- 1正则化逻辑回归(2)
- 2Scratch 之 3D 介绍及教程_scratch3d游戏教程
- 3【Unity】【ARPG开发日志】【36】制作二段攻击动画_unity 2段攻击动画
- 4Unity XR Interaction Toolkit 组件解析(一)Action-based 和 Device-based 的区别_actionbasedcontroller
- 5Springboot集成Redis
- 6el-autocomplete匹配搜索使用_el-autocomplete 搜索
- 7ps查看mysql进程数_ps查看进程
- 8深度学习基础知识②_深度学习的[-1,1,conv]
- 9vue+element ui 后台管理系统(递归生成可伸缩侧边栏)_sidebarlist
- 10BSV 上的安全多方计算_安全多方计算允许多方在其输入上共同计算一个函数,同时保持每个输入的私有性
[python]解析通达信盘后数据获取历史日线数据_lc1文件
赞
踩
转自:http://bbs.pinggu.org/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=4804415&page=1
平时我们在做 离线的模型 回溯测试时候,需要历史的k线数据。
可是通达信 的日线数据如下:
日线数据在
通达信的安装目录: vipdoc\sh\lday 下面
本地的通达信 是没有开放api和外部的 自己的交易回溯测试 工具或框架 进行交互的。
虽然 我们也可以 通过 sina 的api ,或者 yahoo,或者 juhe聚合数据,或者 wind 或者 tushare (http://tushare.org/index.html),或者 通联金融大数据 等 网络的api接口 获取 股票的 历史K线数据, 但是网络的开销总是会比较耗时一些。
其实可以通过 python来 解析 通达信 的这些 day 文件的数据,变成 我们熟悉的csv格式的数据。
- #!/usr/bin/python
- def exactStock(fileName, code):
- ofile = open(fileName,'rb')
- buf=ofile.read()
- ofile.close()
- num=len(buf)
- no=num/32
- b=0
- e=32
- items = list()
- for i in range(int(no)):
- a=unpack('IIIIIfII',buf[b:e])
- year = int(a[0]/10000);
- m = int((a[0]%10000)/100);
- month = str(m);
- if m <10 :
- month = "0" + month;
- d = (a[0]%10000)%100;
- day=str(d);
- if d< 10 :
- day = "0" + str(d);
- dd = str(year)+"-"+month+"-"+day
- openPrice = a[1]/100.0
- high = a[2]/100.0
- low = a[3]/100.0
- close = a[4]/100.0
- amount = a[5]
- vol = a[6]
- unused = a[7]
- if i == 0 :
- preClose = close
- ratio = round((close - preClose)/preClose*100, 2)
- preClose = close
- item=[code, dd, str(openPrice), str(high), str(low), str(close), str(ratio), str(amount), str(vol)]
- items.append(item)
- b=b+32
- e=e+32
-
- return items
-
- exactStock('E:\\new_tdx\\vipdoc\\sh\\lday\\sh000001.day',"000001")

然后调用 这个方法,就可以把day文件变成csv文件,方便pandas来处理。
(在调用这个py文件前, 先在通达信的 软件 菜单里面 ,把通达信的 历史日K线数据都下载到本地,一次即可下载整个市场所有股票品种的数据。。)
批量处理的,请参考下面脚本
- # coding: UTF-8
- from struct import *
-
- import os
- import sys
-
-
-
- def day2csv_data(dirname,fname,targetDir):
- ofile=open(dirname+os.sep+fname,'rb')
- buf=ofile.read()
- ofile.close()
-
- ifile=open(targetDir+os.sep+fname+'.csv','w')
- num=len(buf)
- no=num/32
- b=0
- e=32
- line=''
- linename=str('date')+','+str('open')+', '+str('high')+' ,'+str('low')+', '+str('close')+' ,'+str('amout')+', '+str('vol')+' ,'+str('str07')+''+'\n'
