热门标签
热门文章
- 1‘error:03000086:digital envelope routines::initialization“处理方法
- 2程序员辞职常用借口_java离职原因怎么写最合适
- 3Ultra96之DPU-1_zcu102-dpu-trd-2019-1-190809.zip
- 4【DataWhale】灵境Agent开发——低代码创建AI智能体_分支链中强制意图的意思
- 5Mogdb 5.0新特性:SQL PATCH绑定执行计划
- 6极客公园对话 Zilliz 星爵:大模型时代,需要新的「存储基建」
- 7用栈实现队列(力扣第232题)
- 8mysql limit实现数据查询分页显示_navicat 查询分页
- 9boss:整个卡尔曼滤波器的简单案例——估计机器人位置
- 10JAVAWEB--封装通用的crud操作(jdbc)
当前位置: article > 正文
ROS探索总结(十四)——move_base(路径规划)_fast-lio进行move_base导航
作者:小小林熬夜学编程 | 2024-04-14 20:42:14
赞
踩
fast-lio进行move_base导航
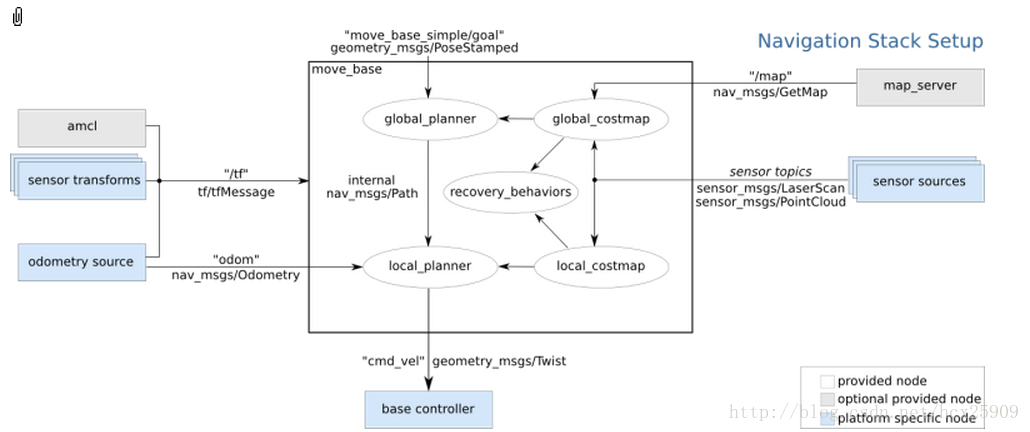
在上一篇的博客中,我们一起学习了ROS定位于导航的总体框架,这一篇我们主要研究其中最重要的move_base包。
在总体框架图中可以看到,move_base提供了ROS导航的配置、运行、交互接口,它主要包括两个部分:
(1) 全局路径规划(global planner):根据给定的目标位置进行总体路径的规划;
(2) 本地实时规划(local planner):根据附近的障碍物进行躲避路线规划。
一、数据结构
ROS中定义了MoveBaseActionGoal数据结构来存储导航的目标位置数据,其中最重要的就是位置坐标(position)和方向(orientation)。
rosmsg show MoveBaseActionGoal
[move_base_msgs/MoveBaseActionGoal]:
std_msgs/Header header
uint32 seq
time stamp
string frame_id
actionlib_msgs/GoalID goal_id
time stamp
string id
move_base_msgs/MoveBaseGoal goal
geometry_msgs/PoseStamped target_pose
std_msgs/Header header
uint32 seq
time stamp
string frame_id
geometry_msgs/Pose pose
geometry_msgs/Point position
float64 x
float64 y
float64 z
geometry_msgs/Quaternion orientation
float64 x
float64 y
float64 z
float64 w
move_base使用前需要配置一些参数:运行成本、机器人半径、到达目标位置的距离,机器人移动的速度,这些参数都在rbx1_nav包的以下几个配置文件中:
• base_local_planner_params.yaml
• costmap_common_params.yaml
• global_costmap_params.yaml
• local_costmap_params.yaml
• base_local_planner_params.yaml
• costmap_common_params.yaml
• global_costmap_params.yaml
• local_costmap_params.yaml
三、全局路径规划(global planner)
在ROS的导航中,首先会通过全局路径规划,计算出机器人到目标位置的全局路线。这一功能是navfn这个包实现的。
