热门标签
热门文章
- 1机器学习---迁移学习
- 2护网2024-攻防对抗解决方案思路_2024护网
- 3《啊哈!算法》笔记——C语言、MATLAB 只有五行的算法——Floyd-Warshall_floyd-warshall算法代码matlab
- 4Elasticsearch-高级搜索(拼音|首字母|简繁|二级搜索)_java整合elasticsearch 7.17.5 实现中文+拼音+简繁搜索
- 5SWAN之ikev2协议multi-auth-rsa-eap-sim-id配置测试_leftauth=cert
- 6VS Code主题设置(美化VS Code)(主题+背景+图标+特效+字体)_vscode主题
- 7Datawhale AI夏令营- 讯飞机器翻译挑战赛baseline解析
- 8CentOS7安装部署git和gitlab_centos7下载安装gitlab
- 9大数据工程师简历怎么写,更受到HR青睐?_大数据技术简历
- 10换新电脑,怎么迁移旧电脑数据到新电脑_电脑迁移 csdn
当前位置: article > 正文
循环生成对抗网络CycleGAN
作者:在线问答5 | 2024-07-19 23:55:54
赞
踩
循环生成对抗网络
图像到图像的转换的目标是使用配准的图像对训练集来学习输入图像和输出图像之间的映射,而CycleGAN中使用的方法是缺少配对训练集的情况下进行图像转换。
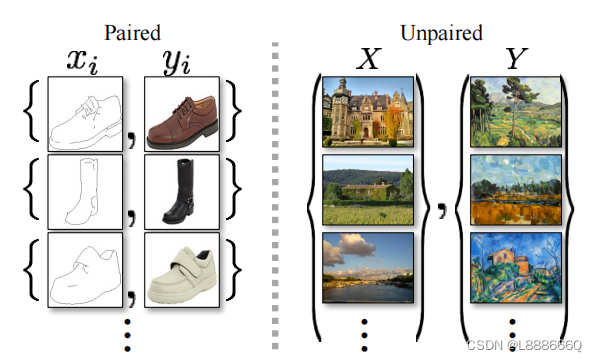
传统的图像转换如上图左,训练集是配对的x,y图像{xi,yi};如上图右,训练集是源域{xi},目标域{yi},但二者之间未给定配对关系。
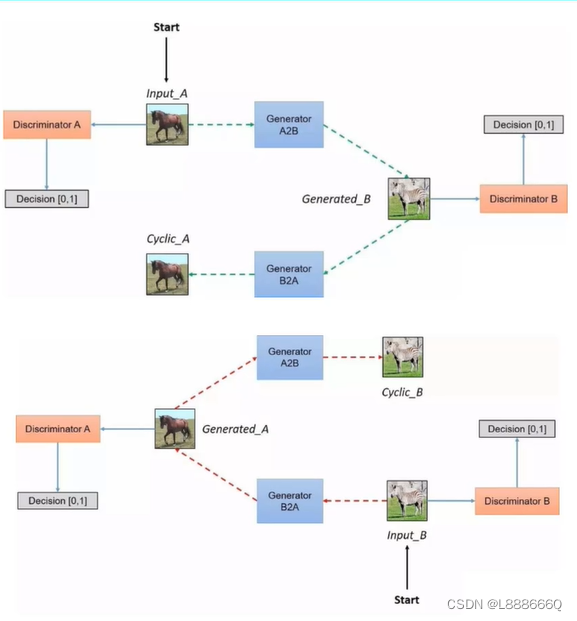
网络结构
涉及4个网络,生成器A2B,生成器B2A,判别器A判别器B
4种损失函数:G网络(用MSELoss计算)、D网络(用MSELoss计算)、Cycle(原始输入和Cycl输出,用L1Loss计算)、identify(对于生成器A2B用B作为输入,用L1Loss计算;对于生成器B2A用A作为输入,用L1Loss计算)
self.loss_names = ['D_A', 'G_A', 'cycle_A', 'idt_A', 'D_B', 'G_B', 'cycle_B', 'idt_B']
生成器网络结构:输入-->普通卷积-->图像越来越小,特征图越来越多-->反卷积-->图像越来越大,特征图越来越少-->输出(与输入相同大小)
判别器网络结构:输入-->普通卷积-->升维操作特征图越来越多-->假如得到MxNx512特征图,再经过卷积到得MxNx1的矩阵(后面需要针对每个像素点计算Loss)-->输出
Cycle_gan_model.py
- import torch
- import itertools
- from util.image_pool import ImagePool
- from .base_model import BaseModel
- from . import networks
-
-
- class CycleGANModel(BaseModel):
- """
- This class implements the CycleGAN model, for learning image-to-image translation without paired data.
- The model training requires '--dataset_mode unaligned' dataset.
- By default, it uses a '--netG resnet_9blocks' ResNet generator,
- a '--netD basic' discriminator (PatchGAN introduced by pix2pix),
- and a least-square GANs objective ('--gan_mode lsgan').
