- 1thinkphp日志泄漏漏洞_Thinkphp5 远程代码执行漏洞事件分析报告
- 2数据要素时代,企业数据如何安全合规流通?
- 3【深度学习】Transformer长大了,它的兄弟姐妹们呢?(含Transformers超细节知识点)...
- 4下载AOSP源码编译、调试、刷机_aosp_arm64-exp-u1b1.230908.003-10811961-24d7d0fa
- 5最强Node js 后端框架学习看这一篇文章就够_使用node写后台 框架
- 6Laravel 6 - 第十五章 验证器
- 7IDEA上配置Maven环境
- 8python 文本分类卡方检验_中文文本分类:你需要了解的10项关键内容
- 9程序员年龄大了,真的会失业吗?那么以后该怎么办_游戏开发年龄大了怎么办
- 10详解UART通信协议以及FPGA实现
python自动化之路-day3_python之路3
赞
踩
首先分享:消费者行为学。5分钟商学院。(app得到),琳达看美国
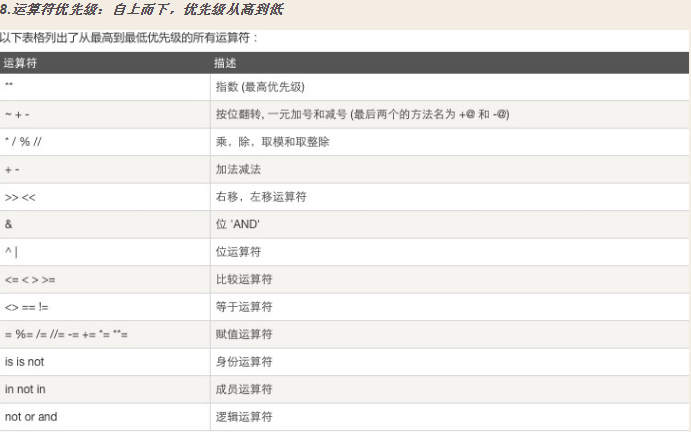
一.运算符
1.算数运算符:
+ 两个对象相加
- 得到负数或者一个数减去另一个数
* 两个数相乘或返回一个被重复若干次的字符串
>>> a*3
'aaa'
>>> a
'a'
>>>
/ 除
% 取膜,返回除法的余数
** 幂指数,返回一个数的另一个数的次幂
// 取整除-返回商的整数部分
>>> 9//3
3
>>> 8//3
2
2.比较运算符
== 等于 比较对象是否相等 包括(字符串,字典,数字,列表) 返回一个bool值 ->true 或 false
!= 不等于 比较两个对象是否不相等
<> 不等于 比较两个对象是否相等,这个运算符类似不等于!= 不常用
> 大于
< 小于
>= 大于等于
<= 小于等于
竟然比较运算符的返回值是bool值 -> True 或者 false
3.赋值运算符
= 简单的赋值运算符
+= 加法赋值运算符 c+=a等效于c=c+a
-= 减法复制运算符 c-=a 等效于c=c-a
*= 乘法赋值运算符 c*=a等效于c=c-a
/= 除法赋值运算符 c/=a等效于c=c/a
%/ 取膜赋值运算符 c%a等效于c=c%a
**= 幂赋值运算符 c**=a等效于c=c**a
//= 取整除赋值运算符 c//=a等效于c=c//a
4.位运算符
& 按位与运算符:参与运算的两个值,如果两个相应位都为1,则按位的结果为1,否则为0
| 按位或运算符:只要对应的二个二进制位有一个为1时,结果位就为1.
