- 1xilinx fpga opencl加速RTL Kernel Examples_xilinx opencl
- 2大数据开发实战:Stream SQL实时开发二
- 3llama-factory SFT系列教程 (三),chatglm3-6B 大模型命名实体识别实战_chatglm3 命名实体识别
- 4Python、Pytorch、Pycharm安装教程及注意事项_pytorch和python版本
- 5NX/UG二次开发-矩阵-UFUN函数UF_mtx***_ug计算矩阵
- 6Android手机平板两不误,使用Fragment实现兼容手机和平板的程序
- 7机器学习实战:决策树与随机森林预测心脏病分类问题_机器学习heart disease
- 8Selenium之浏览器无头模式、多线程调用浏览器运行实战。_options = webdriver.firefoxoptions()
- 9nginx伪静态try_files命令解读_nginxw tryfiles
- 10uniapp自定义导航栏_uniapp :isback
ThingsBoard架构及技术栈
赞
踩
前言
通过了解架构及技术栈,初步认识ThingsBoard
架构
通过官方文档可知ThingsBoard有两种架构模式
- monolithic architecture
单体架构,将所有的内容聚合在单个应用中
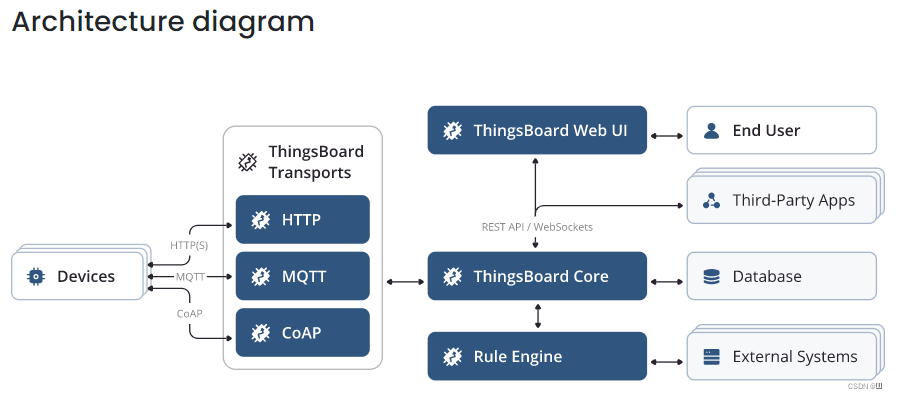
- Microservices architecture
微服务架构,包括Core(核心)、Transport(传输)、Rule Engine(规则引擎)、JavaScript Executor(JavaScript执行器)、Web UI(界面)等多个服务,服务之间使用消息队列通信
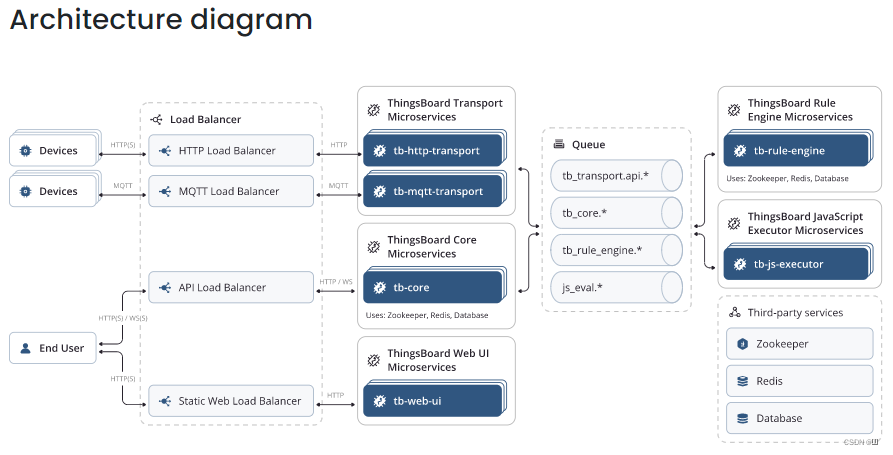
技术栈
框架相关
Spring
作为平台的整体框架Spring Boot
Spring的引导,提高了开发效率Maven
提供了包的依赖关系管理
通信相关
-
protobuf(Protocol Buffers)
Google推出的一种数据描述语言,用于定义与语言无关的数据结构
可根据具体的语言动态生成对应的数据结构,后缀为 .protosyntax = "proto3"; package msgqueue; option java_package = "org.thingsboard.server.common.msg.gen"; option java_outer_classname = "MsgProtos"; // Stores message metadata as map of strings message