- 1Android Studio使用Kotlin开发Android入门_android studio 的kotlin
- 2Ollama--本地大语言模型LLM运行专家_ollama 模型
- 3无需租云服务器,Linux本地搭建web服务,并内网穿透发布公网访问_linux apache2 .内网穿透
- 4文本向量表征工具,实现了Word2Vec、RankBM25、Sentence-BERT、CoSENT,开箱即用
- 5IntelliJ IDEA常用插件 提高开发效率_sonarlint 卡顿
- 6缓存踩踏:Facebook史上最严重的宕机事件分析
- 7【网络】gateway 可以提供的一些功能之一 “ 提供web静态资源服务 ”
- 8解决MATLAB显示failed to initialize java
- 9计算机应用技术的历史与现状,浅析计算机应用技术的现状及发展趋势
- 10vue2 el-select 改造成下拉树,支持数据回显_el-tree-select vue 2
中文分词(1)--NLTK的基础使用
赞
踩
1 NLTK简介
NLTK(Natural language Toolkit):自然语言工具包,Python编程语言实现的统计自然语言处理(NLP)工具。它是由宾夕法尼亚大学计算机和信息科学的史蒂芬-伯德和爱德华·洛珀编写的。 NLTK支持NLP研究和教学相关的领域,包括经验语言学,认知科学,人工智能,信息检索和机器学习。 在25个国家中已有 32所大学将NLTK作为教学工具。
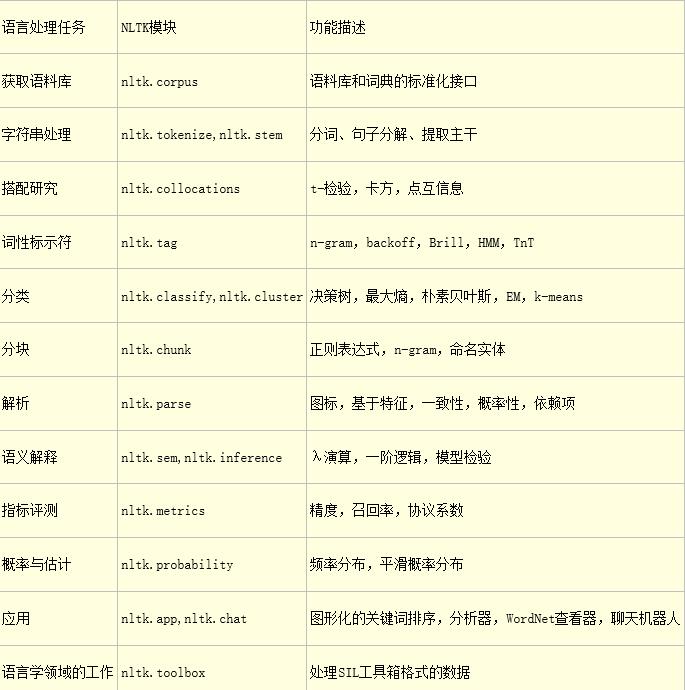
NLTK模块及功能介绍:
1 NLTK安装
1 查看python版本
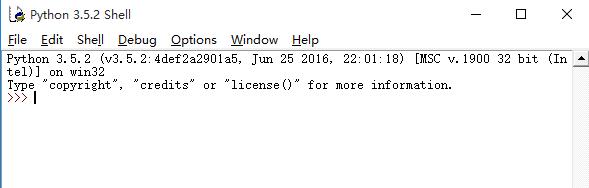
2 windows系统下载NLTK如下文件nltk-3.2.1.win32.exe,并执行exe文件,会自动匹配到python安装路径,如果没有找到路径说明nltk版本不正确,去官网选择正确版本号下载。
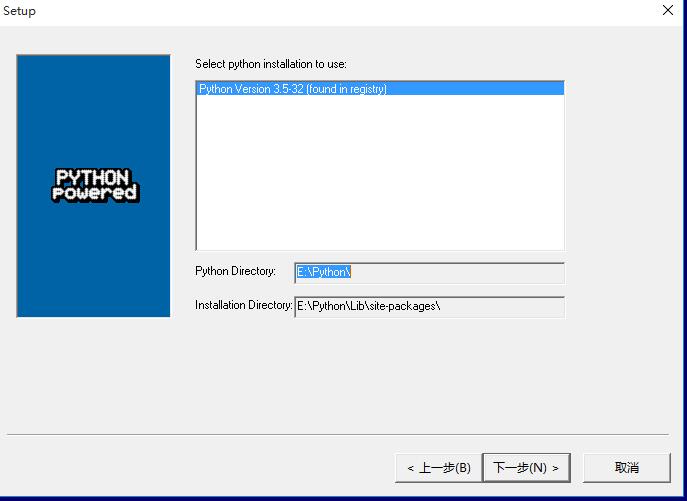
3 安装成功后,打开python编辑器,输入import nltk和nltk.download()下载NLTK_DATA,具体看下图,选中book,修改下载路径E:\Python\nltk_data,点击下载。(book包含了数据案例和内置函数)
|
1
2
|
>>> import nltk
>>> nltk.download()
|
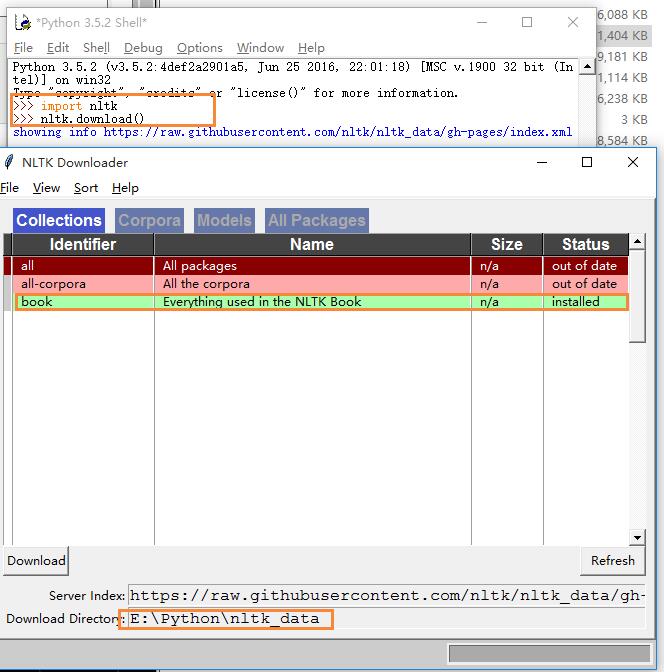
4 在计算机-属性-高级系统设置-高级-环境变量-系统变量-path:E:\Python\nltk_data
5.打开python解释器,输入form nltk.book import *,如下图表示安装成功。

