- 1王道数据结构——线性表和单链表操作_王道数据结构相线性表和链表
- 2使用Flink实现MySQL到Kafka的数据流转换_flink 消费mysql到kafka
- 3天池NLP新闻文本分类学习赛心得-Task2_新闻文本分类项目难吗
- 4专访微软战略安全官裔云天:做好网站安全的纵深防御
- 5Nat. Rev. Genet. | 通过可解释人工智能从深度学习中获得遗传学见解
- 62024年最新猿创征文|我的技术成长之路&;&;C++_c++抽奖程序,2024年最新从零开始学大数据开发编程
- 72024简约唯美的个人引导页源码
- 8Hadoop伪分布式集群搭建_在sbin目录中vim start-dfs.sh
- 9软件测试中年危机?30岁大关?“我“该如何破局...
- 10机器学习-KNN最近邻算法原理及实践_knn算法实验原理
Java数据结构-线性表_java线性表
赞
踩
一、简介
线性表是最基本、最简单、也是最常用的一种数据结构。一个线性表是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。
前驱元素:
若A元素在B元素的前面,则称A为B的前驱元素
后继元素:
若B元素在A元素的后面,则称B为A的后继元素
线性表的特征:
数据元素之间具有一种“一对一”的逻辑关系。
- 第一个数据元素没有前驱,这个数据元素被称为头结点;
- 最后一个数据元素没有后继,这个数据元素被称为尾结点;
- 除了第一个和最后一个数据元素外,其他数据元素有且仅有一个前驱和一个后继。 如果把线性表用数学语言来定义,则可以表示为(a1,…ai-1,ai,ai+1,…an),ai-1领先于ai,ai领先于ai+1,称ai-1是ai的前驱元素,ai+1是ai的后继元素
线性表的分类:
线性表中数据存储的方式可以是顺序存储,也可以是链式存储,按照数据的存储方式不同,可以把线性表分为顺序表和链表。
二、顺序表实现
顺序表是计算机内存中以数组的形式保存的线性表,线性表的顺序存储是指用一组地址连续的存储单元,依次存储线性表中的各个元素,使得线性表中在逻辑结构上相邻的数据元素存储在相邻的物理存储单元中,即通过数据元素物理存储的相邻关系来反映数据元素之间逻辑上的相邻关系。
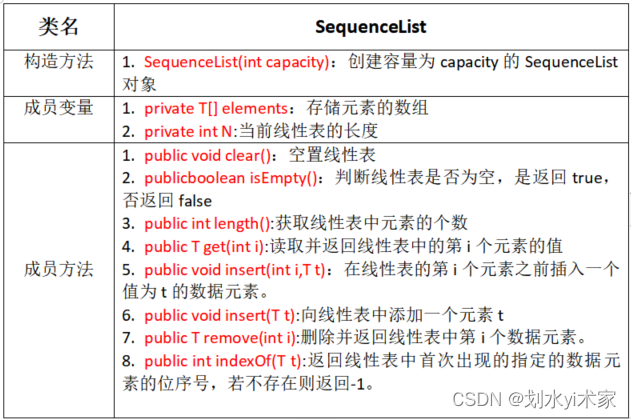
 顺序表API设计
顺序表API设计
import java.util.Iterator; /* 顺序表的实现 */ public class SequenceList<T> implements Iterable<T>{ // 存储元素的数组 private T[] elements; // 记录当前顺序表中的元素个数 private int N; // 构造方法 public SequenceList(int capacity){ // 初始化数组 this.elements = (T[]) new Object[capacity]; // 初始化长度 this.N = 0; } // 将一个线性表置为空表 public void clear(){ this.N = 0; } // 判断当前线性表是否为空表 public boolean isEmpty(){ return N == 0; } // 获取线性表的长度 public int length(){ return N; } // 获取指定位置的元素 public T get(int i){ // 安全性校验 if (i < 0 || i >= N) return null; return elements[i]; } // 向线型表中添加元素t public void insert(T t){ // 当前容量已不足,准备扩容,此处设定扩大 2 倍 if (N == elements.length){ resize(2 * elements.length); } elements[N++] = t; } // 在 i 索引处插入元素t public void insert(int i, T t){ // 安全性校验 if (i < 0 || i >= N) return; if (N == elements.length){ resize(2 * elements.length); } // 先把i索引处的元素及其后面的元素依次向后移动一位 for(int index = N; index > i; index--){ elements[index] = elements[index-1]; } // 再把t元素放到i索引处即可 elements[i] = t; // 元素个数+1 N ++; } // 删除指定位置i处的元素,并返回该元素 public T remove(int i){ // 安全性校验 if (i < 0 || i >= N) return null; // 记录索引i处的值 