- 1Java中判断数组是否为空_java判断字节数组是否全为零
- 2调用百度智能云OCR接口识别身份证和户口本_package com.baidu.ocr.user;
- 3备份android分区,备份分区
- 4【Linux成长史】Linux编辑器-gcc/g++使用_linux中文本编辑器gcc
- 5【Teamcity】(一)基于Teamcity加Docker Compose自动部署前端VUE项目,自动发布_teamcity 和portainer
- 62023秋招华为AI算法工程师面经分享
- 7Flutter界面实战_flutter 怎么获取组件实例
- 8美团外卖小程序_美团代码行数
- 9TIKZ——LaTeX基本绘图
- 10Java小游戏-猜数字_编写猜数字游戏程序,并输出一共猜了多少次?
Elasticsearch:倒数排序融合 - Reciprocal rank fusion (RRF)_rrf算法
赞
踩
注意:RRF 在 Elastic Stack 8.8 中正式提供。
倒数排序融合(RRF)是一种将具有不同相关性指标的多个结果集组合成单个结果集的方法。 RRF 无需调优,不同的相关性指标也不必相互关联即可获得高质量的结果。该方法的优势在于不利用相关分数,而仅靠排名计算。相关分数存在的问题在于不同模型的分数范围差。
使用 Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF) 的简化混合搜索
通常,最好的排名是通过组合多种排名方法来实现的,例如 BM25 和生成密集向量嵌入的 ML 模型。 在实践中,将结果集组合成一个单一的组合相关性排名结果集被证明是非常具有挑战性的。 当然,理论上你可以将每个结果集的分数归一化(因为原始分数在完全不同的范围内),然后进行线性组合,根据每个排名的分数加权和排序最终结果集方法。 只要你提供正确的权重,Elasticsearch 就支持它并且运行良好。 为此,你需要了解环境中每种方法得分的统计分布,并有条不紊地优化权重。 实际上,这超出了绝大多数用户的能力。
另一种方法是 RRF 算法,它提供了出色的排序方法零样本混合,正如学术研究所证明的那样。 如果你不了解不同方法中排名分数的确切分布,这不仅是最好的混合方式,而且客观上也是混合排名方法的好方法 —— 即使你知道如何归一化及分数的分布情况,也很难被击败。 基本概念是结果的组合顺序由每个结果集中每个文档的位置(和存在)定义。 因此可以方便地忽略排名分数。
Elastic 8.8 支持具有多个密集向量查询和在倒排索引上运行的单个查询的 RRF。 在不久的将来,我们希望支持来自 BM25 和 Elastic 的检索模型(两者都是稀疏向量)的混合结果,从而产生同类最佳的零样本集(无域内训练)排名方法。
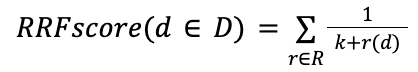
- D - 文档集
- R - 一组排名作为 1..|D| 的排列
- K - 通常默认设置为 60
RRF 使用以下公式来确定对每个文档进行排名的分数:
- score = 0.0
- for q in queries:
- if d in result(q):
- score += 1.0 / ( k + rank( result(q), d ) )
- return score
-
- # where
- # k is a ranking constant
- # q is a query in the set of queries
- # d is a document in the result set of q
- # result(q) is the result set of q
- # rank( result(q), d ) is d's rank within the result(q) starting from 1
倒数排序融合 API
你可以将 RRF 用作搜索的一部分,以使用来自:
- 1 个查询(query)和 1 个或多个 kNN 搜索
- 2 个或更多 kNN 搜索
rrf 参数是一个可选对象,定义为搜索请求 rank parameter 的一部分。 rrf 对象包含以下参数:
| 条目 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| rank_constant | (可选,整数)此值确定每个查询的单个结果集中的文档对最终排名结果集的影响程度。 较高的值表示排名较低的文档具有更大的影响力。 此值必须大于或等于 1。默认为 60。 |
| window_size | (可选,整数)此值确定每个查询的单个结果集的大小。 较高的值将以性能为代价提高结果相关性。 最终排名的结果集被修剪为搜索请求的 <<search-size-param, size>。 window_size 必须大于或等于 size 且大于或等于 1。默认为 100。 |
使用 RRF 的示例请求:
- GET example-index/_search
- {
- "query": {
- "term": {
- "text": "shoes"
- }
- },
- "knn": {
- "field": "vector",
- "query_vector": [1.25, 2, 3.5],
- "k": 50,
- "num_candidates": 100
- },
- "rank": {
- "rrf": {
- "window_size": 50,
- "rank_constant": 20
- }
- }
- }