6 接下来在64位win10下安装pip,numpy,scipy,下载并解压pip-8.1.2.tar.gz,win+R环境进入解压路径,安装setup.py文件,完成pip工具安装,然后配置下环境变量,yourpath\Python\Scripts
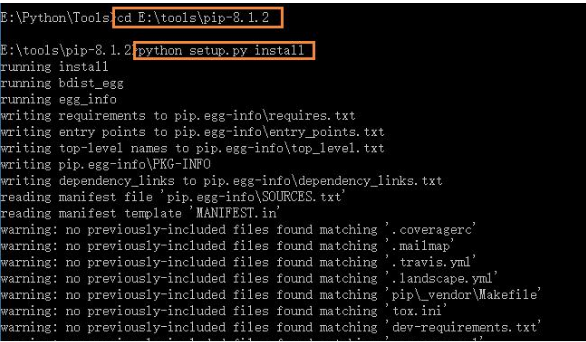
NLTK核心包:(包下载)
- NLTK-Data:分析和处理语言的语料库
- NumPy:科学计算库
- Matplotlib:数据可视化2D绘图库
- NetworkX:存储和操作有节点和边组成的网络结构函数库
7 通过pip工具安装numpy包,下载numpy-1.11.2+mkl-cp35-cp35m-win32.whl 进入下载路径下,输入如下指令安装。