T current = elements[i]; // 索引i后面元素依次向前移动一位即可 for(int index = i; index < N - 1; index++){ elements[index] = elements[index + 1]; } // 元素个数-1 N --; if (N < elements.length / 4){ resize(elements.length / 2); } return current; } // 查找t元素第一次出现的位置 public int indexOf(T t){ for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){ if (elements[i].equals(t)){ return i; } } return -1; } // 根据参数newSize,重置 elements 的大小 public void resize(int newSize){ // 定义一个临时数组,指向原数组 T[] temp = elements; // 创建新数组 elements = (T[])new Object[newSize]; //把原数组的数据拷贝到新数组即可 for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){ elements[i] = temp[i]; } } /* 重写iterator方法 实现顺序表的遍历 */ @Override public Iterator<T> iterator() { return new MyIterator(); } private class MyIterator implements Iterator{ private int cusor; public MyIterator(){ this.cusor = 0; } @Override public boolean hasNext() { return cusor < N; } @Override public Object next() { return elements[cusor++]; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
三、链表
链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续,非顺序的存储结构,其物理结构不能只管的表示数据元素的逻辑结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。链表由一系列的节点(链表中的每一个元素称为节点)组成,结点可以在运行时动态产生。
节点API设计
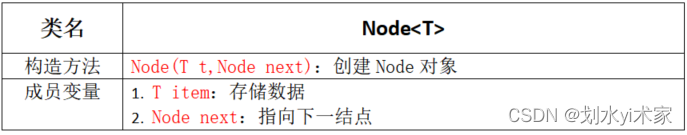
/*
结点类
*/
class Node {
// 存储数据
T item;
// 下一个结点
Node next;
public Node(T item, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
1. 单向链表实现
单向链表是链表的一种,它由多个结点组成,每个结点都由一个数据域和一个指针域组成,数据域用来存储数据,指针域用来指向其后继结点。链表的头结点的数据域不存储数据,指针域指向第一个真正存储数据的结点。
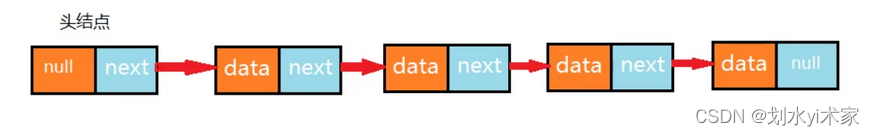
单向链表API设计
import java.util.Iterator; public class LinkList<T> implements Iterable<T>{ /* 结点类 */ private class Node { // 存储数据 T item; // 下一个结点 Node next; public Node(T item, Node next) { this.item = item; this.next = next; } } // 记录头结点 private Node head; // 记录链表的长度 private int N; public LinkList() { // 初始化头结点 头结点不存放值, 只记录下一节点的地址 this.head = new Node(null,null); // 初始化元素个数 this.N = 0; } // 清空链表 public void clear() { head.next = null; this.N = 0; } // 获取链表的长度 public int length() { return N; } // 判断链表是否为空 public boolean isEmpty() { return N == 0; } // 获取指定位置 i 处 (i 从 0 开始)的元素 public T