^ 按位异或运算符:当两对应的二进制相异时,结果为1. 相同时为0
~ 按位取反运算符:对数据的每个二进制取反,即把1变为0,把0变为1
<< 左移动运算符:运算数的各二进制位全部左移若干位,由“<<”
>> 右移动运算符:全部数据右移动
5.逻辑运算符
and 布尔“与” 。
注解:1.在python中,and和or执行布尔逻辑演算,和你所期待的一样,但是他们并不返回bool布尔值;而是,返回他们实际进行比较的
值之一。2.在布尔上下文中从左到右的演算表达式的值,如果布尔所有值都为真,那么and返回最后一个值
3.如果布尔上下文中的某个值为假,则and返回第一个假值
or注解:
1.使用or时,在布尔上下文中从左到右演算值。如果第一个为真,则立即返回
2.如果所有的值都为假,or返回最后一个假值
3.注意or在布尔上下文中会一直进行表达式演算直到找到第一个真值,然后就会忽略剩余的比较值
not 布尔“非”
6.成员运算符
in 如果在指定的序列中找到值返回True,否则返回false
not in 如果在是定的序列中没有找到值返回True
7.身份运算符
is,is not
二. 字典
1.定义
刚刚得知的pycharm快捷键。 ctrl + d 未选中时,复制当前行到下一行,选中时复制粘贴选中部分
定义:{key1:value1,key2:value2},key-value结构,key必须可hash
1.可存放多个值
2.可修改指定key对应的值,可变
3.无序
2.字典的创建
person = { "name":"sb","age":"18"} #键值必须是不变类型,如字符串,数字,元组
person2 = dict(name="sb",age="19")
test = {}.fromkeys(["k1","k2"],[])
3.字典的工厂函数集
person = { "name":"sb","age":"18"}
person2 = dict(name2="sb",age="19")
test = {}.fromkeys(["k1","k2"],[])
print(person.items())
print(person.keys())
# print(person.clear())
print(person.copy(),id(person),id(person.copy())) #浅copy
print(person.get("name"))
print(person.values(),type(person.values())) #获取字典的全部value
# print(person,person2,test)
for i in person.values():
print(i) #循环输出value
print(person.get("name")) #获得某键值的value,没有此键值返回为none
print(person.pop("age")) #指定删除键值指定的value
print(person) #输出对比删除后字典
print(person.clear()) #删除所有的items,返回值为none
print(person)
# print(person.popitem())
data=person.update(person2) #用其他字典更新本字典
print(person)
person.setdefault("stu","zongyimin") #添加字典元素
print(person)
4.字典基本的增删查改:
#增加
person["name"]="苍老师"
print(person)
#类似与字典类方法
data2 = person.setdefault("sex") #可同时添加键值和value
print(person)
#修改
person["name"]="一本道"
person["sex"]="female"
print(person) #也可以用update的方法修改字典
#删除
person.pop("stu")
del person["sex"]
print(person)
person.popitem() #随机删除
#查找
print("name" in person ) #比较运算符,成员运算符返回值都是bool类型
print(person.get("name")) #获取value
person["dasd"] #如果key不存在,就报错。get不会报
5.循环
#循环
for key in person:
print(key,person[key]) #遍历循环key值
for key,v in person.items(): #先把字典转换成列表list,数据量大时莫用
print(key,v,type(key),type(v))
#字典根据键值key索引,列表根据下标素索引
#enumerate() 方法只用于列表list
print(person.items()) #返回列表list
程序练习:
未完待续。。。。
三.集合
定义:由不同元素组成的集合,集合中是一组无序排列的可hash值,可以作为字典的key值
特性:集合的目的是将不同的数据存放在一起,不同的集合间用来做关系,无需纠结于集合中单个值
1,.集合的创建
#定义可变集合
set_test = set("hello")
print(set_test) #无序
set_test2 = {1,2,3,4,5}
print(set_test2)
f_set_test =frozenset(set_test) #改为不可变集合
print(f_set_test)
2.集合的常用操作:关系运算
in, not in , == ,!= ,& ,-
3.方法工厂函数set()
#增加集合元素
set_test2.add(6) #添加一个元素到集合,如果元素存在则没有任何影响
print(set_test2)
set_test2.update(set_test) #更新集合,添加多项
print(set_test2)
set_test3 = {6,7,8,9,0}
print(set_test2.union(set_test3)) #Return the union of sets as a new set.