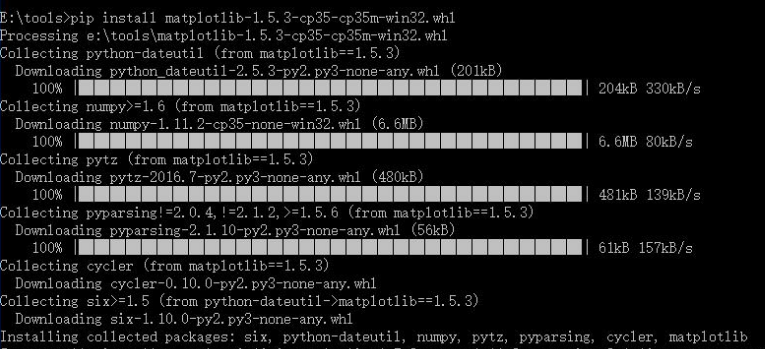
8 通过pip工具安装Matplotlib包,下载matplotlib-1.5.3-cp35-cp35m-win32.whl进入下载路径下,输入如下指令安装。
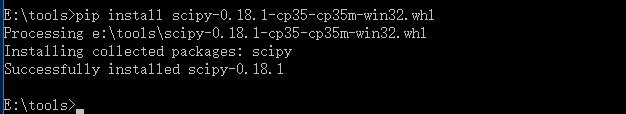
9 通过pip工具安装scipy包,下载scipy-0.18.1-cp35-cp35m-win32.whl 进入下载路径下,输入如下指令安装。
至此,完成所有操作,根据项目需要可以下载相应的包,点击这里基本包都有了。

3 NLTK基本操作
NLTK的book模块加载所有文档
|
1
2
3
4
|
>>> import nltk
>>>
from
nltk.corpus import *
>>> text1
<Text: Moby Dick
by
Herman Melville 1851>
|
函数concordance搜索指定内容

函数similar查找相似上下文

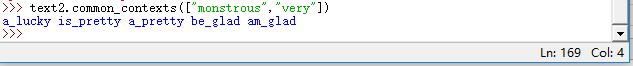
函数common_contexts共用多个词汇的上下文
函数dispersion_plot离散图表示词汇分布情况
判断词在文本中的位置,从开头算起有多少词出现,可以离散图表示,每一列代表一个单词,每一行代表有个文本
>>> text4.dispersion_plot(["citizens","democracy","freedom","duties","America"])

函数len()计数词汇
>>> len(text3)
44764
词汇表排序
>>> sorted(set(text3))

词汇表大小
>>> len(set(text3))
2789
每个词平均使用次数
>>> len(text3)/len(set(text3))
16.050197203298673
特定词在文本中出现的次数
>>> text3.count("smote")
5
特定词在文本中所占的百分比
>>> 100*text4.count('a')/len(text4)
1.4643016433938312
函数计算百分比
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
>>> def lexical_diversity(text):
return
len(text)/len(
set
(text))
>>> lexical_diversity(text4)
14.941049825712529
>>> lexical_diversity(text3)
16.050197203298673
>>> def percentage(count,total):
return
100 * count / total
>>> percentage(text4.count(
"a"
),len(text4))
1.4643016433938312
|
索引列表

NLTK搜索函数FreqDist()
查询文本text1中词汇分布情况,诸如the使用了13721次
|
1
2
3
|
>>> fdist1=FreqDist(text1)
>>> fdist1
FreqDist({
','
: 18713,
'the'
: 13721,
'.'
: 6862,
'of'
: 6536,
'and'
: 6024,
'a'
: 4569,
'to'
: 4542,
';'
: 4072,
'in'
: 3916,
'that'
: 2982, ...})
|
指定查询某个词的使用频率
|
1
2
|
>>> fdist1[
'whale'
]
906
|
指定常用词累积频率图
fdist1.plot(50,cumulative=True),text1中50个常用词的累积频率图,这些词占了所有标识的将近一半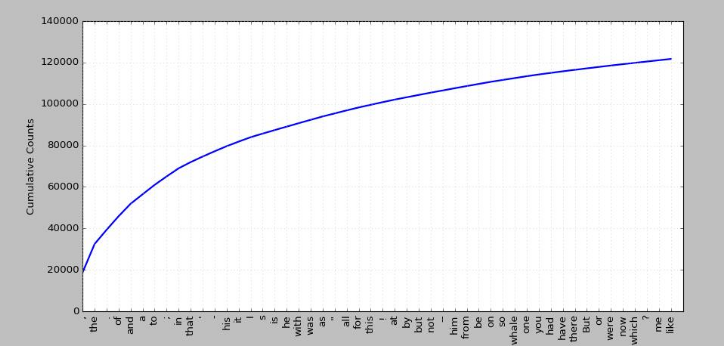
函数fdist1.hapaxes()低频词出现1次查找
细粒度查询
>>> V=set(text1)
>>> longwords=[w for w in V if len(w) > 15]
>>> sorted(longwords)