get(int i) { // 安全性校验 if (i < 0 || i >= N) return null; // 通过循环,从头结点开始往后找,依次找 i 次,就可以找到对应的元素 Node node = head.next; for(int index = 0; index < i; index++){ node = node.next; } return node.item; } // 向链表中添加元素t public void insert(T t) { // 找到尾结点 Node node = head; while(node.next != null){ node = node.next; } // 创建新结点,保存元素t Node newNode = new Node(t, null); // 让当前最后一个结点指向新结点 node.next = newNode; // 元素的个数+1 N ++; } // 向指定位置 i 处 (i 从 0 开始),添加元素t public void insert(int i, T t) { // 安全性校验 if (i < 0 || i >= N) return; // 找到 i 位置前一个结点 Node pre = head; for(int index = 0; index < i; index++){ pre = pre.next; } // 找到 i 位置的结点 Node curr = pre.next; // 创建新结点,并且新结点需要指向原来i位置的结点 Node newNode = new Node(t, curr); // 原来 i 位置的前一个节点指向新结点即可 pre.next = newNode; // 元素的个数+1 N ++; } // 删除指定位置 i 处 (i 从 0 开始)的元素,并返回被删除的元素 public T remove(int i) { // 安全性校验 if (i < 0 || i >= N) return null; // 找到i位置的前一个节点 Node pre = head; for(int index = 0; index < i; index++){ pre = pre.next; } // i 位置的结点 Node curr = pre.next; // 找到i位置的下一个结点 // i位置的前一个结点指向 i位置的下一个结点 pre.next = curr.next; // 元素个数-1 N--; return curr.item; } // 查找元素t在链表中第一次出现的位置 public int indexOf(T t) { if (t == null) return -1; // 从头结点开始,依次找到每一个结点,取出item,和t比较,如果相同,就找到了 Node node = head; for(int i = 0; node.next != null; i++){ node = node.next; if (t.equals(node.item)){ return i; } } return -1; } @Override public Iterator<T> iterator() { return new MyIterator(); } private class MyIterator implements Iterator{ private Node node; public MyIterator(){ this.node = head; } @Override public boolean hasNext() { return node.next != null; } @Override public Object next() { node = node.next; return node.item; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
2. 双向链表实现
双向链表也叫双向表,是链表的一种,它由多个节点组成,每个结点都由一个数据域和两个指针域组成,数据域用来存储数据,其中一个指针域用来指向其后继结点,另一个指针域用来指向其前驱结点。链表的头结点的数据域不存储数据,指向前驱结点的指针域值为null,指向后继结点的指针域指向第一个真正存储数据的结点。
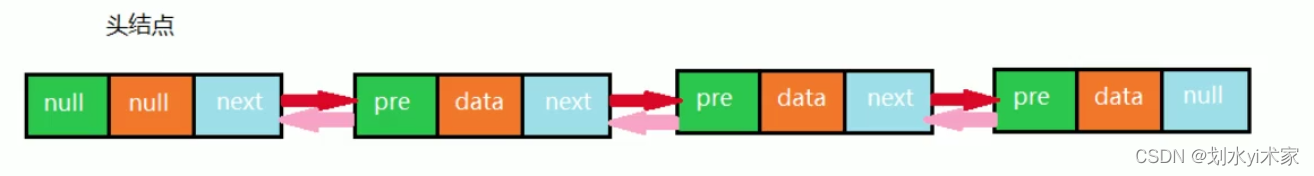
按照面向对象的思想,我们需要设计一个类,来描述结点这个事物。由于结点是属于链表的,所以我们把结点类作为链表类的一个内部类来实现。
结点API设计
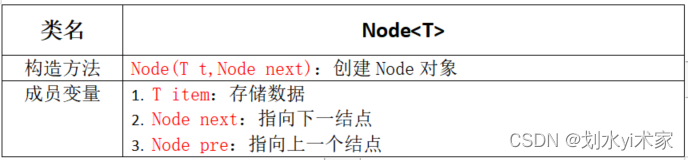
