- 1PyQt5,PyQt-tools安装与Qt designer,pyuic,qrcToPy的配置_pyqt tools
- 2Qt Quick 简介
- 3伦理与人工智能:构建公正和负责任的智能系统
- 4python建立客户端wesocket_python websocket客户端
- 5Codeforces 145 E-Lucky Queries 【线段树】_长度为n只包含0到4
- 6Hadoop入门学习笔记——五、在虚拟机中部署Hive
- 7vue/react前端面试题整理——HTTP/HTTPS_vue http传输协议
- 8【docker】dcoker-compose介绍_decker-compose
- 9There is no getter for property named ‘xxxxx’ in ‘class com.xxx.xx.xx.xxxx‘”,_there is no getter for property named 'student_id'
- 10『C++成长记』内存管理
[深度学习框架]PyTorch常用代码段_class convnet(nn.module): def __init__(self, num_c
赞
踩
PyTorch最好的资料是官方文档。本文是PyTorch常用代码段,在参考资料[1](张皓:PyTorch Cookbook)的基础上做了一些修补,方便使用时查阅。
1. 基本配置
导入包和版本查询
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision
print(torch.__version__)
print(torch.version.cuda)
print(torch.backends.cudnn.version())
print(torch.cuda.get_device_name(0))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
可复现性
在硬件设备(CPU、GPU)不同时,完全的可复现性无法保证,即使随机种子相同。但是,在同一个设备上,应该保证可复现性。具体做法是,在程序开始的时候固定torch的随机种子,同时也把numpy的随机种子固定。
np.random.seed(0)
torch.manual_seed(0)
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(0)
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
显卡设置
如果只需要一张显卡
# Device configuration
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')- 1
如果需要指定多张显卡,比如0,1号显卡。
import os
os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = '0,1'- 1
也可以在命令行运行代码时设置显卡:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 python train.py清除显存
torch.cuda.empty_cache()也可以使用在命令行重置GPU的指令
nvidia-smi --gpu-reset -i [gpu_id]2. 张量(Tensor)处理
张量的数据类型
PyTorch有9种CPU张量类型和9种GPU张量类型。
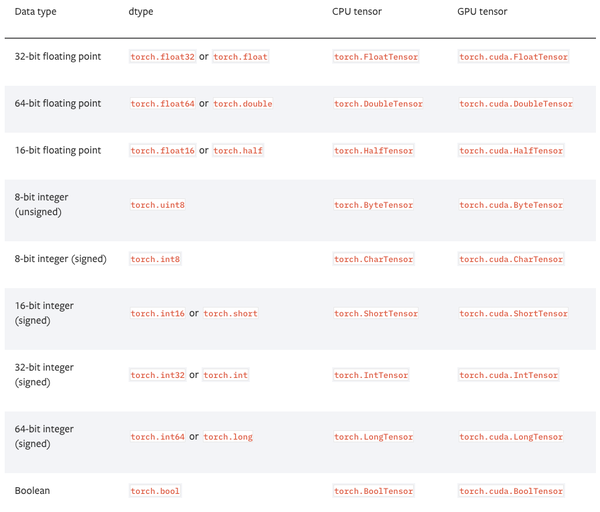

张量基本信息
tensor = torch.randn(3,4,5)
print(tensor.type()) # 数据类型
print(tensor.size()) # 张量的shape,是个元组
print(tensor.dim()) # 维度的数量- 1
- 2
- 3
命名张量
张量命名是一个非常有用的方法,这样可以方便地使用维度的名字来做索引或其他操作,大大提高了可读性、易用性,防止出错。
# 在PyTorch 1.3之前,需要使用注释
# Tensor[N, C, H, W]
images = torch.randn(32, 3, 56, 56)
images.sum(dim=1)
images.select(dim=1, index=0)
# PyTorch 1.3之后
NCHW = [‘N’, ‘C’, ‘H’, ‘W’]
images = torch.randn(32, 3, 56, 56, names=NCHW)
images.sum('C')
images.select('C', index=0)
# 也可以这么设置
tensor = torch.rand(3,4,1,2,names=('C', 'N', 'H', 'W'))
# 使用align_to可以对维度方便地排序
tensor = tensor.align_to('N', 'C', 'H', 'W')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
数据类型转换
# 设置默认类型,pytorch中的FloatTensor远远快于DoubleTensor
torch.set_default_tensor_type(torch.FloatTensor)