TbMsgMetaDataProto { map<string, string> data = 1; } // Stores stack of nested (caller) rule chains message TbMsgProcessingStackItemProto { int64 ruleChainIdMSB = 1; int64 ruleChainIdLSB = 2; int64 ruleNodeIdMSB = 3; int64 ruleNodeIdLSB = 4; } message TbMsgProcessingCtxProto { int32 ruleNodeExecCounter = 1; repeated TbMsgProcessingStackItemProto stack = 2; } message TbMsgProto { string id = 1; string type = 2; string entityType = 3; int64 entityIdMSB = 4; int64 entityIdLSB = 5; int64 ruleChainIdMSB = 6; int64 ruleChainIdLSB = 7; int64 ruleNodeIdMSB = 8; int64 ruleNodeIdLSB = 9; int64 clusterPartition = 10; TbMsgMetaDataProto metaData = 11; // Transaction Data (12) was removed in 2.5 int32 dataType = 13; string data = 14; int64 ts = 15; // Will be removed in 3.4. Moved to processing context int32 ruleNodeExecCounter = 16; int64 customerIdMSB = 17; int64 customerIdLSB = 18; TbMsgProcessingCtxProto ctx = 19; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
如上使用
proto3协议定义了org.thingsboard.server.common.msg.gen.MsgProtos类
用于传输数据的结构定义 -
HTTP(Hyper Text Transfer Protocol)
超文本传输协议,最常见的数据传输协议
用于设备和ThingsBoard间的数据交互,以及用户与ThingsBoard间的操作交互等 -
MQTT(Message Queuing Telemetry Transport)