/* 结点类 */ private class Node{ // 存储数据 public T item; // 指向上一个结点 public Node pre; // 指向下一个结点 public Node next; public Node(T item, Node pre, Node next) { this.item = item; this.pre = pre; this.next = next; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
双向链表API设计
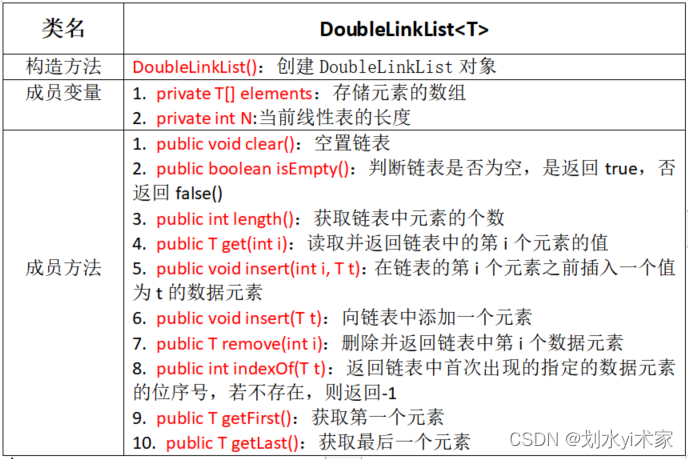
import java.util.Iterator; public class DoubleLinkList<T> implements Iterable<T> { // 首结点 private Node head; // 尾结点 private Node last; // 链表的长度 private int N; // 结点类 private class Node{ public Node(T item, Node pre, Node next) { this.item = item; this.pre = pre; this.next = next; } // 存储数据 public T item; // 指向上一个结点 public Node pre; // 指向下一个结点 public Node next; } public DoubleLinkList() { // 初始化头结点和尾结点 this.head = new Node(null,null,null); this.last = null; // 初始化元素个数 this.N = 0; } // 清空链表 public void clear(){ this.head.next = null; this.head.pre = null; this.head.item = null; this.last = null; this.N = 0; } // 获取链表长度 public int length(){ return N; } // 判断链表是否为空 public boolean isEmpty(){ return N == 0; } // 获取第一个元素 public T getFirst(){ if (isEmpty()) return null; return head.next.item; } // 获取最后一个元素 public T getLast(){ if (isEmpty()) return null; return last.item; } // 插入元素t public void insert(T t){ if (isEmpty()){ // 如果链表为空: // 创建新的结点 Node newNode = new Node(t, head, null); // 让新节点赋值尾结点 last = newNode; // 让头结点指向尾结点 head.next = last; }else { // 如果链表不为空 // 创建新的结点 Node newNode = new Node(t, last, null); // 尾结点指向新结点 last.next = newNode; // 让新节点赋值尾结点 last = newNode; } // 元素个数+1 N ++; } // 向指定位置 i 处 (i 从 0 开始),添加元素t public void insert(int i,T t){ // 安全性校验 if (i < 0 || i >= N) return; // 找到 i 位置的前一个结点 Node pre = head; for(int index = 0; index < i; index++){ pre = pre.next; } // 找到 i 位置的结点 Node curr = pre.next; // 创建新结点 Node newNode = new Node(t, pre, curr); // 让 i 位置的前一个结点指向新结点 pre.next = newNode; // 让 i 位置的下一个结点指向新节点 curr.pre = newNode; // 元素个数+1 N ++; } // 获取指定位置 i 处 (i 从 0 开始)的元素 public T get(int i){ // 安全性校验 if (i < 0 || i >= N) return null; Node node = head.next; for(int index = 0; index < i; index++){ node = node.next; } return node.item; } // 找到元素t在链表中第一次出现的位置 public int indexOf(T t){ if (t == null) return -1; Node node = head; for(int i = 0; node.next != null; i++){ node = node.next; if (t.equals(node.item)){ return i; } } return -1; } // 删除指定位置 i 处 (i 从 0 开始)的元素,并返回被删除的元素 public T remove(int i){ // 安全性校验 if (i < 0 || i >= N) return null; // 找到i位置的前一个结点 Node pre = head; for(int index = 0; index < i; index++){ pre = pre.next; } // 找到 i 位置的结点 Node curr = pre.next; // 让 i 位置的前一个结点指向 i 位置的下一个结点 pre.next = curr.next; // 让 i 位置的下一个结点指向 i 位置的前一个结点 curr.next.pre = pre; // 元素的个数-1 N --; return curr.item; } @Override public Iterator<T> iterator() { return new MyIterator(); } private class MyIterator implements Iterator{ private Node node; public MyIterator(){ this.node = head; } @Override public boolean hasNext() { return node.next != null; } @Override public Object next() { node = node.next; return node.item; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
3. 单链表反转问题
单链表反转,这里介绍4种方法。
① 通过栈实现
基本思想:
- 先让链表所有结点入栈
- 依次出栈,再使用尾插法重新插入
这种方法思路简单易于理解。但空间复杂度与时间复杂度均为o(n),不建议使用
public void reverse(){ LinkedList<Node> list = new LinkedList<>(); Node cur = head.next; // 链表所有结点入栈 while (cur != null){ list.add(cur); cur = cur.next; } // 使用尾插法重新插入 Node tail = head; int index = list.size() - 1; while (index >= 0){ Node pop = list.get(index --); tail.next = pop; tail = pop; tail.next = null; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
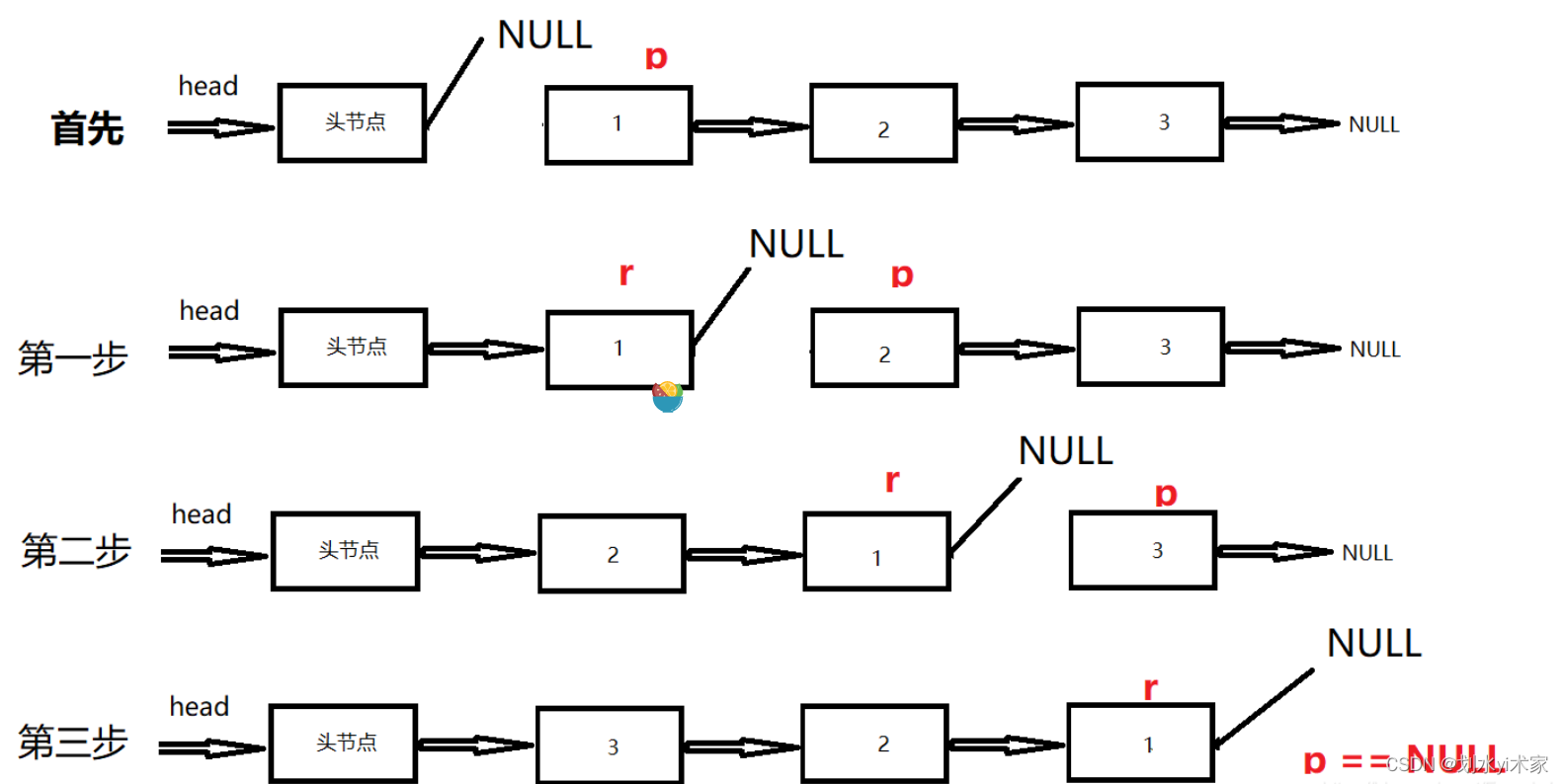
② 头插法
大致思想就是把结点依次放到头节点的下一个位置。为什么头插可以实现链表的反转呢?试想一下,我们把链表的每个节点(头节点除外),按顺序一个一个地放到头节点的后面,那么不就可以实现链表的反转了吗?(如图所示)
public void reverse(){
Node cur = head.next;
head.next = null;
while (cur != null){
// 临时变量存储下一个元素
Node temp = cur.next;
// 开始头插
cur.next = head.next;
head.next = cur;
cur = temp;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
③ 三指针法
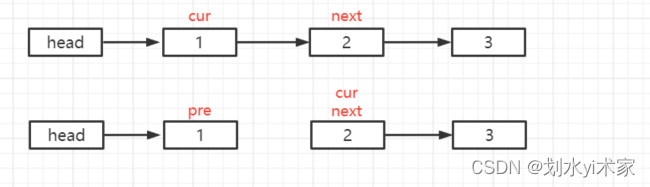
三指针:
- Node cur : 记录当前的节点;
- Node pre : 记录当前节点的上一个节点;
- Node next: 记录当前节点的下一个节点(即剩下的节点);
在链表反转的过程中,我们只要让当前节点 cur 指向上一个节点 pre ,是不是就大体上实现了这两个节点的反转了?
当我们 cur 指向pre 后,我们让上一个节点 pre 的位置移到 cur 这里,再把 cur 移到它下一个节点,那怎么记录它下一个节点呢,我们之前不是用 next来记录的吗,就让 cur 移到 next 的位置就行了。
这样依次循环下去,最后再把头节点指向 pre 就行了,就实现了链表的反转了。
我先将代码放在这里,等会再结合代码做个案例讲解。
public void reverse(){
Node pre = null;
Node cur = null;
Node next = null;