# 类型转换
tensor = tensor.cuda()
tensor = tensor.cpu()
tensor = tensor.float()
tensor = tensor.long()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
torch.Tensor与np.ndarray转换
除了CharTensor,其他所有CPU上的张量都支持转换为numpy格式然后再转换回来。
ndarray = tensor.cpu().numpy()
tensor = torch.from_numpy(ndarray).float()
tensor = torch.from_numpy(ndarray.copy()).float() # If ndarray has negative stride.- 1
- 2
Torch.tensor与PIL.Image转换
# pytorch中的张量默认采用[N, C, H, W]的顺序,并且数据范围在[0,1],需要进行转置和规范化
# torch.Tensor -> PIL.Image
image = PIL.Image.fromarray(torch.clamp(tensor*255, min=0, max=255).byte().permute(1,2,0).cpu().numpy())
image = torchvision.transforms.functional.to_pil_image(tensor) # Equivalently way
# PIL.Image -> torch.Tensor
path = r'./figure.jpg'
tensor = torch.from_numpy(np.asarray(PIL.Image.open(path))).permute(2,0,1).float() / 255
tensor = torchvision.transforms.functional.to_tensor(PIL.Image.open(path)) # Equivalently way- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
np.ndarray与PIL.Image的转换
image = PIL.Image.fromarray(ndarray.astype(np.uint8))
ndarray = np.asarray(PIL.Image.open(path))- 1
从只包含一个元素的张量中提取值
value = torch.rand(1).item()张量形变
# 在将卷积层输入全连接层的情况下通常需要对张量做形变处理,
# 相比torch.view,torch.reshape可以自动处理输入张量不连续的情况。
tensor = torch.rand(2,3,4)
shape = (6, 4)
tensor = torch.reshape(tensor, shape)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
打乱顺序
tensor = tensor[torch.randperm(tensor.size(0))] # 打乱第一个维度水平翻转
# pytorch不支持tensor[::-1]这样的负步长操作,水平翻转可以通过张量索引实现
# 假设张量的维度为[N, D, H, W].
tensor = tensor[:,:,:,torch.arange(tensor.size(3) - 1, -1, -1).long()]- 1
- 2
复制张量
# Operation | New/Shared memory | Still in computation graph |
tensor.clone() # | New | Yes |
tensor.detach() # | Shared | No |
tensor.detach.clone()() # | New | No |- 1
- 2
- 3
张量拼接
'''
注意torch.cat和torch.stack的区别在于torch.cat沿着给定的维度拼接,
而torch.stack会新增一维。例如当参数是3个10x5的张量,torch.cat的结果是30x5的张量,
而torch.stack的结果是3x10x5的张量。
'''
tensor = torch.cat(list_of_tensors, dim=0)
tensor = torch.stack(list_of_tensors, dim=0)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
将整数标签转为one-hot编码
# pytorch的标记默认从0开始
tensor = torch.tensor([0, 2, 1, 3])
N = tensor.size(0)
num_classes = 4
one_hot = torch.zeros(N, num_classes).long()
one_hot.scatter_(dim=1, index=torch.unsqueeze(tensor, dim=1), src=torch.ones(N, num_classes).long())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
