热门标签
热门文章
- 1git常用回滚命令_git rollback命令
- 2工作记录------PostMan自测文件导入、导出功能_postman 导出pdf
- 3Linux 环境配置 VScode copilot_linux copilot
- 4FPGA-图像处理-仿真_vivado图像处理仿真
- 5Windows下常用的DOS命令_windows dos命令
- 6【主色提取】模糊C均值(FCM )聚类算法和彩色图像快速模糊C均值( CIQFCM )聚类算法_什么是fcm聚类
- 7WebUI自动化学习(Selenium+Python+Pytest框架)002_pyhton使用pytest框架写webui自动化
- 8Golang中的字符串迭代与索引_go 字符索引
- 9未来10年云计算发展前景如何?云计算的优势在哪里?_云计算在未来5-10年对商业和社会产生的影响和变化
- 109.4.k8s的控制器资源(job控制器,cronjob控制器)
当前位置: article > 正文
【数据结构】队列(queue)-顺序队列(动态图解、c++、java)
作者:不正经 | 2024-05-07 23:58:30
赞
踩
顺序队列
GitHub同步更新(已分类):Data_Structure_And_Algorithm-Review
公众号:URLeisure 的复习仓库
公众号二维码见文末
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
什么是队列?
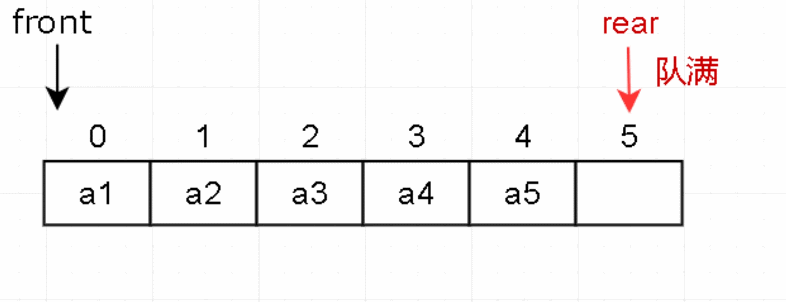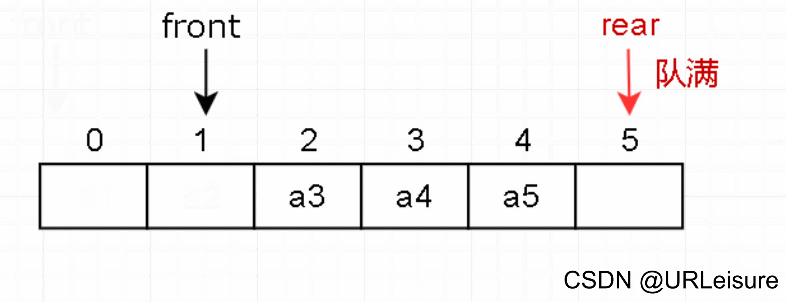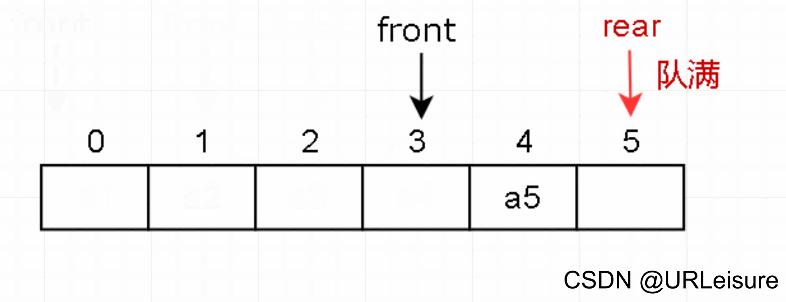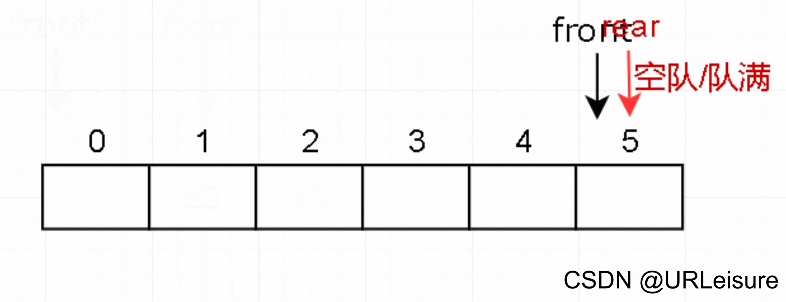
- 队列是一种特殊的线性表,特殊之处在于它只允许在表的前端(front)进行删除操作,而在表的后端(rear)进行插入操作,和栈一样,队列是一种操作受限制的线性表。
- 进行插入操作的端称为队尾,进行删除操作的端称为队头。
- 这种先进先出(First In First Out,FIFO)的线性序列,称为“队列”。它的操作受限,只能在两端操作:一端进,一端出。
- 进的一端称为队尾(rear),出的一端称为队头(front)。队列可以用顺序存储,也可以用链式存储。
顺序队列概述(图解)
- 队列犹如火车穿山洞,先进去的部分先出来。(图片来源:淘宝)

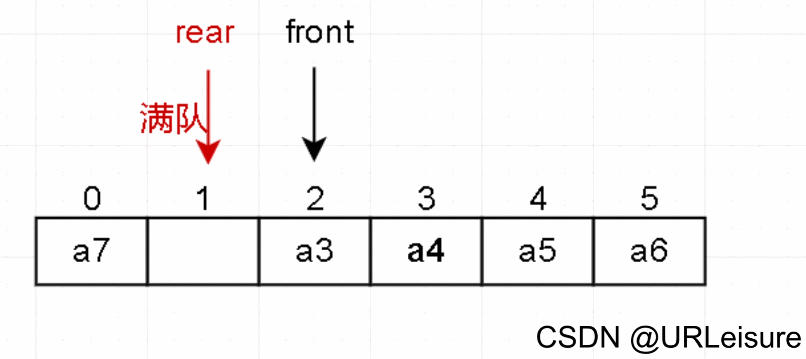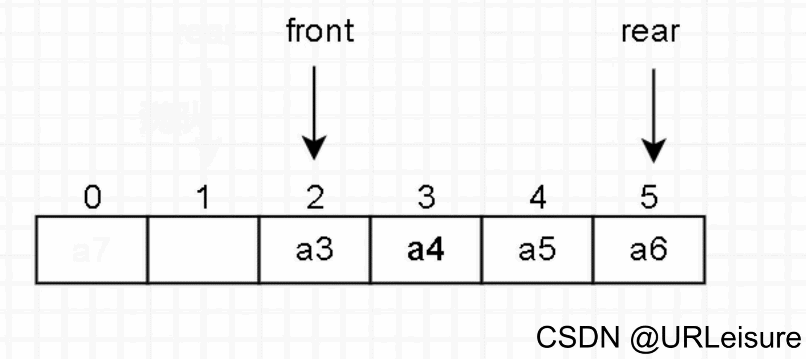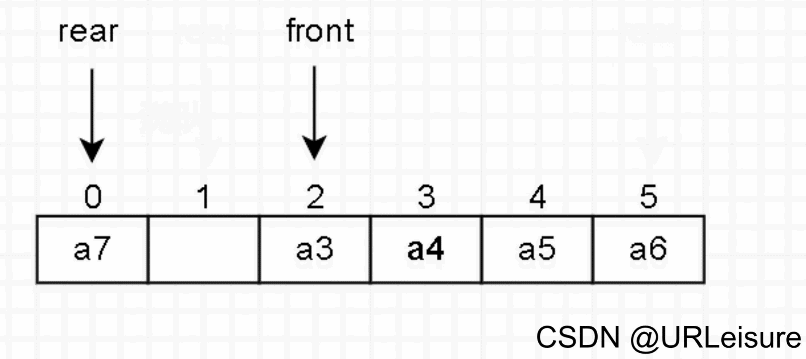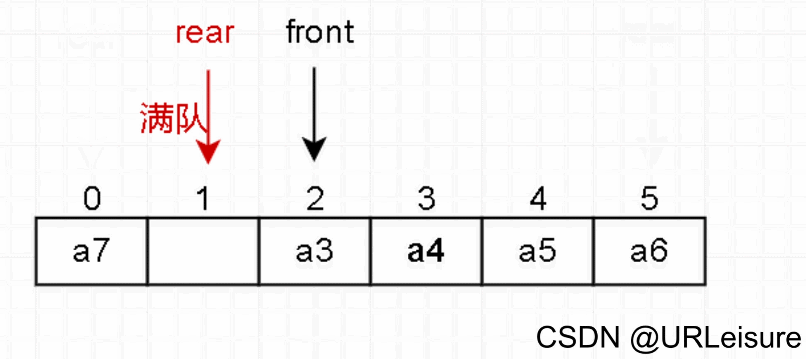
- 队列的顺序存储采用一段连续的空间存储数据元素,并用两个整形变量记录对头和队尾元素的下标。

顺序队列的基本操作
- 首先定义一个结构体(内部类),包含基地址和头尾索引。
c++代码如下(示例):
struct SqQueue{
int *base;//基地址
int front,rear;//头索引 尾索引
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
java代码如下(示例):
private class SqQueue{
int []base;
int front,rear;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
1. 初始化