#删除
set_test2.remove(2) #删除一项,元素必须存在。如果元素不存在则抛出错误
print(set_test2)
print(len(set_test2) ) #集合的长度
set_test2.pop() #随机删除一个元素
print(set_test2)
set_test2.discard(5) #删除一个元素,如果元素存在则删除。如果不存在不报错
print(set_test2)
print(set_test2.difference(set_test)) #相当于s1-s2,去重
m = [1,1,1,2,2,2,2,3,3,3,6,6,8,8,9,9,0,"a","b","c","d"]
n=set(m)
print(n) #列表变集合set
c = list(n) #集合变列表list
print(c)
四.字符串(补充比较)
字符串方法
string1 = "woshi yige geshou "
print(string1.index("i")) #返回索引位置,与find不同的是:一个知道次元素,一个不知道次元素
print(string1.find("g")) #字符串中没有此元素则返回-1,如果有
# string1.index()
print(string1[5])
print(string1.capitalize()) #没有参数,首字母大写
print(string1.center(30,"*")) # Return S centered in a string of length width
print(string1.count("o")) #返回字符的个数,参数可以有start:end
print(string1.endswith(" ")) #查看字符串是不是以某个字符结束,返回值为
# string1.format() #格式化输出
print('{name} {age}'.format(age=12,name='lhf'))
print(string1.isdigit()) #判断字符串中字符是不是都为数字,返回值为bool值
print(string1.islower()) #判断都是小写字母才返回true
print(string1.lstrip()) #去掉空格
string1.replace() #字符串替换
string1.strip() #前后去掉空格
string1.translate()
五.列表
#列表方法
m.pop()
m.append("m")
print(m)
s1 ={1,2,3,4,"a"}
s1.update((1,2,3,4,5),(1,2,3))
print(s1)#一个集合按照另一个集合更新
#增加
print("-----------------------------------------")
s1.add("hello")
print(s1)
n = ["mmmm"]
m.extend(n)
#删除
s1.pop() #无序随机删除
print(s1)
s1.remove("a")
print(s1)
s1.discard("w") #不报错的删除,不确定元素
#查
m.copy() #浅copy类似与软连接,你修改文件,浅copy之前的文件也会改变,深copy就是又生成一个文件
m.count(1)
print(m,"********")
print(m.index(1))
print(m.index("a"))
#改
print(m.insert(1,"kk"))
六.文件操作
# file = open("test.txt","w+")
# file.close()
f = open("test.txt",encoding="utf-8") #默认打开时 read模式
# print(f.readline().strip()) #去掉换行 空格
print(f.readline().strip())
print(f.readline().strip())
print(f.readline().strip())
f.close()
f = open("test.txt",encoding="utf-8")
# print(f.readlines())
for index,line in enumerate(f.readlines()):
if index <5:
print(line.strip()) #全部读取,不要用
else:
break
f.close()
f = open("test.txt",encoding="utf-8")
for i in range(5):
print(f.readline().strip())
f.close()
f = open("test.txt",encoding="utf-8")
for line in f:
print(line.strip()) #一行行读硬盘
f.close()
f1 = open("","w") #创建写模式。覆盖数据
f.write("我哎北京")
f.close() #关闭文件自动保存
#
f2 = open("","a") #追加模式
# r+ 读写 w+ 写读 a+ 追加读
f3 = open("myfile","r+") #混合模式
#
f.closed #返回bool
f.encoding #文件编码 cp936 -》gbk
f.fileno() #操作系统接口
f.flush() #时时刷新数据到硬盘
f.name #打印文件名
#
f.seek() #寻找
f.tell() #告知当前光标位置
f.truncate() #截断 从光标的位置截断.对二进制文件
#
f.writelines()
程序练习一:
1.python脚本实现简单的shell sed 功能
代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
# python sed.py 旧内容 新内容 文件
import os,sys,time
def use_way(): #定义函数输出使用脚本方式
print("Please use this script like 'python script.py old_str new_str file'")
if len(sys.argv)== 4:
if os.path.isfile(sys.argv[3]): #判断是不是文件
name = sys.argv[3]
file1 = open(sys.argv[3]) #打开文件
file2 = open("file_new","w") #创建文件名为file_new的文件
old_str = sys.argv[1]
new_str = sys.argv[2]
for line in file1: #遍历输出文件内容,返回值为字符串
if old_str in line:
line = line.replace(old_str,new_str) #替换旧内容
file2.write(line) #循环写内容到文件file2
file2.flush() #时刻刷新数据到硬盘
file1.close()
file2.close() #关闭文件
os.rename("file_new",name) #重命名文件
else:
print("try again! Bye!")
else: #输入方式错误,提示重新输入
use_way()
exit()
程序二:2.修改haproxy配置文件1、查
输入:www.oldboy.org
获取当前backend下的所有记录
2、新建
输入:
arg = {
'bakend': 'www.oldboy.org',
'record':{
'server': '100.1.7.9',
'weight': 20,
'maxconn': 30
}
}
3、删除
输入:
arg = {
'bakend': 'www.oldboy.org',
'record':{
'server': '100.1.7.9',
'weight': 20,
'maxconn': 30
}
}
原配置文件:
global
log 127.0.0.1 local2
daemon
maxconn 256
log 127.0.0.1 local2 info
defaults
log global
mode http
timeout connect 5000ms
timeout client 50000ms
timeout server 50000ms
option dontlognull
listen stats :8888
stats enable
stats uri /admin
stats auth admin:1234
frontend oldboy.org
bind 0.0.0.0:80
option httplog
option httpclose
option forwardfor
log global
acl www hdr_reg(host) -i www.oldboy.org
use_backend www.oldboy.org if www
backend www.oldboy.org
server 100.1.7.9 100.1.7.9 weight 20 maxconn 3000
代码如下:
未完待续。。。