热门标签
热门文章
- 1经典排序算法的VC实现_vc实现文件按时间顺序排列
- 22024年软件测试最全当前软件测试市场现状,2024年最新跳槽大厂必看
- 3模块化 git管理_gitlab 一个项目多个模块
- 4SpringBoot狂神08-(实现WebMvcConfigurer扩展配置)
- 5网络分析工具介绍_常见的网络分析工具有哪些及其区别
- 6利用python求解规划问题_python规划求解
- 7我好像发现了车载测试面试成功的秘籍
- 8视觉Transformer笔记_transformerconv
- 9Node.js的安装和环境配置以及历史版本_nodejs历史版本安装及环境配置
- 10KAN网络技术最全解析—最热KAN能否干掉MLP和Transformer?(收录于GPT-4/ChatGPT技术与产业分析)
当前位置: article > 正文
Python调用MindOpt求解二次规划问题的几点总结_python 二次规划求解器
作者:不正经 | 2024-05-19 14:02:34
赞
踩
python 二次规划求解器
简介
本篇文章是系列文章的第三篇,MindOpt对于python的支持还是挺不错的,我已经编写了建模优化线性规划和混合整数线性规划问题的例子,下文我会对Python调用MindOpt建模优化二次规划问题进行总结。
如何获取MindOpt求解器
求解器安装包的发布渠道。请大家:
- 前往 https://www.aliyun.com/product/ai/opt 来下载求解器软件。
- 在阿里云上获取免费授权码:
• 请大家迁移到“云鉴权”自助申请licenseKey,配置fl_client.ini。新的“云鉴权”不需要绑定机器ID,只要阿里云账号并联网就好。
关于求解器的使用文档,请参考:https://help.aliyun.com/document_detail/298219.htm
二次规划定义
在前文线性规划问题示例中,讲述到线性规划在我个人认为是在线性的目标和约束中,找出一个最优解。而本文的二次规划,是非线性规划中的一类。具体地说,是一个线性约束的、二次规划问题,就是优化(最小化或最大化)二次函数目标的问题。
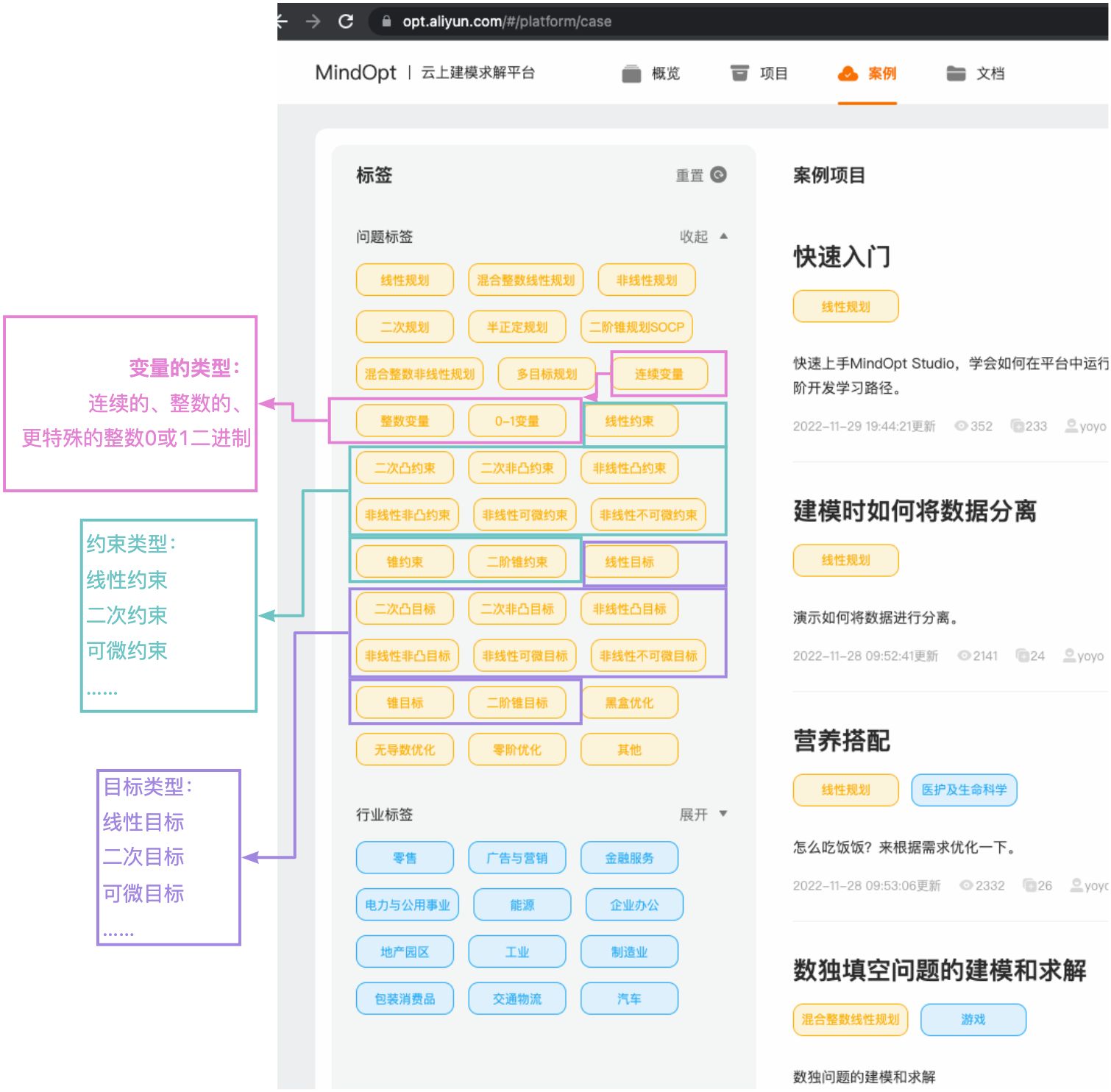
关于优化的类别,有很多,比如MindOpt的案例广场的标签里面提到的问题标签,就列出了常见的数学规划的类型。其中关于变量、约束、目标这建模三要素,进行罗列:
- 关于变量:取值有连续的,有整数的,还有更特殊的二进制(0或1)的,
- 关于约束和目标:一般用变量的函数变换来表达,其中约束再增加它函数的取值范围。
- 当函数是变量的线性关系时,比如x的1次方相加,我们称呼为线性约束、线性的目标。(如果变量也是连续的,这个就是线性规划问题啦。)
- 当函数是变量的是二次关系的时候,比如函数中有 x的2次方项。我们称呼为二次约束,或二次目标。
- 函数还会有凸函数和非凸函数,数学里面都代表不同的特性,大家可以再多去查阅材料。
本文主要讲 凸二次规划,Convex Quadratic Programming。
二次规划问题:

""" /** * Description * ----------- * * Linear optimization (row-wise input). * * Formulation * ----------- * * Minimize * obj: 1 x0 + 1 x1 + 1 x2 + 1 x3 * + 1/2 [ x0^2 + x1^2 + x2^2 + x3^2 + x0 x1] * Subject To * c1 : 1 x0 + 1 x1 + 2 x2 + 3 x3 >= 1 * c2 : 1 x0 - 1 x2 + 6 x3 = 1 * Bounds * 0 <= x0 <= 10 * 0 <= x1 * 0 <= x2 * 0 <= x3 * End */ """ from mindoptpy import * if __name__ == "__main__": MDO_INFINITY = MdoModel.get_infinity() # Step 1. Create a model and change the parameters. model = MdoModel() try: # Step 2. Input model. # Change to minimization problem. model.set_int_attr(MDO_INT_ATTR.MIN_SENSE, 1) # Add variables. x = [] x.append(model.add_var(0.0, 10.0, 1.0, None, "x0", False)) x.append(model.add_var(0.0, MDO_INFINITY, 