基于发布/订阅模式的协议,支持三种质量等级,广泛应用于物联网
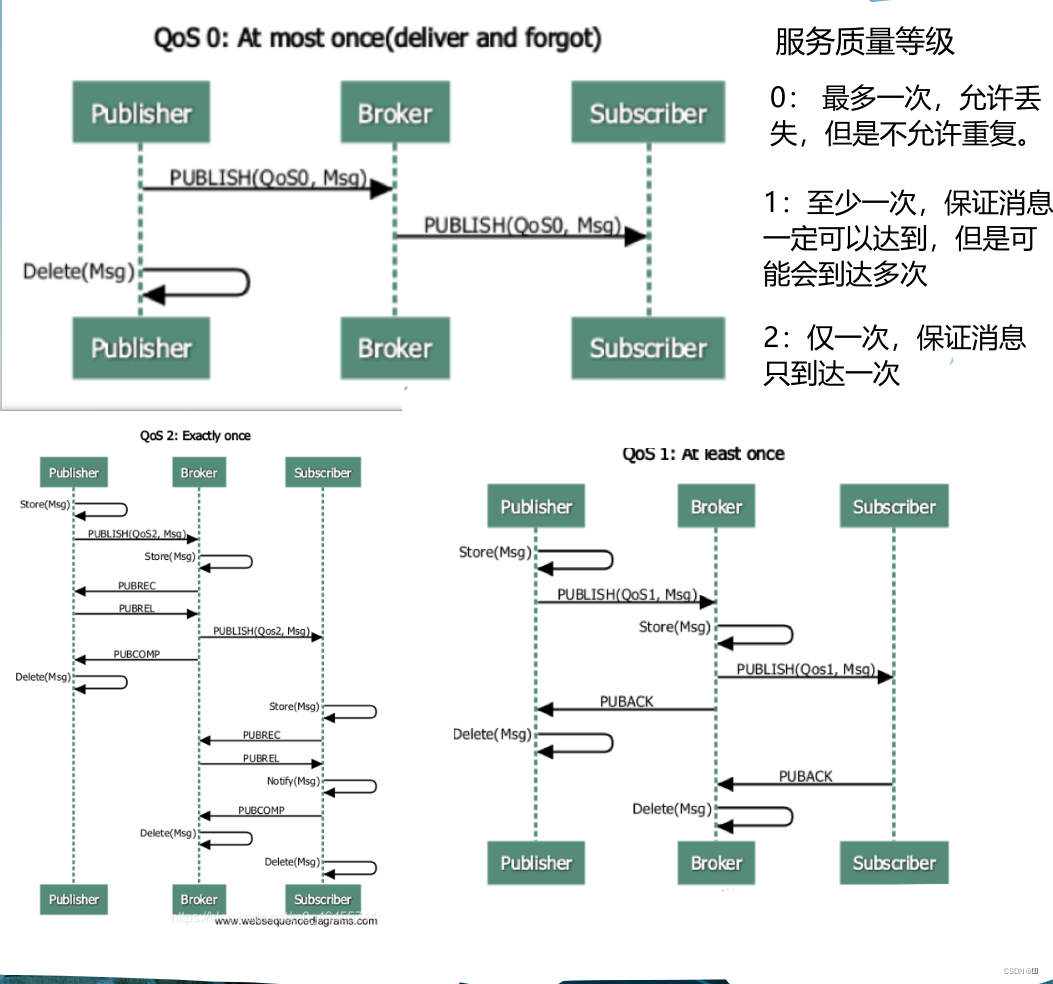
用于设备和
ThingsBoard间的数据交互 -
CoAP(Constrained Application Protocol)
基于UDP的REST风格协议,相较于HTTP更加轻量级
虽然是UDP,但通过消息类型支持消息的可靠传输
4种消息类型如下:- CON
需要被确认的请求,接收方必须响应,用以消息的可靠传输 - NON
无需被确认的请求,接收方不必响应 - ACK
确认消息,表示接收方收到了CON消息 - RST
复位消息,表示接收方收到的CON消息异常
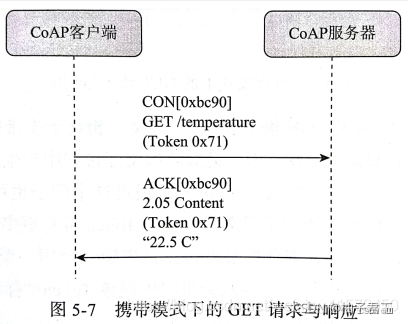
用于设备和
ThingsBoard间的数据交互 - CON
-
LwM2M(Lightweight Machine to Machine)
是CoAP的上层协议,基于对象/资源模型进行交互,对象是资源的集合,需要实例化后使用
主要组成部分:- LwM2M Server
服务端,接收客户端的注册,与客户端进行数据交互 - LwM2M Client
客户端,注册至服务端后,才可通信,向服务端上报数据,响应服务端请求 - LwM2M Bootstrap Server
引导服务端,用于向客户端提供通信相关配置(服务端地址), 根据引导方式可省略 - SmartCard
智能卡,作用同LwM2M Bootstrap Server
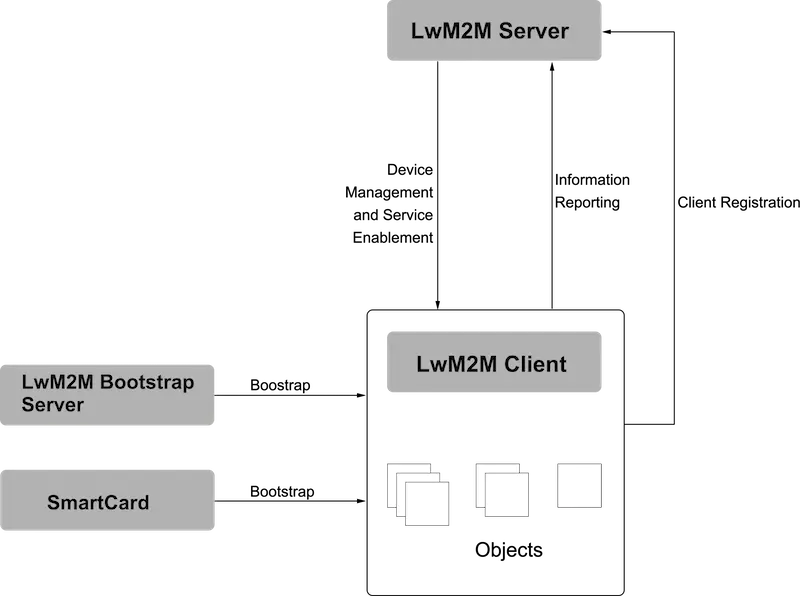
用于设备和
ThingsBoard间的数据交互 - LwM2M Server
-
SNMP(Simple Network Management Protocol)
基于UDP的网络管理协议,采用特殊的客户机/服务器模式进行通信
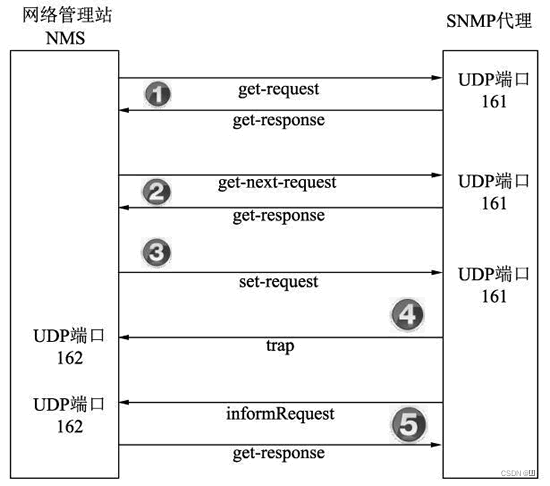
用于设备和
ThingsBoard间的数据交互 -
Netty
一个基于JAVA NIO的高性能的、异步事件驱动的通信框架,可由开发者自定义传输协议
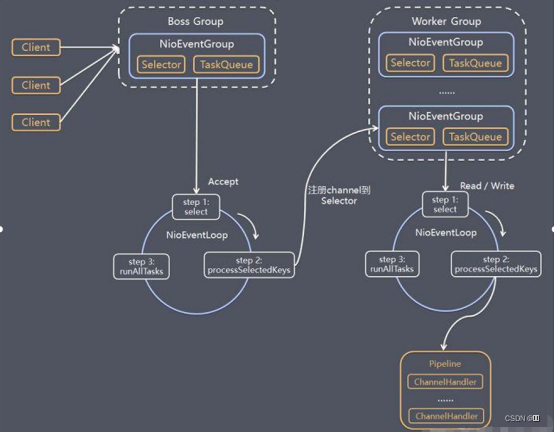
主要用于实现
ThingsBoard中MQTT服务端与客户端 -
gRPC(google Remote Procedure Call)
google推出的基于HTTP/2远程调用框架
HTTP/2相较于HTTP/1.x主要有如下优势:- 二进制格式传输
相较于文本格式,体积更小,性能更高 - 多路复用
通过将数据包分为HEADERS帧和DATA帧,实现一个连接并发多个请求 - 服务端推送
在客户端请求前主动发送数据,对于一个客户端请求可响应多次