得到非零元素
torch.nonzero(tensor) # index of non-zero elements
torch.nonzero(tensor==0) # index of zero elements
torch.nonzero(tensor).size(0) # number of non-zero elements
torch.nonzero(tensor == 0).size(0) # number of zero elements- 1
- 2
- 3
判断两个张量相等
torch.allclose(tensor1, tensor2) # float tensor
torch.equal(tensor1, tensor2) # int tensor- 1
张量扩展
# Expand tensor of shape 64*512 to shape 64*512*7*7.
tensor = torch.rand(64,512)
torch.reshape(tensor, (64, 512, 1, 1)).expand(64, 512, 7, 7)- 1
- 2
矩阵乘法
# Matrix multiplcation: (m*n) * (n*p) * -> (m*p).
result = torch.mm(tensor1, tensor2)
# Batch matrix multiplication: (b*m*n) * (b*n*p) -> (b*m*p)
result = torch.bmm(tensor1, tensor2)
# Element-wise multiplication.
result = tensor1 * tensor2- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
计算两组数据之间的两两欧式距离
利用broadcast机制
dist = torch.sqrt(torch.sum((X1[:,None,:] - X2) ** 2, dim=2))3. 模型定义和操作
一个简单两层卷积网络的示例
# convolutional neural network (2 convolutional layers)
class ConvNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=10):
super(ConvNet, self).__init__()
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 16, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2),
nn.BatchNorm2d(16),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2))
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2),
nn.BatchNorm2d(32),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2))
self.fc = nn.Linear(7*7*32, num_classes)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.layer1(x)
out = self.layer2(out)
out = out.reshape(out.size(0), -1)
out = self.fc(out)
return out
model = ConvNet(num_classes).to(device)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
双线性汇合(bilinear pooling)
X = torch.reshape(N, D, H * W) # Assume X has shape N*D*H*W
X = torch.bmm(X, torch.transpose(X, 1, 2)) / (H * W) # Bilinear pooling
assert X.size() == (N, D, D)
X = torch.reshape(X, (N, D * D))
X = torch.sign(X) * torch.sqrt(torch.abs(X) + 1e-5) # Signed-sqrt normalization
X = torch.nn.functional.normalize(X) # L2 normalization- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
多卡同步 BN(Batch normalization)
当使用 torch.nn.DataParallel 将代码运行在多张 GPU 卡上时,PyTorch 的 BN 层默认操作是各卡上数据独立地计算均值和标准差,同步 BN 使用所有卡上的数据一起计算 BN 层的均值和标准差,缓解了当批量大小(batch size)比较小时对均值和标准差估计不准的情况,是在目标检测等任务中一个有效的提升性能的技巧。
sync_bn = torch.nn.SyncBatchNorm(num_features, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True,
track_running_stats=True)- 1
将已有网络的所有BN层改为同步BN层
def convertBNtoSyncBN(module, process_group=None):
'''Recursively replace all BN layers to SyncBN layer.
Args:
module[torch.nn.Module]. Network
'''
if isinstance(module, torch.nn.modules.batchnorm._BatchNorm):
sync_bn = torch.nn.SyncBatchNorm(module.num_features, module.eps, module.momentum,
module.affine, module.track_running_stats, process_group)
sync_bn.running_mean = module.running_mean
sync_bn.running_var = module.running_var
if module.affine:
sync_bn.weight = module.weight.clone().detach()
sync_bn.bias = module.bias.clone().detach()
return sync_bn
else:
for name, child_module in module.named_children():
setattr(module, name) = convert_syncbn_model(child_module, process_group=process_group))
return module
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
类似 BN 滑动平均
如果要实现类似 BN 滑动平均的操作,在 forward 函数中要使用原地(inplace)操作给滑动平均赋值。
class BN(torch.nn.Module)
def __init__(self):
...
self.register_buffer('running_mean', torch.zeros(num_features))
def forward(self, X):
...