cur = head.next;
while (cur != null){
next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
head.next = pre;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
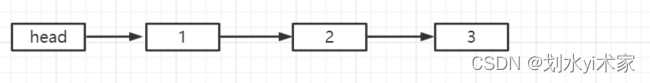
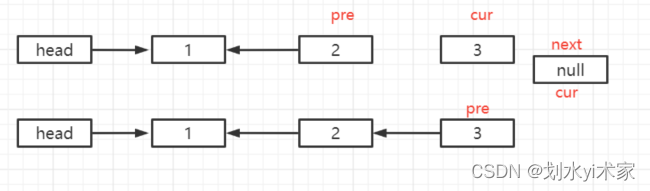
案例:
现有一组链表,如下所示:
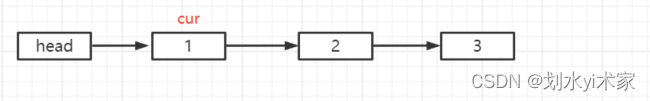
首先,我们将 cur 赋值为 head.next 即 1 处。
现在开始进入第一次循环,经过第一次循环后,链表就变为了以下情况
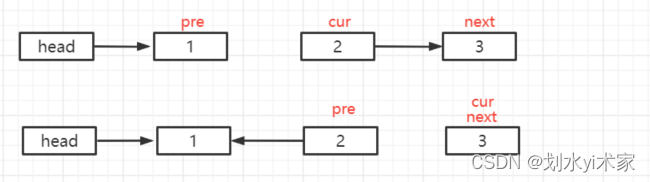
进行第二次循环,链表情况如下
现在最后一次循环,链表变为如下
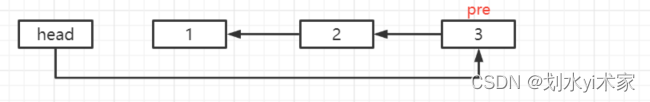
再执行最后一步,让 head.next 指向 pre
到这里,反转就结束了
④ 递归
基本思想:
- 反转入口从 head.next 开始,通过递归,如果当前结点有下一个结点,就继续递归调用反转函数,直到最后一个结点,让头结点指向最后一个结点。
- 其他结点:让后一个结点指向前一个结点
// 用来反转整个链表 public void reverse(){ // 判断当前链表是否为空链表,如果是空链表,则结束运行,如果不是,则调用重载的reverse方法完成反转 if (isEmpty()) return; reverse(head.next); } // 反转指定的结点 curr,并把反转后的结点返回 public Node reverse(Node curr){ if (curr.next == null){ head.next = curr; return curr; } // 递归的反转当前结点curr的下一个结点;返回值就是链表反转后,当前结点的上一个结点 Node pre = reverse(curr.next); // 让返回的结点的下一个结点变为当前结点curr; pre.next = curr; // 把当前结点的下一个结点变为null curr.next = null; return curr; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
个人感觉最好理解的还是使用栈以及头插法最容易理解,三指法是性能最佳的,递归是最难理解的。
4. 快慢指针问题
快慢指针指的是定义两个指针,这两个指针的移动速度一快一慢,以此来制造出自己想要的差值,这个差值可以让我们找到链表上相应的结点。一般情况下,快指针的移动步长为慢指针的两倍。
① 中间值问题
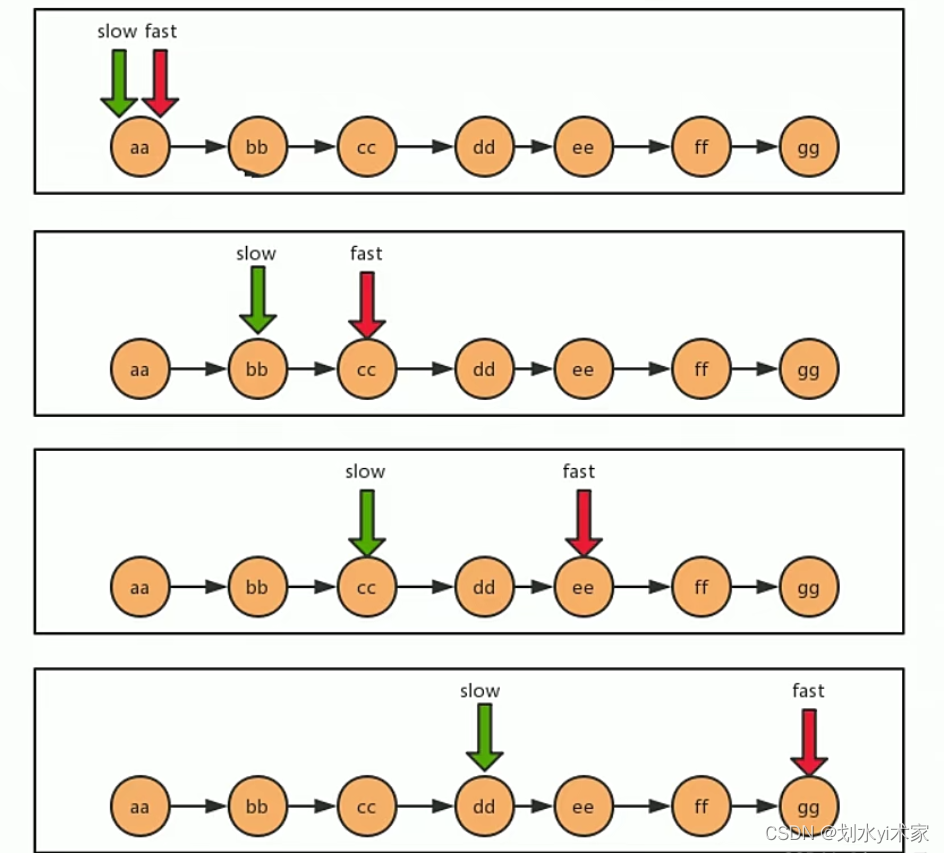
利用快慢指针,我们把一个链表看成一个跑道,假设a的速度是b的两倍,那么当a跑完全程后,b刚好跑一半,依次来达到找到中间结点的目的。
如下图:最开始,slow和fast指针都指向链表的第一个结点,然后slow每次移动一个指针,fast每次移动两个指针
public class FastSlowTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 创建结点 Node<String> first = new Node<String>("aa", null); Node<String> second = new Node<String>("bb", null); Node<String> third = new Node<String>("cc", null); Node<String> fourth = new Node<String>("dd", null); Node<String> fifth = new Node<String>("ee", null); Node<String> six = new Node<String>("ff", null); Node<String> seven = new Node<String>("gg", null); // 完成结点之间的指向 first.next = second; second.next = third; third.next = fourth; fourth.next = fifth; fifth.next = six; six.next = seven; // 查找中间值 String mid = getMid(first); System.out.println("中间值为:"+mid); } /** * @param first 链表的首结点 * @return 链表的中间结点的值 */ public static String getMid(Node<String> first) { // 定义快慢指针 Node<String> fast = first; Node<String> slow = first; //使用两个指针遍历链表,当快指针指向的结点没有下一个结点了,就可以结束了,结束之后,慢指针指向的结点就是中间值 while(fast != null && fast.next != null){ // 变化fast的值和slow的值 fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; } return slow.item; } // 结点类 private static class Node<T> { // 存储数据 T item; // 下一个结点 Node next; public Node(T item, Node next) { this.item = item; this.next = next; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
② 判断单向链表是否有环
使用快慢指针的思想,还是把链表比作一条跑道,链表中有环,那么这条跑道就是一条圆环跑道,在一条圆环跑道中,两个人有速度差,那么迟早两个人会相遇,只要相遇那么就说明有环。
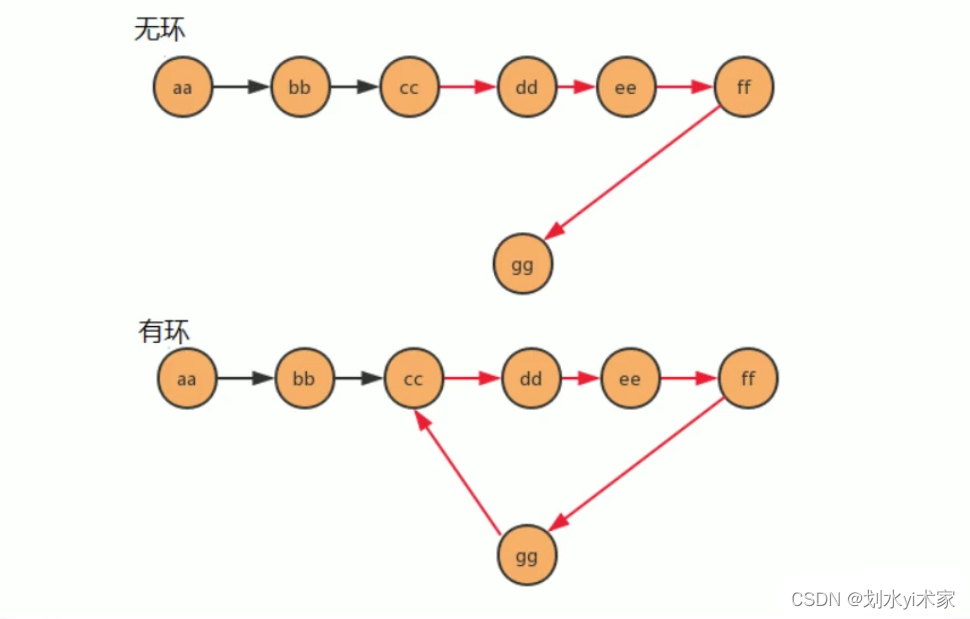
public class CircleListCheckTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 创建结点 Node<String> first = new Node<String>("aa", null); Node<String> second = new Node<String>("bb", null); Node<String> third = new Node<String>("cc", null); Node<String> fourth = new Node<String>("dd", null); Node<String> fifth = new Node<String>("ee", null); Node<String> six = new Node<String>("ff", null); Node<String> seven = new Node<String>("gg", null); // 完成结点之间的指向 first.next = second; second.next = third; third.next = fourth; fourth.next = fifth; fifth.next = six; six.next = seven; // 产生环 seven.next = third; // 判断链表是否有环 boolean circle = isCircle(first); System.out.println("first链表中是否有环:" + circle); } /** * 判断链表中是否有环 * @param first 链表首结点 * @return ture为有环,false为无环 */ public static boolean isCircle(Node<String> first) { // 定义快慢指针 Node<String> fast = first; Node<String> slow = first; // 遍历链表,如果快慢指针指向了同一个结点,那么证明有环 while(fast != null && fast.next != null){ // 变换fast和slow fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if (fast.equals(slow)){ return true; } } return false; } // 结点类 private static class Node<T> { // 存储数据 T item; // 下一个结点 Node next; public Node(T item, Node next) { this.item = item; this.next = next; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
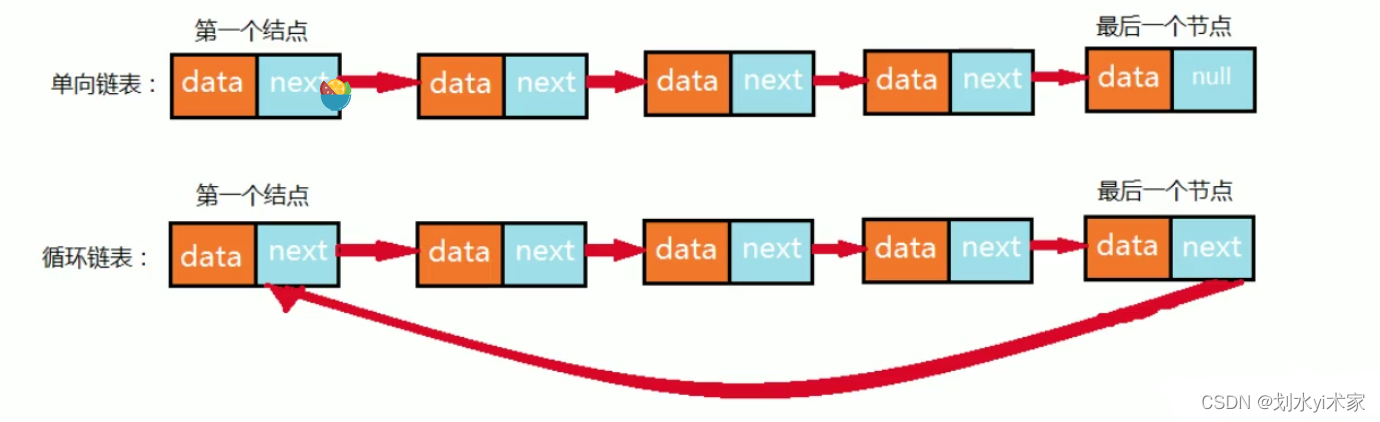
5. 循环链表问题
循环链表,顾名思义,链表整体要形成一个圆环状,在单向链表中,最后一个结点的指针为null,不指向任何结点,因为没有下一个元素了。要实现循环链表,我们只需要让单向链表的最后一个结点的指针指向头结点即可。
