热门标签
热门文章
- 1大屏设计器-可视化-echarts
- 2掌握Python操作Word:从基础到高级全覆盖_python word编辑
- 3正确解决 Error: error:0308010C:digital envelope routines::unsupported 异常的有效方法_error in index.js from terser error: error:0308010
- 4大模型训练、多模态数据处理与融合_大模型和多模态的关系
- 5独立开发者用微信小程序赚钱_微信小程序收益 csdn
- 6mysql : grant权限命令汇总_mysql grant
- 7linux的shell后门尝试以及Cython转成C代码编译
- 8java开发应届生面试题,升职加薪必看
- 92.如何在Linux中加入新驱动_linux 如何添加 新驱动
- 10matlab 投票法_张量投票算法及其使用并分析.pdf
当前位置: article > 正文
stm32毕业设计 超声波雷达可视化系统_stm32 超声波 雷达 图像
作者:代码探险家 | 2024-06-25 07:19:29
赞
踩
stm32 超声波 雷达 图像
1 简介
Hi,大家好,今天向大家介绍一个超级炫酷的单片机项目,非常适合用于毕设
基于单片机的超声波雷达设计
大家可用于 课程设计 或 毕业设计
2 如何设计
软件部分
1、绘制雷达表盘
2、增加扫描线
3、实现拖影效果
4、实现目标扫描点显示(渐出效果)
硬件部分
1、准备器材(arduino UNO、360度舵机、超声波传感器、扩展板)
2、雷达平台
调试
1、串口通讯接受数据
2、扫描点的显示函数改造
3 实现效果
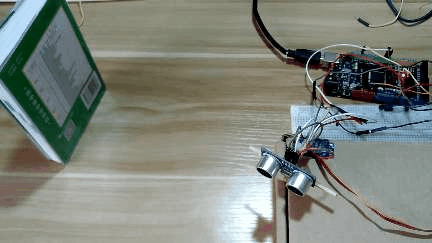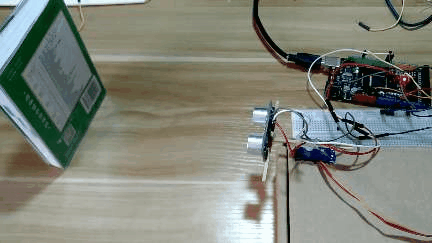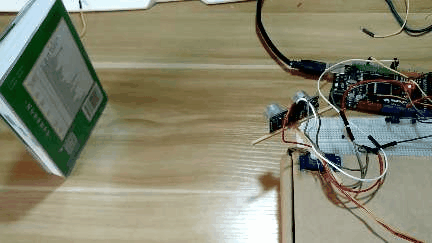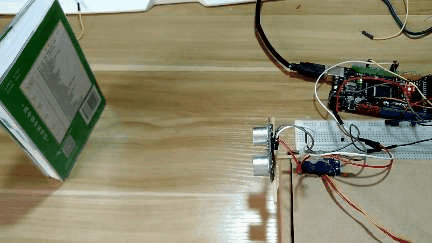

4 设计原理
超声波检测原理

线电波(微波)从雷达发射到自由空间,其中一些波被反射物体拦截,并从不同的方向上进行反射。这些波中一些波会引回雷达,被雷达接受并且放大。如果这些波在其原点再次被接收,则意味着物体在传播方向上。
现代雷达系统非常先进,并用于高度多样化的应用中,例如空中交通管制,防空系统,雷达天文学,反导系统,外层空间监视系统等等。
超声波传感器:
超声波传感器:用于测量目标或物体到传感器的距离,它通过发射超声波来检测物体并将反射波转换为电信号。这些声波的传播速度快于人类可以听到的声音的速度。

发送器:使用压电晶体发出声音
接收器:接收从目标传播回来的声音
计算公式:D =½T x C(D =距离,T =时间,C = 343米/秒)
超声波传感器主要用于汽车自动停车技术和防撞安全系统中。此外,还用于机器人障碍物检测系统,制造技术等。
伺服电机:
伺服马达:一个简单的DC马达,它可以伺服机器的控制下完成特定的角度旋转。且该电机只会旋转特定的程度,然后停止。伺服电机是一种闭环机构,它使用位置反馈来控制速度和位置。
该闭环系统包括:控制电路、伺服电动机、轴、电位计、驱动齿轮、放大器、编码器/分解器。
5 部分实现代码
部分代码
// 包含Servo库 #include <Servo.h>. // 定义超声波传感器的Tirg和回波引脚 const int trigPin = 10; const int echoPin = 11; //持续时间和距离的变量 long duration; int distance; Servo myServo; // 创建用于控制伺服电机的伺服对象 void setup() { pinMode(trigPin, OUTPUT); // 将trigPin设置为输出 pinMode(echoPin, INPUT); //将echoPin设置为输入 Serial.begin(9600); myServo.attach(12); // 定义伺服电机连接在哪个销上 } void loop() { // 将伺服电机从15度旋转到165度 for(int i=15;i<=165;i++){ myServo.write(i); delay(30); distance = calculateDistance();// 调用一个函数来计算超声波传感器为每度测量的距离 Serial.print(i); // 将当前度数发送到串行端口 Serial.print(","); // 在处理IDE中稍后需要的上一个值旁边发送加法字符以进行索引 Serial.print(distance); // 将距离值发送到串行端口 Serial.print("."); // 在处理IDE中稍后需要的上一个值旁边发送加法字符以进行索引 } // 从165度到15度重复前面的行 for(int i=165;i>15;i--){ myServo.write(i); delay(30); distance = calculateDistance(); Serial.print(i); Serial.print(","); Serial.print(distance); Serial.print("."); } } // 用于计算超声波传感器测量的距离的函数 int calculateDistance(){ digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW); delayMicroseconds(2); // 将trigPin设置为高状态10微秒 digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH); delayMicroseconds(10); digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW); duration = pulseIn(echoPin, HIGH); // 读取echoPin,以微秒为单位返回声波传播时间 distance= duration*0.034/2; return distance; } processing代码: import processing.serial.*; // 导入用于串行通信的库 import java.awt.event.KeyEvent; // 导入用于从串行端口读取数据的库 import java.io.IOException; Serial myPort; // defines Object Serial // 化解变量 String angle=""; String distance=""; String data=""; String noObject; float pixsDistance; int iAngle, iDistance; int index1=0; int index2=0; PFont orcFont; void setup() { size (1200, 700); // ***将此更改为您的屏幕分辨率*** smooth(); myPort = new Serial(this,"COM5", 9600); // 启动串行通信 myPort.bufferUntil('.'); // 从串行端口读取数据,直到字符“.”。实际上它读到了:角度,距离。 } void draw() { fill(98,245,31); // 模拟运动模糊和运动线的缓慢衰减 noStroke(); fill(0,4); rect(0, 0, width, height-height*0.065); fill(98,245,31); // green color //调用绘制雷达的函数 drawRadar(); drawLine(); drawObject(); drawText(); } void serialEvent (Serial myPort) { // 开始从串行端口读取数据 //从串行端口读取到字符“.”的数据,并将其放入字符串变量“data”中。 data = myPort.readStringUntil('.'); data = data.substring(0,data.length()-1); index1 = data.indexOf(","); // 找到字符','并将其放入变量“index1” angle= data.substring(0, index1); // 读取从位置“0”到变量index1位置的数据,或者这是Arduino板发送到串行端口的角度值 distance= data.substring(index1+1, data.length()); // 读取从位置“index1”到距离值的数据pr的末尾的数据 // 将字符串变量转换为整数 iAngle = int(angle); iDistance = int(distance); } void drawRadar() { pushMatrix(); translate(width/2,height-height*0.074); // 将起始坐标移动到新位置 noFill(); strokeWeight(2); stroke(98,245,31); // 绘制弧线 arc(0,0,(width-width*0.0625),(width-width*0.0625),PI,TWO_PI); arc(0,0,(width-width*0.27),(width-width*0.27),PI,TWO_PI); arc(0,0,(width-width*0.479),(width-width*0.479),PI,TWO_PI); arc(0,0,(width-width*0.687),(width-width*0.687),PI,TWO_PI); // 绘制角线 line(-width/2,0,width/2,0); line(0,0,(-width/2)*cos(radians(30)),(-width/2)*sin(radians(30))); line(0,0,(-width/2)*cos(radians(60)),(-width/2)*sin(radians(60))); line(0,0,(-width/2)*cos(radians(90)),(-width/2)*sin(radians(90))); line(0,0,(-width/2)*cos(radians(120)),(-width/2)*sin(radians(120))); line(0,0,(-width/2)*cos(radians(150)),(-width/2)*sin(radians(150))); line((-width/2)*cos(radians(30)),0,width/2,0); popMatrix(); } void