navfn通过Dijkstra最优路径的算法,计算costmap上的最小花费路径,作为机器人的全局路线。将来在算法上应该还会加入A*算法。
具体见:http://www.ros.org/wiki/navfn?distro=fuerte
navfn通过Dijkstra最优路径的算法,计算costmap上的最小花费路径,作为机器人的全局路线。将来在算法上应该还会加入A*算法。
具体见:http://www.ros.org/wiki/navfn?distro=fuerte
四、本地实时规划(local planner)
本地的实时规划是利用base_local_planner包实现的。该包使用Trajectory Rollout 和Dynamic Window approaches算法计算机器人每个周期内应该行驶的速度和角度(dx,dy,dtheta velocities)。

base_local_planner这个包通过地图数据,通过算法搜索到达目标的多条路经,利用一些评价标准(是否会撞击障碍物,所需要的时间等等)选取最优的路径,并且计算所需要的实时速度和角度。
其中,Trajectory Rollout 和Dynamic Window approaches算法的主要思路如下:
(1) 采样机器人当前的状态(dx,dy,dtheta);
(2) 针对每个采样的速度,计算机器人以该速度行驶一段时间后的状态,得出一条行驶的路线。
(3) 利用一些评价标准为多条路线打分。
(4) 根据打分,选择最优路径。
(5) 重复上面过程。
具体参见:http://www.ros.org/wiki/base_local_planner?distro=groovy
其中,Trajectory Rollout 和Dynamic Window approaches算法的主要思路如下:
(1) 采样机器人当前的状态(dx,dy,dtheta);
(2) 针对每个采样的速度,计算机器人以该速度行驶一段时间后的状态,得出一条行驶的路线。
(3) 利用一些评价标准为多条路线打分。
(4) 根据打分,选择最优路径。
(5) 重复上面过程。
具体参见:http://www.ros.org/wiki/base_local_planner?distro=groovy
五、ArbotiX仿真——手动设定目标
在这一步,我们暂时使用空白地图(blank_map.pgm),就在空地上进行无障碍仿真。
首先运行ArbotiX节点,并且加载机器人的URDF文件。
首先运行ArbotiX节点,并且加载机器人的URDF文件。
roslaunch rbx1_bringup fake_turtlebot.launch
然后运行move_base和加载空白地图的launch文件(fake_move_base_blank_map.launch):
roslaunch rbx1_nav fake_move_base_blank_map.launch
该文件的具体内容如下:
<launch>
<!-- Run the map server with a blank map -->
<node name="map_server" pkg="map_server" type="map_server" args="$(find rbx1_nav)/maps/blank_map.yaml"/>
<include file="$(find rbx1_nav)/launch/fake_move_base.launch" />
<!-- Run a static transform between /odom and /map -->
<node pkg="tf" type="static_transform_publisher" name="odom_map_broadcaster" args="0 0 0 0 0 0 /map /odom 100" />
</launch>
其中调用了fake_move_base.launch文件,是运行move_base节点并进行参数配置。