- 顺序队列定义好了之后,还要先定义一个最大的分配空间,顺序结构都是如此,需要预先分配空间。

c++代码如下(示例):
bool InitQueue(SqQueue &Q){
Q.base = new int[Maxsize];//分配空间
if(!Q.base){//创建失败
return false;
}
Q.front = Q.rear = 0;
return true;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
java代码如下(示例):
public boolean initQueue(){
q = new SqQueue();
q.base = new int[maxsize];
if(q.base == null){
return false;
}
q.front = q.rear = 0;
return true;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
2. 入队
-
判断队列是否已满。
-
元素放入队尾 rear 的位置,然后 rear 后移一位。
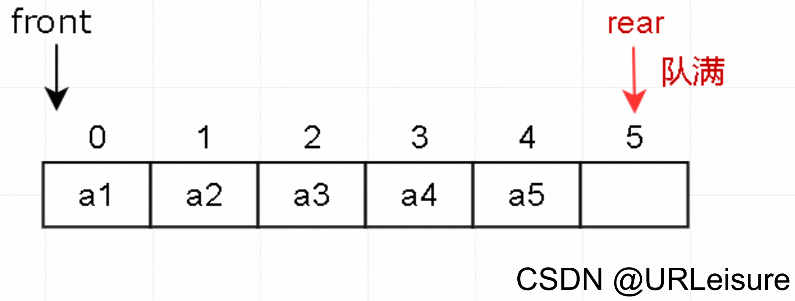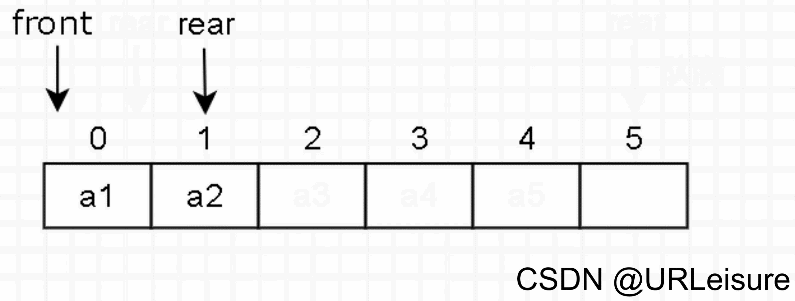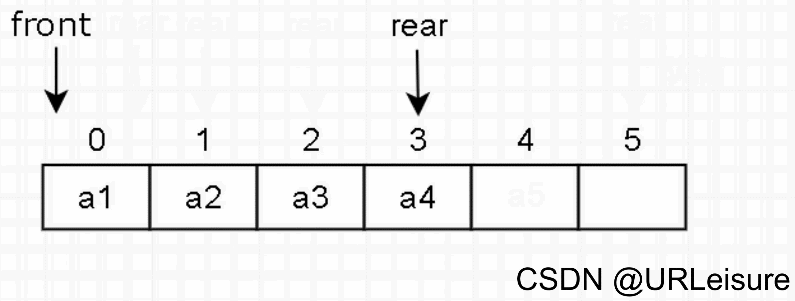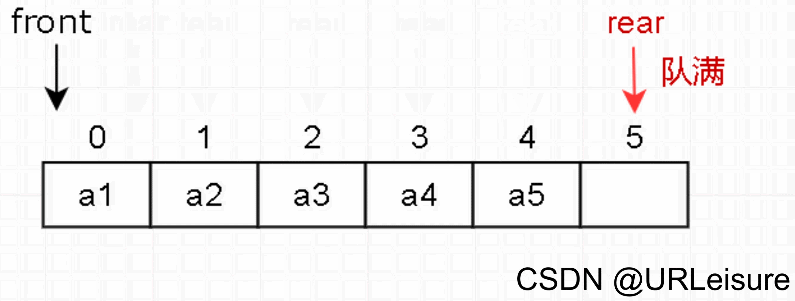
c++代码如下(示例):
bool EnQueue(SqQueue &Q,int e){
if(Q.rear>Maxsize - 1){//队满
return false;
}
Q.base[Q.rear++] = e;//Q.base[Q.rear] = e; Q.rear++;
return true;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
java代码如下(示例):
public boolean enQueue(int e){
if(q.rear > maxsize-1){
return false;
}
q.base[q.rear++] = e;
return true;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
3. 出队
-
判断队列是否为空。
-
元素出队,然后队头 front 后移一位。
(在总结时会说明为何 front 后移之后还是队满状态。)
c++代码如下(示例):
bool DeQueue(SqQueue &Q,int &e){//e为出队元素值
if(Q.front == Q.rear){//队空
return false;
}
e = Q.base[Q.front++];//出队
return true;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
java代码如下(示例):
public int deQueue(){
if(q.rear == q.front){
return -1;
}
return q.base[q.front++];
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
4. 查看队头元素
- 没什么好说的,太简单了。确保队列含有元素就行。
c++代码如下(示例):
int GetHead(SqQueue Q){
if(Q.front != Q.rear){//队列非空
return Q.base[Q.front];
}
