- 1一起自学SLAM算法:3.4 图像特征点提取_slam中常用的特征点提取方法
- 2毕业设计微信小程序选题_小程序可以作为小挑课题吗
- 3java api传文件到hdfs_通过javaAPI上传文件到HDFS文件系统
- 4【pytest】parametrize获取参数的几种常用形式
- 5一文搞懂微调技术和RAG技术区别
- 6[数据结构]二叉树的链式存储结构_二叉树的链式存储结构代码
- 7fiddler抓取手机app或小程序包_fiddler抓小程序包提示运行环境问题
- 8供应商管理软件有哪些 好用的供应商管理软件推荐
- 9C++之拷贝构造
- 10HDLBits(九)学习笔记——verilog实现移位寄存器、More Circuits(三输入查找表)_8位移位寄存器verilog代码
图灵学院:用 Explain 查看 SQL 的执行计划_查看sql执行计划
赞
踩
文章目录
一、Explain 概述
1.1 Explain 含义及作用
Explain是 SQL 分析工具中非常重要的一个功能,它可以模拟优化器执行查询语句,帮助我们理解查询是如何执行的;分析查询执行计划可以帮助我们发现查询瓶颈,优化查询性能。Explain 主要有以下几个作用:
① 表的读取顺序
② SQL执行时查询操作类型
③可以使用哪些索引
④ 实际使用哪些索引
⑤每张表有多少行记录被扫描
⑥SQL语句性能分析
1.2 Explain 的基本用法
Explain select * from users;
- 1

注:暂时大体有个印象,后文每列的属性都会逐一讲解。
二、Explain 返回列详解
2.1 数据准备
CREATE TABLE users ( id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, email VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL, password VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; CREATE TABLE products ( id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, price FLOAT NOT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; CREATE TABLE orders ( id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, user_id INT NOT NULL, order_date DATETIME NOT NULL, total_price FLOAT NOT NULL, product_id INT NOT NULL, FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES users(id), FOREIGN KEY (product_id) REFERENCES products(id) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; alter table users add index index_name_email (name,email); INSERT INTO users (name, email, password) VALUES ('张三', 'zhangsan@example.com', 'password123'), ('李四', 'lisi@example.com', 'password123'), ('王五', 'wangwu@example.com', 'password123'), ('赵六', 'zhaoli@example.com', 'password123'), ('钱七', 'qianqi@example.com', 'password123'); INSERT INTO products (name, price) VALUES ('产品 1', 10.00), ('产品 2', 15.00), ('产品 3', 20.00), ('产品 4', 12.00), ('产品 5', 18.00); INSERT INTO orders (user_id, order_date, total_price, product_id) VALUES (1, '2023-02-18 10:00:00', 100.00, 1), (2, '2023-02-18 11:00:00', 50.00, 2), (3, '2023-02-18 12:00:00', 20.00, 3), (4, '2023-02-18 13:00:00', 15.00, 4), (5, '2023-02-18 14:00:00', 25.00, 5);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
数据说明:新建了三张表:users、orders、products,并给用户表的名字和邮箱字段添加了联合索引,三张表之间的关系如下:

此外,由于订单表关联用户表和产品表,因此在建表的时候,mysql 会为 订单表添加如下两个索引:

2.2 id 列
每个 select 都有一个对应的 id 号,并且是从 1 开始自增的。id 列对应以下四种情况:
① 如果 id 序号相同,从上往下执行。
② 如果 id 序号不同,序号大先执行。
③ 如果两种都存在,先执行序号大,在同级从上往下执行。
④ 如果显示 NULL,最后执行。表示结果集,并且不需要使用它来进行查询。
另外,table 列指查询要用的表。
-
情况一:id 列相同: 序号大先执行explain SELECT users.name, orders.total_price, products.price FROM users INNER JOIN orders ON users.id = orders.user_id INNER JOIN products ON orders.product_id = products.id;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
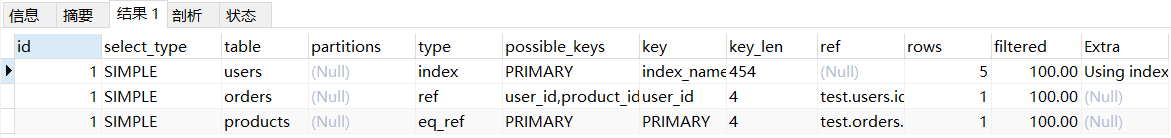
说明:先执行 users 表,然后再执行 orders 表,最后执行 products 表。
注:mysql 8 版本和 5 版本是有些差别的,mysql 8 版本优化器会对查询进行优化,先查 orders 表。 -
情况二:id 列不同,序号大先执行explain select * from orders where product_id = (select id from products where products.price = 10);- 1
- 2
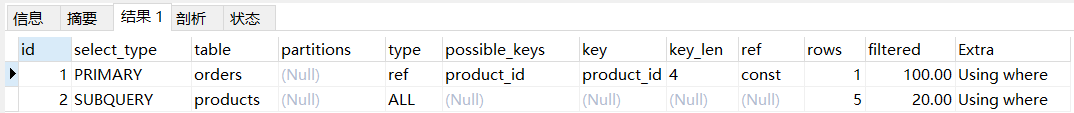
说明:先执行了子查询中的 select 语句,即查询了 products 表,然后再进行的外部查询。
-
情况三:两种都存在,先执行序号大,在同级从上往下执行set session optimizer_switch='derived_merge=off'; -- 关闭MySQL5.7对衍生表合并优化 explain select orders.* from (select id from products) as temp inner join orders on temp.id = orders.product_id; set session optimizer_switch='derived_merge=on'; -- 还原配置- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
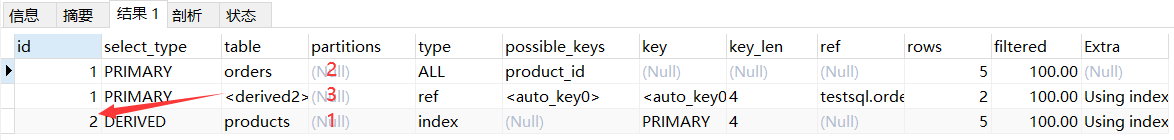
说明:先查询产品表、然后关联订单表、再做了一个数据比对。<derived2> 表示 id = 2 的那行记录是衍生表类型。
-
情况四:显示NULLexplain select id from users union select id from products; -- 使用 union 将结果集拼接- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
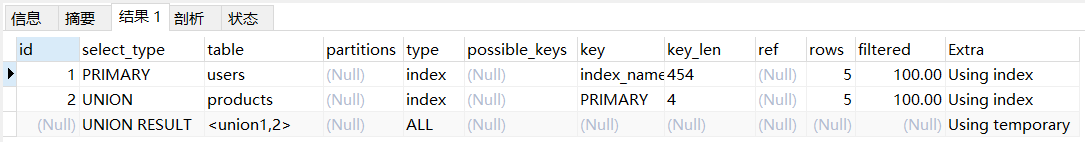
说明:最后一行为拼接结果集, id 列为NULL,表示最后执行,依赖于前面两条记录,只做了结果集存储与展示。注: mysql 8 版本在最后一种情况不会显示 NULL。
mysql 的优化器对 sql 语句也会进行优化,如下面的例子:
explain
select * from users where id in (select user_id from orders where id = 1);
show WARNINGS;
- 1
- 2
- 3
正常来说,id 列应该对应 id 列不同的情况。但是优化之后,会有以下结果:

通过 show WARNINGS; 的结果2中的 Message 为优化后的语句,即优化器进行复杂的计算发现连接查询的效率更高。

/* select#1 */
SELECT
'1' AS `id`,
'张三' AS `name`,
'zhangsan@example.com' AS `email`,
'password123' AS `password`
FROM
`testsql`.`orders`
JOIN `testsql`.`users`
WHERE
TRUE
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
2.3 select_type 列
select_type 列表示查询语句执行的查询操作类型。
2.3.1 simple
simple:简单 select,不包括 union 与子查询。
Explain select * from users;
Explain select * from users inner join orders on users.id = orders.user_id;
- 1
- 2
- 3