然后调用rviz就可以看到机器人了。
rosrun rviz rviz -d `rospack find rbx1_nav`/nav_fuerte.vcg
我们先以1m的速度进行一下测试:
让机器人前进一米:
rostopic pub /move_base_simple/goal geometry_msgs/PoseStamped \
'{ header: { frame_id: "base_link" }, pose: { position: { x: 1.0, y: 0, z: 0 }, orientation: { x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 1 } } }'
让机器人后退一米,回到原来的位置:
rostopic pub /move_base_simple/goal geometry_msgs/PoseStamped \
'{ header: { frame_id: "map" }, pose: { position: { x: 0, y: 0, z: 0 }, orientation: { x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 1 } } }'
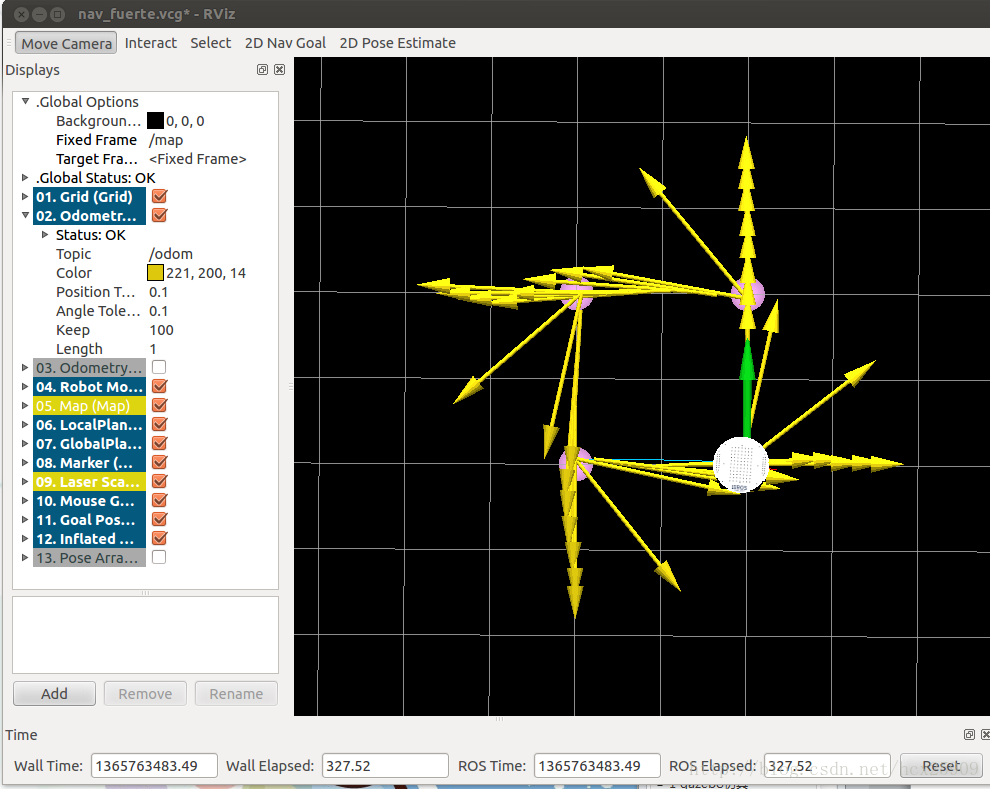
在rviz中的轨迹图如下:

在机器人移动过程中,有一条蓝色的线(被黄线挡住了)就是机器人的全局规划的路径;红色的箭头是实施规划的路线,会不断更新,有的时候会呈现很大的弧线,那是因为机器人在转向的过程中尽量希望保持平稳的角度。如果觉得路径规划的精度不够,可以修改配置文件中的pdist_scale参数进行修正。
然后我们可以认为的确定目标位置,点击rviz上方的2D Nav Goal按键,然后左键选择目标位置,机器人就开始自动导航了。
然后我们可以认为的确定目标位置,点击rviz上方的2D Nav Goal按键,然后左键选择目标位置,机器人就开始自动导航了。

六、ArbotiX仿真——带有障碍物的路径规划
首先我们让机器人走一个正方形的路线。先通过上面的命令,让机器人回到原始位置(0,0,0),然后按reset按键,把所有的箭头清除。接着运行走正方形路径的代码:
rosrun rbx1_nav move_base_square.py
在rviz中可以看到:
四个顶角的粉色圆盘就是我们设定的位置,正方形比较规则,可见定位还是比较准确的。然我们先来分析一下走正方形路线的代码:
- #!/usr/bin/env python
- import roslib; roslib.load_manifest('rbx1_nav')
- import rospy
- import actionlib
- from actionlib_msgs.msg import *
- from geometry_msgs.msg import Pose, Point, Quaternion, Twist
- from move_base_msgs.msg import MoveBaseAction, MoveBaseGoal
- from tf.transformations import quaternion_from_euler
- from visualization_msgs.msg import Marker
- from math import radians, pi
-
- class MoveBaseSquare():
- def __init__(self):
- rospy.init_node('nav_test', anonymous=False)
-
- rospy.on_shutdown(self.shutdown)
-
- # How big is the square we want the robot to navigate?