self.running_mean += momentum * (current - self.running_mean)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
计算模型整体参数量
num_parameters = sum(torch.numel(parameter) for parameter in model.parameters())查看网络中的参数
可以通过model.state_dict()或者model.named_parameters()函数查看现在的全部可训练参数(包括通过继承得到的父类中的参数)
params = list(model.named_parameters())
(name, param) = params[28]
print(name)
print(param.grad)
print('-------------------------------------------------')
(name2, param2) = params[29]
print(name2)
print(param2.grad)
print('----------------------------------------------------')
(name1, param1) = params[30]
print(name1)
print(param1.grad)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
模型可视化(使用pytorchviz)
类似 Keras 的 model.summary() 输出模型信息(使用pytorch-summary )
模型权重初始化
注意 model.modules() 和 model.children() 的区别:model.modules() 会迭代地遍历模型的所有子层,而 model.children() 只会遍历模型下的一层。
# Common practise for initialization.
for layer in model.modules():
if isinstance(layer, torch.nn.Conv2d):
torch.nn.init.kaiming_normal_(layer.weight, mode='fan_out',
nonlinearity='relu')
if layer.bias is not None:
torch.nn.init.constant_(layer.bias, val=0.0)
elif isinstance(layer, torch.nn.BatchNorm2d):
torch.nn.init.constant_(layer.weight, val=1.0)
torch.nn.init.constant_(layer.bias, val=0.0)
elif isinstance(layer, torch.nn.Linear):
torch.nn.init.xavier_normal_(layer.weight)
if layer.bias is not None:
torch.nn.init.constant_(layer.bias, val=0.0)
# Initialization with given tensor.
layer.weight = torch.nn.Parameter(tensor)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
提取模型中的某一层
modules()会返回模型中所有模块的迭代器,它能够访问到最内层,比如self.layer1.conv1这个模块,还有一个与它们相对应的是name_children()属性以及named_modules(),这两个不仅会返回模块的迭代器,还会返回网络层的名字。
# 取模型中的前两层
new_model = nn.Sequential(*list(model.children())[:2]
# 如果希望提取出模型中的所有卷积层,可以像下面这样操作:
for layer in model.named_modules():
if isinstance(layer[1],nn.Conv2d):
conv_model.add_module(layer[0],layer[1])- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
部分层使用预训练模型
注意如果保存的模型是 torch.nn.DataParallel,则当前的模型也需要是
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('model.pth'), strict=False)将在 GPU 保存的模型加载到 CPU
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('model.pth', map_location='cpu'))导入另一个模型的相同部分到新的模型
模型导入参数时,如果两个模型结构不一致,则直接导入参数会报错。用下面方法可以把另一个模型的相同的部分导入到新的模型中。
# model_new代表新的模型
# model_saved代表其他模型,比如用torch.load导入的已保存的模型
model_new_dict = model_new.state_dict()
model_common_dict = {k:v for k, v in model_saved.items() if k in model_new_dict.keys()}
model_new_dict.update(model_common_dict)
model_new.load_state_dict(model_new_dict)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
4. 数据处理
计算数据集的均值和标准差
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from PIL import Image
def compute_mean_and_std(dataset):
# 输入PyTorch的dataset,输出均值和标准差
mean_r = 0
mean_g = 0
mean_b = 0
for img, _ in dataset:
img = np.asarray(img) # change PIL Image to numpy array
mean_r += np.mean(img[:, :, 0])
mean_g += np.mean(img[:, :, 1])
mean_b += np.mean(img[:, :, 2])
mean_r /= len(dataset)
mean_g /= len(dataset)
mean_b /= len(dataset)
diff_r = 0
diff_g = 0
diff_b = 0
N = 0
for img, _ in dataset:
img = np.asarray(img)
diff_r += np.sum(np.power(img[:, :, 0] - mean_r, 2))
diff_g += np.sum(np.power(img[:, :, 1] - mean_g, 2))
diff_b += np.sum(np.power(img[:, :, 2] - mean_b, 2))
N += np.prod(img[:, :, 0].shape)
std_r = np.sqrt(diff_r / N)
std_g = np.sqrt(diff_g / N)
std_b = np.sqrt(diff_b / N)
mean = (mean_r.item() / 255.0, mean_g.item() / 255.0, mean_b.item() / 255.0)
std = (std_r.item() / 255.0, std_g.item() / 255.0, std_b.item() / 255.0)
return mean, std
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
得到视频数据基本信息
import cv2
video = cv2.VideoCapture(mp4_path)
height = int(video.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
width = int(video.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
num_frames = int(video.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
fps = int(video.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS))
video.release()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
TSN 每段(segment)采样一帧视频
K = self._num_segments
if is_train:
if num_frames > K:
# Random index for each segment.
frame_indices = torch.randint(
high=num_frames // K, size=(K,), dtype=torch.long)
frame_indices += num_frames // K * torch.arange(K)
else:
frame_indices = torch.randint(
high=num_frames, size=(K - num_frames,), dtype=torch.long)
frame_indices = torch.sort(torch.cat((
torch.arange(num_frames), frame_indices)))[0]
else:
if num_frames > K:
# Middle index for each segment.
frame_indices = num_frames / K // 2
frame_indices += num_frames // K * torch.arange(K)
else:
frame_indices = torch.sort(torch.cat((
torch.arange(num_frames), torch.arange(K - num_frames))))[0]
assert frame_indices.size() == (K,)
return [frame_indices[i] for i in range(K)]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
常用训练和验证数据预处理
其中 ToTensor 操作会将 PIL.Image 或形状为 H×W×D,数值范围为 [0, 255] 的 np.ndarray 转换为形状为 D×H×W,数值范围为 [0.0, 1.0] 的 torch.Tensor。
train_transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose([
torchvision.transforms.RandomResizedCrop(size=224,
scale=(0.08, 1.0)),
torchvision.transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
torchvision.transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.485, 0.456, 0.406),
std=(0.229, 0.224, 0.225)),
])
val_transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose([
torchvision.transforms.Resize(256),
torchvision.transforms.CenterCrop(224),
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
torchvision.transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.485, 0.456, 0.406),
std=(0.229, 0.224, 0.225)),
])- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
5. 模型训练和测试
分类模型训练代码
# Loss and optimizer
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
# Train the model
total_step = len(train_loader)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for i ,(images, labels) in enumerate(train_loader):
images = images.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
# Forward pass
outputs = model(images)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
# Backward and optimizer
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if (i+1) % 100 == 0:
print('Epoch: [{}/{}], Step: [{}/{}], Loss: {}'
.format(epoch+1, num_epochs, i+1, total_step, loss.item()))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
分类模型测试代码
# Test the model
model.eval() # eval mode(batch norm uses moving mean/variance
#instead of mini-batch mean/variance)
with torch.no_grad():
correct = 0
total = 0
for images, labels in test_loader:
images = images.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
outputs = model(images)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()print('Test accuracy of the model on the 10000 test images: {} %'
.format(100 * correct / total))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
自定义loss
继承torch.nn.Module类写自己的loss。
class MyLoss(torch.nn.Moudle):
def __init__(self):
super(MyLoss, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x, y):
loss = torch.mean((x - y) ** 2)
return loss- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
标签平滑(label smoothing)
写一个label_smoothing.py的文件,然后在训练代码里引用,用LSR代替交叉熵损失即可。label_smoothing.py内容如下:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class LSR(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, e=0.1, reduction='mean'):
super().__init__()
self.log_softmax = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)
self.e = e
self.reduction = reduction
def _one_hot(self, labels, classes, value=1):
"""
Convert labels to one hot vectors
Args:
labels: torch tensor in format [label1, label2, label3, ...]
classes: int, number of classes
value: label value in one hot vector, default to 1
Returns:
return one hot format labels in shape [batchsize, classes]
"""
one_hot = torch.zeros(labels.size(0), classes)
#labels and value_added size must match
labels = labels.view(labels.size(0), -1)
value_added = torch.Tensor(labels.size(0), 1).fill_(value)
value_added = value_added.to(labels.device)
one_hot = one_hot.to(labels.device)
one_hot.scatter_add_(1, labels, value_added)
return one_hot
def _smooth_label(self, target, length, smooth_factor):
"""convert targets to one-hot format, and smooth
them.