注:mysql 8版本,对于本例中的第二条 sql 语句,会先执行订单表再执行用户表。

2.3.2 primary
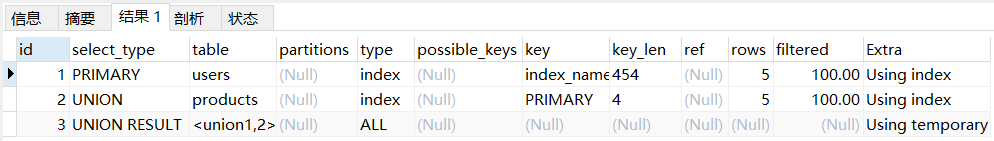
primary:复杂查询中最外层查询,比如使用 union 或 union all 时,id 为 1 的记录 select_type 通常是 primary。
explain
select id from users -- 标记为 PRIMARY
union
select id from products; -- 标记为 UNION
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
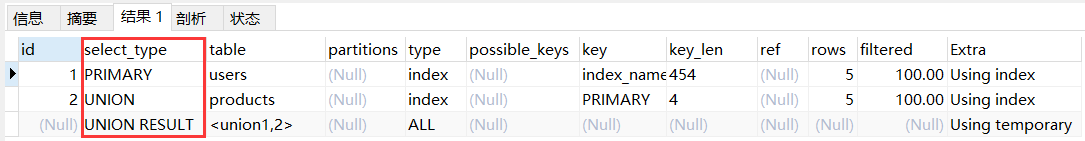
注:mysql 8 版本,id列会有所不同。
2.3.3 subquery
subquery:指在 select 语句中出现的子查询语句,结果不依赖于外部查询(不在from语句中)。
explain
select orders.*,(select name from products where id = 1) from orders;
- 1
- 2

说明:由于子查询的结果没有依赖于外部的 orders 表,因此 products 的查询类型是 SUBQUERY。
2.3.4 dependent subquery
dependent subquery:指在 select 语句中出现的查询语句,结果依赖于外部查询。
explain
select orders.*,(select name from products where products.id = orders.user_id) from orders;
- 1
- 2

