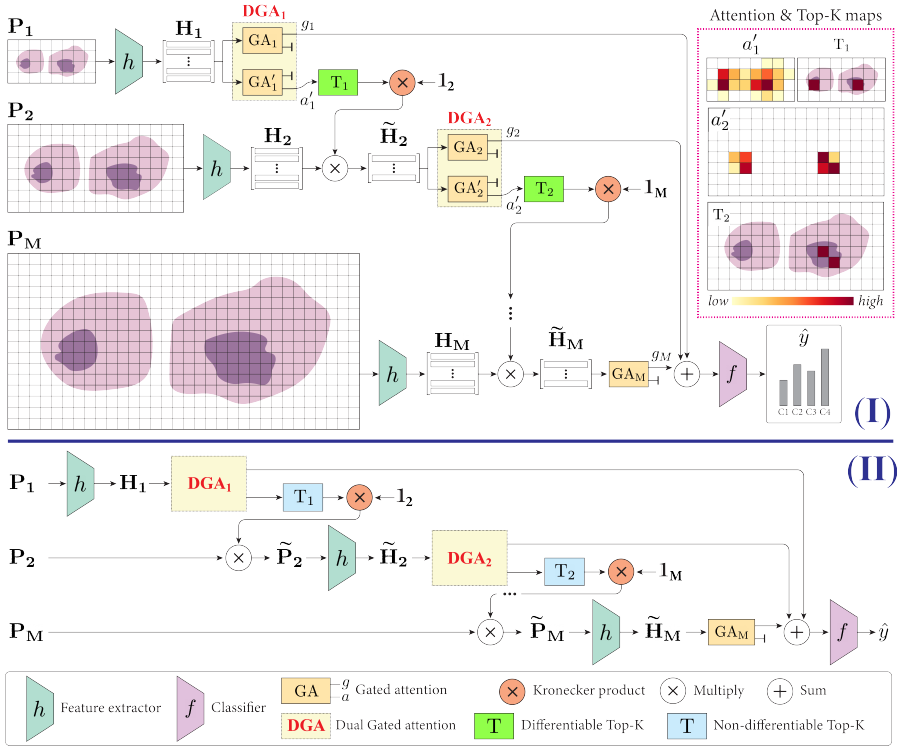
2.3.1 训练阶段
- m = 1 m=1 m=1时特征矩阵 H 1 \mathbf{H}_1 H1通过双门注意力 (DGA) 模块;
- DGA包含两个独立的门注意模块 GA 1 \text{GA}_1 GA1和 GA 1 ′ \text{GA}_1' GA1′;
- GA 1 \text{GA}_1 GA1在低缩放下获得基于注意力池化的最优WSI级表示;
- GA 1 ′ \text{GA}_1' GA1′获取有价值的注意力权重 a 1 ′ \mathbf{a}_1' a1′,以促进更高放大倍率的区块选择;
- 可微top- K K K选择模块 T 1 \mathbf{T}_1 T1被用于选择最有信息的区块;
- 选择过程持续到最大放大倍率 M M M;
- 被选择区块特征 H ~ M \tilde{H}_M H~M通过最后一个门控注意力块 GA M \text{GA}_M GAM来获取特征表示 g M \mathbf{g}_M gM;
- 加和池化用于汇聚多尺度,并使用分类器 f ( ⋅ ) f(\cdot) f(⋅)获取WSI标签 y ^ ∈ C \hat{y}\in C y^∈C;
2.3.2 推理阶段
- 去掉可微top- K K K模块中的扰动,使其变为不可微;
- 区块选择直接在WSI区块上进行;