- # 设定正方形的尺寸,默认是一米
- square_size = rospy.get_param("~square_size", 1.0) # meters
-
- # Create a list to hold the target quaternions (orientations)
- # 创建一个列表,保存目标的角度数据
- quaternions = list()
-
- # First define the corner orientations as Euler angles
- # 定义四个顶角处机器人的方向角度(Euler angles:http://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E6%AC%A7%E6%8B%89%E8%A7%92)
- euler_angles = (pi/2, pi, 3*pi/2, 0)
-
- # Then convert the angles to quaternions
- # 将上面的Euler angles转换成Quaternion的格式
- for angle in euler_angles:
- q_angle = quaternion_from_euler(0, 0, angle, axes='sxyz')
- q = Quaternion(*q_angle)
- quaternions.append(q)
-
- # Create a list to hold the waypoint poses
- # 创建一个列表存储导航点的位置
- waypoints = list()
-
- # Append each of the four waypoints to the list. Each waypoint
- # is a pose consisting of a position and orientation in the map frame.
- # 创建四个导航点的位置(角度和坐标位置)
- waypoints.append(Pose(Point(square_size, 0.0, 0.0), quaternions[0]))
- waypoints.append(Pose(Point(square_size, square_size, 0.0), quaternions[1]))
- waypoints.append(Pose(Point(0.0, square_size, 0.0), quaternions[2]))
- waypoints.append(Pose(Point(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), quaternions[3]))
-
- # Initialize the visualization markers for RViz
- # 初始化可视化标记
- self.init_markers()
-
- # Set a visualization marker at each waypoint
- # 给每个定点的导航点一个可视化标记(就是rviz中看到的粉色圆盘标记)
- for waypoint in waypoints:
- p = Point()
- p = waypoint.position
- self.markers.points.append(p)
-
- # Publisher to manually control the robot (e.g. to stop it)
- # 发布TWist消息控制机器人
- self.cmd_vel_pub = rospy.Publisher('cmd_vel', Twist)
-
- # Subscribe to the move_base action server
- # 订阅move_base服务器的消息
- self.move_base = actionlib.SimpleActionClient("move_base", MoveBaseAction)
-
- rospy.loginfo("Waiting for move_base action server...")
-
- # Wait 60 seconds for the action server to become available
- # 等待move_base服务器建立
- self.move_base.wait_for_server(rospy.Duration(60))
-
- rospy.loginfo("Connected to move base server")
- rospy.loginfo("Starting navigation test")
-
- # Initialize a counter to track waypoints
- # 初始化一个计数器,记录到达的顶点号
- i = 0
-
- # Cycle through the four waypoints
- # 主循环,环绕通过四个定点
- while i < 4 and not rospy.is_shutdown():
- # Update the marker display
- # 发布标记指示四个目标的位置,每个周期发布一起,确保标记可见
- self.marker_pub.publish(self.markers)
-
- # Intialize the waypoint goal
- # 初始化goal为MoveBaseGoal类型
- goal = MoveBaseGoal()
-
- # Use the map frame to define goal poses
- # 使用map的frame定义goal的frame id
- goal.target_pose.header.frame_id = 'map'
-
- # Set the time stamp to "now"
- # 设置时间戳
- goal.target_pose.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
-
- # Set the goal pose to the i-th waypoint
- # 设置目标位置是当前第几个导航点
- goal.target_pose.pose = waypoints[i]
-
- # Start the robot moving toward the goal
- # 机器人移动
- self.move(goal)
-
- i += 1
-
- def move(self, goal):
- # Send the goal pose to the MoveBaseAction server
- # 把目标位置发送给MoveBaseAction的服务器
- self.move_base.send_goal(goal)
-
- # Allow 1 minute to get there
- # 设定1分钟的时间限制
- finished_within_time = self.move_base.wait_for_result(rospy.Duration(60))
-
- # If we don't get there in time, abort the goal
- # 如果一分钟之内没有到达,放弃目标
- if not finished_within_time:
- self.move_base.cancel_goal()
- rospy.loginfo("Timed out achieving goal")
- else:
- # We made it!