- CycleGAN paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1703.10593.pdf
- """
- @staticmethod
- def modify_commandline_options(parser, is_train=True):
- """Add new dataset-specific options, and rewrite default values for existing options.
- Parameters:
- parser -- original option parser
- is_train (bool) -- whether training phase or test phase. You can use this flag to add training-specific or test-specific options.
- Returns:
- the modified parser.
- For CycleGAN, in addition to GAN losses, we introduce lambda_A, lambda_B, and lambda_identity for the following losses.
- A (source domain), B (target domain).
- Generators: G_A: A -> B; G_B: B -> A.
- Discriminators: D_A: G_A(A) vs. B; D_B: G_B(B) vs. A.
- Forward cycle loss: lambda_A * ||G_B(G_A(A)) - A|| (Eqn. (2) in the paper)
- Backward cycle loss: lambda_B * ||G_A(G_B(B)) - B|| (Eqn. (2) in the paper)
- Identity loss (optional): lambda_identity * (||G_A(B) - B|| * lambda_B + ||G_B(A) - A|| * lambda_A) (Sec 5.2 "Photo generation from paintings" in the paper)
- Dropout is not used in the original CycleGAN paper.
- """
- parser.set_defaults(no_dropout=True) # default CycleGAN did not use dropout
- if is_train:
- parser.add_argument('--lambda_A', type=float, default=10.0, help='weight for cycle loss (A -> B -> A)')
- parser.add_argument('--lambda_B', type=float, default=10.0, help='weight for cycle loss (B -> A -> B)')
- parser.add_argument('--lambda_identity', type=float, default=0.5, help='use identity mapping. Setting lambda_identity other than 0 has an effect of scaling the weight of the identity mapping loss. For example, if the weight of the identity loss should be 10 times smaller than the weight of the reconstruction loss, please set lambda_identity = 0.1')
-
- return parser
-
- def __init__(self, opt):
- """Initialize the CycleGAN class.
- Parameters:
- opt (Option class)-- stores all the experiment flags; needs to be a subclass of BaseOptions
- """
- BaseModel.__init__(self, opt)
- # specify the training losses you want to print out. The training/test scripts will call <BaseModel.get_current_losses>
- self.loss_names = ['D_A', 'G_A', 'cycle_A', 'idt_A', 'D_B', 'G_B', 'cycle_B', 'idt_B']
- # specify the images you want to save/display. The training/test scripts will call <BaseModel.get_current_visuals>
- visual_names_A = ['real_A', 'fake_B', 'rec_A']
- visual_names_B = ['real_B', 'fake_A', 'rec_B']
- if self.isTrain and self.opt.lambda_identity > 0.0: # if identity loss is used, we also visualize idt_B=G_A(B) ad idt_A=G_A(B)
- visual_names_A.append('idt_B')
- visual_names_B.append('idt_A')
-
- self.visual_names = visual_names_A + visual_names_B # combine visualizations for A and B
- # specify the models you want to save to the disk. The training/test scripts will call <BaseModel.save_networks> and <BaseModel.load_networks>.
- if self.isTrain:
- self.model_names = ['G_A', 'G_B', 'D_A', 'D_B']
- else: # during test time, only load Gs
- self.model_names = ['G_A', 'G_B']
-
- # define networks (both Generators and discriminators)
- # The naming is different from those used in the paper.
- # Code (vs. paper): G_A (G), G_B (F), D_A (D_Y), D_B (D_X)
- self.netG_A = networks.define_G(opt.input_nc, opt.output_nc, opt.ngf, opt.netG, opt.norm,
- not opt.no_dropout, opt.init_type, opt.init_gain, self.gpu_ids)
- self.netG_B = networks.define_G(opt.output_nc, opt.input_nc, opt.ngf, opt.netG, opt.norm,
- not opt.no_dropout, opt.init_type, opt.init_gain, self.gpu_ids)
-
- if self.isTrain: # define discriminators
- self.netD_A = networks.define_D(opt.output_nc, opt.ndf, opt.netD,
- opt.n_layers_D, opt.norm, opt.init_type, opt.init_gain, self.gpu_ids)
- self.netD_B = networks.define_D(opt.input_nc, opt.ndf, opt.netD,
- opt.n_layers_D, opt.norm, opt.init_type, opt.init_gain, self.gpu_ids)
-
- if self.isTrain:
- if opt.lambda_identity > 0.0: # only works when input and output images have the same number of channels
- assert(opt.input_nc == opt.output_nc)
- self.fake_A_pool = ImagePool(opt.pool_size) # create image buffer to store previously generated images
- self.fake_B_pool = ImagePool(opt.pool_size) # create image buffer to store previously generated images
- # define loss functions
- self.criterionGAN = networks.GANLoss(opt.gan_mode).to(self.device) # define GAN loss.
- self.criterionCycle = torch.nn.L1Loss()
- self.criterionIdt = torch.nn.L1Loss()
- # initialize optimizers; schedulers will be automatically created by function <BaseModel.setup>.