Args:
target: target in form with [label1, label2, label_batchsize]
length: length of one-hot format(number of classes)
smooth_factor: smooth factor for label smooth
Returns:
smoothed labels in one hot format
"""
one_hot = self._one_hot(target, length, value=1 - smooth_factor)
one_hot += smooth_factor / (length - 1)
return one_hot.to(target.device)
def forward(self, x, target):
if x.size(0) != target.size(0):
raise ValueError('Expected input batchsize ({}) to match target batch_size({})'
.format(x.size(0), target.size(0)))
if x.dim() < 2:
raise ValueError('Expected input tensor to have least 2 dimensions(got {})'
.format(x.size(0)))
if x.dim() != 2:
raise ValueError('Only 2 dimension tensor are implemented, (got {})'
.format(x.size()))
smoothed_target = self._smooth_label(target, x.size(1), self.e)
x = self.log_softmax(x)
loss = torch.sum(- x * smoothed_target, dim=1)
if self.reduction == 'none':
return loss
elif self.reduction == 'sum':
return torch.sum(loss)
elif self.reduction == 'mean':
return torch.mean(loss)
else:
raise ValueError('unrecognized option, expect reduction to be one of none, mean, sum')
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
或者直接在训练文件里做label smoothing
for images, labels in train_loader:
images, labels = images.cuda(), labels.cuda()
N = labels.size(0)
# C is the number of classes.
smoothed_labels = torch.full(size=(N, C), fill_value=0.1 / (C - 1)).cuda()
smoothed_labels.scatter_(dim=1, index=torch.unsqueeze(labels, dim=1), value=0.9)
score = model(images)
log_prob = torch.nn.functional.log_softmax(score, dim=1)
loss = -torch.sum(log_prob * smoothed_labels) / N
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
Mixup训练
beta_distribution = torch.distributions.beta.Beta(alpha, alpha)
for images, labels in train_loader:
images, labels = images.cuda(), labels.cuda()
# Mixup images and labels.
lambda_ = beta_distribution.sample([]).item()
index = torch.randperm(images.size(0)).cuda()
mixed_images = lambda_ * images + (1 - lambda_) * images[index, :]
label_a, label_b = labels, labels[index]
# Mixup loss.
scores = model(mixed_images)
loss = (lambda_ * loss_function(scores, label_a)
+ (1 - lambda_) * loss_function(scores, label_b))
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
L1 正则化
l1_regularization = torch.nn.L1Loss(reduction='sum')
loss = ... # Standard cross-entropy loss
for param in model.parameters():
loss += torch.sum(torch.abs(param))
loss.backward()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
不对偏置项进行权重衰减(weight decay)
pytorch里的weight decay相当于l2正则
bias_list = (param for name, param in model.named_parameters() if name[-4:] == 'bias')
others_list = (param for name, param in model.named_parameters() if name[-4:] != 'bias')
parameters = [{'parameters': bias_list, 'weight_decay': 0},
{'parameters': others_list}]
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(parameters, lr=1e-2, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=1e-4)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
梯度裁剪(gradient clipping)
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm=20)得到当前学习率
# If there is one global learning rate (which is the common case).
lr = next(iter(optimizer.param_groups))['lr']
# If there are multiple learning rates for different layers.
all_lr = []
for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
all_lr.append(param_group['lr'])- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
另一种方法,在一个batch训练代码里,当前的lr是optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr']
学习率衰减
# Reduce learning rate when validation accuarcy plateau.
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, mode='max', patience=5, verbose=True)
for t in range(0, 80):
train(...)
val(...)
scheduler.step(val_acc)
# Cosine annealing learning rate.
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(optimizer, T_max=80)
# Reduce learning rate by 10 at given epochs.
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(optimizer, milestones=[50, 70], gamma=0.1)
for t in range(0, 80):
scheduler.step()
train(...)
val(...)
