热门标签
热门文章
- 1python--WebUI自动化_python webui自动化
- 2hive hbase 映射表_presto 查询hive映射hbase
- 3【OpenCV】第十七章: 图像分割与提取_bgdmodel = np.zeros
- 4zoj 3846 GCD Reduce(数论)
- 5计算机网络(全)
- 6python性能分析之log_python複製log和讀取log耗費的電腦資源相同嗎
- 7【Unity】框架设计(三) Odin编辑器窗口扩展,Asset资源的创建和管理(脚本文件创建、预制体、System.IO、AssetDatabase、Selection)_unity odin menueditorwindow
- 8卑微且强大的Gumbel分布
- 9时序预测 | MATLAB实现NARX非线性自回归外生模型房价预测_narx 预测
- 10Windows下深度学习标注工具LabelImg安装和使用指南_win10下安装labelimg
当前位置: article > 正文
C语言手撕顺序表
作者:小丑西瓜9 | 2024-02-16 22:13:23
赞
踩
C语言手撕顺序表
目录
一、概念
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
顺序表一般分为
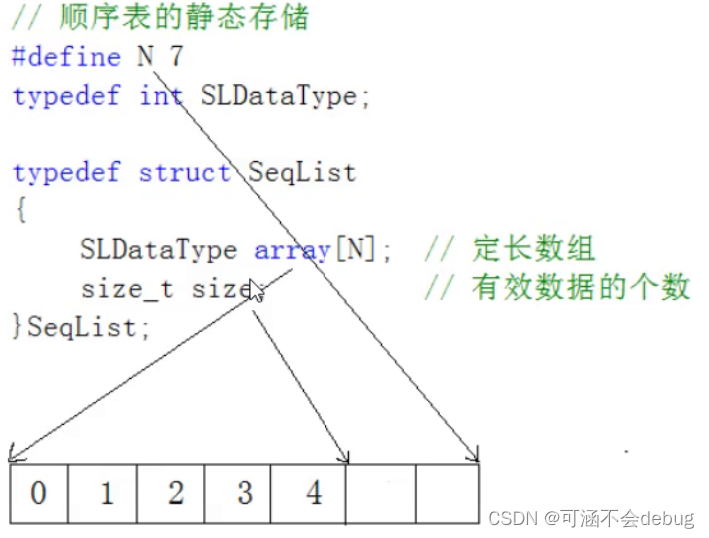
1、静态顺序表:使用定长数组存储元素。
2、动态顺序表:使用动态开辟的数组存储
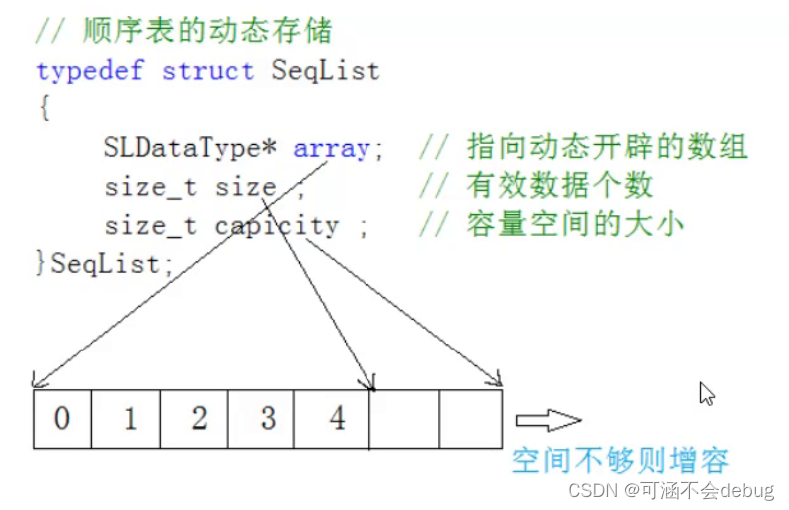
我们一般使用动态顺序表,因为静态顺序表的数组大小固定的,而动态可以根据我们需求的不同去在线扩容,所以接下来的文章围绕如何实现动态顺序表来讲解。
二、接口实现
对数据结构我们一般采用增删查改去实现。
- #pragma once
-
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <assert.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include<string.h>
-
- typedef int SLDateType;
- typedef struct SeqList
- {
- SLDateType* a;
- int size;//存储有效数据的大小
- int capacity;//空间大小
- }SeqList;
-
- // 对数据的管理:增删查改
- void SeqListInit(SeqList* ps);
- void SeqListDestroy(SeqList* ps);
-
- void SeqListPrint(SeqList* ps);
- void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* ps, SLDateType x);//尾插
- void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* ps, SLDateType x);//头插
- void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* ps);//头删
- void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* ps);//尾删
- void SeqListCheckCapacity(SeqList* ps);//检查是否需要扩容
- // 顺序表查找
- int SeqListFind(SeqList* ps, SLDateType x);
- // 顺序表在pos位置插入x
- void SeqListInsert(SeqList* ps, int pos, SLDateType x);
- // 顺序表删除pos位置的值
- void SeqListErase(SeqList* ps, int pos);
- //修改特定位置的值
- void SeqListModify(SeqList* ps, int pos,int value);

1、对顺序表的初始化
- void SeqListInit(SeqList* ps)
- {
- ps->a = (SLDateType*)malloc(sizeof(SLDateType) * 4);
- if (ps->a == NULL)//需要检查动态开辟内存是否开辟成功
- {
- perror(malloc);
- exit(-1);//直接程序退出,因为空间都开辟失败,后面没法写
- }
- ps->size = 0;
- ps->capacity = 4;
- }
2、对数据的销毁
因为我们是动态开辟的内存,最后肯定是需要free释放。
- void SeqListDestroy(SeqList* ps)
- {