在上面的示例中,我们首先执行 kNN 搜索以获取其全球前 50 名的结果。 然后我们执行查询以获取其全球前 50 名的结果。 之后,在一个协调节点上,我们将 knn 搜索结果与查询结果结合起来,根据 RRF 方法对它们进行排序,得到最终的 top 10 结果。
请注意,如果来自 knn 搜索的 k 大于 window_size,则结果将被截断为 window_size。 如果 k 小于 window_size,则结果为 k 大小。
倒数排序融合支持的功能
RRF 确实支持:
RRF 目前不支持:
使用不支持的功能作为使用 RRF 的搜索的一部分将导致异常。
倒数排序融合完整示例
我们首先为具有文本字段、向量字段和整数字段的索引创建映射,同时索引多个文档。 对于这个例子,我们将使用一个只有一个维度的向量来使排名更容易解释。
- PUT example-index
- {
- "mappings": {
- "properties": {
- "text": {
- "type": "text"
- },
- "vector": {
- "type": "dense_vector",
- "dims": 1,
- "index": true,
- "similarity": "l2_norm"
- },
- "integer": {
- "type": "integer"
- }
- }
- }
- }
-
- PUT example-index/_doc/1
- {
- "text" : "rrf",
- "vector" : [5],
- "integer": 1
- }
-
- PUT example-index/_doc/2
- {
- "text" : "rrf rrf",
- "vector" : [4],
- "integer": 2
- }
-
- PUT example-index/_doc/3
- {
- "text" : "rrf rrf rrf",
- "vector" : [3],
- "integer": 1
- }
-
- PUT example-index/_doc/4
- {
- "text" : "rrf rrf rrf rrf",
- "integer": 2
- }
-
- PUT example-index/_doc/5
- {
- "vector" : [0],
- "integer": 1
- }
-
- POST example-index/_refresh

现在,我们使用带有查询、kNN 搜索和术语聚合的 RRF 执行搜索。
- GET example-index/_search
- {
- "query": {
- "term": {
- "text": "rrf"
- }
- },
- "knn": {
- "field": "vector",
- "query_vector": [
- 3
- ],
- "k": 5,
- "num_candidates": 5
- },
- "rank": {
- "rrf": {
- "window_size": 5,
- "rank_constant": 1
- }
- },
- "size": 3,
- "aggs": {
- "int_count": {
- "terms": {
- "field": "integer"
- }
- }
- }
- }

我们收到带有排名 hits 和术语聚合结果的响应。 请注意,_score 为 null,我们改为使用 _rank 来显示排名靠前的文档。
- {
- "took": 16,
- "timed_out": false,
- "_shards": {
- "total": 1,
- "successful": 1,
- "skipped": 0,
- "failed": 0
- },
- "hits": {
- "total": {
- "value": 5,
- "relation": "eq"
- },
- "max_score": null,
- "hits": [
- {
- "_index": "example-index",
- "_id": "3",
- "_score": null,
- "_rank": 1,
- "_source": {
- "text": "rrf rrf rrf",
- "vector": [
- 3
- ],
- "integer": 1
- }
- },
- {
- "_index": "example-index",
- "_id": "2",
- "_score": null,
- "_rank": 2,
- "_source": {
- "text": "rrf rrf",
- "vector": [
- 4
- ],
- "integer": 2
- }
- },
- {
- "_index": "example-index",
- "_id": "4",
- "_score": null,
- "_rank": 3,
- "_source": {
- "text": "rrf rrf rrf rrf",
- "integer": 2
- }
- }
- ]
- },
- "aggregations": {
- "int_count": {
- "doc_count_error_upper_bound": 0,
- "sum_other_doc_count": 0,
- "buckets": [
- {
- "key": 1,
- "doc_count": 3
- },
- {
- "key": 2,
- "doc_count": 2
- }
- ]
- }
- }
- }