- # print line
- ifile.write(linename)
- # for i in xrange(no):
- for i in range(int(no)):
- a=unpack('IIIIIfII',buf[b:e])
- line=str(a[0])+','+str(a[1]/100.0)+', '+str(a[2]/100.0)+' ,'+str(a[3]/100.0)+', '+str(a[4]/100.0)+' ,'+str(a[5])+', '+str(a[6])+' ,'+str(a[7])+''+'\n'
- # print line
- ifile.write(line)
- b=b+32
- e=e+32
- ifile.close()
-
-
-
- # pathdir='/vipdoc/sh/lday'
- pathdir='X:\\股票\\解析通达信day日线数据\\day'
- # targetDir='/_python_gp_tdx/data_gupiao/sh/lday'
- targetDir='X:\\股票\\解析通达信day日线数据\\day'
-
- listfile=os.listdir(pathdir)
-
-
- for f in listfile:
-
- day2csv_data(pathdir,f,targetDir)
- else:
- print ('The for '+pathdir+' to '+targetDir+' loop is over')
-
-
-
-

调用示例:
pathdir='/vipdoc/sh/lday'
targetDir='/python_data_gupiao/sh/lday'
listfile=os.listdir(pathdir)
for f in listfile:
day2csv_data(pathdir,f,targetDir)
最终的效果如下:
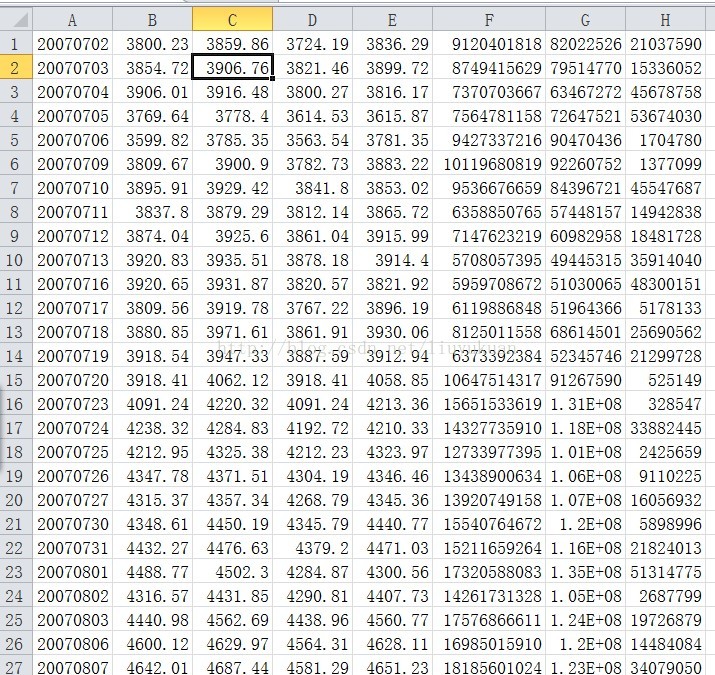
打开这些文件如下:
是不是很熟悉的csv或者excel的格式。。。
这个格式的数据,
大家就 可以用 python的数据分析的库 pandas 的 pd.read_csv 方法来读取了。
这样速度回比较快,而且python调用 通达信的历史数据 ,就很方便了。
【扩展】:如何用python读取通达信的lc1文件
2020年10月26日,修正了日期的解析功能。
- # 通达信5分钟线*.lc5文件和*.lc1文件
- # 文件名即股票代码
- # 每32个字节为一个5分钟数据,每字段内低字节在前
- # 00 ~ 01 字节:日期,整型,设其值为num,则日期计算方法为:
- # year=floor(num/2048)+2004;
- # month=floor(mod(num,2048)/100);
- # day=mod(mod(num,2048),100);
- # 02 ~ 03 字节: 从0点开始至目前的分钟数,整型
- # 04 ~ 07 字节:开盘价,float型
- # 08 ~ 11 字节:最高价,float型
- # 12 ~ 15 字节:最低价,float型
- # 16 ~ 19 字节:收盘价,float型
- # 20 ~ 23 字节:成交额,float型
- # 24 ~ 27 字节:成交量(股),整型
- # 28 ~ 31 字节:(保留)
-
- from struct import *
- import numpy as np
- import pandas as pd
-
- ofile=open('sz000005.lc5','rb')
-
- buf=ofile.read()
- ofile.close()
-
- num=len(buf)
- no=num//32
- # 原来是这样的,在python2中, '整数 / 整数 = 整数',以上面的 100 / 2 就会等于 50, 并且是整数。
- # 而在python3中, ‘整数/整数 = 浮点数’, 也就是100 / 2 = 50.0, 不过,使用 '//'就可以达到原python2中'/'的效果。
-
- b=0
- e=32
- dl = []
- for i in range(no):
- a=unpack('hhfffffii',buf[b:e])
- dl.append([str(int(a[0]/2048)+2004)+'-'+str(int(a[0]%2048/100)).zfill(2)+'-'+str(a[0]%2048%100).zfill(2),str(int(a[1]/60)).zfill(2)+':'+str(a[1]%60).zfill(2)+':00',a[2],a[3],a[4],a[5],a[6],a[7]])
- b=b+32
- e=e+32
- df = pd.DataFrame(dl, columns=['date','time','open','high','low','close','amount','volume'])
- print(df)