- state = self.move_base.get_state()
- if state == GoalStatus.SUCCEEDED:
- rospy.loginfo("Goal succeeded!")
-
- def init_markers(self):
- # Set up our waypoint markers
- # 设置标记的尺寸
- marker_scale = 0.2
- marker_lifetime = 0 # 0 is forever
- marker_ns = 'waypoints'
- marker_id = 0
- marker_color = {'r': 1.0, 'g': 0.7, 'b': 1.0, 'a': 1.0}
-
- # Define a marker publisher.
- # 定义一个标记的发布者
- self.marker_pub = rospy.Publisher('waypoint_markers', Marker)
-
- # Initialize the marker points list.
- # 初始化标记点的列表
- self.markers = Marker()
- self.markers.ns = marker_ns
- self.markers.id = marker_id
- self.markers.type = Marker.SPHERE_LIST
- self.markers.action = Marker.ADD
- self.markers.lifetime = rospy.Duration(marker_lifetime)
- self.markers.scale.x = marker_scale
- self.markers.scale.y = marker_scale
- self.markers.color.r = marker_color['r']
- self.markers.color.g = marker_color['g']
- self.markers.color.b = marker_color['b']
- self.markers.color.a = marker_color['a']
-
- self.markers.header.frame_id = 'map'
- self.markers.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
- self.markers.points = list()
-
- def shutdown(self):
- rospy.loginfo("Stopping the robot...")
- # Cancel any active goals
- self.move_base.cancel_goal()
- rospy.sleep(2)
- # Stop the robot
- self.cmd_vel_pub.publish(Twist())
- rospy.sleep(1)
-
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- try:
- MoveBaseSquare()
- except rospy.ROSInterruptException:
- rospy.loginfo("Navigation test finished.")

但是,在实际情况中,往往需要让机器人自动躲避障碍物。move_base包的一个强大的功能就是可以在全局规划的过程中自动躲避障碍物,而不影响全局路径。障碍物可以是静态的(比如墙、桌子等),也可以是动态的(比如人走过)。
现在我们尝试在之前的正方形路径中加入障碍物。把之前运行fake_move_base_blank_map.launch的中断Ctrl-C掉,然后运行:
然后就会看到在rviz中出现了障碍物。然后在运行之前走正方形路线的代码:
这回我们可以看到,在全局路径规划的时候,机器人已经将障碍物绕过去了,下过如下图:
现在我们尝试在之前的正方形路径中加入障碍物。把之前运行fake_move_base_blank_map.launch的中断Ctrl-C掉,然后运行:
roslaunch rbx1_nav fake_move_base_obstacle.launch然后就会看到在rviz中出现了障碍物。然后在运行之前走正方形路线的代码:
rosrun rbx1_nav move_base_square.py 这回我们可以看到,在全局路径规划的时候,机器人已经将障碍物绕过去了,下过如下图:

在上图中,黑色的线是障碍物,周围浅色的椭圆形是根据配置文件中的inflation_radius参数计算出来的安全缓冲区。全局规划的路径基本已经是最短路径了。在仿真的过程中也可以动态重配置那四个配置文件,修改仿真参数。
----------------------------------------------------------------
欢迎大家转载我的文章。
转载请注明:转自古-月
欢迎继续关注我的博客
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/小小林熬夜学编程/article/detail/424015
推荐阅读
相关标签