查询文本中单词长度大于7并且出现次数超过7次的
>>> sorted(w for w in set(text1) if len(w) > 7 and fdist1[w] > 7)

词语搭配个双连词
搭配:不经常在一起出现的词序列,如red wine是搭配而the wine就不是。另一个特点就是词不能被类似的词置换,如maroon wine(栗色酒)就不行
bigrams():获取搭配,提前文本词汇的双连词
>>> from nltk import bigrams
>>> from collections import Counter
>>> b = bigrams('This is a test')
>>> Counter(b)
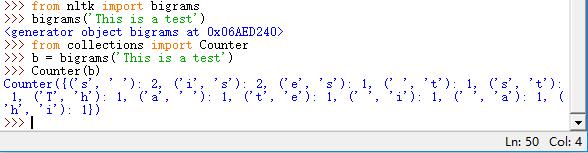
双连词的搭配
>>> text4.collocations()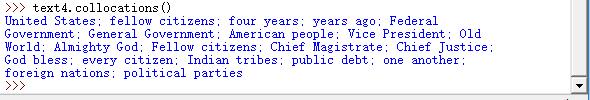
计算词长分布
>>> fdist=FreqDist([len(w) for w in text8])
>>> fdist
>>> fdist.keys()
词长频率统计
>>> fdist.items()
词数最多的长度
>>> fdist.max()
查找词长为3的百分比
>>> fdist.freq(3)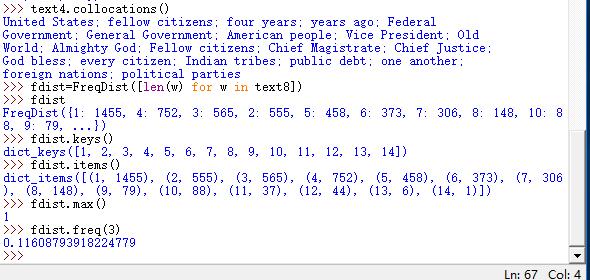
NLTK频率分布类中定义的函数
- fdist=FreqDist(Samples) 创建包含给定样本的频率分布
- fdist.inc(Sample) 增加样本
- fdist['monstrous'] 计数给定样本出现的次数
- fdist.freq('monstrous') 给定样本的频率
- fdist.N() 样本总数
- fdist.keys() 以频率递减顺序排序样本链表
- for sample in fdist: 以频率递减顺序遍历样本
- fdist.max() 数值最大的样本
- fdist.tabulate() 绘制频率分布表
- fdist.plot() 绘制频率分布图
- fdist.plot(cumulative=True)绘制累积频率分布图
- fdist1<fdist2 测试样本在fdist1中出现的频率是否小于fdist2
回到python:决策与控制
控制:按照我们意愿去处理关键特征
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
>>> sent7=[
'married'
,
'have'
,
'long'
,
'Seeking'
,
'country'
,
'nights'
,
'at'
,
'well'
,
'walks'
,
'home'
,
'would'
]
>>> [w
for
w
in
sent7
if
len(w)<4]
[
'at'
]
>>> [w
for
w
in
sent7
if
len(w)<=4]
[
'have'
,
'long'
,
'at'
,
'well'
,
'home'
]
>>> [w
for
w
in
sent7
if
len(w)==4]
[
'have'
,
'long'
,
'well'
,
'home'
]
>>> [w
for
w
in
sent7
if
len(w)!=4]
[
'married'
,
'Seeking'
,
'country'
,
'nights'
,
'at'
,
'walks'
,
'would'
]
|
共同的模式是:[w for w in text if condition],其中condition是一个python的测试
词汇比较运算
- s.startswith(t) 测试是否t开头
- s.endswith(t) 测试是否t结尾
- t in s 测试s是否包含t
- s.islower() 测试s所有字符是否都是小写字母
- s.isupper() 测试s所有字符是否都是大写字母
- s.isalpha() 测试s所有字符是否都是字母
- s.isalnum() 测试s所有字符是否都是字母或数字
- s.isdigit() 测试s所有字符是否都是数字
- s.istitle() 测试s所有词首字母都是大写
条件:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
sorted([w
for
w
in
set
(text1)
if
w.endswith(
'ableness'
)])
sorted([term
for
term
in
set
(text4)
if
'gnt'
in
term])
sorted([item
for
item
in
set
(text6)
if
item.istitle()])
sorted([item
for
item
in
set
(text7)
if
item.isdigit()])
>>> sorted([w
for
w
in
set
(text7)
if
'-'
and
'index'
in
w ])
[
'Stock-index'
,
'index'
,
'index-arbitrage'
,
'index-fund'
,
'index-options'
,
'index-related'
,
'indexers'
,
'indexes'
,
'stock-index'
]
>>> sorted([w
for
w
in
set
(text3)
if
w.istitle() and len(w)>11 ])
[
'Allonbachuth'
,
'Beerlahairoi'
,
'Chedorlaomer'
,
'Hazezontamar'
,
'Jegarsahadutha'
,
'Jehovahjireh'
,
'Peradventure'
,
'Zaphnathpaaneah'
]
>>> sorted([w
for
w
in
set
(text7)
if
not w.islower()])
>>> sorted([w
for
w
in
set
(text7)
if
w.islower()])
>>> sorted([w
for
w
in
set
(text7)
if
'cie'
in
w or
'cei'
in
w])
|
4 NLTK统计大秦帝国第一部词链表
下载孙皓晖先生的《大秦帝国.zip》文件,里面按照语料大小包含5个文件,分别是30852词的p1.txt、70046词的p2.txt、111970词的p3.txt、1182769词的p5.txt、419275词的p10.txt.本事了节选大秦帝国第一部673167字的dqdg.txt
打开Python编辑器,导出NLTK,并统计大秦帝国第一部共计多少字。(注:在读取文本的时候,python 3.5 IDLE 执行起来比较卡比较慢,采用pycharm就效率高很多了)
|
1
2
|
>>> with open(r
"C:\Users\cuitbnc\Desktop\dqdg.txt"
,
"r+"
)
as
f:
str=f.read()
|