drawObject() { pushMatrix(); translate(width/2,height-height*0.074); // 将起始坐标移动到新位置 strokeWeight(9); stroke(255,10,10); // red color pixsDistance = iDistance*((height-height*0.1666)*0.025); // 覆盖从厘米到像素的传感器距离 // 将范围限制为40厘米 if(iDistance<40){ // 根据角度和距离绘制对象 line(pixsDistance*cos(radians(iAngle)),-pixsDistance*sin(radians(iAngle)),(width-width*0.505)*cos(radians(iAngle)),-(width-width*0.505)*sin(radians(iAngle))); } popMatrix(); } void drawLine() { pushMatrix(); strokeWeight(9); stroke(30,250,60); translate(width/2,height-height*0.074); // 将起始坐标移动到新位置 line(0,0,(height-height*0.12)*cos(radians(iAngle)),-(height-height*0.12)*sin(radians(iAngle))); // 根据角度画线 popMatrix(); } void drawText() { //在屏幕上绘制文本 pushMatrix(); if(iDistance>40) { noObject = "Out of Range"; } else { noObject = "In Range"; } fill(0,0,0); noStroke(); rect(0, height-height*0.0648, width, height); fill(98,245,31); textSize(25); text("10cm",width-width*0.3854,height-height*0.0833); text("20cm",width-width*0.281,height-height*0.0833); text("30cm",width-width*0.177,height-height*0.0833); text("40cm",width-width*0.0729,height-height*0.0833); textSize(40); text("Robu.in", width-width*0.875, height-height*0.0277); text("Angle: " + iAngle +" °", width-width*0.48, height-height*0.0277); text("Distance: ", width-width*0.26, height-height*0.0277); if(iDistance<40) { text(" " + iDistance +" cm", width-width*0.225, height-height*0.0277); } textSize(25); fill(98,245,60); translate((width-width*0.4994)+width/2*cos(radians(30)),(height-height*0.0907)-width/2*sin(radians(30))); rotate(-radians(-60)); text("30°",0,0); resetMatrix(); translate((width-width*0.503)+width/2*cos(radians(60)),(height-height*0.0888)-width/2*sin(radians(60))); rotate(-radians(-30)); text("60°",0,0); resetMatrix(); translate((width-width*0.507)+width/2*cos(radians(90)),(height-height*0.0833)-width/2*sin(radians(90))); rotate(radians(0)); text("90°",0,0); resetMatrix(); translate(width-width*0.513+width/2*cos(radians(120)),(height-height*0.07129)-width/2*sin(radians(120))); rotate(radians(-30)); text("120°",0,0); resetMatrix(); translate((width-width*0.5104)+width/2*cos(radians(150)),(height-height*0.0574)-width/2*sin(radians(150))); rotate(radians(-60)); text("150°",0,0); popMatrix(); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
6 最后
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/代码探险家/article/detail/755477
推荐阅读
相关标签