说明:由于子查询的结果依赖于外部的 orders 表的 user_id,因此 products 的查询类型是 DEPENDENTSUBQUERY。
2.3.5 derived
derived:派生表,在 FROM 子句的查询语句,表示从外部数据源中推导出来的,而不是从 SELECT 语句中的其他列中选择出来的。
derived 或者理解为临时表。
set session optimizer_switch='derived_merge=off'; -- 关闭 MySQL5.7 对衍生表合并优化
explain
select * from (select user_id from orders where id = 1) as temp;
set session optimizer_switch='derived_merge=on'; -- 还原配置
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
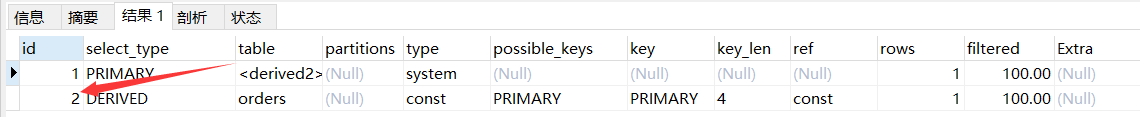
说明:先执行的是 orders 表,查询到的记录定义成了 temp 表。因此查询类型是 DERIVED,即派生表。最后执行的是 temp 表,来源是派生表,查询类型是 PRIMARY。
2.3.6 union
union:分为 union 与 union all 两种。
若第二个 select 出现在 union 之后,则被标记为 union;
如果 union 被 from 子句的子查询包含,那么第一个 select 会被标记为 derived;
union 会针对相同的结果集进行去重,union all 不会进行去重处理。
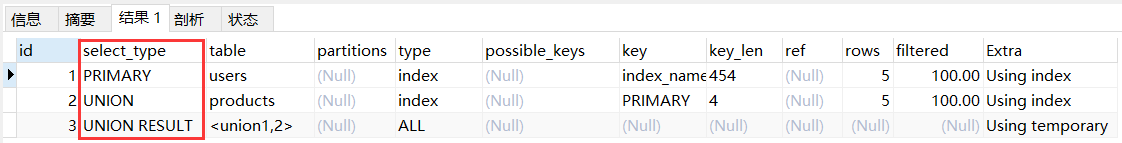
explain
select * from (
select id from products where price = 10
union
select id from orders where user_id in (1,2)
union
select id from users where name = '张三' ) as temp;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
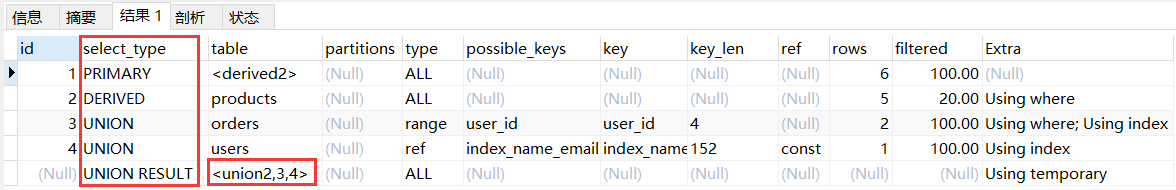
说明:union 会对结果进行去重,因此结果集先放到 UNION RESULT 这个区域当中,表示 ID 为 2 3 4 的结果集拼接到一块。
另外,mysql 8 版本会在 id 上有一些区别;也可以通过查看 Extra 列来查看 UNION RESULT 这个区域是临时的。
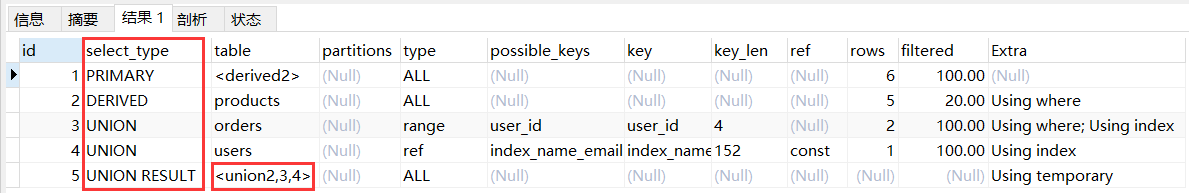
explain
select * from (
select id from products where price = 10
union all
select id from orders where user_id in (1,2)
union all
select id from users where name = '张三' ) as temp;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
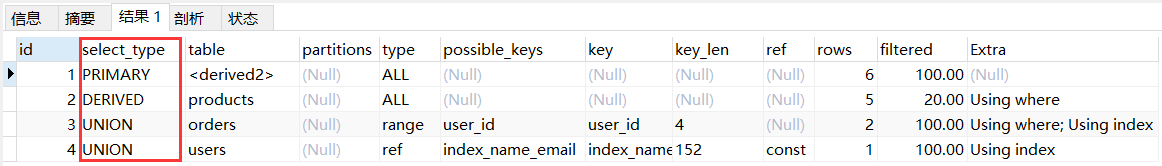
2.3.7 dependent union
dependent union:当 union 作为子查询时,其中第一个 union 为 dependent subquery,第二个 union 为 dependent union。
explain
select * from orders where id in (
select id from products where price = 10
union
select id from orders where user_id = 2
union
select id from users where name = '张三' );
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
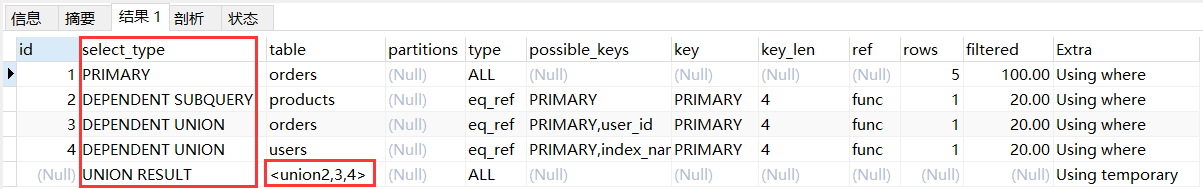
说明:与上文 union 关键字的区别在于上文的代表是一个临时表,而现在是一个子查询,需要被标记。
mysql 8 版本与 5 版本在 id 列上有一定的区别。
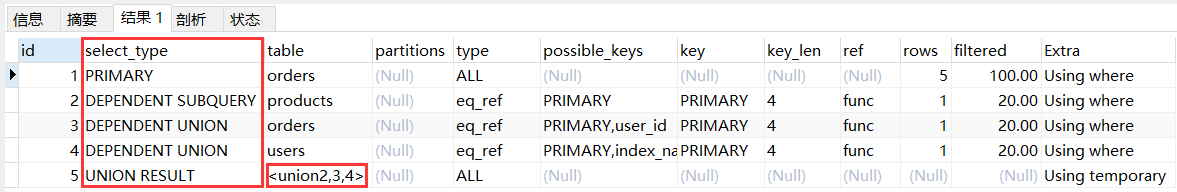
2.3.8 union result
union result:如果两个查询中有相同的列,则会对这些列进行重复删除,只保留一个表中的列。
explain
select id from users
union
select id from products;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
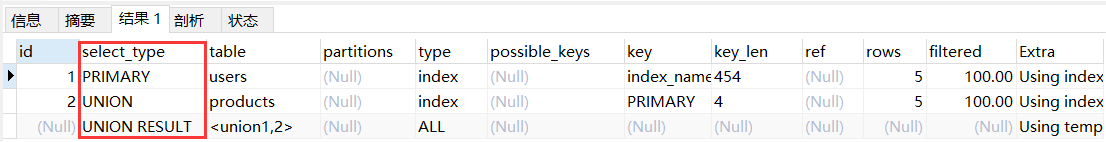
注:mysql 8 版本与 5 版本在 id 列上有一定的区别。

