热门标签
热门文章
- 1python批量检索文献_我要用python 建一个快速的检索类网站 很小规模 如果有对此非常熟悉的 推荐一个框架...
- 2秒杀项目07-安全优化
- 3LeetCode 算法:找到字符串中所有字母异位词c++
- 4基于AppBuilder自定义组件开发大模型应用
- 5LangChain的函数,工具和代理(六):Conversational agent_langchain agent调用函数
- 6Redis Desktop Manager2022中文 附安装教程(附使用)_redis desktop manager 2022
- 7工业大数据的应用有哪些_工业大数据应用
- 8Java:SpringBoot整合Druid实现双数据源_springboo配置双数据源并集成durid加密数据库
- 9网络空间安全论文笔记4_mvp: detecting vulnerabilities using patch-enhance
- 10c语言整人程序(1)_c语言整人代码
当前位置: article > 正文
neo4j 图数据库 py2neo 操作 示例代码_py2neo的relationshipmatcher
作者:喵喵爱编程 | 2024-07-11 13:27:58
赞
踩
py2neo的relationshipmatcher
摘要
利用py2neo包,实现把excel表里面的数据,插入到neo4j 图数据库中;
- 创建新(节点或关系)到neo4j图数据库中;
- 能够获取neo4j 中已有的(节点或关系),不再创建新(节点或关系);
前置
安装py2neo: pip install py2neo
安装neo4j软件,请自行安装
NodeMatcher & RelationshipMatcher
代码由 Jupyter 编写,建议使用vscode
from py2neo import Graph, Node, NodeMatcher, RelationshipMatcher
import pandas as pd
# 连接到Neo4j数据库
graph = Graph("bolt://localhost:7687", auth=("neo4j", "你设置的密码"))
node_matcher = NodeMatcher(graph)
relationship_matcher = RelationshipMatcher(graph)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
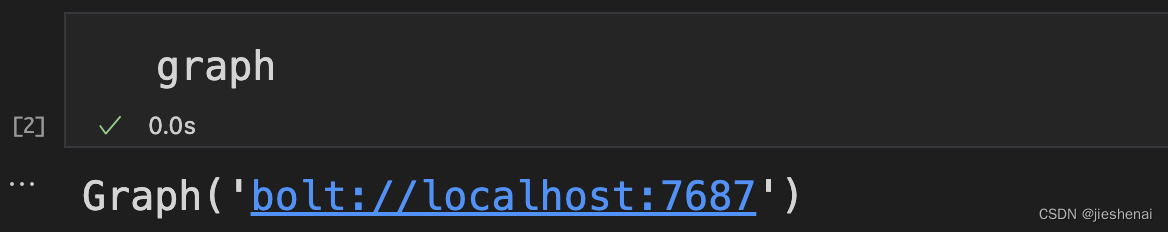
TODO: 设置neo4j 远程连接
创建节点
node = Node("Person", name="Alice", age=18)
graph.create(node)
- 1
- 2
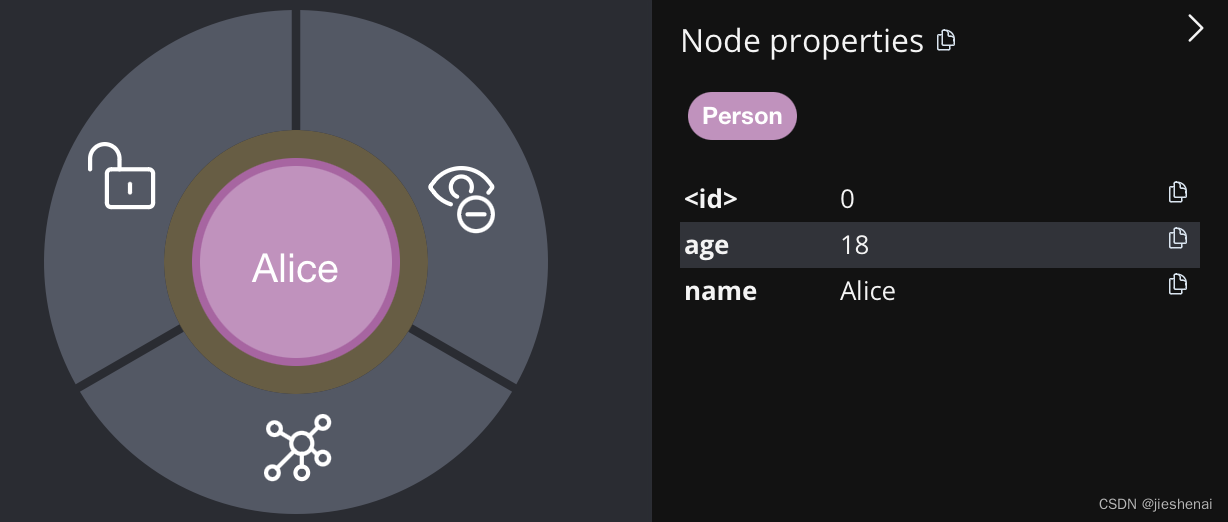
查询获取节点
# 拿到匹配到的第一个节点
node_matcher.match('Person', name='Alice').first()
# 拿到可匹配到的所有
node_matcher.match('Person', name='Alice').all()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
节点有则查询,无则创建
def get_node(class_, **kwargs):
if node := node_matcher.match(class_, **kwargs):