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { // 构建节点 Node<Integer> first = new Node<Integer>(1,null); Node<Integer> second = new Node<Integer>(2,null); Node<Integer> third = new Node<Integer>(3,null); Node<Integer> fourth = new Node<Integer>(4null); Node<Integer> fifth = new Node<Integer>(5null; Node<Integer> sixth = new Node<Integer>(6null); Node<Integer> seventh = new Node<Integer>(7null); // 构建单链表 first.next = second; second.next = third; third.next = fourth; fourth.next = fifth; fifth.next = sixth; sixth.next = seventh; // 构建循环链表,让最后一个结点指向第一个结点 seventh.next = firth; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
① 约瑟夫问题
已知 n 个人(以编号 1,2,3,…,n 分别表示)围坐在一张圆桌周围,从编号为 k 的人开始顺时针报数,数到 m 的那个人出列;他的下一个人又从 1 还是顺时针开始报数,数到 m 的那个人又出列;依次重复下去,要求找到最后出列的那个人?
public class JosephTest { /** * 解决约瑟夫问题 * @param peopleCount 人总数 * @param start 从谁开始 取值范围 [1, peopleCount] * @param m 报数报到几 * @return 最后出列的人的号数 取值范围 [1, peopleCount] */ public static int josephSolve(int peopleCount, int start, int m){ // 构建循环链表,包含 peopleCount 个结点,分别存储 1 ~ peopleCount 之间的值 // 用来记录头结点 Node head = null; // 使用尾插法建立循环链表 Node tail = null; for(int i = 1; i <= peopleCount; i++){ // 如果是第一个结点 if (i == 1){ head = new Node<>(i,null); tail = head; continue; } // 如果不是第一个结点 Node newNode = new Node<>(i, null); tail.next = newNode; tail = newNode; } // 建立循环 tail.next = head; // 记录每次遍历拿到的结点,从第 start 个人开始 Node<Integer> node = head; while (-- start > 0){ node = node.next; } // count计数器,模拟报数 int count=0; // 记录当前结点的上一个结点 // 遍历循环链表 Node<Integer> last = null; while(node != node.next){ // 模拟报数 count ++; if (count == m){ // 如果是 m ,则把当前结点删除调用,打印当前结点,重置 count=0,让当前结点node后移 last.next = node.next; System.out.print(node.item + ","); count = 0; node = node.next; }else{ //如果不是m,让last变为当前结点,让当前结点后移; last = node; node = node.next; } } return node.item; } public static void main(String[] args) { int k = josephSolve(5, 2,3); //打印最后一个元素 System.out.println("\n\n 最后出列的人为: " + k); } // 结点类 private static class Node<T> { // 存储数据 T item; // 下一个结点 Node next; public Node(T item, Node next) { this.item = item; this.next = next; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81