2.4 table 列
table列:查询所涉及的表名。如果有多个表,将显示多行记录。
2.5 partitions 列
partitions列:表分区情况。
查询语句所涉及的表的分区情况。具体来说,它会显示出查询语句在哪些分区上执行,以及是否使用了分区裁剪等信息。如果没有分区,该项为NULL。
2.6 type 列 ★
type 列,指查询所使用的访问类型。
效率从高到低分别为:system > const > eq_ref > ref > fulltext > ref_or_null > range > index > ALL。
一般来说保证 range 级别,最好能达到 ref 级别。
2.6.1 system
system:const类型的一种特殊场景,查询的表只有一行记录的情况,并且该表使用的存储引擎的统计数据是精确的。
InnoDb 存储引擎的统计数据不是精确的,虽然只有一条数据但是 type 类型为 ALL;
DROP TABLE t;
CREATE TABLE t(i INT) ENGINE=InnoDb;
INSERT INTO t VALUES(1);
explain select * from t;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

Memory 存储引擎的统计数据是精确的,所以当只有一条记录的时候 type 类型为 system。
DROP TABLE tt;
CREATE TABLE tt(i INT) ENGINE=memory;
INSERT INTO tt VALUES(1);
explain select * from tt;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

2.6.2 const
const:基于主键或唯一索引查看一行,当 MySQL 对查询某部分进行优化,并转换为一个常量时,使用这些类型访问转换成常量查询,效率高。
explain
select * from orders where id = 1;
- 1
- 2

2.6.3 eq_ref
eq_ref:基于主键或唯一索引连接两个表,对于每个索引键值,只有一条匹配记录,被驱动表的类型为’eq_ref’。
explain
select users.* from users inner join orders on users.id = orders.id;
-- 将用户表的 ID 和订单表的 ID 进行匹配
- 1
- 2
- 3