查看大秦帝国第一部总共有多大的用字量,即不重复词和符合的尺寸:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
>>> len(
set
(str))
4053
>>> len(str)/len(
set
(str))
166.09104367135456
|
实验可知用了4053个尺寸的词汇表,平均每个词使用了166次,那么常用词分布如何呢?既然是大秦帝国,那么秦字使用了多少次呢?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
>>> str.count(
"秦"
)
3538
>>> str.count(
"大秦"
)
14
>>> str.count(
"国"
)
6536
|
可以知道,秦用词3538次,大秦用了14次,因为讲的各国之间的事情,国也是高频词6536次。如上所述大秦帝国第一部总词汇表673167,整个词汇累积分布如何?
>>> fdist=FreqDist(str)
>>> fdist.plot()
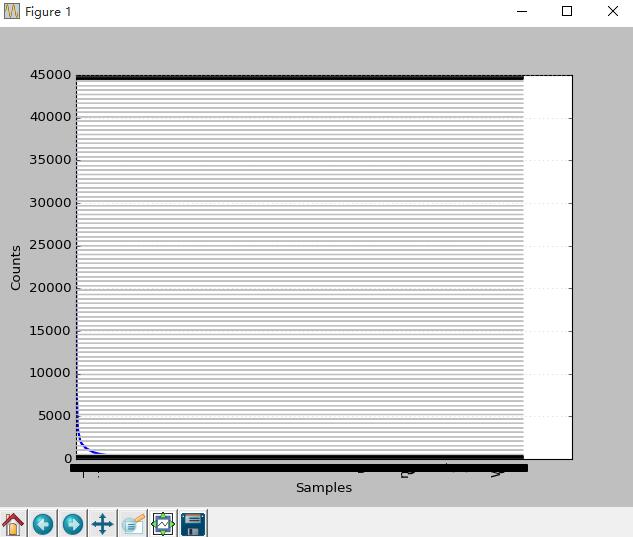
这个图横坐标表示词的序列,纵坐标表示词频。表说明词频大于5000的非常少,说明高频词不多。低频词特别多。后面进一步探究下.
看看整本书的累积分布情况如何?
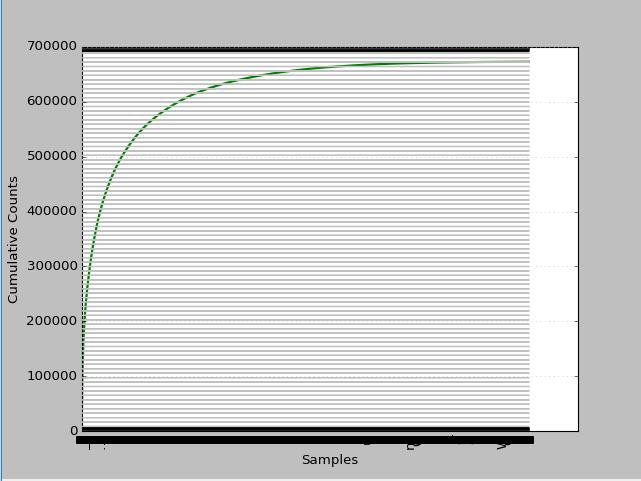
分析上图我们不难发现,3万以下是低频词大于30%,高频词大于1.4%,中频占68.6%(偏低中频2万左右占29.85%,偏高中频占8.96%)
研究下高频率的1000个词情况?看看都有哪些?
>>> sorted(set(str[:1000]))