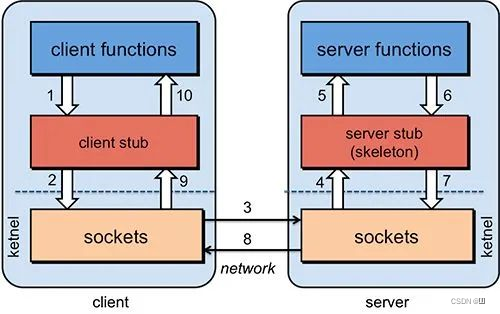
主要用于设备和
ThingsBoard间的数据交互 - 二进制格式传输
-
Azure Service Bus
微软在Azure上提供的一种云消息服务,和RabbitMQ、KafKa一样作为消息通信服务 -
Pubsub(Google Cloud Pub/Sub)
一种具有传递和接受消息的事件驱动以及流分析系统,跟KafKa比较相似 -
SQS(Amazon Simple Queue Service)
一个分布式的消息队列服务
提供了两种队列:- 标准
近乎无限的吞吐量,至少传递一次消息,尽量保证顺序传递 - FIFO(先进先出)
高吞吐量,仅传递一次消息,严格保证消息的顺序
- 标准
-
Kafka
一种高吞吐量、持久性、分布式的发布订阅的消息队列系统 -
RabbitMQ
一个由erlang开发的AMQP(Advanced Message Queue高级消息队列协议)的开源实现,性能较好 -
Memory
ThingsBoard实现的基于内存的消息队列
数据存储相关
-
PostgreSQL
免费的开源关系型数据库
相较于MySQL:- SQL的标准实现上更完善,功能实现更严谨
- 优化器功能更完整,支持更多类型的索引,复杂查询能力更强
- 数据使用堆表存放,存储量较大
- 主备为物理复制,数据一致性更可靠,性能更高
- 分区个数达至千万时,处理能力较差
MVCC(Multi-Version Concurrency Control)基于新旧数据一同管理模式,需要定期VACUUM清理旧数据,存在额外的消耗
用于存储非遥测数据,根据存储模式也可存储遥测数据
-
Cassandra
由Facebook开发的、用于大数据的、开源分布式的NoSQL存储系统
具有以如下特性:- 高可扩展性
通过增加集群中的节点数量即可增加吞吐量 - 灵活的数据结构
可存储结构化、半结构化及非结构化等多种数据类型 - 便捷的数据分发
分布式架构支持多个数据中心间的数据复制及分发 - 高可靠性
不依赖外部组件(如ZooKeeper)的对等分布式架构,数据分布在集群中的所有节点间,无中心节点,无单点故障
提供了类似SQL的COL语句
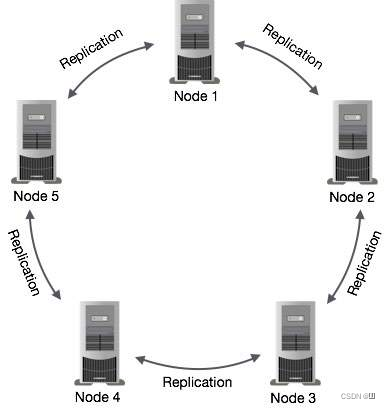
用于存储遥测数据
- 高可扩展性
其他
Actor
一种分布式并发编程模式,旨在将资源私有化在Actor模型中,Actor模型间通过消息队列通信,异步串行地处理消息,以避免多线程对于共享资源的竞争
Actor模型由三部分组成:- state(状态)
内部私有地属性,可以理解为资源 - behavior(行为)
处理state逻辑,可以理解为方法 - MailBox(邮箱)