说明:possible_keys 是推荐使用的索引,key 是真实使用的索引。优化器认为对于 users 表,全表扫描的效率是更高的。被驱动表则会被标记为 eq_ref,其中 possible_keys 和使用的 key 都是 primary,即主键索引。
2.6.4 ref
ref:基于非唯一索引连接两个表或通过二级索引列与常量进行等值匹配,可能会存在多条匹配记录。
-- 关联查询,使用非唯一索引进行匹配。
explain
select users.* from users inner join orders on users.id = orders.user_id;
- 1
- 2
- 3
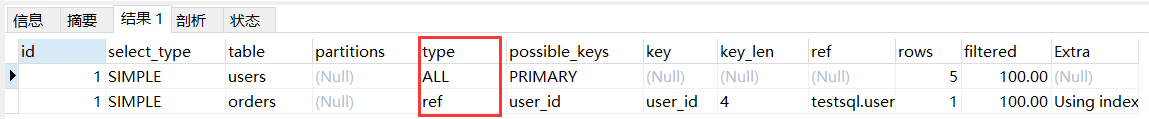
-- 简单查询,使用二级索引列匹配。
explain
select * from orders where user_id = 1;
- 1
- 2
- 3

2.6.5 range
range:使用非唯一索引扫描部分索引,比如使用索引获取某些范围区间的记录。
explain
select * from orders where user_id > 3;
- 1
- 2

2.6.6 index
index:扫描整个索引就能拿到结果,一般是二级索引,这种查询一般为使用覆盖索引(需优化,缩小数据范围)。
explain
select user_id from orders;
- 1
- 2

2.6.7 all
all:扫描整个表进行匹配,即扫描聚簇索引树(需优化,添加索引优化)。
explain
select * from users;
- 1
- 2

注:一般情况下,聚簇索引等同于主键索引。
2.6.8 null
null:MySQL 在优化器分解语句就已经可以获取到结果,执行时甚至不用访问表或索引。
explain
select min(id) from users;
- 1
- 2

2.7 possible_keys 列
possible_keys 列:表示在查询中 可能 使用到某个索引或多个索引;如果没有选择索引,显示 null。
2.8 key 列
key 列:表示在查询中 实际 使用的索引,如果没有使用索引,显示 null。
对应 possible_keys 和 key 有以下四种关系,以 A 索引为例:
- 可能使用 A 索引,实际也使用 A 索引。
- 可能使用 A 索引,实际没有使用 A 索引。
- 可能不使用索引,实际使用 A 索引。
- 可能不使用索引,实际也不使用 索引。
2.9 key_len 列
key_len 列:表示当优化器决定使用 某个索引 执行查询时,该索引记录的最大长度(主要使用在联合索引)。联合索引可以通过这个值算出具体使用了索引中的哪些列。
联合索引可以通过这个值算出具体使用了索引中的哪些列。
-
使用单例索引explain select * from users where id = 1;- 1
- 2

说明: id 是整形类型占 4 个字节。 -
使用联合索引explain select * from users where name = '张三' and email = 'zhangsan@example.com'; -- key_len:454- 1
- 2

说明:name 字段:3 * 50 + 2 = 152,email 字段:3 * 100 +2 = 302,加 2 表示变长字符串。CREATE TABLE `users` ( `id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(50) NOT NULL, -- 3*50+2 = 152 `email` varchar(100) NOT NULL, -- 3*100+2 = 302 `password` varchar(100) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), KEY `index_name_email` (`name`,`email`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb3;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
计算规则如下:
- 字符串:
char(n):n 个字节
varchar(n):如果是 uft-8(utf8mb3):3n+2 字节;如果是 utf8mb4:4n+2 字节。加的 2 字节表示当前为变长字符串,即动态列。 - 数值类型:
tinyint:1 字节
smallint:2 字节
int:4 字节
bigint:8 字节 - 时间类型:
date:3 字节
timestamp:4 字节
datetime:8 字节
字段如果为 NULL,需要 1 个字节记录是否为 NULL。
| 列类型 | key_len | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| id int | key_len = 4+1 | 允许 NULL,加 1 字节 |
| id int not null | key_len = 4 | 不允许 NULL |
| user char(30) utf8 | key_len = 30*3+1 | 允许 NULL,加 1 字节 |
| user varchar(30) not null utf8 | key_len = 30*3+2 | 动态列类型,加 2 字节 |
| user varchar(30) utf8 | key_len = 30*3+2+1 | 动态列类型,加 2 字节;允许 NULL,再加上 1 字节 |
| detail text(10) utf8 | key_len = 30*3+2+1 | TEXT 列截取部分,被视为动态列类型,加 2 字节;且允许 NULL |
如在 users 表中添加 num 字段:

当执行以下语句时,会有如下输出:
alter table users add index index_num (num); -- 添加索引
explain
select * from users where num = 111;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

说明:smallint 是 2 字节,允许为空再加 1 字节。
2.10 ref 列
ref 列表示将哪个字段或常量和 key 列所使用的字段进行比较。
当使用索引列等值查询时,与索引列进行等值匹配的对象信息。
-
常量匹配explain select * from users where name = '张三' and email = 'zhangsan@example.com';- 1
- 2

-
字段匹配explain select users.* from users inner join orders on users.id = orders.id;- 1
- 2
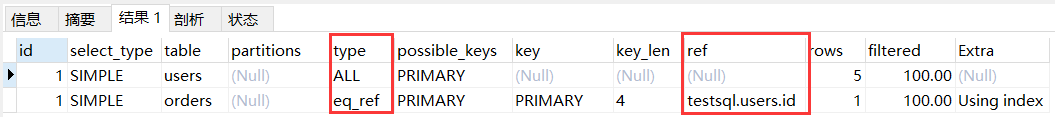
优化器认为对于 users 表,全表扫描的效率是更高的。然后扫描 orders 表,并标记为 eq_ref,eq_ref 等值匹配的值是 testsql.users.id,即 users 表的主键,其中 testsql 是数据库的名。 -
函数匹配explain select users.* from users inner join orders on users.id = trim(orders.id);- 1
- 2
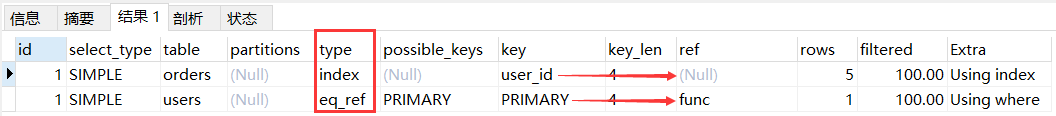
说明:orders 表通过索引扫描,key 列为 user_id(二级索引),因为如果可以通过二级索引获取到目标数据,就不会通过聚簇索引树,因此 ref 为空。而对于 users 表,其 eq_ref 等值匹配的信息是 trim( xxx ) 函数,因此 ref 为 func。
2.11 rows列
rows 列:全表扫描时表示需要扫描表的行数估计值;索引扫描时表示扫描索引的行数估计值;值越小越好(不是结果集中的行数)
-
全表扫描explain select * from orders where user_id >= 3 and total_price = 25;- 1
- 2

说明:orders 表一共有五条数据,根据二级索引 user_id 进行查找 user_id >= 3 的数据,一共有三条。但优化器经过计算,发现全表扫描的效率更高,因此选择全表扫描。rows 表示一共有 5 行数据,filtered 表示 20%,即最终结果为 1 条数据,则 1 / 5 = 20%。
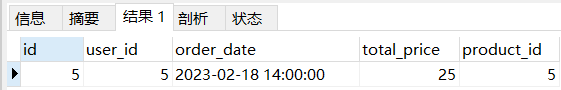
mysql 8 版本与 5 版本有所不同,会获取某些范围区间的记录。

-
索引扫描explain select * from orders where user_id > 3;- 1
- 2

说明:orders 表根据二级索引进行查找找到的数据有两条,没有其他的 and 条件过滤,因此 filtered 为 2/2=100%。
2.12 Extra列
Extra 列表示 SQL 执行查询的一些额外信息。
2.12.1 Using Index
Using index:使用非主键索引树就可以查询所需要的数据。一般是覆盖索引,即查询列都包含在辅助索引树叶子节点中,不需要回表查询。
explain
select user_id,id from orders where user_id = 1;
- 1
- 2