# 节点存在,则获取
return node.first()
else:
# 节点不存在,则创建
node = Node(class_, **kwargs)
graph.create(node)
return node
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
运行
创建关系
Alice - Friend -> Bob
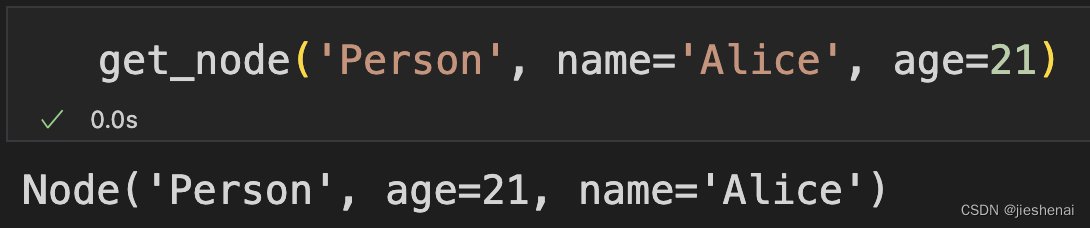
node1 = get_node('Person', name='Alice', age=21)
node2 = get_node('Person', name='Bob', age=20)
graph.create(
Relationship(node1, 'Friend', node2)
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

查询关系
查询 node1 和 node2 之间是否有 Friend 关系
node1 = get_node('Person', name='Alice', age=21)
node2 = get_node('Person', name='Bob', age=20)
relationship_matcher.match(
[node1, node2],
r_type='Friend'
).first()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
关系有则查询,无则创建
def get_relation(node1, node2, r_type):
if r := relationship_matcher.match(
[node1, node2],
r_type=r_type
):
return r.first()
else:
r = Relationship(node1, r_type, node2)
graph.create(r)
return r
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
运行
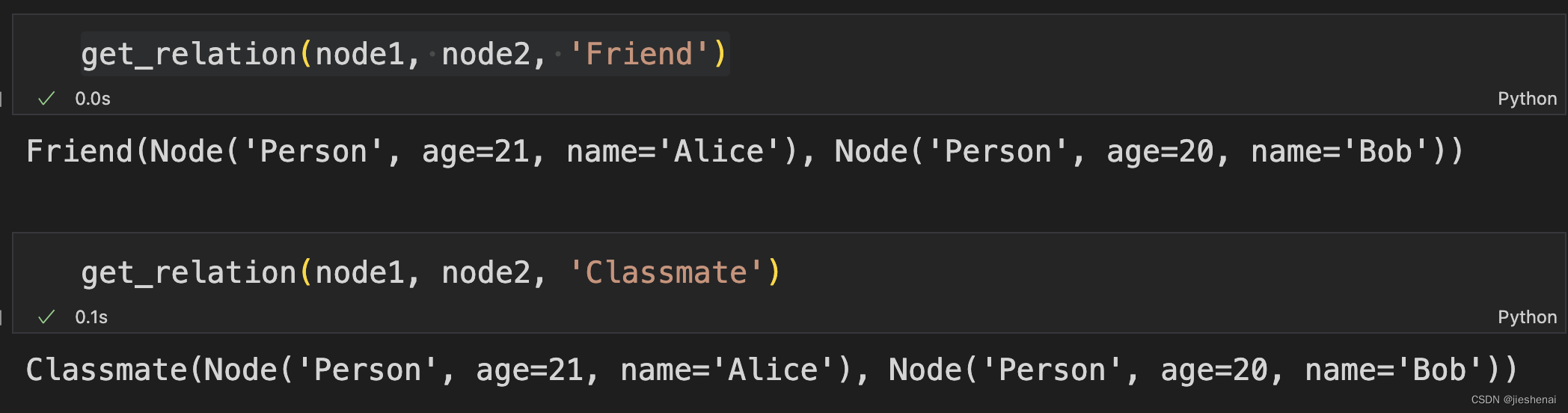
# 查询已有关系
get_relation(node1, node2, 'Friend')
# 创建新关系
get_relation(node1, node2, 'Classmate')
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Cypher语句
虽然 在 NodeMatcher & RelationshipMatcher 介绍的接口已经能够满足大部分情况的使用,本文仍想提供一种使用cypher语句的插入数据到neo4j图数据库的思路。
创建节点
graph.run(
"create (n:Person {name:'js'}) return n"
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
graph.run(
"MERGE (n:Person {name: $name}) \
ON CREATE SET n.created_at = timestamp() \
return n",
name='Cyder'
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
封装类
上述内容的使用还是有所不便,故提供Neo4jDriver分装类,简化用户操作。