- self.optimizer_G = torch.optim.Adam(itertools.chain(self.netG_A.parameters(), self.netG_B.parameters()), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.beta1, 0.999))
- self.optimizer_D = torch.optim.Adam(itertools.chain(self.netD_A.parameters(), self.netD_B.parameters()), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.beta1, 0.999))
- self.optimizers.append(self.optimizer_G)
- self.optimizers.append(self.optimizer_D)
-
- def set_input(self, input):
- """Unpack input data from the dataloader and perform necessary pre-processing steps.
- Parameters:
- input (dict): include the data itself and its metadata information.
- The option 'direction' can be used to swap domain A and domain B.
- """
- AtoB = self.opt.direction == 'AtoB'
- self.real_A = input['A' if AtoB else 'B'].to(self.device)
- self.real_B = input['B' if AtoB else 'A'].to(self.device)
- self.image_paths = input['A_paths' if AtoB else 'B_paths']
-
- def forward(self):
- """Run forward pass; called by both functions <optimize_parameters> and <test>."""
- self.fake_B = self.netG_A(self.real_A) # G_A(A)
- self.rec_A = self.netG_B(self.fake_B) # G_B(G_A(A))
- self.fake_A = self.netG_B(self.real_B) # G_B(B)
- self.rec_B = self.netG_A(self.fake_A) # G_A(G_B(B))
-
- def backward_D_basic(self, netD, real, fake):
- """Calculate GAN loss for the discriminator
- Parameters:
- netD (network) -- the discriminator D
- real (tensor array) -- real images
- fake (tensor array) -- images generated by a generator
- Return the discriminator loss.
- We also call loss_D.backward() to calculate the gradients.
- """
- # Real
- pred_real = netD(real)
- loss_D_real = self.criterionGAN(pred_real, True)
- # Fake
- pred_fake = netD(fake.detach())
- loss_D_fake = self.criterionGAN(pred_fake, False)
- # Combined loss and calculate gradients
- loss_D = (loss_D_real + loss_D_fake) * 0.5
- loss_D.backward()
- return loss_D
-
- def backward_D_A(self):
- """Calculate GAN loss for discriminator D_A"""
- fake_B = self.fake_B_pool.query(self.fake_B)
- self.loss_D_A = self.backward_D_basic(self.netD_A, self.real_B, fake_B)
-
- def backward_D_B(self):
- """Calculate GAN loss for discriminator D_B"""
- fake_A = self.fake_A_pool.query(self.fake_A)
- self.loss_D_B = self.backward_D_basic(self.netD_B, self.real_A, fake_A)
-
- def backward_G(self):
- """Calculate the loss for generators G_A and G_B"""
- lambda_idt = self.opt.lambda_identity
- lambda_A = self.opt.lambda_A
- lambda_B = self.opt.lambda_B
- # Identity loss
- if lambda_idt > 0:
- # G_A should be identity if real_B is fed: ||G_A(B) - B||
- self.idt_A = self.netG_A(self.real_B)
- self.loss_idt_A = self.criterionIdt(self.idt_A, self.real_B) * lambda_B * lambda_idt
- # G_B should be identity if real_A is fed: ||G_B(A) - A||
- self.idt_B = self.netG_B(self.real_A)
- self.loss_idt_B = self.criterionIdt(self.idt_B, self.real_A) * lambda_A * lambda_idt
- else:
- self.loss_idt_A = 0
- self.loss_idt_B = 0
-
- # GAN loss D_A(G_A(A))
- self.loss_G_A = self.criterionGAN(self.netD_A(self.fake_B), True)
- # GAN loss D_B(G_B(B))
- self.loss_G_B = self.criterionGAN(self.netD_B(self.fake_A), True)
- # Forward cycle loss || G_B(G_A(A)) - A||
- self.loss_cycle_A = self.criterionCycle(self.rec_A, self.real_A) * lambda_A
- # Backward cycle loss || G_A(G_B(B)) - B||
- self.loss_cycle_B = self.criterionCycle(self.rec_B, self.real_B) * lambda_B
- # combined loss and calculate gradients
- self.loss_G = self.loss_G_A + self.loss_G_B + self.loss_cycle_A + self.loss_cycle_B + self.loss_idt_A + self.loss_idt_B
- self.loss_G.backward()
-
- def optimize_parameters(self):
- """Calculate losses, gradients, and update network weights; called in every training iteration"""
- # forward
- self.forward() # compute fake images and reconstruction images.
- # G_A and G_B
- self.set_requires_grad([self.netD_A, self.netD_B], False) # Ds require no gradients when optimizing Gs
- self.optimizer_G.zero_grad() # set G_A and G_B's gradients to zero
- self.backward_G() # calculate gradients for G_A and G_B
- self.optimizer_G.step() # update G_A and G_B's weights
- # D_A and D_B
- self.set_requires_grad([self.netD_A, self.netD_B], True)
- self.optimizer_D.zero_grad() # set D_A and D_B's gradients to zero
- self.backward_D_A() # calculate gradients for D_A
- self.backward_D_B() # calculate graidents for D_B
- self.optimizer_D.step() # update D_A and D_B's weights

声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/在线问答5/article/detail/854161
推荐阅读
相关标签