查看1000个高频词分布如何?
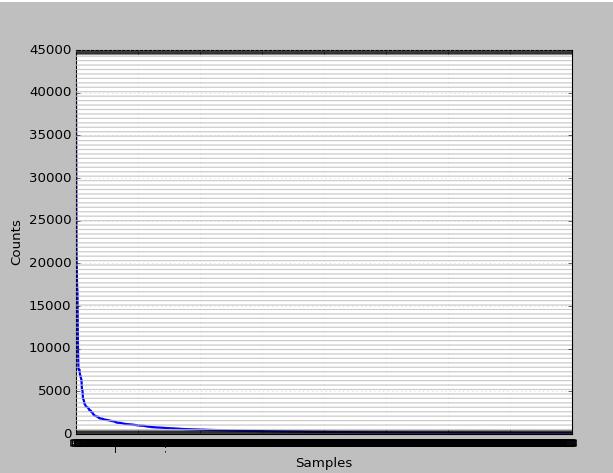
1000个高频的累计分布又如何?
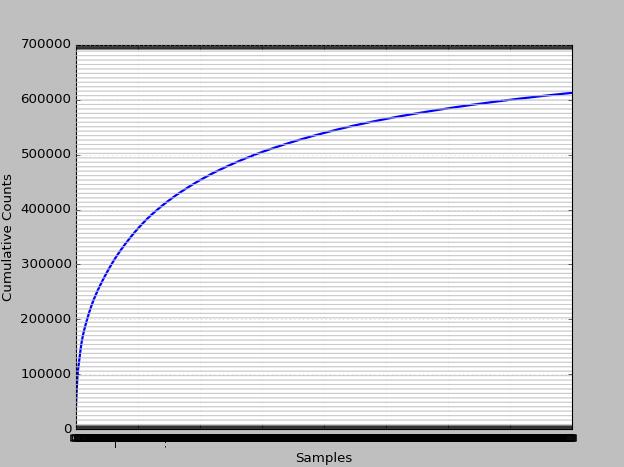
初略估计下大于占了80%以上。频率最高的前100词的分布如何?