即接收消息的队列,用于存储接收到的消息并在空闲时处理
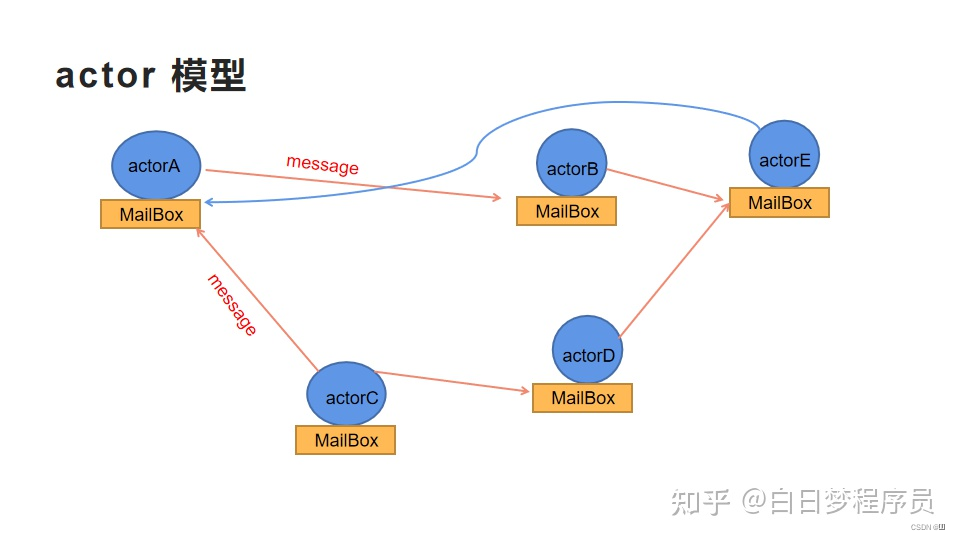
- state(状态)
caffeine
一款高性能的本地缓存组件,官方文档
主要提供了4种缓存添加策略:- 手动加载
Cache<Key, Graph> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder() .expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES) .maximumSize(10_000) .build(); // 查找一个缓存元素, 没有查找到的时候返回null Graph graph = cache.getIfPresent(key); // 查找缓存,如果缓存不存在则生成缓存元素, 如果无法生成则返回null graph = cache.get(key, k -> createExpensiveGraph(key)); // 添加或者更新一个缓存元素 cache.put(key, graph); // 移除一个缓存元素 cache.invalidate(key);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 自动加载
LoadingCache<Key, Graph> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder() .maximumSize(10_000) .expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES) .build(key -> createExpensiveGraph(key)); // 查找缓存,如果缓存不存在则生成缓存元素, 如果无法生成则返回null Graph graph = cache.get(key); // 批量查找缓存,如果缓存不存在则生成缓存元素 Map<Key, Graph> graphs = cache.getAll(keys);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 手动异步加载
AsyncCache<Key, Graph> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder() .expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES) .maximumSize(10_000) .buildAsync(); // 查找一个缓存元素, 没有查找到的时候返回null