return -1;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
java代码如下(示例):
public int getHead(){
if(q.rear != q.front){
return q.base[q.front];
}
return -1;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
5. 队列长度
c++代码如下(示例):
int QueueLength(SqQueue Q){
return (Q.rear-Q.front);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
java代码如下(示例):
public int queueLength(){
return q.rear-q.front;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
6. 释放空间
- java 自动释放,c++ 需手动释放。
c++代码如下(示例):
void DestroyList(SqQueue &Q){
if(Q.base){
delete []Q.base;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
完整代码
c++代码如下(示例):
#include<iostream>
#define Maxsize 7
using namespace std;
struct SqQueue {
int *base;
int front, rear;
};
bool InitQueue(SqQueue &Q) {
Q.base = new int[Maxsize];
if (!Q.base) {
return false;
}
Q.front = Q.rear = 0;
return true;
}
bool EnQueue(SqQueue &Q, int e) {
if (Q.rear > Maxsize - 1) {
return false;
}
Q.base[Q.rear++] = e;
return true;
}
bool DeQueue(SqQueue &Q, int &e) {
if (Q.front == Q.rear) {
return false;
}
e = Q.base[Q.front++];
return true;
}
int GetHead(SqQueue Q) {
if (Q.front != Q.rear) {
return Q.base[Q.front];
}
return -1;
}
int QueueLength(SqQueue Q) {
return (Q.rear - Q.front);
}
void DestroyList(SqQueue &Q) {
if (Q.base) {
delete []Q.base;
}
}
int main() {
SqQueue Q;
int n, e;
InitQueue(Q);
cout << "输入元素个数" << endl;
cin >> n;
cout << "依次输入元素入队" << endl;
while (n--) {
cin >> e;
EnQueue(Q, e);
}
cout << "队列长度:" << QueueLength(Q) << endl;
cout << "队头元素:" << GetHead(Q) << endl;
cout << "开始出队:" << endl;
while (DeQueue(Q, e)) {
cout << "出队元素:" << e << endl;
}
cout << "队列长度:" << QueueLength(Q) << endl;