让我们分解一下这些点击率是如何排名的。 我们首先分别运行查询和 kNN 搜索,以收集它们各自的命中率。
首先,我们查看查询的 hits。
- GET example-index/_search?filter_path=**.hits
- {
- "query": {
- "term": {
- "text": "rrf"
- }
- }
- }
上面的命令显示的结果为:
- {
- "hits": {
- "hits": [
- {
- "_index": "example-index",
- "_id": "4",
- "_score": 0.16152832, [1]
- "_source": {
- "text": "rrf rrf rrf rrf",
- "integer": 2
- }
- },
- {
- "_index": "example-index",
- "_id": "3",
- "_score": 0.15876243, [2]
- "_source": {
- "text": "rrf rrf rrf",
- "vector": [
- 3
- ],
- "integer": 1
- }
- },
- {
- "_index": "example-index",
- "_id": "2",
- "_score": 0.15350538, [3]
- "_source": {
- "text": "rrf rrf",
- "vector": [
- 4
- ],
- "integer": 2
- }
- },
- {
- "_index": "example-index",
- "_id": "1",
- "_score": 0.13963442, [4]
- "_source": {
- "text": "rrf",
- "vector": [
- 5
- ],
- "integer": 1
- }
- }
- ]
- }
- }

- [1] rank 1, _id 4
- [2] rank 2, _id 3
- [3] rank 3, _id 2
- [4] rank 4, _id 1
请注意,我们的第一个命中没有 vector 字段的值。 现在,我们查看 kNN 搜索的结果。
- GET example-index/_search?filter_path=**.hits
- {
- "knn": {
- "field": "vector",
- "query_vector": [
- 3
- ],
- "k": 5,
- "num_candidates": 5
- }
- }
上面搜索的结果为:
- {
- "hits": {
- "hits": [
- {
- "_index": "example-index",
- "_id": "3", [1]
- "_score": 1,
- "_source": {
- "text": "rrf rrf rrf",
- "vector": [
- 3
- ],
- "integer": 1
- }
- },
- {
- "_index": "example-index",
- "_id": "2", [2]
- "_score": 0.5,
- "_source": {
- "text": "rrf rrf",
- "vector": [
- 4
- ],
- "integer": 2
- }
- },
- {
- "_index": "example-index",
- "_id": "1", [3]
- "_score": 0.2,
- "_source": {
- "text": "rrf",
- "vector": [
- 5
- ],
- "integer": 1
- }
- },
- {
- "_index": "example-index",
- "_id": "5", [4]
- "_score": 0.1,
- "_source": {
- "vector": [
- 0
- ],
- "integer": 1
- }
- }
- ]
- }
- }

- [1] rank 1, _id 3
- [2] rank 2, _id 2
- [3] rank 3, _id 1
- [4] rank 4, _id 5
我们现在可以获取两个单独排名的结果集并将 RRF 公式应用于它们以获得我们的最终排名。
- # doc | query | knn | score
- _id: 1 = 1.0/(1+4) + 1.0/(1+3) = 0.4500
- _id: 2 = 1.0/(1+3) + 1.0/(1+2) = 0.5833
- _id: 3 = 1.0/(1+2) + 1.0/(1+1) = 0.8333
- _id: 4 = 1.0/(1+1) = 0.5000
- _id: 5 = 1.0/(1+4) = 0.2000
我们根据 RRF 公式对文档进行排名,其中 window_size 为 5,截断 RRF 结果集中底部的 2 个文档,大小为 3。我们以 _id: 3 作为 _rank: 1, _id: 2 作为 _rank: 2, 及 _id: 4 作为 _rank: 3。这个排名符合预期的原始 RRF 搜索的结果集。