CompletableFuture<Graph> graph = cache.getIfPresent(key); // 查找缓存元素,如果不存在,则异步生成 graph = cache.get(key, k -> createExpensiveGraph(key)); // 添加或者更新一个缓存元素 cache.put(key, graph); // 移除一个缓存元素 cache.synchronous().invalidate(key);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 自动异步加载
AsyncLoadingCache<Key, Graph> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder() .maximumSize(10_000) .expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES) // 你可以选择: 去异步的封装一段同步操作来生成缓存元素 .buildAsync(key -> createExpensiveGraph(key)); // 你也可以选择: 构建一个异步缓存元素操作并返回一个future .buildAsync((key, executor) -> createExpensiveGraphAsync(key, executor)); // 查找缓存元素,如果其不存在,将会异步进行生成 CompletableFuture<Graph> graph = cache.get(key); // 批量查找缓存元素,如果其不存在,将会异步进行生成 CompletableFuture<Map<Key, Graph>> graphs = cache.getAll(keys);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 手动加载
Redis(Remote Dictionary Server)
Key-Value存储系统,由于对数据的操作均在内存中执行,性能高效Node.js
一个跨平台的JavaScript运行环境,实现了JavaScript在服务端的应用AntiSamy
是OWASP的一个开源项目,分为Java和.Net版
通过对用户输入的内容进行检查,根据策略过滤非法字符,确保输入的安全性
被广泛应用于Web服务对存储型和反射型XSS的防御中Guava
Google对JavaAPI补充的开源库,为了方便编码,并减少编码错误
用于提供集合,缓存,支持原语句,并发性,常见注解,字符串处理,I/O和验证的实用方法ZooKeeper
分布式协调服务,常用于集群管理、分布式锁等