1.0, None, "x1", False)) x.append(model.add_var(0.0, MDO_INFINITY, 1.0, None, "x2", False)) x.append(model.add_var(0.0, MDO_INFINITY, 1.0, None, "x3", False)) # Add constraints. # Note that the nonzero elements are inputted in a row-wise order here. model.add_cons(1.0, MDO_INFINITY, 1.0 * x[0] + 1.0 * x[1] + 2.0 * x[2] + 3.0 * x[3], "c0") model.add_cons(1.0, 1.0, 1.0 * x[0] - 1.0 * x[2] + 6.0 * x[3], "c1") # Add quadratic objective matrix Q. # # Note. # 1. The objective function is defined as c^Tx + 1/2 x^TQx, where Q is stored with coordinate format. # 2. Q will be scaled by 1/2 internally. # 3. To ensure the symmetricity of Q, user needs to input only the lower triangular part. # # Q = [ 1.0 0.5 0 0 ] # [ 0.5 1.0 0 0 ] # [ 0.0 0.0 1.0 0 ] # [ 0 0 0 1.0 ] model.set_quadratic_elements([ x[0], x[1], x[1], x[2], x[3] ], [ x[0], x[0], x[1], x[2], x[3] ], [ 1.0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 ]) # Step 3. Solve the problem and populate the result. model.solve_prob() model.display_results() except MdoError as e: print("Received Mindopt exception.") print(" - Code : {}".format(e.code)) print(" - Reason : {}".format(e.message)) except Exception as e: print("Received exception.") print(" - Reason : {}".format(e)) finally: # Step 4. Free the model. model.free_mdl()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
总结
1.创建模型
- 创建一个空的模型
model = MdoModel()
- 1
2.定义目标函数
- 利用Python API mindoptpy.MdoModel.set_int_attr() 将目标函数改为最小化
- 也可以选择这个模型属性model.set_int_attr(“MinSense”, 1) 数字1代表最小化,0代表最大化
- (MDO_INT_ATTR.MIN_SENSE, 1)和(“MinSense”, 1)的含义是一样的
model.set_int_attr(MDO_INT_ATTR.MIN_SENSE, 1)
- 1
3.定义求解变量
- mindoptpy.MdoModel.add_var()此函数可向模型引入一个新的变量,()里可以添加四个优化变量,定义其下界、上界、名称和类型
- 0.0是新增变量的下界,10和MDO_INFINITY是上界,没有值可以用无穷大来表示即MDO_INFINITY
- 1.0为新变量的目标系数
- None是包含非零元素的列对象,默认为None
- ""中是变量的名字,False代表不可指定是否为整数变量的布尔标志
x = []
x.append(model.add_var(0.0, 10.0, 1.0, None, "x0", False))
x.append(model.add_var(0.0, MDO_INFINITY, 1.0, None, "x1", False))
x.append(model.add_var(0.0, MDO_INFINITY, 1.0, None, "x2", False))