from py2neo import Graph, Node, NodeMatcher, RelationshipMatcher, Relationship # 连接到Neo4j数据库 class Neo4jDriver: def __init__(self, url, username, password): self.graph = Graph(url, auth=(username, password)) self.node_matcher = NodeMatcher(self.graph) self.relationship_matcher = RelationshipMatcher(self.graph) def query_node(self, class_, **kwargs): if node := self.node_matcher.match(class_, **kwargs): # 节点存在,则获取 return node.first() def create_node(self, class_, **kwargs): """ 不创建重复节点 """ # 节点存在,则获取 if node := self.query_node(class_, **kwargs): return node # 节点不存在,则创建 node = Node(class_, **kwargs) self.graph.create(node) return node def query_relationship(self, start_node, rel, end_node): r = self.relationship_matcher.match( [start_node, end_node], r_type=rel ) return r.first() def create_relationship(self, start_node, rel, end_node): if r := self.query_relationship(start_node, rel, end_node): return r self.graph.create( Relationship(start_node, rel, end_node) )
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
封装类的使用如下:
# 使用自己的url, username, password,我使用自定义的private起到保密作用 from private import url, username, password driver = Neo4jDriver(url, username, password) # 创建节点 data = { "name": "Jie", "age": 18 } node1 = driver.create_node('Person', **data) print(node1) # 查询节点 node2 = driver.query_node('Person', name='Jie') print(node2) # 查询到节点后,修改节点,再保存到neo4j node2.update({'age':18}) driver.graph.push(node2)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
本文内容由网友自发贡献,转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/喵喵爱编程/article/detail/810454
推荐阅读
相关标签