- free(ps->a);
- ps->a = NULL;
- ps->size = 0;
- ps->capacity = 0;
- }
3、对数据的打印
因为我们时刻要检查每一部分代码的正确性,需要数据检验,所以需要专门一个打印函数
- void SeqListPrint(SeqList* ps)
- {
- for (int i=0;i<ps->size;i++)
- {
- printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);
- }
- }
4、检查是否需要扩容
因为动态内存,每当我们插入新的数据时,总需要将存储有效数据的大小增加,当我们开辟的空间不够时,就需要扩容,利用realloc函数的性质。
- void SeqListCheckCapacity(SeqList* ps)
- {
- if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
- {
- SLDateType* tmp = (SLDateType*)realloc(ps->a, ps->capacity * 2 * sizeof(SLDateType));
- //注意动态内存开辟的单位都是字节
- if (tmp == NULL)
- {
- perror(realloc);
- exit(-1);
- }
- ps->a = tmp;
- ps->capacity *= 2;
- }
- }
5、尾插
- void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* ps, SLDateType x)
- {
- //先考虑空间大小够不够,需不需要扩容
- SeqListCheckCapacity(ps);
- ps->a[ps->size] = x;
- ps->size++;
- }
6、头插
头插还需要用memmove函数去挪动数据
- void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* ps, SLDateType x)
- {
- //也需要考虑扩容的问题
- SeqListCheckCapacity(ps);
- memmove(ps->a + 1, ps->a, ps->size*sizeof(SLDateType));
- ps->size++;
- ps->a[0] = x;
- }
7、尾删
我们需要检查size是否已经小于0,防止数组的越界,一般用assert去暴力的检查
- void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* ps)
- {
- assert(ps->size > 0);//暴力的检查
- /*if (ps->size == 0)
- return;*/
- //温柔的检查
- ps->size--;
- }
8、头删
- void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* ps)
- {
- assert(ps->size > 0);
- memmove(ps->a, ps->a + 1, ps->size* sizeof(SLDateType));
- ps->size--;
- }
9、在pos位置插入x
- void SeqListInsert(SeqList* ps, int pos, SLDateType x)
- {
- SeqListCheckCapacity(ps);
- assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
- memmove(ps->a+pos + 1, ps->a+pos, sizeof(SLDateType)*(ps->size-pos));
- ps->a[pos] = x;
- ps->size++;
- }
10、在pos位置处删除x
- void SeqListErase(SeqList* ps, int pos)
- {
- assert(ps->size > 0);
- memmove(ps->a + pos, ps->a + pos + 1,sizeof(SLDateType)*(ps->size-pos-1));
- ps->size--;
- }
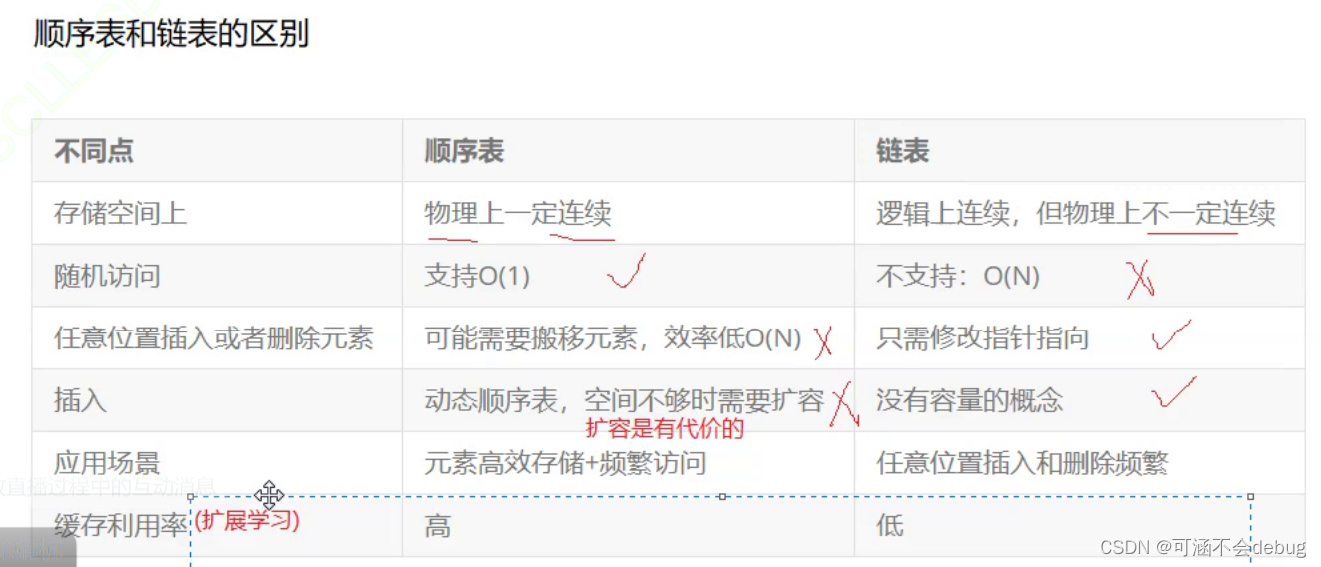
三、顺序表和单链表区别
心得:
顺序表开启了数据结构的的序章,顺序表算是很简单的数据结构了,从此我们需要敲一部分代码,编译一次,不能一股脑的输出,结果编译发现好多个bug,需要写一部分,编译一部分,这样才更加的有持续性。
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/小丑西瓜9/article/detail/97182
推荐阅读
相关标签