# Learning rate warmup by 10 epochs.
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda=lambda t: t / 10)
for t in range(0, 10):
scheduler.step()
train(...)
val(...)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
优化器链式更新
从1.4版本开始,torch.optim.lr_scheduler 支持链式更新(chaining),即用户可以定义两个 schedulers,并交替在训练中使用。
import torch
from torch.optim import SGD
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import ExponentialLR, StepLR
model = [torch.nn.Parameter(torch.randn(2, 2, requires_grad=True))]
optimizer = SGD(model, 0.1)
scheduler1 = ExponentialLR(optimizer, gamma=0.9)
scheduler2 = StepLR(optimizer, step_size=3, gamma=0.1)
for epoch in range(4):
print(epoch, scheduler2.get_last_lr()[0])
optimizer.step()
scheduler1.step()
scheduler2.step()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
模型训练可视化
PyTorch可以使用tensorboard来可视化训练过程。
安装和运行TensorBoard。
pip install tensorboard
tensorboard --logdir=runs- 1
使用SummaryWriter类来收集和可视化相应的数据,放了方便查看,可以使用不同的文件夹,比如'Loss/train'和'Loss/test'。
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
import numpy as np
writer = SummaryWriter()
for n_iter in range(100):
writer.add_scalar('Loss/train', np.random.random(), n_iter)
writer.add_scalar('Loss/test', np.random.random(), n_iter)
writer.add_scalar('Accuracy/train', np.random.random(), n_iter)
writer.add_scalar('Accuracy/test', np.random.random(), n_iter)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
保存与加载断点
注意为了能够恢复训练,我们需要同时保存模型和优化器的状态,以及当前的训练轮数。
start_epoch = 0
# Load checkpoint.
if resume: # resume为参数,第一次训练时设为0,中断再训练时设为1
model_path = os.path.join('model', 'best_checkpoint.pth.tar')
assert os.path.isfile(model_path)
checkpoint = torch.load(model_path)
best_acc = checkpoint['best_acc']
start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch']
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['model'])
optimizer.load_state_dict(checkpoint['optimizer'])
print('Load checkpoint at epoch {}.'.format(start_epoch))
print('Best accuracy so far {}.'.format(best_acc))
# Train the model
for epoch in range(start_epoch, num_epochs):
...
# Test the model
...
# save checkpoint
is_best = current_acc > best_acc
best_acc = max(current_acc, best_acc)
checkpoint = {
'best_acc': best_acc,
'epoch': epoch + 1,
'model': model.state_dict(),
'optimizer': optimizer.state_dict(),
}
model_path = os.path.join('model', 'checkpoint.pth.tar')
best_model_path = os.path.join('model', 'best_checkpoint.pth.tar')
torch.save(checkpoint, model_path)
if is_best:
shutil.copy(model_path, best_model_path)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
提取 ImageNet 预训练模型某层的卷积特征
# VGG-16 relu5-3 feature.
model = torchvision.models.vgg16(pretrained=True).features[:-1]
# VGG-16 pool5 feature.
model = torchvision.models.vgg16(pretrained=True).features
# VGG-16 fc7 feature.
model = torchvision.models.vgg16(pretrained=True)
model.classifier = torch.nn.Sequential(*list(model.classifier.children())[:-3])
# ResNet GAP feature.
model = torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
model = torch.nn.Sequential(collections.OrderedDict(
list(model.named_children())[:-1]))
with torch.no_grad():
model.eval()
conv_representation = model(image)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
提取 ImageNet 预训练模型多层的卷积特征
class FeatureExtractor(torch.nn.Module):
"""Helper class to extract several convolution features from the given
pre-trained model.
Attributes:
_model, torch.nn.Module.