覆盖索引举例:
当执行 select * from user where age = 35; 这条 sql 的时候,会先从索引页中查出来 age = 35 对应的主键 id,之后再回表到聚簇索引中,查询其它字段的值。
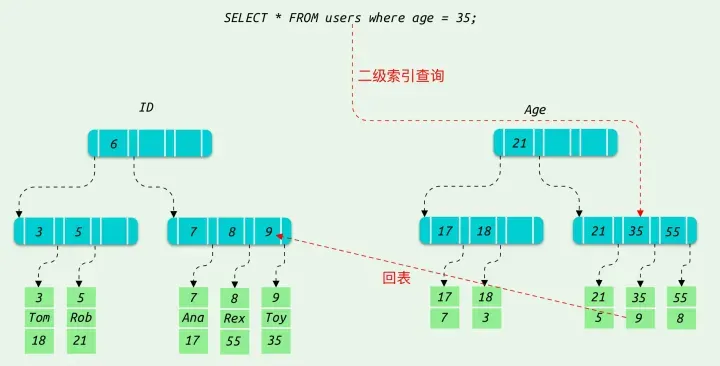
那么当执行 select id from users where age = 35;,先从索引页中查出来 age = 35 对应的主键 id 。之后,惊讶的发现,需要查询字段的 id 值已经查到了,那次此时就不需要回表了,这种情况成为 索引覆盖。
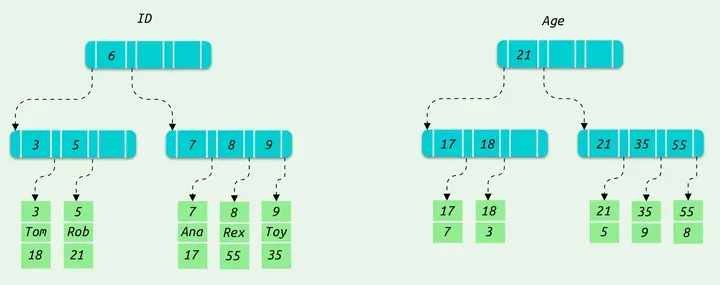
总结:需要查询的字段都在索引列中的情况就被称为覆盖索引。
2.12.2 Using where
Using where:不通过索引查询所需要的数据。
explain
select * from orders where total_price = 100;
- 1
- 2

explain
select * from orders where user_id = 1 and total_price = 100;
- 1
- 2

说明:where 条件中既有索引,也有非索引的情况下,也会被标记 Using where。
2.12.3 Using index condition
Using index condition:表示查询列不被索引覆盖,where 条件中是一个索引范围查找,过滤完索引后回表找到所有符合条件的数据行。
explain
select * from orders where user_id > 3;
- 1
- 2

2.12.4 Using temporary
Using temporary:表示需要使用临时表来处理查询。
例1:total_price 列无索引,需要创建一张临时表进行去重。
explain
select distinct total_price from orders;
- 1
- 2

说明:因此可通过对该待去重字段添加索引,即可完成优化。
例2:name 列有联合索引。
explain
select distinct name from users;
- 1
- 2

说明:因为索引树就是一个排好序的数据结构,因此去重相对简单高效。
2.12.5 Using filesort
Using filesort:当查询中包含 order by 操作而且无法利用索引完成的排序操作,数据较少时从内存排序,如果数据较多需要在磁盘中排序。 需优化成索引排序。
例1:total_price 列无索引,无法通过索引进行排序。需要先保存 total_price 与对应的主键 id,然后在排序 total_price 查找数据。
explain
select total_price from orders order by total_price;
- 1
- 2

说明:也可添加索引,进行优化。
例2:name 列有索引,因索引已经是排好序的所以直接读取就可以了。
explain
select name from users order by name;
- 1
- 2

2.12.6 Select tables optimized away
Select tables optimized away:使用某些聚合函数(min,max)来访问某个索引值。
type 列为空时,优化器阶段,就会获取到索引的最小值与最大值并进行返回,不需要访问表和索引。
explain
select min(id) from users;
- 1
- 2

explain
select min(password) from users;
- 1
- 2