DestroyList(Q);
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
java代码如下(示例):
import java.util.Scanner;
public class A {
private static Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
private static final int maxsize = 7;
private static class SqQueue {
int[] base;
int front, rear;
}
private static SqQueue q;
public static boolean initQueue() {
q = new SqQueue();
q.base = new int[maxsize];
if (q.base == null) {
return false;
}
q.front = q.rear = 0;
return true;
}
public static boolean enQueue(int e) {
if (q.rear > maxsize - 1) {
return false;
}
q.base[q.rear++] = e;
return true;
}
public static int deQueue() {
if (q.rear == q.front) {
return -1;
}
return q.base[q.front++];
}
public static int getHead() {
if (q.rear != q.front) {
return q.base[q.front];
}
return -1;
}
public static int queueLength() {
return q.rear - q.front;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n, x;
initQueue();
System.out.println("输入元素个数");
n = input.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入每个元素");
while (n-- > 0) {
x = input.nextInt();
enQueue(x);
}
System.out.println("队列元素个数:" + queueLength());
System.out.println("队头元素是:" + getHead());
System.out.println("开始出队:");
while ((x = deQueue()) != -1) {
System.out.println("队头元素为:" + x);
}
System.out.println("队列元素个数:" + queueLength());
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
总结
-
从图解和代码不难看出,当rear指向Maxsize位置时,有元素出队,但当前还是队满状态。这种情况称为“假溢出”。
-
解决的方法也很简单,如图。需要用到简单的循环操作,在下下下下下一篇的文章中会有另一种队列——循环队列,来实现此方法。
关注公众号,感受不同的阅读体验

下期预告: 顺序栈
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/不正经/article/detail/551847
推荐阅读
相关标签