_layers_to_extract, list<str> or set<str>
Example:
>>> model = torchvision.models.resnet152(pretrained=True)
>>> model = torch.nn.Sequential(collections.OrderedDict(
list(model.named_children())[:-1]))
>>> conv_representation = FeatureExtractor(
pretrained_model=model,
layers_to_extract={'layer1', 'layer2', 'layer3', 'layer4'})(image)
"""
def __init__(self, pretrained_model, layers_to_extract):
torch.nn.Module.__init__(self)
self._model = pretrained_model
self._model.eval()
self._layers_to_extract = set(layers_to_extract)
def forward(self, x):
with torch.no_grad():
conv_representation = []
for name, layer in self._model.named_children():
x = layer(x)
if name in self._layers_to_extract:
conv_representation.append(x)
return conv_representation
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
微调全连接层
model = torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
for param in model.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
model.fc = nn.Linear(512, 100) # Replace the last fc layer
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.fc.parameters(), lr=1e-2, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=1e-4)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
以较大学习率微调全连接层,较小学习率微调卷积层
model = torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
finetuned_parameters = list(map(id, model.fc.parameters()))
conv_parameters = (p for p in model.parameters() if id(p) not in finetuned_parameters)
parameters = [{'params': conv_parameters, 'lr': 1e-3},
{'params': model.fc.parameters()}]
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(parameters, lr=1e-2, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=1e-4)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
6. 其他注意事项
- 不要使用太大的线性层。因为nn.Linear(m,n)使用的是 O(mn)O(mn) 的内存,线性层太大很容易超出现有显存。
- 不要在太长的序列上使用RNN。因为RNN反向传播使用的是BPTT算法,其需要的内存和输入序列的长度呈线性关系。
- model(x) 前用 model.train() 和 model.eval() 切换网络状态。
- 不需要计算梯度的代码块用 with torch.no_grad() 包含起来。
- model.eval() 和 torch.no_grad() 的区别在于,model.eval() 是将网络切换为测试状态,例如 BN 和dropout在训练和测试阶段使用不同的计算方法。torch.no_grad() 是关闭 PyTorch 张量的自动求导机制,以减少存储使用和加速计算,得到的结果无法进行 loss.backward()。
- model.zero_grad()会把整个模型的参数的梯度都归零, 而optimizer.zero_grad()只会把传入其中的参数的梯度归零.
- torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss 的输入不需要经过 Softmax。torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss 等价于 torch.nn.functional.log_softmax + torch.nn.NLLLoss。
- loss.backward() 前用 optimizer.zero_grad() 清除累积梯度。
- torch.utils.data.DataLoader 中尽量设置 pin_memory=True,对特别小的数据集如 MNIST 设置 pin_memory=False 反而更快一些。num_workers 的设置需要在实验中找到最快的取值。
- 用 del 及时删除不用的中间变量,节约 GPU 存储。
- 使用 inplace 操作可节约 GPU 存储,如
x = torch.nn.functional.relu(x, inplace=True)- 减少 CPU 和 GPU 之间的数据传输。例如如果你想知道一个 epoch 中每个 mini-batch 的 loss 和准确率,先将它们累积在 GPU 中等一个 epoch 结束之后一起传输回 CPU 会比每个 mini-batch 都进行一次 GPU 到 CPU 的传输更快。
- 使用半精度浮点数 half() 会有一定的速度提升,具体效率依赖于 GPU 型号。需要小心数值精度过低带来的稳定性问题。
- 时常使用 assert tensor.size() == (N, D, H, W) 作为调试手段,确保张量维度和你设想中一致。
- 除了标记 y 外,尽量少使用一维张量,使用 n*1 的二维张量代替,可以避免一些意想不到的一维张量计算结果。
- 统计代码各部分耗时
with torch.autograd.profiler.profile(enabled=True, use_cuda=False) as profile:
...
print(profile)
# 或者在命令行运行
python -m torch.utils.bottleneck main.py- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 使用TorchSnooper来调试PyTorch代码,程序在执行的时候,就会自动 print 出来每一行的执行结果的 tensor 的形状、数据类型、设备、是否需要梯度的信息。
# pip install torchsnooper
import torchsnooper
# 对于函数,使用修饰器
@torchsnooper.snoop()
# 如果不是函数,使用 with 语句来激活 TorchSnooper,把训练的那个循环装进 with 语句中去。
with torchsnooper.snoop():
原本的代码- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 模型可解释性,使用captum库