x.append(model.add_var(0.0, MDO_INFINITY, 1.0, None, "x3", False))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
4.定义约束条件
- mindooptpy.MdoModel.add_cons()此函数可向模型引入一个新的约束,()里可以输入约束的左右侧值,以及表达式
- 1.0为新约束的左侧值,或临时线性对象。
- MDO_INFINITY和10为新约束的右侧值,或者一个约束名称的字符串
- "c0、c1"为这条约束的名字
model.add_cons(1.0, MDO_INFINITY, 1.0 * x[0] + 1.0 * x[1] + 2.0 * x[2] + 3.0 * x[3], "c0")
model.add_cons(1.0, 1.0, 1.0 * x[0] - 1.0 * x[2] + 6.0 * x[3], "c1")
- 1
- 2
5.设置目标的二次项系数
- mindoptpy.MdoModel.set_quadratic_elements()此函数会修改二次规划的二次项矩阵中所有指定元素的值
- 前两组输入向量分别表示二次项中所有非零项的两个变量的索引
- 最后一组输入向量是与之相对应的非零系数值
- 为了确保 Q 的对称性,用户只需要输入其下三角形部分,并且在求解器内部会乘以 1/2
# Add quadratic objective matrix Q.
#
# Note.
# 1. The objective function is defined as c^Tx + 1/2 x^TQx, where Q is stored with coordinate format.
# 2. Q will be scaled by 1/2 internally.
# 3. To ensure the symmetricity of Q, user needs to input only the lower triangular part.
#
# Q = [ 1.0 0.5 0 0 ]
# [ 0.5 1.0 0 0 ]
# [ 0.0 0.0 1.0 0 ]
# [ 0 0 0 1.0 ]
model.set_quadratic_elements([ x[0], x[1], x[1], x[2], x[3] ], [ x[0], x[0], x[1], x[2], x[3] ], [ 1.0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 ])
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
6.设置参数:
可以通过mindooptpy.MdoModel.set_real_param()设置,例如设置求解时间上限等:
model.set_real_param("MaxTime", 7200.0)
# MindOpt 当前使用墙上时间作为默认计时。
# 如果将该值设置为0,则不会施加求解时间限制。
- 1
- 2
- 3
设置求解方法:
model.set_int_param("Method", 2) # 内点法
model.set_int_param("Method", 1) # 对偶单纯形法
model.set_int_param("Method", 0) # 原始单纯形法
model.set_int_param("Method", -1) # 让求解器决定(并发优化)
model.set_int_param("Method", -2) # 使用多线程单纯形法
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
7.求解QP模型
- 模型输入后,我们接着用mindoptpy.MdoModel.solve_prob()来求解问题。
- 并用mindoptpy.MdoModel.display_results()呈现求解结果。
model.solve_prob()
model.display_results()
- 1
- 2
更多Python 接口函数使用方式
MindOpt最新版本1.1.1支持更多API、语法更简洁
下载地址、API查询地址
联系我们
钉钉群号:32451444
邮箱地址:solver.damo@list.alibaba-inc.com
更多更新通知:https://solver.damo.alibaba.com
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,转载请注明出处:【wpsshop博客】
推荐阅读
相关标签