前100个词也就是大约0.02%的词在本书的累积分布情况怎样呢?
>>> fdist=FreqDist(str)
>>> fdist.plot(100,cumulative=True)
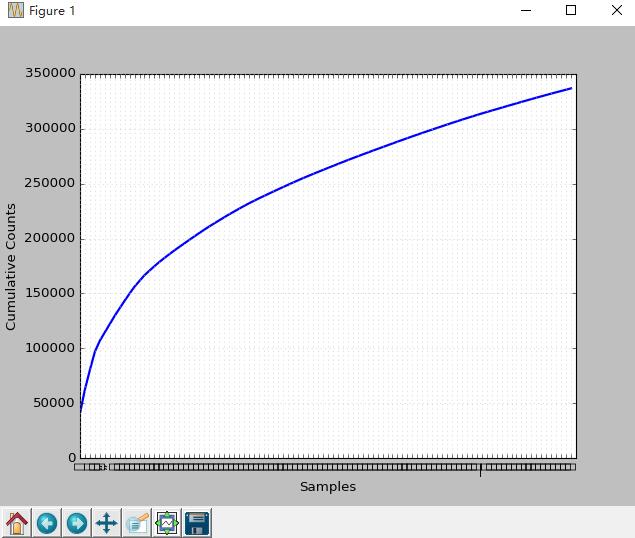
如图可知,前0.2%词汇占据整本书的50%以上的比例。国、旗、秦、魏、队、阅等跟战争相关词汇使用较多。那么低频词如何呢?有时候低频词也具有其特殊的研究价值。
>>> FreqDist(str).hapaxes()

统计可知大约有4053个词出现一次,占比0.6%
词语内部搭配又是如何?
|
1
2
|
>>>
from
collections import Counter
>>> V=Counter(str)
|
大秦帝国第一部用词统计
查看词汇
>>> sorted(V.keys())

查看词汇频率排名
>>> sorted(V.values())

查询词频在[0--100]的词有多少?
>>> len([w for w in V.values() if w<100])
3103
查询词频在[100--1000]的词有多少?
>>> len([w for w in V.values() if w>100 and w<1000])
819
查询词频在[1000-5000]的词有多少?
>>> len([w for w in V.values() if w>1000 and w<5000])
113
查询词频在[5000--]的词有多少?
>>> len([w for w in V.values() if w>5000])
14
双连词:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
import nltk
from
nltk.book import *
from
nltk import bigrams
from
collections import Counter
with open(r
"C:\Users\cuitbnc\Desktop\dqdg.txt"
,
"r"
)
as
f:
str=f.read()
V=bigrams(str)
W=Counter(V)
print(W)
|
结果
5 自动理解自然语言
词意消歧
看下面歧义的句子:词意消歧就是分析出特定上下文的词被赋予的哪个意思。
- 1.川大学生上网成瘾如患绝症。歧义在于“川大学生”(1)四川大学的学生(2)四川的大学生
- 2.两代教授,人格不同。歧义:“两代”(1)两位代理教授(2)两个时代的教授
- 3.被控私分国有资产,专家总经理成了被告人。歧义:“专家总经理”(1)专家和总经理(2)有专家身份的总经理
- 4.新生市场苦熬淡季。歧义:“新生”(1)新学生的市场(2)新产生的市场
- 5.朝鲜十年走近国际社会一步。歧义:“十年走近国际社会一步”(1)每十年就向国际社会走近一步(2)最近十年间向国际社会走近了一步
- 6.新汽车牌照。歧义:“新”(1)新的汽车(2)新的牌照
- 7.咬死了猎人的狗。歧义:(1)猎人的狗被咬死了(2)把猎人咬死了的那条狗
- 8.菜不热了。歧义:“热”(1)指菜凉了(2)指菜不加热了
- 9.还欠款四万元。歧义:“还”(1)读huai(2)读hai
- 10.北京人多。歧义:(1)北京/人多(2)北京人/多
指代消解
指代消解是解决“谁对谁做了 什么”,处理如上所述自然语言的问题,下面看看例子
- (1)美国政府表示仍然支持强势美元,但这到底只是嘴上说说还是要采取果断措施,经济学家对此的看法是否定的。
- (2)今天老师又在班会上表扬了自己,但是我觉得还需要继续努力。
- (3)三妹拉着葛姐的手说,她老家在偏远的山区,因为和家里赌气才跑到北京打工的,接着她又哭泣起自己的遭遇来。
- (4)当他把证书发给小钱时,他对他笑了。
- (5)小明和肖华去公园玩,他摔了一跤,他急忙把他扶起来.
- (6)星期天,小雨和小英到田老师家补习功课,她一早就打电话给她约好在红旗饭店吃早餐.


